Long-Term Peatland Condition Assessment via Surface Motion Monitoring Using the ISBAS DInSAR Technique over the Flow Country, Scotland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
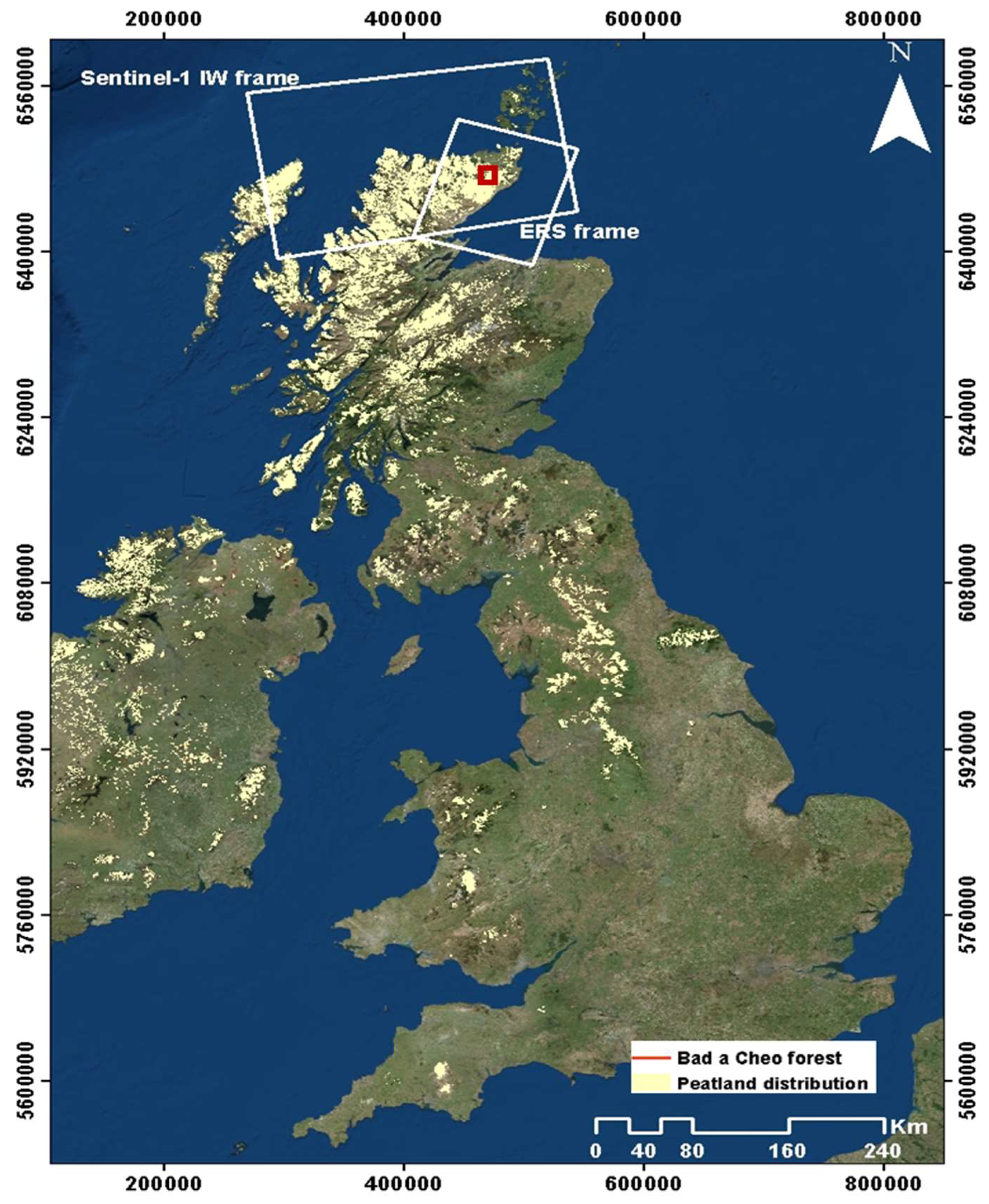
2. Study Area and Data
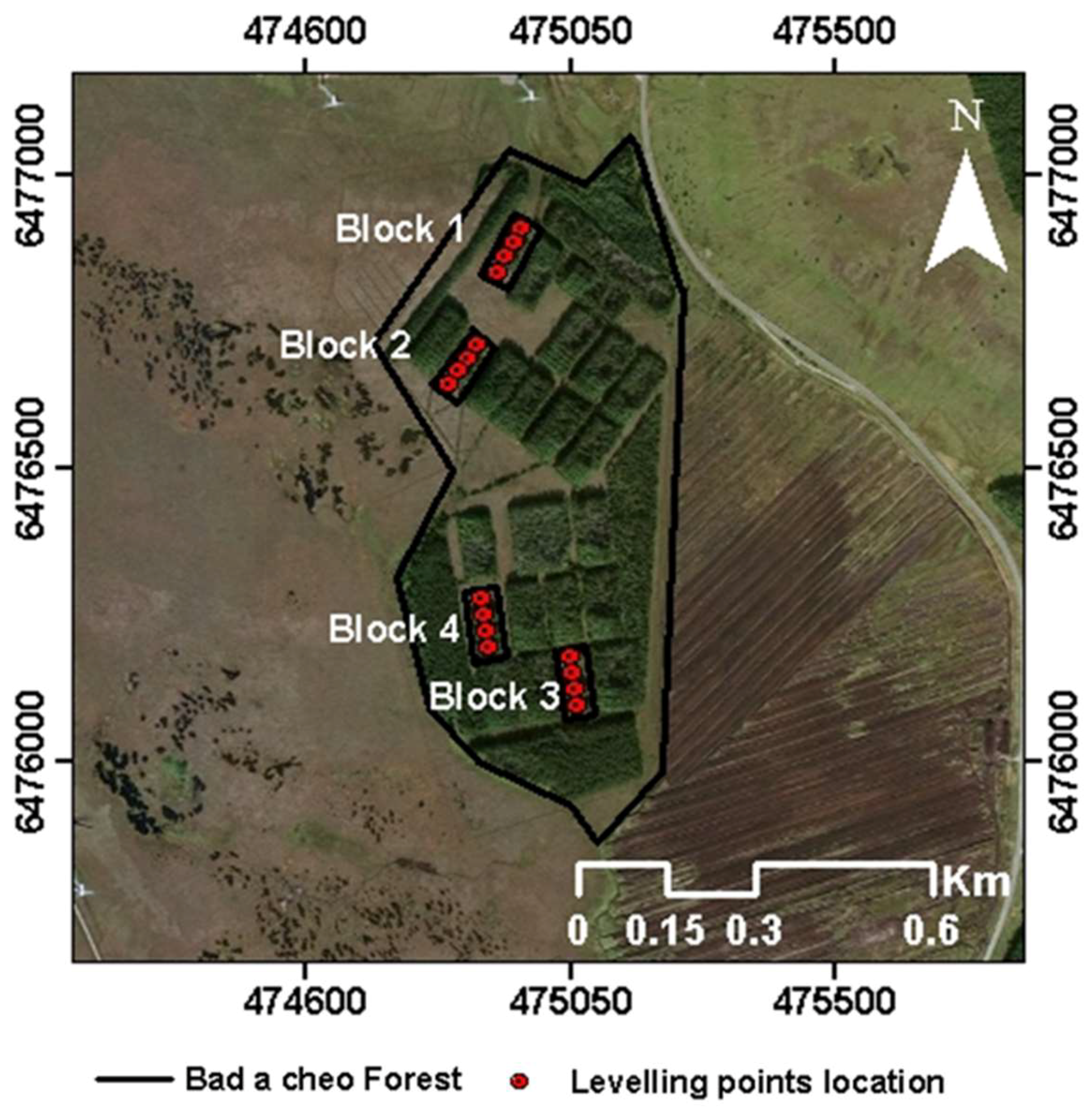
2.1. Site Selection
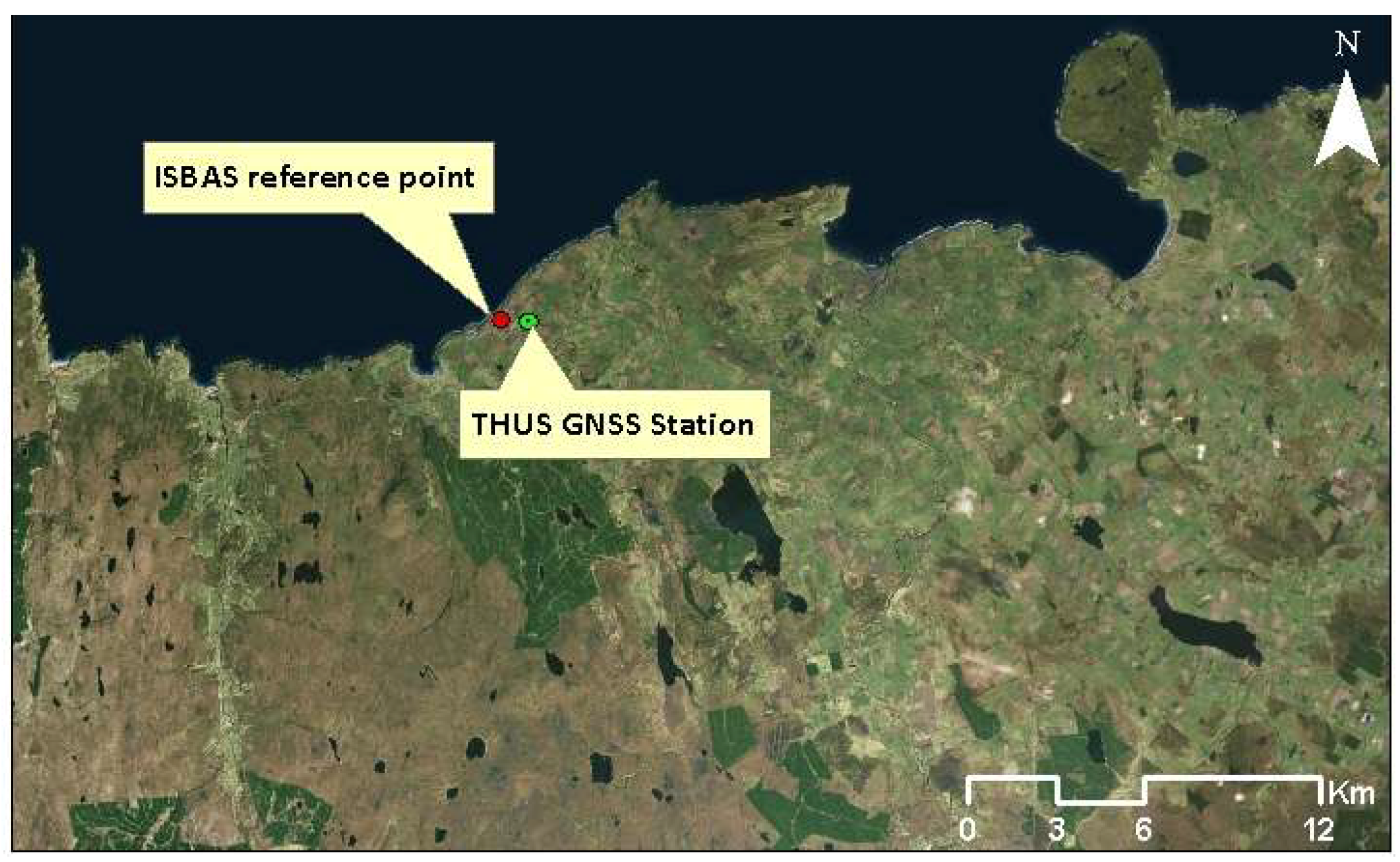
2.2. Data
3. Methods
3.1. Data Processing of SAR Data Using ISBAS
3.1.1. ERS ISBAS Processing
3.1.2. Sentinel-1 ISBAS Processing
3.2. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Qualitative Analysis
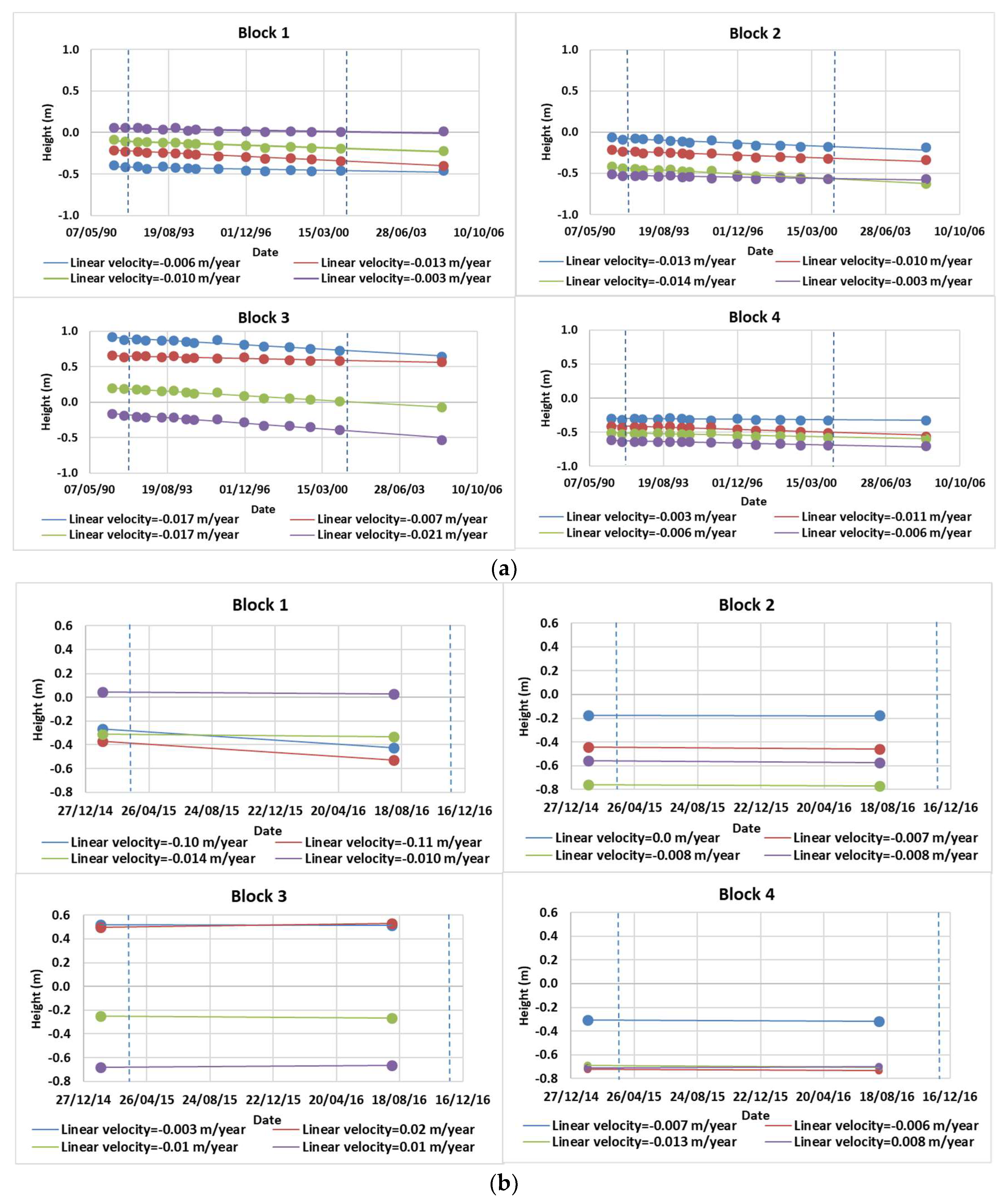
4.2. Quantitative Analyses
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sensor | Date | Date | Date | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS1/2 SAR (master) | 01/09/1997 | 0 | 19/02/1996 | 192.9915 | 04/05/1998 | 67.58448 |
| 01/05/1992 | −1150.67 | 24/03/1996 | −1059.98 | 08/06/1998 | 281.1085 | |
| 05/06/1992 | −463.967 | 29/04/1996 | −74.7054 | 13/07/1998 | −906.11 | |
| 23/10/1992 | −354.538 | 12/08/1996 | −301.134 | 17/08/1998 | −671.416 | |
| 27/11/1992 | 373.7755 | 16/09/1996 | −466.298 | 21/09/1998 | −448.835 | |
| 05/02/1993 | −886.408 | 21/10/1996 | 134.4231 | 04/01/1999 | −1303.58 | |
| 12/03/1993 | −132.305 | 25/11/1996 | 493.7614 | 06/09/1999 | −931.75 | |
| 16/04/1993 | 416.4579 | 30/12/1996 | −412.738 | 11/10/1999 | −775.74 | |
| 25/06/1993 | −667.167 | 03/02/1997 | −47.1075 | 15/11/1999 | −116.601 | |
| 09/04/1995 | −705.743 | 10/03/1997 | −330.688 | 20/12/1999 | −616.819 | |
| 18/06/1995 | −585.937 | 14/04/1997 | 252.1142 | 28/02/2000 | −753.803 | |
| 19/06/1995 | −676.698 | 19/05/1997 | −521.969 | 03/04/2000 | −145.465 | |
| 24/07/1995 | −352.885 | 23/06/1997 | −450.927 | 12/06/2000 | −892.831 | |
| 27/08/1995 | −359.637 | 28/07/1997 | −318.959 | 17/07/2000 | −951.859 | |
| 28/08/1995 | −375.164 | 06/10/1997 | −181.017 | 04/12/2000 | 174.1707 | |
| 01/10/1995 | −151.308 | 10/11/1997 | −500.615 | |||
| 02/10/1995 | 136.2102 | 15/12/1997 | −807.807 | |||
| 11/12/1995 | −217.744 | 19/01/1998 | −578.707 |
