Laboratory Salinization of Brazilian Alluvial Soils and the Spectral Effects of Gypsum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sample Collection
2.2. Soil Sample Preparation
2.3. Spectral Data Measurement
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
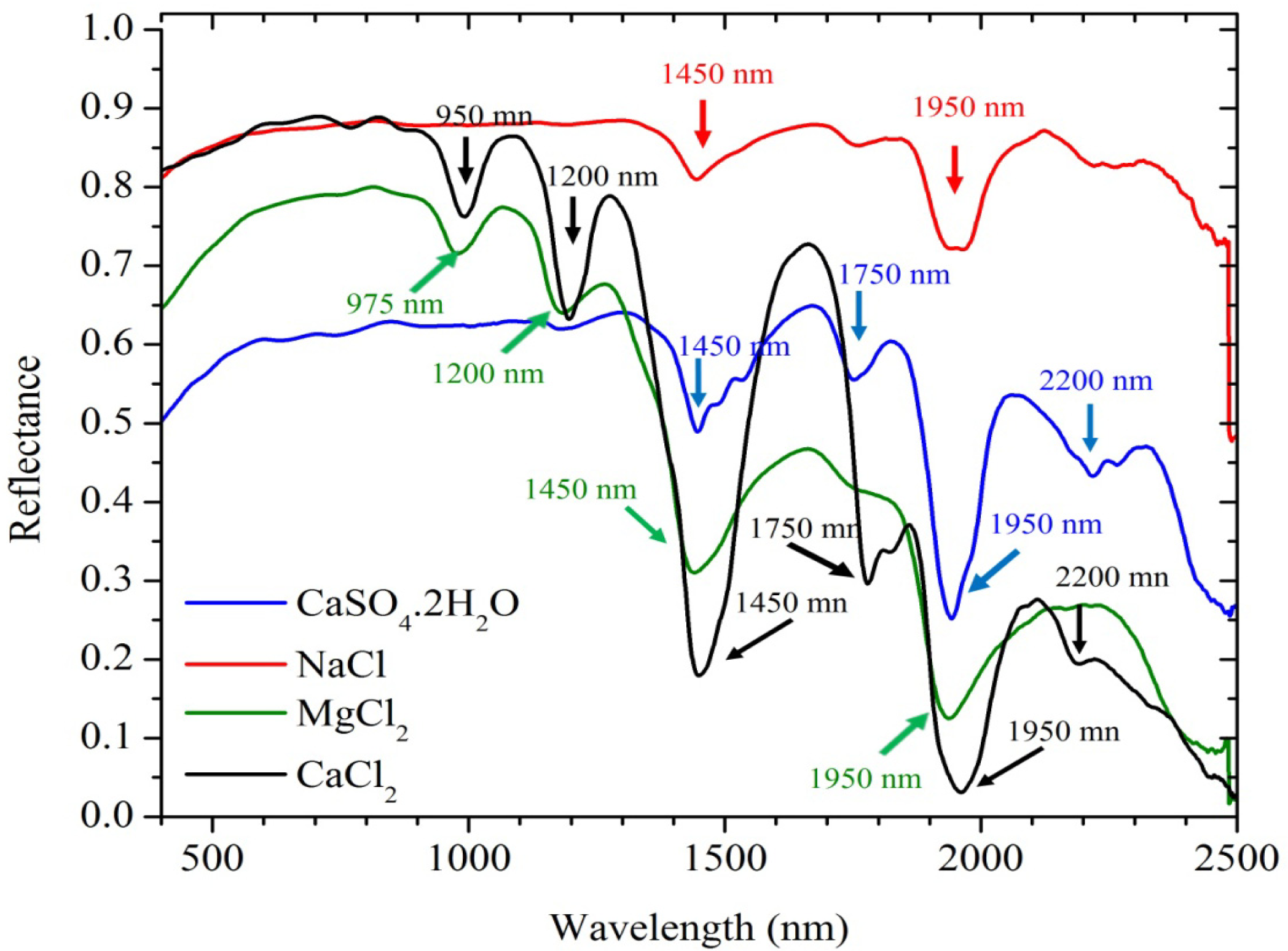
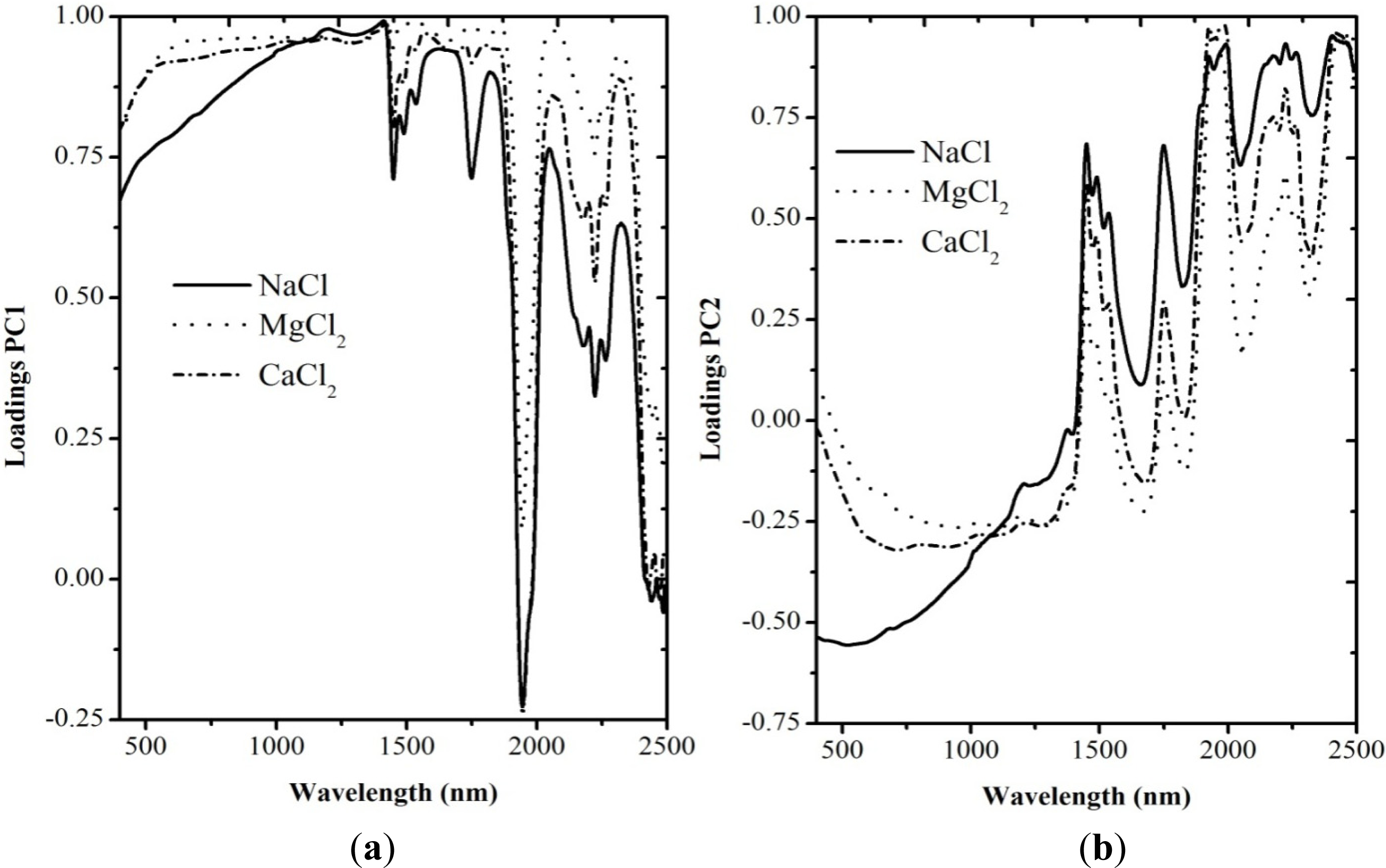
3.2. Spectral Data Analysis
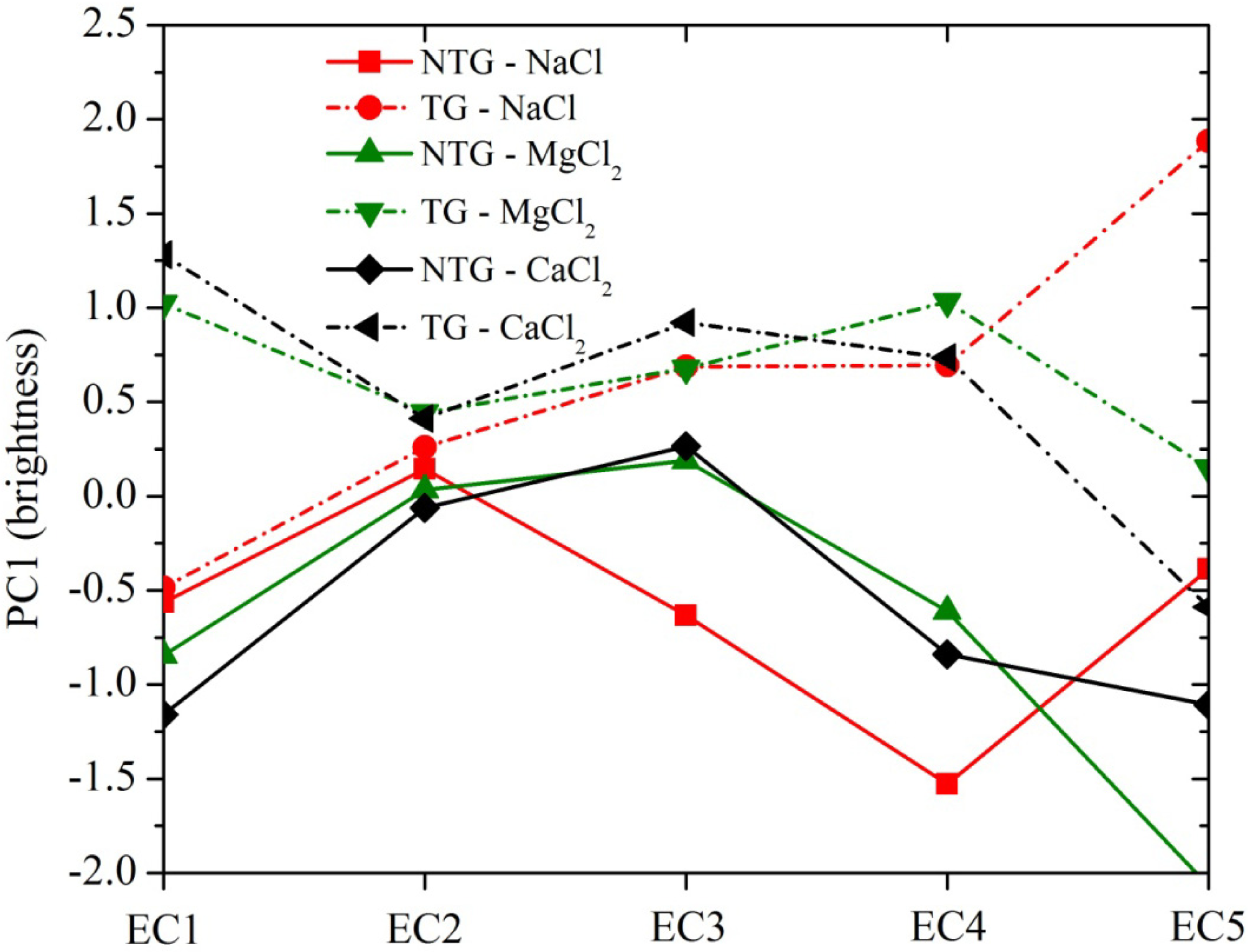
3.3. Effects of EC on the Spectra for NTG and TG Soils
3.4. Relationship of EC with Spectral Reflectance for NTG and TG Soils
3.5. Relationship of Band Depth with EC for NTG and TG Soils
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote sensing of soil salinity: Potentials and constraints. Remote Sens. Environ 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, R. Soils and food sufficiency. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev 2009, 29, 113–133. [Google Scholar]
- D’Odorico, P.; Bhattachan, A.; Davis, K.F.; Ravi, S.; Runyan, C.W. Global desertification: Drivers and feedbacks. Adv. Water Resour 2013, 51, 326–344. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, M.J.; Carvalho, J.A.; Silva, E.L.; Miguel, D.S. Efeito da irrigação com água salina em um solo cultivado com feijoeiro (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Ciência Agrotecnológica 2003, 27, 443–450. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Crops and Drops: Making the Best Use of Water for Agriculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2002; p. 28.
