Virtual Power Plant Operational Strategies: Models, Markets, Optimization, Challenges, and Opportunities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To analyze different VPP models for different market mechanisms. In this regard, this paper describes different energy market structures and thoroughly explains the role of VPP in each market.
- To address different energy management algorithms within VPP considering various resources such as renewable-based/conventional DGs, battery energy storage, responsive loads, and EVs.
- To compare different planning methods of VPPs in terms of solution methods to optimize VPPs.
- To examine the use of blockchain in the structure of VPPs and the benefits of using this technology.
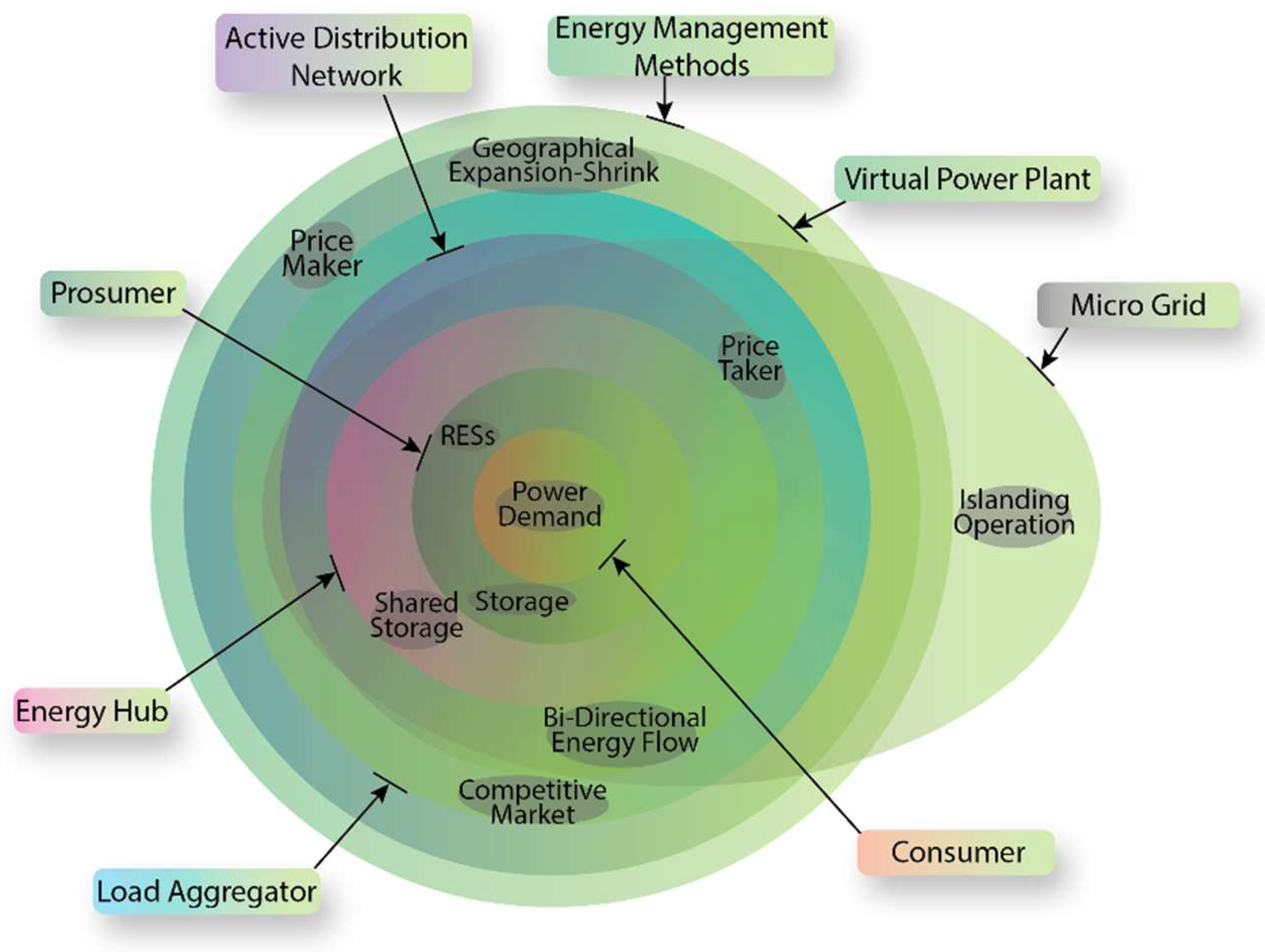
2. VPP Definition
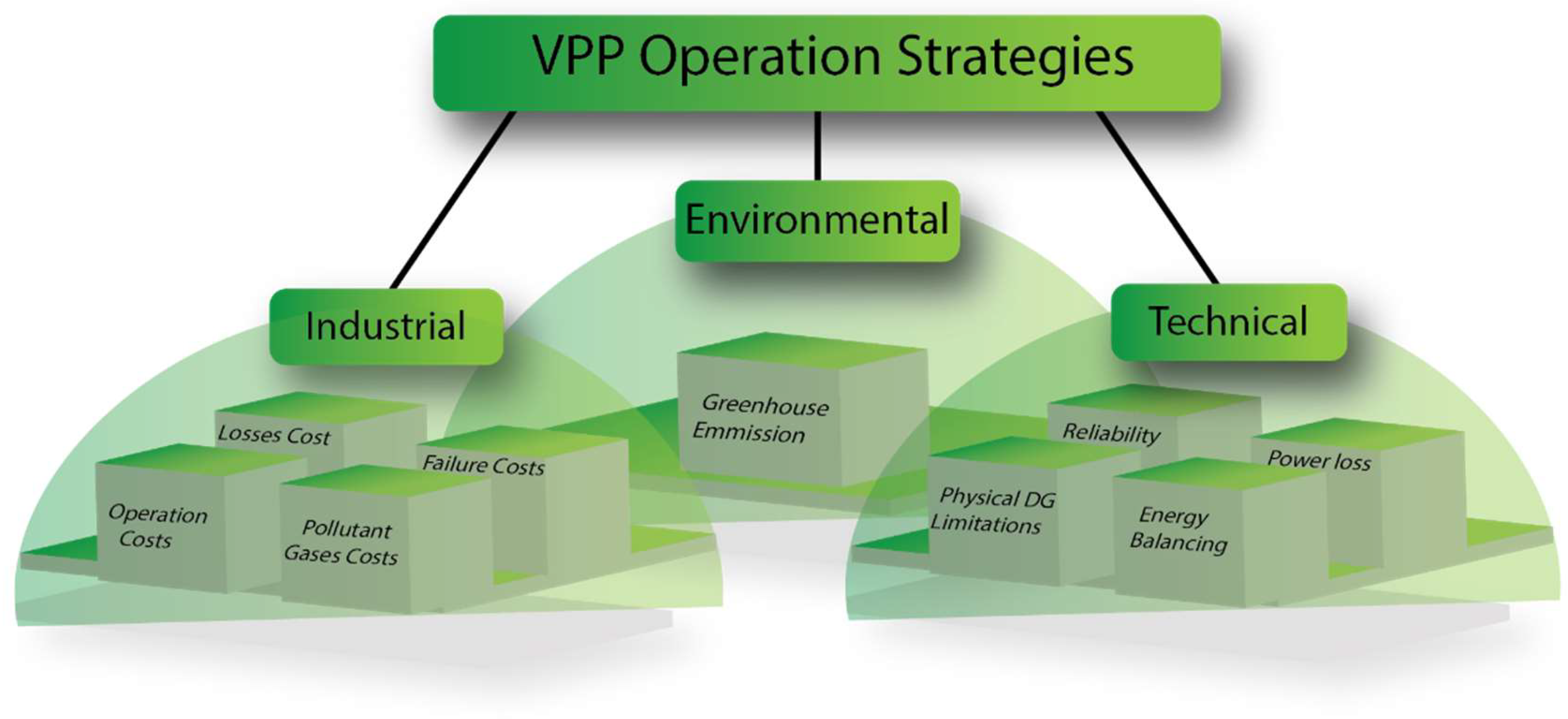
Operating Strategies of VPPs
- -
- In the economic objective, the objective function is to minimize the total costs with respect to less impact on the network. This option may be considered by DG owners or operators. The main limitations in the economic viewpoint are the physical limitations of DGs which may affect the economic dispatch. The impact of VPP on reducing losses cost is because of the elimination of the transmission lines since these resources are close to the load location. In fact, when transmission lines are removed, power is generated near local loads, which can reduce losses. In this case, the network operator can also benefit from this issue. As a result, electric power can be delivered to the customer at a lower price due to reduced losses. Exploiting VPP could also reduce the failure cost and the number of emission pollutants that enter the air; therefore, the cost of these items will be avoided or will be very low.
- -