| Sensor | Date | Date | Date | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1 SAR (master) | 06/01/2016 | 0 | 11/02/2016 | −20.1934 | 17/05/2016 | −68.1864 |
| 12/03/2015 | −137.863 | 20/09/2015 | −172.334 | 04/07/2016 | −33.4788 | |
| 24/03/2015 | −103.956 | 02/10/2015 | −137.917 | 16/07/2016 | −74.9726 | |
| 05/04/2015 | 19.43112 | 19/11/2015 | −140.413 | 28/07/2016 | −103.857 | |
| 17/04/2015 | −43.1853 | 01/12/2015 | −106.561 | 09/08/2016 | −126.395 | |
| 29/04/2015 | −110.733 | 13/12/2015 | −30.4015 | 21/08/2016 | −93.4495 | |
| 11/05/2015 | −109.989 | 25/12/2015 | 46.00938 | 02/09/2016 | 47.7846 | |
| 23/05/2015 | −152.891 | 18/01/2016 | −105.138 | 14/09/2016 | −41.6521 | |
| 04/06/2015 | −66.0013 | 30/01/2016 | −55.1947 | 26/09/2016 | −95.1289 | |
| 16/06/2015 | −8.50102 | 23/02/2016 | −29.215 | 08/10/2016 | −134.011 | |
| 28/06/2015 | −138.549 | 30/03/2016 | −165.673 | 20/10/2016 | −99.668 | |
| 10/07/2015 | −102.089 | 11/04/2016 | −180.54 | 01/11/2016 | 5.327293 | |
| 22/07/2015 | −168.35 | 23/04/2016 | −40.095 | 13/11/2016 | 3.495892 | |
| 15/08/2015 | −38.7049 | 05/05/2016 | −67.1433 | 25/11/2016 | −47.841 | |
| 27/08/2015 | −49.7186 | 29/05/2016 | −130.991 | 07/12/2016 | −120.063 | |
| 08/09/2015 | −149.49 | 10/06/2016 | −134.575 |
References
- Zanello, F.; Teatini, P.; Putti, M.; Gambolati, G. Long term peatland subsidence: Experimental study and modeling scenarios in the Venice coastland. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooijer, A.; Page, S.; Jauhiainen, J.; Lee, W.; Lu, X.; Idris, A.; Anshari, G. Subsidence and carbon loss in drained tropical peatlands. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 1053–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holden, J. Peatland hydrology and carbon release: Why small-scale process matters. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2005, 363, 2891–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Loisel, J.; Brosseau, D.P.; Beilman, D.W.; Hunt, S.J. Global peatland dynamics since the last glacial maximum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, C.; Lock, M.A.; Reynolds, B. Climatic change and the release of immobilized nutrients from welsh riparian wetland soils. Ecol. Eng. 1993, 2, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschke, S.; Bousquet, P.; Ciais, P.; Saunois, M.; Canadell, J.G.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Bergamaschi, P.; Bergmann, D.; Blake, D.R.; Bruhwiler, L.; et al. Three decades of global methane sources and sinks. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykanen, H.; Alm, J.; Lang, K.; Silvola, J.; Martikainen, P.J. Emissions of CH4, N2O and CO2 from a virgin fen and a fen drained for grassland in finland. J. Biogeogr. 1995, 22, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C.; MacDonald, G.M.; Velichko, A.A.; Beilman, D.W.; Borisova, O.K.; Frey, K.E.; Kremenetski, K.V.; Sheng, Y. Siberian peatlands a net carbon sink and global methane source since the early Holocene. Science 2004, 303, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crichton, K.A.; Anderson, K.; Bennie, J.J.; Milton, E.J. Characterizing peatland carbon balance estimates using freely available Landsat ETM+ data. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, S.; Waldron, S.; Gilvear, D.; Grieve, I.; Armstrong, A.; Bragg, O.; Brewis, F.; Cooper, M.; Dargie, T.; Duncan, C.; et al. The price of knowledge in the knowledge economy: Should development of peatland in the UK support a research levy? Land Use Policy 2013, 32, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R.; Charman, D.J.; Everingham, F.; O’Reilly, R.M.; Palmer, M.A.; Rowell, T.A.; Stroud, D.A. The Flow Country: The Peatlands of Caithness and Sutherland; Joint Nature Conservation Committee: Peterborough, UK, 1988.
- Baird, A.J.; Belyea, L.R.; Morris, P.J. Upscaling of peatland-atmosphere fluxes of methane: Small-scale heterogeneity in process rates and the pitfalls of “bucket-and-slab” models. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 2009, 184, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Bain, C.G.; Bonn, A.; Stoneman, R.; Chapman, S.; Coupar, A.; Evans, M.; Gearey, B.; Howat, M.; Joosten, H.; Keenleyside, C.; et al. IUCN UK Commission of Inquiry on Peatlands; Project Report; IUCN UK Peatland Programme: Edinburgh, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shotbolt, L.; Anderson, A.; Townend, J. Changes to blanket bog adjoining forest plots at Bad a′ Cheo, Rumster Forest, Caithness. Forestry 1998, 71, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.; Gascoign, M.; Bosanko, N.R. Erosion and natural revegetation associated with surface land drains in upland peatlands. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.; Ray, D.; Pyatt, D. Physical and hydrological impacts of blanket bog afforestation at Bad a′ Cheo, Caithness: The first 5 years. Forestry 2000, 73, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannell, M.G.R.; Dewar, R.C.; Pyatt, D.G. Conifer plantations on drained peatlands in Britain—A net gain or loss of carbon. Forestry 1993, 66, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambolati, G.; Putti, M.; Teatini, P.; Camporese, M.; Ferraris, S.; Stori, G.G.; Nicoletti, V.; Silvestri, S.; Rizzetto, F.; Tosi, L. Peat land oxidation enhances subsidence in the Venice watershed. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2005, 86, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchunder, S.J.; Brown, L.E.; Holden, J. Environmental effects of drainage, drain-blocking and prescribed vegetation burning in UK upland peatlands. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 49–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R. The Great Flow—An International Responsibility; New Scientist Publications Expediting Inc.: Elmont, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, L.E.; Holden, J.; Chapman, P.J. Restoration of blanket peatlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lees, K.J.; Quaife, T.; Artz, R.R.E.; Khomik, M.; Clark, J.M. Potential for using remote sensing to estimate carbon fluxes across northern peatlands—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novellino, A.; Cigna, F.; Sowter, A.