Vegetation Index Differencing for Broad-Scale Assessment of Productivity Under Prolonged Drought and Sequential High Rainfall Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
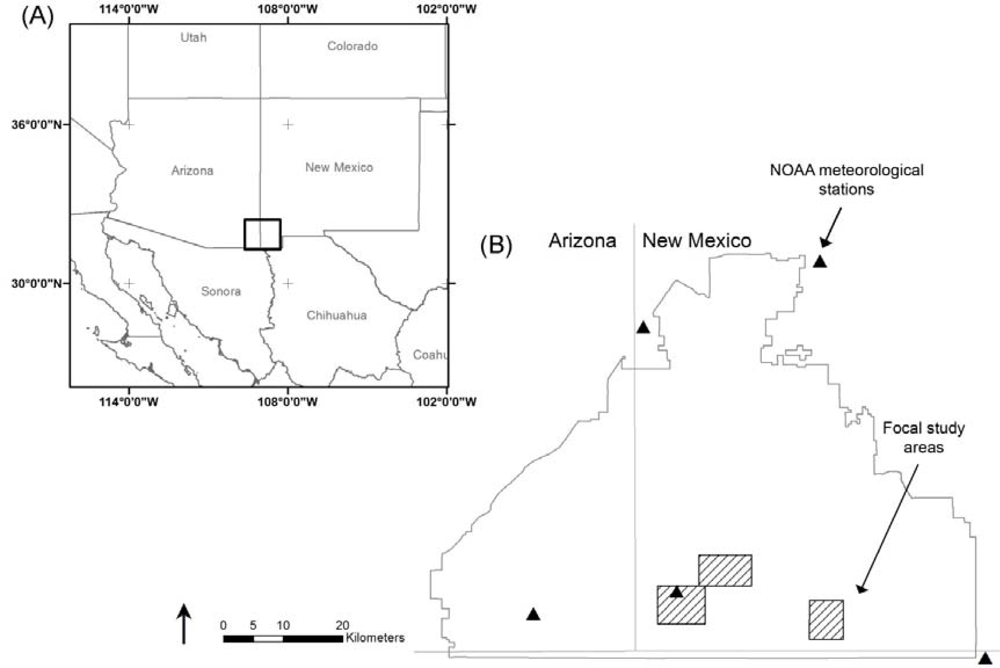
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Vegetation Index Differencing
2.3. Change Assessment
2.3.1. Z-Score Calculation
2.3.2. Minimum Mapping Unit and Selection of Focal Areas
2.4. Ecological Sites and State Mapping
3. Results
3.1. Patch Size Distributions for Positive and Negative Growing Season Anomalies
3.2. Ecological State Responses
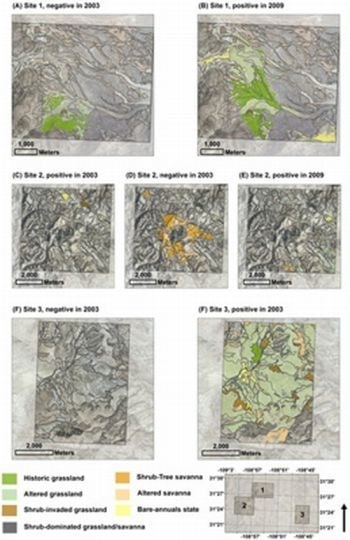
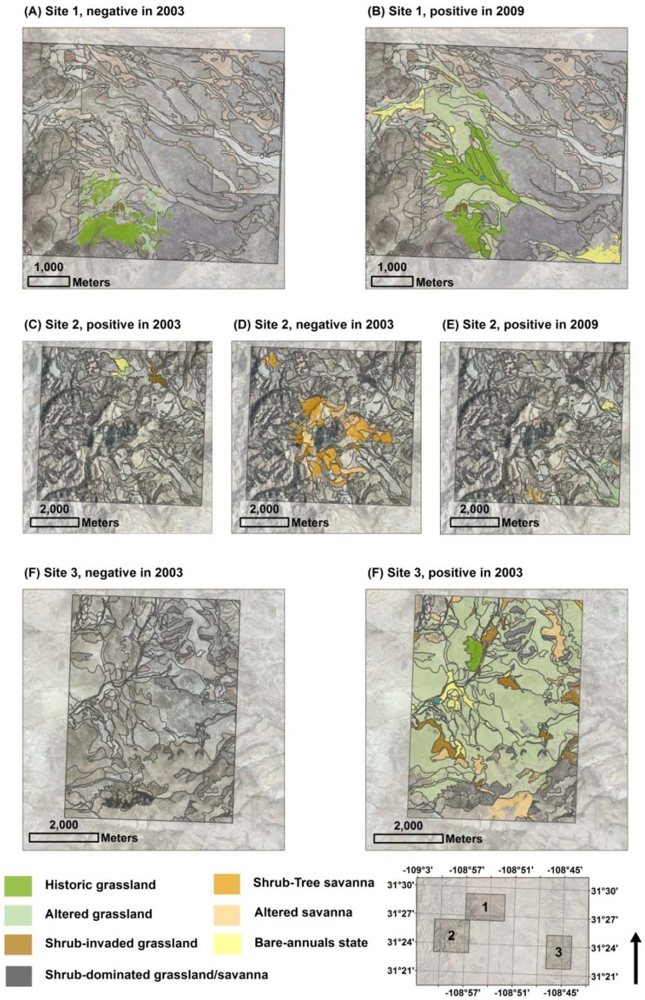
3.2.1. Historic Grassland and Altered Grassland: Decrease of NDVI in 2003
3.2.2. Historic Grassland and Altered Grassland: Increase of NDVI in 2009
3.2.3. Bare-Annuals: Increase of NDVI in 2003 and 2009
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Overpeck, J.; Udall, B. Dry times ahead. Science 2010, 328, 1642–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Woodhouse, C.A.; Overpeck, J.T. 2000 years of drought variability in the central United States. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc 1998, 79, 2693–2714. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, L.A. An Analysis of the Range Forage Situation in the United States: 1989–2040; General Technical Report RM-180; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Range and Forest Experiment Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1989; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- Briske, D.D.; Fuhlendorf, S.D.; Smeins, F.E. State-and-transition models, thresholds, and rangeland health: A synthesis of ecological concepts and perspectives. Rangel. Ecol. Manage 2005, 58, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bestelmeyer, B.T.; Brown, J.R.; Havstad, K.M.; Alexander, R.; Chavez, G.; Herrick, J.E. Development and use of state-and-transition models for rangelands. J. Range Manage 2003, 56, 114–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bestelmeyer, B.T.; Tugel, A.J.; Peacock, G.L.; Robinett, D.G.; Shaver, P.L.; Brown, J.R.; Herrick, J.E.; Sanchez, H.; Havstad, K.M. State-and-transition models for heterogeneous landscapes: A strategy for development and application. Rangel. Ecol. Manage 2009, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Briske, D.D.; Bestelmeyer, B.T.; Stringham, T.K.; Shaver, P.L. Recommendations for development of resilience-based state-and-transition models. Rangel. Ecol. Manage 2008, 61, 359–367. [Google Scholar]