- From a technical point of view, the network performance is improved. The purpose of network performance is to minimize power losses and improve voltage fluctuations and network congestion without considering resource costs or revenues. This option is mostly considered by system operators [37].
- -
- The environmental objective function is considered regardless of the economic or technical aspects and only based on the need for reducing greenhouse gases. This option is fully supported by regulatory schemes.
3. Uncertainties in the VPP
3.1. Uncertainty of Renewable Energy Resources
3.2. Market Price Uncertainty
3.3. Load Uncertainty in VPPs
3.4. Modeling Uncertainties
4. Energy Management of VPPs
5. Planning of VPPs in the Power System
- -
- MGs can be operated connected to or disconnected from the main grid, while VPPs can only operate in a grid-connected manner.
- -
- MGs usually require some level of energy storage. However, the presence or absence of storage in VPPs is not very important.
- -
- MGs depend on hardware changes such as inverters and smart switches, while VPPs heavily depend on smart metering and information technology.
- -
- MGs include a fixed set of resources in a limited geographic area, while VPPs can combine a wide variety of resources in large geographic areas.
- -
- MGs are usually traded in retail markets, while VPPs can also be traded in wholesale markets.
- -
- MGs may face legal and political obstacles, while VPPs could be implemented based on the current structure and legal tariffs.
5.1. Classical Method in Optimal Planning of VPPs
5.2. Heuristic and Meta-Heuristic Methods in VPP Planning
5.3. VPP Planning Methods Based on Learning
- -
- Policy determines how to deal with each action and how to make decisions in different situations.
- -
- The reward function determines the goal of the learner function. The purpose of this function is to give a reward for each action of the agent so that the reward increases as the goal gets closer.