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D. Exploitation of the intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) algorithm with cosmo-skymed data for landslide inventory mapping in north-western Sicily, Italy. Geomorphology 2017, 280, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofani, V.; Del Ventisette, C.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Integration of remote sensing techniques for intensity zonation within a landslide area: A case study in the northern Apennines, Italy. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; Joughin, I.R.; Li, F.K.; Madsen, S.N.; Rodriguez, E.; Goldstein, R.M. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 333–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-W.; Lu, Z.; Gutenberg, L.; Zhu, Z. Characterizing hydrologic changes of the Great Dismal Swamp using SAR/InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgmann, R.; Hilley, G.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F. Resolving vertical tectonics in the San Francisco bay area from permanent scatterer InSAR and GPS analysis. Geology 2006, 34, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Monitoring landslides and tectonic motions with the permanent scatterers technique. Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuti, P.; Casagli, N.; Farina, P.; Marks, F.; Ferretti, A.; Menduni, G. Land subsidence in the Arno River Basin studied through SAR Interferometry. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Land Subsidence, Shanghai, China, 23–28 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Osmanoglu, B.; Dixon, T.H.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Jiang, Y. Mexico City subsidence observed with persistent scatterer InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Bozzano, F.; Marra, F.; Wegmuller, U.; Cinti, F.R.; Moro, M.; Saroli, M. Subsidence induced by urbanisation in the city of Rome detected by advanced InSAR technique and geotechnical investigations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3160–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Del