- Steele, C.M.; Bestelmeyer, B.T.; Burkett, L.M.; Smith, P.L.; Yanoff, S. Spatially explicit representation of state-and-transition models. Rangel. Ecol. Manage 2012, 65, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, R.F. Detecting forest canopy change due to insect activity using Landsat MSS. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 1983, 49, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Alphan, H. Comparing the utility of image algebra operations for characterizing landscape changes: The case of the Mediterranean coast. J. Environ. Manage 2011, 92, 2961–2971. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A. Review article: Digital change detection techniques using remotely-sensed data. Int. J. Remote Sens 1989, 10, 989–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.; Anderson, M.; Belward, A.; Bindschadler, R.; Cohen, W.; Gao, F.; Goward, S.N.; Helder, D.; Helmer, E.; et al. Free access to Landsat imagery. Science 2008, 320, 1011–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.E. Biotic Communities: Southwestern United States and Northwestern Mexico; University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1994; p. 342. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, P.S., Jr. Image-based atmospheric corrections--revisited and improved. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 1996, 62, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, A.J.; Walter-Shea, E.A.; Ji, L.; Vina, A.; Hayes, M.; Svoboda, M.D. Drought monitoring with NDVI-based standardized vegetation index. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 2002, 68, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- National Resources Conservation Service. Land Resource Regions and Major Land Resource Areas of the United States, the Caribbean, and the Pacific Basin; USDA Arigcultural Handbook 296; National Resource Conservation Service, USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; p. 682. [Google Scholar]
- USDA-NRCS. Ecological Site Description: Clay Loam Upland (R041XA109AZ); National Resource Conservation Service, USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sheley, R.L.; James, J.J.; Rinella, M.J.; Bluemthal, D.; di Tomaso, J.M. Invasive Plant Management on Anticipated Conservation Benefits: A Scientific Assessment. In Conservation Benefits of Rangeland Practices—Assessment, Recommendations, and Knowledge Gaps; Briske, D.D., Ed.; US Department of Agriculture Natural Resource Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- USDA-NRCS. Ecological Site Description: Loamy Bottom (RO41XA114AZ); National Resource Conservation Service, USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, J.A.; Bastin, G.N.; Wallace, J.F.; McVicar, T.R. Assessing