- -
- The model of the RL problem is probabilistic and stochastic, and its states are non-deterministic. For one action, it can go to all states but with one probability.
| Algorithm | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| IP and LP | - Simplicity - ease of use - Place of reassessment - Improving the quality of decision-making | - Inability to deal with uncertainties - Necessary need for objective function and constraints |
| MILP | - Flexibility in model development - Accurate modeling capability - Convergence to the final solution | - Difficult to understand - Hard implementation of the algorithm - Slow solving speed—high cost for large-scale issues |
| PEM | - Low cost - Proper accuracy - Balance between speed and accuracy | - Low accuracy for multidimensional environments - Recognizable pattern of restriction - Weakness in handling samples with high distribution |
| PSO | - Easy implementation - Parallel computing capability - Fast and easy convergence - Low computational cost | - Lack of a precise theoretical basis - Instability in solving scattered problems - Convergence to local optimality in complexity problems |
| Algorithms based on machine learning | - Fast and cheap generalization - Data analysis - Production and extraction of problem features | - High knowledge is needed for implementation |
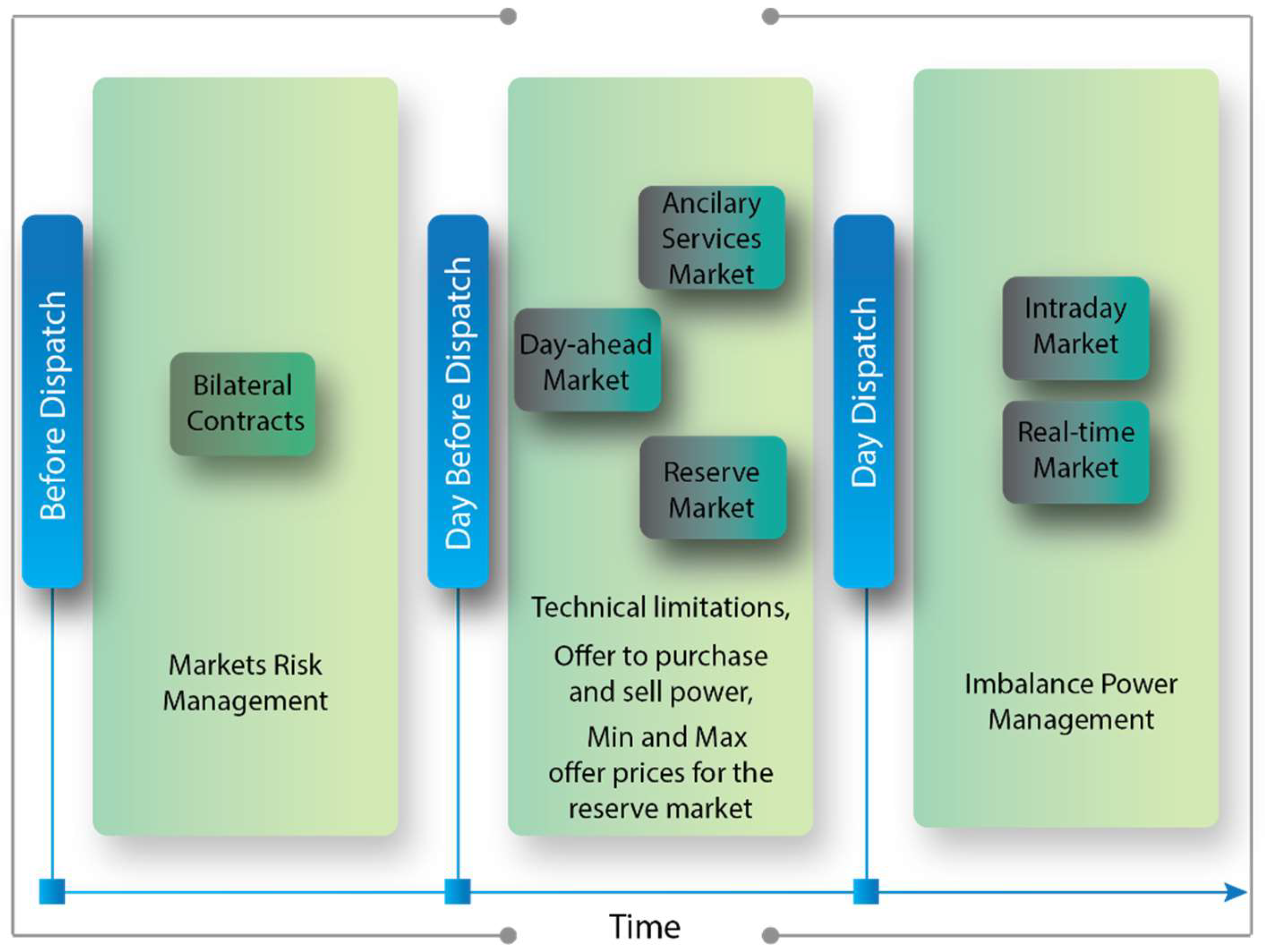
6. Participation of VPPs in Electricity Markets
- Penetration pricing or pricing to gain market share: Some power companies adopt this pricing policy to penetrate the market and gain a part of the market for a short period of time. These power companies offer some of their services for free or at a low price for selling energy for a limited period of several months.
- Economic price or no low-frill price: The pricing strategies of these products are considered as no low-frill prices where the cost of marketing a product is minimized. Economical pricing is determined for a certain period when the company does not spend more on advertising products and services.