Ventisette, C.; Liguori, V.; Casagli, N. Advanced radar-interpretation of insar time series for mapping and characterization of geological processes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 865–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cigna, F.; Del Ventisette, C.; Liguori, V.; Casagli, N. Insar Time-Series Analysis for Management and Mitigation of Geological Risk in Urban Area. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 1924–1927. [Google Scholar]
- Hilley, G.E.; Burgmann, R.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Rocca, F. Dynamics of slow-moving landslides from permanent scatterer analysis. Science 2004, 304, 1952–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, S.; Atzori, S.; Tolomei, C.; Allievi, J.; Ferretti, A.; Rocca, F.; Prati, C.; Stramondo, S.; Feuillet, N. Inflation rate of the colli albani volcanic complex retrieved by the permanent scatterers SAR interferometry technique. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizzani, P.; Berardino, P.; Casu, F.; Euillades, P.; Manzo, M.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Zeni, G.; Lanari, R. Surface deformation of Long Valley caldera and mono basin, California, investigated with the ISBAS-InSAR approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Strozzi, T.; Tosi, L.; Wegmüller, U.; Werner, C.; Carbognin, L. Assessing short- and long-time displacements in the Venice coastland by Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometric point target analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chang, N.B.; Li, S. Applications of SAR Interferometry in Earth and environmental science research. Sensors 2009, 9, 1876–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowter, A.; Bateson, L.; Strange, P.; Ambrose, K.; Syafiudin, M.F. DInSAR estimation of land motion using intermittent coherence with application to the south Derbyshire and Leicestershire coalfields. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, L.; Cigna, F.; Boon, D.; Sowter, A. The application of the Intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) InSAR method to the South Wales Coalfield, UK. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf. 2015, 34, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cigna, F.; Sowter, A.; Jordan, C.J.; Rawlins, B.G. Intermittent Small BAseline Subset (ISBAS) monitoring of land covers unfavourable for conventional c-band InSAR: Proof-of-concept for peatland environments in North Wales, UK. In Proceedings of the SPIE Remote Sensing, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11 November 2014; pp. 924305–924306. [Google Scholar]
- Sowter, A.; Amat, M.B.; Cigna, F.; Marsh, S.; Athab, A.; Alshammari, L. Mexico city land subsidence in 2014–2015 with Sentinel-1 IW TOPS: Results using the intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) technique. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Sowter, A. The relationship between intermittent coherence and precision of ISBAS InSAR ground motion velocities: ERS-1/2 case studies in the UK. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowter, A.; Athab, A.; Novellino, A.; Grebby, S.; Gee, D. Supporting energy regulation by monitoring land motion on a regional and national scale: A case study of Scotland. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2017, 232, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gee, D.; Sowter, A.; Novellino, A.; Marsh, S.; Gluyas, J. Monitoring land motion due to natural gas extraction: Validation of the Intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) dinsar algorithm over gas fields of North Holland, The Netherlands. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 1338–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowter, A. Phase ambiguity determination for the positioning of interferometric SAR data. Photogramm. Rec. 2003, 18, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Change (Scotland) Act 2009. Available online: http://www.Gov.Scot/topics/environment/climatechange/2009climatechangeact (accessed on 1 November 2017).