landscape health by scaling with remote sensing: When is it not enough? Landscape Ecol 2007, 22, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Forbis, T.A.; Provencher, L.; Turner, L.; Medlyn, G.; Thompson, J.; Jones, G. A method for landscape-scale vegetation assessment: Application to great basin rangeland ecosystems. Rangel. Ecol. Manage 2007, 60, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.C.; Kline, K.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Kovalskyy, V.; Hansen, M.; Loveland, T.R.; Vermote, E.; Zhang, C.S. Web-enabled Landsat Data (WELD): Landsat ETM plus composited mosaics of the conterminous United States. Remote Sens. Environ 2010, 114, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Coppin, P.; Jonckheere, I.; Nackaerts, K.; Muys, B.; Lambin, E. Digital change detection methods in ecosystem monitoring: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens 2004, 25, 1565–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Karl, J.W.; Herrick, J.E.; Browning, D.M. A vision for rangeland management based on best available knowledge and information. Rangel. Ecol. Manage 2012, 65, 638–646. [Google Scholar]
- Briske, D.D.; Fuhlendorf, S.D.; Smeins, F.E. A unified framework for assessment and application of ecological thresholds. Rangel. Ecol. Manage 2006, 59, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.R.J.; Blackmon, C.; Spann, G.W. Land use change detection using Landsat data. Remote Sens. Earth Resour 1977, 5, 79–91. [Google Scholar]

| Type 1 Ecological Sites | Condition | Ecological State | Area (AS, [Ha]) | % of MBA |
| Clay Hills, Clay Loam Upland, Draw, Gravelly Slopes, Hills (41.1&), Loamy, Loamy Bottom, Loamy Upland | Reference | Historic grassland | 1,426.97 | 12.48 |
| Altered | Altered grassland | 4,111.91 | 35.96 | |
| Altered | Shrub-invaded grassland | 441.91 | 3.86 | |
| Degraded | Shrub-dominated grassland | 10.73 | 0.09 | |
| Degraded | Bare-Annuals | 505.69 | 4.42 | |
| Total | 6,497.21 | 56.82 | ||
| Type 2 Ecological sites | Condition | Ecological state | Area (AS, [Ha]) | % of MBA |
| Hills (42.2*) | Reference | Shrub-Tree Savanna | 1,716.83 | 15.01 |
| Altered | Altered Savanna | 3,007.03 | 26.30 | |
| Degraded | Shrub-dominated Savanna | 213.54 | 1.87 | |
| Total | 4,937.40 | 43.18 | ||
| Negative Change 2003 | Ecological State | Area of Change (DAS [Ha]) | Total State Area (AS [Ha]) | % Age of Total State Area (DAS/AS) |
| Type 1 Ecological sites | ||||
| Clay Loam Upland, Gravelly Slopes, Hills (41.1), Loamy, Loamy Bottom | Historic grassland | 110.60 | 1,426.97 | 7.75 |
| Altered grassland | 51.11 | 4,111.58 | 1.24 | |