- Using psychological pricing strategies: Psychological pricing strategies are an approach to elicit the consumer’s emotional response rather than their logical response. For example, a company prices its product at $99 instead of $100. The product is priced at $100, making the customer feel that the product is not too expensive. For most consumers, price is a factor in whether or not to buy a product.
6.1. Bilateral Contracts
6.2. VPP in the Day-Ahead Market
6.3. VPP in the Ancillary Services Market
6.4. VPP in the Reserve Market
6.5. Virtual Powerhouse in Daily Markets
| Reference | Market Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| [87,88] | Day-ahead | Offer to buy and sell energy for every hour of the next day Increasing the flexibility of the power system—high operating profit |
| [90,91] | Ancillary services market | Increasing security and reliability of power generation and transmission—the balance of generation and demand at any time |
| [94] | Reserve market | Management of excess power generation to ensure supply of demand and security of power supply |
| [95] | Daily market | - Adjusting the price of energy trading in the future market—reducing the cost of supply and demand imbalance |
| [96] | Real-time market | - Management of power fluctuations between supply and demand and network security |
6.6. VPP in Real-Time Market
7. Challenges of Using VPPs
7.1. Challenges of Control and Operation System
7.2. Communication and Information Challenges of VPPs
7.3. Power Exchange Challenges
7.4. Blockchain Applications in VPPs
- -
- Exchange of electrical energy
- -
- Effectiveness in responding to the load and checking RESs
8. Conclusions and Future Directions
- To use neural networks for VPP in the electricity markets and the overall modeling of these power plants in the power system.
- To propose novel control methods in the context of VPP.
- To present an appropriate protection scheme for VPP.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADN | Active Distribution Network |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DR | Demand Response |
| DERs | Distributed Energy Resources |
| DG | Distributed Generation |
| DSO | Distribution System Operator |
| EV | Electric Vehicle |
| EIA | Energy Information Administration |
| EMS | Energy Management System |
| EN | Energy Nodes |
| FIT | Feed-In Tariff |
| IP | Integer Programming |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| LP | Linear Programming |
| MDP | Markov Decision Process |
| MF | Membership Function |
| MG | Micro-grid |
| MINLP | Mixed Integer Non-Linear Programming |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| PEM | Point-estimate Method |
| Probability Distribution Function | |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| RES | Renewable Energy Source |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Networks |
| TSO | Transmission System Operator |
| VPP | Virtual Power Plant |
| WT | Wind Turbine |
References
- Amuta, E.O.; Wara, S.T.; Agbetuyi, A.F.; Sawyerr, B.A. Weibull Distribution-Based Analysis for Reliability Assessment of an Isolated Power Micro-Grid System. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 2215–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagappan, A.; Venkatachary, S.K.; Andrews, L.J.B. Augmenting Zero Trust Network Architecture to Enhance Security in VPPs. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency. Key World Energy Statistics 2015; IEA: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Delft, C.E.; Directorate-General for Energy (European Commission); Hinicio; ICF International. Financing the Energy Renovation of Buildings with Cohesion Policy Funding; Technical Guidance; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.-T.; Chen, G.; Li, C. Risk-Averse Energy Trading among Peer-to-Peer Based VPPs: A Stochastic Game Approach. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 132, 107145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Xie, M.; Zhu, J. Robust Optimization Approach with Acceleration Strategies to Aggregate an Active Distribution System as a Virtual Power Plant. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 142, 108316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkens, J.; Thulesius, H.; Schmidt, I.; Carlsson, C. The 2015 National Cancer Program in Sweden: Introducing Standardized Care Pathways in a Decentralized System. Health Policy 2016, 120, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, F.E.Z.; Ibrahim, D.K.; SABRY, W. Virtual Power Plants Modeling and Simulation Using Innovative Electro-Economical Concept. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th Conference on Electrical Machines, Drives and Power Systems (ELMA), Varna, Bulgaria, 6–8 June 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pudjianto, D.; Ramsay, C.; Strbac, G. Virtual Power Plant and System Integration of Distributed Energy Resources. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2007, 1, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Gan, D.; Li, N.; Li, H.; Dai, C. Virtual Power Plant-Based Distributed Control Strategy for Multiple Distributed Generators. IET Control Theory Appl. 2013, 7, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, A.; Goel, L.; Wang, P. Adequacy Assessment of Generating Systems Incorporating Storage Integrated Virtual Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 10, 3440–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubov, D. An Iot Concept of the Small Virtual Power Plant Based on Arduino Platform and Mqtt Protocol. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Applied Internet and Information Technologies, Bitola, Macedonia, 3–4 June 2016; pp. 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Sierla, S.; Pourakbari-Kasmaei, M.; Vyatkin, V. A Taxonomy of Machine Learning Applications for Virtual Power Plants and Home/Building Energy Management Systems. Autom. Constr. 2022, 136, 104174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrane, Z.; Kim, J.; Yoo, K.; Lee, S.H. Fuzzy Logic Supervisor-Based Novel Energy Management Strategy Reflecting Different Virtual Power Plants. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 205, 107731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, Z.; Hooshmand, R.