- Wang, Q.; Pingheng, L.; Chen, X. Modeling salinity effects on soil reflectance under various moisture conditions and its inverse application: A laboratory experiment. Geoderma 2012, 170, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Dehaan, R.; Taylor, G.R. Image-derived spectral endmembers as indicators of salinization. Int. J. Remote Sens 2003, 24, 775–794. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Ding, J.L.; Kelimul, A.; Zhang, F.; Lei, L. Research on remote sensing monitoring of soil salinization based on measured hyperspectral and EM38 data. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal 2013, 33, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Mougenot, B.; Epema, G.F. Pouget. M. Remote sensing of salt affected soils. Remote Sens. Rev 1993, 7, 241–259. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.L.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z.L. A spectral index for estimating soil salinity in the Yellow River Delta Region of China using EO-1 Hyperion data. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 378–388. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Luo, G.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Detecting soil salinity with arid fraction integrated index and salinity index in feature space using Landsat TM imagery. J. Arid Land 2013, 05, 340–353. [Google Scholar]
- Howari, F.M.; Goodell, P.C.; Miyamoto, S. Spectral properties of salt crusts formed on saline soils. J. Environ. Qual 2002, 31, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar]
- Farifteh, J.; Farshad, A.; George, R.J. Assessing salt-affected soils using remote sensing, solute modelling, and geophysics. Geoderma 2006, 130, 191–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bouaziz, M.; Matschullat, J.; Gloaguen, R. Improved remote sensing detection of soil salinity from a semi-arid climate in Northeast Brazil. Comptes Rend. Geosci 2011, 343, 795–803. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, R.M.; Barros, M.F.C. dos Santos, P.M.; Rolim, M.M. Correção de solos salino-sódicos pela aplicação de gesso mineral. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental 2008, 12, 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Lacerda, C.F.; Souza, G.G.; Silva, F.L.B.; Guimarães, F.V.A.; Silva, G.L.; Cavalcante, L.F. Soil salinization and maize and cowpea yield in the crop rotation system using saline waters. Eng. Agrícola 2011, 31, 663–675. [Google Scholar]
- Caires, E.F.; Fonseca, A.F.; Mendes, J.; Chueiri, W.A.; Madruga, E.F. Produção de milho, trigo e soja em função das alterações das características químicas do solo pela aplicação de calcário e gesso na superfície, em sistema de plantio direto. R. Bras. Ci. Solo 1999, 23, 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Farifteh, J.; van der Meer, F.; van der Meijde, M.; Atzberger, C. Spectral characteristics of salt-affected soils: A laboratory experiment. Geoderma 2008, 145, 196–206. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, M.J.N. Geomorfologia. In Instituto de Planejamento do Estado do Ceará—IPLANCE; Atlas do Ceará: Fortaleza, Brazil, 1997; pp. 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, T.I.; Carmona, F.C.; Anghinoni, I.; Genro Junior, S.A.; Marcolin, E. Flooded rice yield as affected by levels of water salinity in different stages of its cycle. R. Bras. Ci. Solo 2010, 34, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, F.C.; Teixeira, A.S. dos; Gondim, R.S. Espacialização da evapotranspiração de referência e precipitação efetiva para estimativa das necessidades de irrigação na região do Baixo Jaguaribe—CE. Revista Ciência Agronômica 2005, 36, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, C.S.M. Relação entre Solos Afetados por sais e Concentração de Metais Pesados em Quatro Perímetros Irrigados no Ceará. Master Dissertation; Universidade Federal do Ceará (UFC): Fortaleza, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, S.N.; Dias, N.S.; Teles Filho, J.F. Recuperação de um solo salinizado devido ao excesso de fertilizantes em ambiente protegido. Irriga 2007, 12, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Embrapa—Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária, Centro Nacional de Pesquisa dos Solos; Manual de Métodos de Análise de solo: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1997; p. 212.