| Shrub-invaded grassland | 10.07 | 441.91 | 2.28 | |
| Bare-Annuals | 0.05 | 505.69 | 0.01 | |
| Total area changed (DA) | 171.84 | |||
| Type 2 Ecological sites | ||||
| Hills (42.2) | Shrub-Tree savanna | 323.03 | 1,716.83 | 18.82 |
| Altered Savanna | 169.12 | 3,007.03 | 5.62 | |
| Shrub-dominated Savanna | 33.42 | 213.54 | 15.65 | |
| Total area changed (DA) | 525.57 | |||
| Positive Change 2003 | Ecological State | Area of Change (DAS [Ha]) | Total State Area (AS [Ha]) | % Age of Total State Area (DAS/AS) |
| Type 1 Ecological sites | ||||
| Gravelly Slopes, Hills (41.1), Loamy Bottom | Altered grassland | 27.31 | 4,111.58 | 0.66 |
| Shrub-invaded grassland | 21.94 | 441.91 | 4.96 | |
| Bare-Annuals | 27.04 | 505.69 | 5.35 | |
| Total area changed (DA) | 76.29 | |||
| Type 2 Ecological sites | ||||
| Hills (42.2) | Shrub-Tree Savanna | 0.81 | 1,716.83 | 0.05 |
| Altered Savanna | 4.20 | 3,007.03 | 0.14 | |
| Total area changed (DA) | 5.01 | |||
| Positive Change 2009 | Ecological State | Area of Change (DAS [Ha]) | Total State Area (AS [Ha]) | % Age of Total State Area (DAS/AS) |
| Type 1 Ecological sites | ||||
| Clay Loam Upland, Draw, Gravelly Slopes, Hills (41.1), Loamy Bottom, Loamy Upland | Historic grassland | 355.68 | 1,426.97 | 24.93 |
| Altered grassland | 2,255.08 | 4,111.58 | 54.85 | |
| Shrub-invaded grassland | 146.29 | 441.91 | 33.11 | |
| Shrub-dominated grassland | 10.73 | 16.85 | 63.70 | |
| Bare-Annuals | 168.40 | 505.69 | 33.30 | |
| Total area changed (DA) | 2,936.18 | |||
| Type 2 Ecological sites | ||||
| Hills (42.2) | Shrub-Tree savanna | 16.97 | 1,716.83 | 0.99 |
| Altered Savanna | 173.69 | 3,007.03 | 5.78 | |
| Shrub-dominated Savanna | 55.91 | 213.54 | 26.18 | |
| Total area changed (DA) | 246.58 | |||
Share and Cite
Browning, D.M.; Steele, C.M. Vegetation Index Differencing for Broad-Scale Assessment of Productivity Under Prolonged Drought and Sequential High Rainfall Conditions. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 327-341. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5010327
Browning DM, Steele CM. Vegetation Index Differencing for Broad-Scale Assessment of Productivity Under Prolonged Drought and Sequential High Rainfall Conditions. Remote Sensing. 2013; 5(1):327-341. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5010327
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrowning, Dawn M., and Caitriana M. Steele. 2013. "Vegetation Index Differencing for Broad-Scale Assessment of Productivity Under Prolonged Drought and Sequential High Rainfall Conditions" Remote Sensing 5, no. 1: 327-341. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5010327