-A.; Soleymani, S. Optimal Integration of Demand Response Programs and Electric Vehicles in Coordinated Energy Management of Industrial Virtual Power Plants. J. Energy Storage 2021, 41, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.; Bordons, C.; Arce, A. Chance Constraints and Machine Learning Integration for Uncertainty Management in Virtual Power Plants Operating in Simultaneous Energy Markets. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 133, 107304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuntoli, M.; Poli, D. Optimized Thermal and Electrical Scheduling of a Large Scale Virtual Power Plant in the Presence of Energy Storages. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 942–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhour, E.; Moghaddas-Tafreshi, S.M. Bidding Strategy of Virtual Power Plant for Participating in Energy and Spinning Reserve Markets—Part I: Problem Formulation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 26, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Summeren, L.F.M.; Wieczorek, A.J.; Bombaerts, G.J.T.; Verbong, G.P.J. Community Energy Meets Smart Grids: Reviewing Goals, Structure, and Roles in Virtual Power Plants in Ireland, Belgium and the Netherlands. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2020, 63, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandžić, H.; Morales, J.M.; Conejo, A.J.; Kuzle, I. Offering Model for a Virtual Power Plant Based on Stochastic Programming. Appl. Energy 2013, 105, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Fan, S.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z.; He, G. An Adaptive Decentralized Economic Dispatch Method for Virtual Power Plant. Appl. Energy 2021, 300, 117347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, W.S.; EL-Sehiemy, R.A.; Azmy, A.M.; Abd el-Ghany, H.A. Identifying Optimal Border of Virtual Power Plants Considering Uncertainties and Demand Response. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 9673–9713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Tan, Z.; Wang, G.; Du, Y.; Pu, L.; Zhang, R. Business Model of Virtual Power Plant Considering Uncertainty and Different Levels of Market Maturity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 131433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; Tian, W.; Li, P.; Tan, Z. Nearly-Zero Carbon Optimal Operation Model and Benefit Allocation Strategy for a Novel Virtual Power Plant Using Carbon Capture, Power-to-Gas, and Waste Incineration Power in Rural Areas. Appl. Energy 2022, 310, 118618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordehi, A.R. A Stochastic Model for Participation of Virtual Power Plants in Futures Markets, Pool Markets and Contracts with Withdrawal Penalty. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Wang, J.; Geng, S.; Pu, L.; Tan, Z. Three-Level Market Optimization Model of Virtual Power Plant with Carbon Capture Equipment Considering Copula—CVaR Theory. Energy 2021, 237, 121620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, P.; Powalko, M.; Rudion, K. Optimal Operation of a Virtual Power Plant. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Calgary, AB, Canada, 26–30 July 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tarazona, C.; Muscholl, M.; Lopez, R.; Passelergue, J.C. Integration of Distributed Energy Resources in the Operation of Energy Management Systems. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE PES/IAS Conference on Sustainable Alternative Energy (SAE), Valencia, Spain, 28–30 September 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan, E.A.; Hossain, M.Z.; Muyeen, S.M.; Fahim, S.R.; Sarker, S.K.; Das, S.K. Towards next Generation Virtual Power Plant: Technology Review and Frameworks. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 150, 111358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.M.; Conejo, A.J.; Giraldi, L.; Le Maitre, O.; Hoteit, I.; Knio, O.M. Sample Average Approximation for Risk-Averse Problems: A Virtual Power Plant Scheduling Application. EURO J. Comput. Optim. 2021, 9, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgamal, A.H.; Kocher-Oberlehner, G.; Robu, V.; Andoni, M. Optimization of a Multiple-Scale Renewable Energy-Based Virtual Power Plant in the UK. Appl. Energy 2019, 256, 113973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bakari, K.; Kling, W.L. Virtual Power Plants: An Answer to Increasing Distributed Generation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT Europe), Gothenburg, Sweden, 11–13 October 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski, T.; Jasiński, M.; Ropuszyńska-Surma, E.; Weglarz, M.; Kaczorowska, D.; Kostyła, P.; Leonowicz, Z.; Lis, R.; Rezmer, J.; Rojewski, W.; et al. A Case Study on Distributed Energy Resources and Energy-Storage Systems in a Virtual Power Plant Concept: Economic Aspects. Energies 2019, 12, 4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.S.B.; Hasan, M.A. Microgrid Architecture, Control, and Operation. In Hybrid-Renewable Energy Systems in Microgrids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, M.; Hänninen, S.; Mäki, K. Survey of Smart Grid Concepts, Architectures, and Technological Demonstrations Worldwide. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE PES Conference on Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Latin America (ISGT LA), Medellin, Colombia, 19–21 October 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Binding, C.; Gantenbein, D.; Jansen, B.; Sundström, O.; Andersen, P.B.; Marra, F.; Poulsen, B.; Træholt, C. Electric Vehicle Fleet Integration in the Danish EDISON Project-a Virtual Power Plant on the Island of Bornholm. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES General Meeting, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 25–29 July 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Fang, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Uncertainties of Virtual Power Plant: Problems and Countermeasures. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 454–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, R.J.; Yu, X.; Sun, C.; Wong, P.S.P.; Zhao, H. Virtual Power Plants for a Sustainable Urban Future. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urcan, D.-C.; BicẶ, D. Simulation Concept of a Virtual Power Plant Based on Real-Time Data Acquisition. In Proceedings of the 2019 54th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Bucharest, Romania, 3–6 September 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Thavlov, A.; Bindner, H.W. An Aggregation Model for Households Connected in the Low-Voltage Grid Using a VPP Interface. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES ISGT Europe 2013, Lyngby, Denmark, 6–9 October 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nosratabadi, S.M.; Hooshmand, R.-A.; Gholipour, E. A Comprehensive Review on Microgrid and Virtual Power Plant Concepts Employed for Distributed Energy Resources Scheduling in Power Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aien, M.; Hajebrahimi, A.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M. A Comprehensive Review on Uncertainty Modeling Techniques in Power System Studies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanzadeh, M.; Sheikh-El-Eslami, M.-K.; Haghifam, M.-R. A Medium-Term Coalition-Forming Model of Heterogeneous DERs for a Commercial Virtual Power Plant. Appl. Energy 2016, 169, 663–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.G.; Zakariazadeh, A.; Jadid, S. Day-Ahead Resource Scheduling of a Renewable Energy Based Virtual Power Plant. Appl. Energy 2016, 169, 324–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Zhong, H.; Xia, Q.; Kang, C.; Wang, X.S.; Tang, H. Estimating the Robust PQ Capability of a Technical Virtual Power Plant under Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 4285–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peik-Herfeh, M.; Seifi, H.; Sheikh-El-Eslami, M.K. Decision Making of a Virtual Power Plant under Uncertainties for Bidding in a Day-Ahead Market Using Point Estimate Method. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 44, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbehzadi, M.; Niknam, T.; Aghaei, J.; Mokryani, G.; Shafie-khah, M.; Catalão, J.P.S. Optimal Operation of Hybrid AC/DC Microgrids under Uncertainty of Renewable Energy Resources: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 109, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosratabadi, S.M.; Hooshmand, R.-A.; Gholipour, E. Stochastic Profit-Based Scheduling of Industrial Virtual Power Plant Using the Best Demand Response Strategy. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Dooner, M.; Clarke, J. Overview of Current Development in Electrical Energy Storage Technologies and the Application Potential in Power System Operation. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 511–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-W. Residential Electricity Demand in Taiwan: Consumption Behavior and Rebound Effect. Energy Policy 2019, 124, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsel, S.R.; Riemke, R.L.; Hoffmann, V.H. Challenges and Solution Technologies for the Integration of Variable Renewable Energy Sources—A Review. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabatha, T.; Hager, J.; Carneiro, B.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. Analyzing Energy Options for Small-Scale off-Grid Communities: A Canadian Case Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Kankam, K.O.; Camarinha-Matos, L.M. Towards Collaborative Virtual Power Plants: Trends and Convergence. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2018, 16, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharaibeh, A.; Salahuddin, M.A.; Hussini, S.J.; Khreishah, A.; Khalil, I.; Guizani, M.; Al-Fuqaha, A. Smart Cities: A Survey on Data Management, Security, and Enabling Technologies. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2456–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, B. Estimating the Cost of Capital for Renewable Energy Projects. Energy Econ. 2020, 88, 104783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.; Garcia, A.S.; Moreno, B.; Diaz, G. Small-Scale Renewable Power Technologies Are an Alternative to Reach a Sustainable Economic Growth: Evidence from Spain. Energy 2019, 167, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jiang, C.; Wang, X. Comprehensive Review on Structure and Operation of Virtual Power Plant in Electrical System. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 13, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancarella, P. MES (Multi-Energy Systems): An Overview of Concepts and Evaluation Models. Energy 2014, 65, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robu, V.; Chalkiadakis, G.; Kota, R.; Rogers, A.; Jennings, N.R. Rewarding Cooperative Virtual Power Plant Formation Using Scoring Rules. Energy 2016, 117, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrasa, M.A.A.; Spooner, T.D.; MacGill, I.F. A Novel Energy Service Model and Optimal Scheduling Algorithm for Residential Distributed Energy Resources. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2011, 81, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonowicz, Ł.; Milewski, J. Virtual Power Plants-General Review: Structure, Application and Optimization. J. Power Technol. 2012, 92, 135–149. [Google Scholar]
- Alahyari, A.; Ehsan, M.; Mousavizadeh, M. A Hybrid Storage-Wind Virtual Power Plant (VPP) Participation in the Electricity Markets: A Self-Scheduling Optimization Considering Price, Renewable Generation, and Electric Vehicles Uncertainties. J. Energy Storage 2019, 25, 100812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.; Tan, Z.; Yuan, J.; Tan, Q.; Li, H.; Dong, F. A Bi-Level Stochastic Scheduling Optimization Model for a Virtual Power Plant Connected to a Wind-Photovoltaic-Energy Storage System Considering the Uncertainty and Demand Response. Appl. Energy 2016, 171, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akkacs, Ö.P.; Çam, E. Optimal Operational Scheduling of a Virtual Power Plant Participating in Day-Ahead Market with Consideration of Emission and Battery Degradation Cost. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, e12418. [Google Scholar]