- Bruneau, P.M.C.; Johnson, S.M. Scotland’s Peatland-Definitions & Information Resources; Scottish Natural Heritage Commissioned Report No. 701; Scottish Natural Heritage: Edinburgh, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.J.; Doin, M.P.; Lopez-Quiroz, P.; Tupin, F.; Fruneau, B.; Pinel, V.; Trouve, E. Mexico City subsidence measured by InSAR time series: Joint analysis using PS and SBAS approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. A quantitative assessment of the sbas algorithm performance for surface deformation retrieval from DInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Two-dimensional phase unwrapping with use of statistical models for cost functions in nonlinear optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2001, 18, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NERC British Isles continuous GNSS Facility. Available online: http://www.Bigf.Ac.Uk/ (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Lanari, R.; Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Zeni, G.; Berardino, P.; Manunta, M.; Pepe, A. An overview of the small baseline subset algorithm: A DInSAR technique for surface deformation analysis. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2007, 164, 637–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Met Office. Available online: http://metoffice.gov.uk (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Shimada, M.; Watanabe, M.; Motooka, T. Subsidence estimation of the peatland forest in the central Kalimantan using the PALSAR time series differential interferometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 1846–1849. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, Z.; Waldron, S.; Tanaka, A. Monitoring peat subsidence and carbon emission in Indonesia peatlands using insar time series. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 6797–6798. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, G.W.; Price, J.S. A conceptual model of volume-change controls on the hydrology of cutover peats. J. Hydrol. 2005, 302, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R.; Birnie, R.; Clough, J. Peat Bog Ecosystems: Peatland Restoration; University of East London: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Crosetto, M.; Gili, J.A.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-Gonzalez, M.; Corominas, J.; Serral, D. Interferometric SAR monitoring of the Vallcebre landslide (Spain) using corner reflectors. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loew, A.; Bell, W.; Brocca, L.; Bulgin, G.E.; Burdanowitz, J.; Calbert, X.; Donner, R.V.; Ghent, D.; Gruber, A.; Kaminski, T.; et al. Validation practices for satellite-based Earth observation data across communities. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 779–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshammari, L.; Large, D.J.; Boyd, D.S.; Sowter, A.; Anderson, R.; Andersen, R.; Marsh, S. Long-Term Peatland Condition Assessment via Surface Motion Monitoring Using the ISBAS DInSAR Technique over the Flow Country, Scotland. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071103
Alshammari L, Large DJ, Boyd DS, Sowter A, Anderson R, Andersen R, Marsh S. Long-Term Peatland Condition Assessment via Surface Motion Monitoring Using the ISBAS DInSAR Technique over the Flow Country, Scotland. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(7):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071103
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshammari, Lubna, David J. Large, Doreen S. Boyd, Andrew Sowter, Russell Anderson, Roxane Andersen, and Stuart Marsh. 2018. "Long-Term Peatland Condition Assessment via Surface Motion Monitoring Using the ISBAS DInSAR Technique over the Flow Country, Scotland" Remote Sensing 10, no. 7: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071103
APA StyleAlshammari, L., Large, D. J., Boyd, D. S., Sowter, A., Anderson, R., Andersen, R., & Marsh, S. (2018). Long-Term Peatland Condition Assessment via Surface Motion Monitoring Using the ISBAS DInSAR Technique over the Flow Country, Scotland. Remote Sensing, 10(7), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071103