- Moreira, R.C.; Galvão, L.S. Variation in spectral shape of urban materials. Remote Sens. Lett 2010, 1, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.N.; Roush, T.L. Reflectance spectroscopy: Quantitative analysis techniques for remote sensing applications. J. Geophys. Res 1984, 89, 6329–6340. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, G.R.; Salisbury, J.W.; Lenhoff, C.J. Visible and near-infrared spectra of minerals and rocks. II. Carbonates. Mod. Geol 1971, 2, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor, I.M.; Pedreño, J.N.; Koch, M.; Gómez, I. Applying imaging spectroscopy techniques to map saline soils with ASTER images. Geoderma 2010, 158, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z. Reflectance spectroscopy for the assessment of soil salt content in soils of the Yellow River Delta of China. Int. J. Remote Sens 2008, 29, 5511–5531. [Google Scholar]










| Attribute | Electrical Conductivity (EC) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC1 | EC2 | EC3 | EC4 | EC5 | |||||||
| NTG | TG | NTG | TG | NTG | TG | NTG | TG | NTG | TG | ||
| NaCl | EC (dS/m) | 6.2 | 6.9 | 18.6 | 34.5 | 35.7 | 40.7 | 49.6 | 64.9 | 112.8 | 138.9 |
| Na+ (Mmol/dm3) | 60.7 | 20.7 | 132.7 | 76.8 | 269.5 | 141.3 | 322.4 | 245.4 | 1101.3 | 486.5 | |
| MgCl2 | EC (dS/m) | 5.6 | 4.8 | 19.3 | 16.9 | 38.3 | 24.6 | 76.3 | 49.3 | 98.8 | 97.8 |
| Mg2+ (Mmol/dm3) | 109.8 | 89.2 | 154.5 | 163 | 189.7 | 209.3 | 208.5 | 234.3 | 235.7 | 239.5 | |
| CaCl2 | EC (dS/m) | 4.6 | 5.2 | 15 | 15.5 | 32 | 29.6 | 76.3 | 51.2 | 101.9 | 103.8 |
| Ca2+ (Mmol/dm3) | 142.8 | 791.4 | 211.1 | 819.4 | 251.9 | 920.7 | 444.1 | 1015 | 628.7 | 1,613.9 | |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, L.C.J.; Dos Santos Teixeira, A.; Galvão, L.S. Laboratory Salinization of Brazilian Alluvial Soils and the Spectral Effects of Gypsum. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2647-2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6042647
Moreira LCJ, Dos Santos Teixeira A, Galvão LS. Laboratory Salinization of Brazilian Alluvial Soils and the Spectral Effects of Gypsum. Remote Sensing. 2014; 6(4):2647-2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6042647
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Luis Clenio J., Adunias Dos Santos Teixeira, and Lênio Soares Galvão. 2014. "Laboratory Salinization of Brazilian Alluvial Soils and the Spectral Effects of Gypsum" Remote Sensing 6, no. 4: 2647-2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6042647
APA StyleMoreira, L. C. J., Dos Santos Teixeira, A., & Galvão, L. S. (2014). Laboratory Salinization of Brazilian Alluvial Soils and the Spectral Effects of Gypsum. Remote Sensing, 6(4), 2647-2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6042647