- Sakr, W.S.; Abd el-Ghany, H.A.; EL-Sehiemy, R.A.; Azmy, A.M. Techno-Economic Assessment of Consumers’ Participation in the Demand Response Program for Optimal Day-Ahead Scheduling of Virtual Power Plants. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, C.; Cui, K.; Jin, Q.; Kong, D. Bi-Level Multi-Time Scale Scheduling Method Based on Bidding for Multi-Operator Virtual Power Plant. Appl. Energy 2019, 249, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Meng, K.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, Z.Y. Optimal Scheduling of Distributed Energy Resources as a Virtual Power Plant in a Transactive Energy Framework. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 3417–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshmand, R.-A.; Nosratabadi, S.M.; Gholipour, E. Event-Based Scheduling of Industrial Technical Virtual Power Plant Considering Wind and Market Prices Stochastic Behaviors—A Case Study in Iran. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1748–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Xu, J.; Liao, S.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ke, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. A Bi-Level Scheduling Model for Virtual Power Plants with Aggregated Thermostatically Controlled Loads and Renewable Energy. Appl. Energy 2018, 224, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.G.; Zakariazadeh, A.; Jadid, S.; Kazemi, A. Stochastic Operational Scheduling of Distributed Energy Resources in a Large Scale Virtual Power Plant. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 82, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadayeghparast, S.; Farsangi, A.S.; Shayanfar, H. Day-Ahead Stochastic Multi-Objective Economic/Emission Operational Scheduling of a Large Scale Virtual Power Plant. Energy 2019, 172, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, K.; Tan, Q.; Tan, Z. Multi-Objective Stochastic Scheduling Optimization Model for Connecting a Virtual Power Plant to Wind-Photovoltaic-Electric Vehicles Considering Uncertainties and Demand Response. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 128, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Ai, Q.; Piao, L. Fuzzy Day-Ahead Scheduling of Virtual Power Plant with Optimal Confidence Level. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2016, 10, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayegan-Rad, A.; Badri, A.; Zangeneh, A. Day-Ahead Scheduling of Virtual Power Plant in Joint Energy and Regulation Reserve Markets under Uncertainties. Energy 2017, 121, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, M.O. Heuristics Based on Mathematical Programming. Surv. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2011, 16, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzbahani, H.M.; Karimipour, H.; Lei, L. A Review on Virtual Power Plant for Energy Management. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, Y. AI, Model Risk Management in AI, Machine Learning & Deep Learning: Princeton Presentations in AI-ML Risk Management & Control Systems (Presentation Slides). In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Deep Learning Conference, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, USA, 21 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Liu, G.; Tang, X.; Lu, J.; Hu, J. An Ensemble Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model with Improved DS Evidence Fusion for Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Tan, Y.; Zheng, K.; Liu, S.; Zhang, K.; Shen, X. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Internet of Things: Model, Applications and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 1722–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Huang, X.; Wu, C.-H.; Tsai, S.-B. Pricing Strategy and Performance Investment Decisions in Competitive Crowdfunding Markets. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 140, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaabadi, S.; Galvani, S.; Talavat, V. Wind Power Offer Strategy in Day-Ahead Market Considering Price Bidding Strategy for Electric Vehicle Aggregators. J. Energy Storage 2022, 51, 104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhu, W.; Liang, L. Pricing Strategy in the Product and Service Market. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. 2021, 6, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Sharma, M.; Basu, S.; Jha, A.K. Uniform or Spatially Differentiated? Pricing Strategies for Information Goods under Simultaneous and Sequential Decision-Making in Multi-Market Context. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2022, 64, 102832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, H.; Mohammadi, M.; Taghe, R. Virtual Power Plant (VPP), Definition, Concept, Components and Types. In Proceedings of the 2011 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 25–28 March 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, W.; Qi, F.; Wang, L.; Zou, B.; Wen, F.; Xue, Y. Optimal Dispatch of a Virtual Power Plant Considering Demand Response and Carbon Trading. Energies 2018, 11, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani-Dabbagh, S.; Sheikh-El-Eslami, M.K. A Profit Sharing Scheme for Distributed Energy Resources Integrated into a Virtual Power Plant. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baringo, L.; Freire, M.; García-Bertrand, R.; Rahimiyan, M. Offering Strategy of a Price-Maker Virtual Power Plant in Energy and Reserve Markets. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2021, 28, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubeau, J.-F.; De Grève, Z.; Vallée, F. Medium-Term Multimarket Optimization for Virtual Power Plants: A Stochastic-Based Decision Environment. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 33, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandžić, H.; Kuzle, I.; Capuder, T. Virtual Power Plant Mid-Term Dispatch Optimization. Appl. Energy 2013, 101, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; He, S.; Wang, M.; Pandžić, H. Bidding Strategy for Virtual Power Plant Considering the Large-Scale Integrations of Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 5890–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yang, H.-T. Optimal Operation and Bidding Strategy of a Virtual Power Plant Integrated with Energy Storage Systems and Elasticity Demand Response. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 79798–79809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajeddini, M.A.; Rahimi-Kian, A.; Soroudi, A. Risk Averse Optimal Operation of a Virtual Power Plant Using Two Stage Stochastic Programming. Energy 2014, 73, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Riaz, S.; Mancarella, P. Integrated Techno-Economic Modeling, Flexibility Analysis, and Business Case Assessment of an Urban Virtual Power Plant with Multi-Market Co-Optimization. Appl. Energy 2020, 259, 114142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.; Ghazvini, M.A.F.; Vale, Z.; de Moura Oliveira, P.B. A Multi-Objective Model for the Day-Ahead Energy Resource Scheduling of a Smart Grid with High Penetration of Sensitive Loads. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 1074–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Mokryani, G.; Campean, F.; Hu, Y.F. Comprehensive Review of VPPs Planning, Operation and Scheduling Considering the Uncertainties Related to Renewable Energy Sources. IET Energy Syst. Integr. 2019, 1, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, M.A.M.; Bouchekara, H.R.E.H. Solving the Problem of Large-Scale Optimal Scheduling of Distributed Energy Resources in Smart Grids Using an Improved Variable Neighborhood Search. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 77321–77335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Lou, S.; Liu, B.; Fan, Z.; Wu, Z. Review on Power Generation and Bidding Optimization of Virtual Power Plant. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICELTICs), Banda Aceh, Indonesia, 18–20 October 2017; pp. 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Afzal, M.; Li, J.; Amin, W.; Huang, Q.; Umer, K.; Ahmad, S.A.; Ahmad, F.; Raza, A. Role of Blockchain Technology in Transactive Energy Market: A Review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesha, D.L.; Balachandra, P. Conceptualization of Blockchain Enabled Interconnected Smart Microgrids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawusu, S.; Zhang, X.; Ahmed, A.; Jamatutu, S.A.; Miensah, E.D.; Amadu, A.A.; Osei, F.A.J. Renewable Energy Sources from the Perspective of Blockchain Integration: From Theory to Application. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Guo, X.; Xie, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, B.; Han, S.; Wu, W.; Sun, L. Virtual Power Plant Platforms and Their Applications in Practice: A Brief Review. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Sustainable Power and Energy Conference (iSPEC), Chengdu, China, 23–25 November 2020; pp. 2071–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Andoni, M.; Robu, V.; Flynn, D.; Abram, S.; Geach, D.; Jenkins, D.; McCallum, P.; Peacock, A. Blockchain Technology in the Energy Sector: A Systematic Review of Challenges and Opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 100, 143–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siano, P.; De Marco, G.; Rolán, A.; Loia, V. A Survey and Evaluation of the Potentials of Distributed Ledger Technology for Peer-to-Peer Transactive Energy Exchanges in Local Energy Markets. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 13, 3454–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, H. Blockchain-Based Decentralized Energy Management Platform for Residential Distributed Energy Resources in a Virtual Power Plant. Appl. Energy 2021, 294, 117026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Mehbodniya, A.; Ambalgi, A.P.; Murali, M.; Sahay, K.B.; Babu, D.V. In a virtual power plant, a blockchain-based decentralized power management solution for home distributed generation. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 49, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Lu, X.; Wang, N.; Wu, J.; Du, X.; Guizani, M. Towards Secure and Efficient Energy Trading in IIoT-Enabled Energy Internet: A Blockchain Approach. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 110, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Targets | Construction Time | VPP Name | Type of DER | Country/Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Development, implementation, and testing of the VPP as well as whether fuel cells can be installed in residential areas | 2001–2005 | VDCPP | Fuel cell | Germany, Netherlands, Spain |
| Provide market mechanism | 2005–2007 | PM VPP | Netherlands | |
| Choosing DER-based systems in order to choose a solution for EU electricity supply with low cost, safety, and high reliability | 2005–2009 | FENIX | GB, Spain, France | |
| Providing the balancing power needed to increase the use of wind power | 2009–2012 | EDISON | EVs | Denmark |
| Active power supply and small-scale generation | 2010–2013 | FLEX POWER | WT | Denmark |
| Implementation of “Smart Distribution” | 2010–2015 | WEB2ENERGY | Germany, Poland | |
| Advanced integration of wind turbines | 2012–2015 | TWENTIES | WT | Belgium, Germany, France |
| Providing network support services, helping to secure demand, and saving customers’ energy costs | 2016–2018 | SA VPP | PV, battery | Australia |
| Reference | Solution Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [56] | MINLP | Presenting a new strategy for providing ancillary energy services |
| [57] | MILP | Maximizing profits and minimizing pollutant emissions in VPP |
| [58] | LP | Optimum scheduling of VPP with battery regardless of cost |
| [59] | MINLP | Planning industrial VPPs |
| [60] | LP | Linear programming of market optimization |
| [61] | MILP | Optimum planning of day-ahead markets |
| [62] | Mathematical programming | Optimal planning of VPP considering battery failure |
| [63] | Mathematical programming | Maximum profit in the market and reduction in pollution |
| [64] | Monte-Carlo | Optimum planning to increase profit by considering DR |
| [65] | MINLP | bi-level planning of VPPs |
| [66] | Scenario-based PSO optimization | Reserve planning and VPP energy |
| [67] | Point Estimation (PE) | Planning resources in the day-ahead market for VPP |
| [68] | Interval optimization | bi-level optimization of VPP |
| [69] | PSO | Multi-objective optimization stochastic programming for VPP |
| [70] | Combination of genetic and Monte Carlo algorithms | Planning VPP uncertainties |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roozbehani, M.M.; Heydarian-Forushani, E.; Hasanzadeh, S.; Elghali, S.B. Virtual Power Plant Operational Strategies: Models, Markets, Optimization, Challenges, and Opportunities. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912486
Roozbehani MM, Heydarian-Forushani E, Hasanzadeh S, Elghali SB. Virtual Power Plant Operational Strategies: Models, Markets, Optimization, Challenges, and Opportunities. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912486
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoozbehani, Mohammad Mohammadi, Ehsan Heydarian-Forushani, Saeed Hasanzadeh, and Seifeddine Ben Elghali. 2022. "Virtual Power Plant Operational Strategies: Models, Markets, Optimization, Challenges, and Opportunities" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912486





