A Sparsity-Based InSAR Phase Denoising Algorithm Using Nonlocal Wavelet Shrinkage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
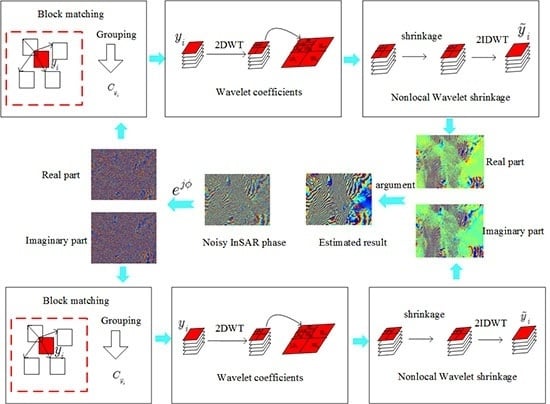
2. Nonlocal Wavelet Shrinkage Method for InSAR Phase Denoising
2.1. Formulation of InSAR Phase Filtering
2.2. Modeling of Nonlocal Wavelet Shrinkage Method
2.3. Nonlocal Estimation of
3. Algorithm Implementation
3.1. Parameter Selection
3.2. Processing Steps
4. Results
4.1. Simulated InSAR Data
4.2. Acquired InSAR Data
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison with Several Interferometric Phase Filters
- (1)
- The Goldstein method and the WInPF method show large numbers of errors in almost all the areas of phase image, especially in areas of low coherence value and high fringe density. The number of residues increases with the increase of noise level. The texture in the region of dense fringes is not well preserved.
- (2)
- The noise suppressing performance of nonlocal based methods is superior than Goldstein and WInPF methods. According to PLOW based on LARK feature method, some phase noise still exists since one cluster may have different noise levels. Some fringes in Figure 6A3 are broken or merged with neighboring fringes.
- (3)
- The filtering performance of BM3D is comparable to NLHoSVD when the coherence is relatively high. Its details preservation are probably weakened with the presence of strong noise or low signal-to-noise ratio in low-coherence areas. The performance of NlHoSVD is better than that of Goldstein, WInPF, BM3D or PLOW. However, the filter employs the simple hard thresholding method such that the nonlocal similarity might not be fully exploited.
- (4)
- Dataset-by-dataset, the proposed method has the least number of residues and the smallest RMSE (Table 2 c.f. Table 5). In the simulation experiment of Data-II, Data-III and Data-IV, the numbers of residues are all zeros. In addition, the method overcomes the problems of the discontinuity and blurring, and suppresses the phase residues of grainy noise even in areas of low coherence and high fringe.
5.2. Fast and Efficient Realization
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. How to Solve l1 − l2 Optimization Problem
References
- Eichel, P.H.; Ghiglia, D.C.; Jakowatz, C.V., Jr. Spotlight SAR Interferometry for Terrain Elevation Mapping and Interferometric Change Detection; SAND93-2072 UC-700; Sandia National Labs.: Albuquerque, NM, USA; AT and T Technologies, Inc.: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1996; Volume 12.
- Lanari, R.; Fornaro, G. Generation of digital elevation models by using SIR-C/X-SAR multifrequency two-pass interferometry: The Etna case study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 1097–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Grunes, M.R.; Reigber, A. A new technique for noise filtering of SAR interferometric phase images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.; Fang, D.; Li, J. A locally adaptive filter of interferometric phase images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Liang, D.; Dong, Z. A New Adaptive Multiresolution noise filtering approach for SAR interferometric phase images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 266–270. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Xia, Y.; Fu, S.; Sun, X. An adaptive contoured window filter for interferometric synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical application. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, I.; Stewart, M.P.; Kampes, B.M.; Perski, Z.; Lilly, P. A modification to the Goldstein radar interferogram filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2114–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bao, Z.; Li, H.; Liao, G. Image autocoregistration and InSAR interferogram estimation using joint subspace projection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 288–297. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Martinez, C.; Fabregas, X. Modeling and reduction of SAR interferometric phase noise in the wavelet domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2553–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.L.; Canovas, X.F.; Chandra, M. SAR interferometric phase noise reduction using wavelet transform. Electron. Lett. 2003, 37, 649–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.; Fu, R.; Dai, Z.; Liu, B. Noise reduction in interferograms using the wavelet packet transform and wiener filtering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 404–408. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.L.; Johnstone, I.M. Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika 1994, 81, 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Bui, T.D.; Krzyzak, A. Image denoising with neighbor dependency and customized wavelet and threshold. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Mercer, B. Interferometric SAR phase filtering in the wavelet domain using simultaneous detection and estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 49, 1396–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xing, M.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Z. Sparse regularization of interferometric phase and amplitude for InSAR image formation based on Bayesian representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2123–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhateja, V.; Tripathi, A.; Gupta, A.; Lay-Ekuakille, A. Speckle suppression in SAR images employing modified anisotropic diffusion filtering in wavelet domain for environment monitoring. Measurement 2015, 74, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Cui, Y.; Zuo, B.; Yang, J.; Song, J. Polarimetric SAR image filtering based on patch ordering and simultaneous sparse coding. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4079–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buadeset, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J. A review of image denoising algorithms, with a new one. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2005, 4, 490–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J.M. Nonlocal image and movie denoising. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 76, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deledalle, C.A.; Denis, L.; Tupin, F. NL-InSAR: Nonlocal interferogram estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, F.; Meng, D.; Hu, D. Nonlocal SAR interferometric phase filtering through higher order singular value decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendur, L.; Selesnick, I.W. Bivariate shrinkage functions for wavelet-based denoising exploiting interscale dependency. IEEE Geosci. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 2744–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.; Canovas, F.; Javier, F. SAR interferometric phase statistics in wavelet domain. Electron. Lett. 2002, 38, 1207–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Zibulevsky, M.; Elad, M. L1-L2 optimization in signal and image processing. Signal Process. Mag. 2010, 27, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Shi, G. Sparsity-based image denoising via dictionary learning and structural clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 457–464.
- Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Dong, Z.; Wu, M. Modified patch-based locally optimal wiener method of interferometric SAR phase filtering. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Milanfar, P. Automatic parameter selection for denoising algorithms using no-reference measure of image content. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 3116–3132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Ying, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Q. Fast non-local algorithm for image denoising. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–11 October 2006; pp. 1429–1432.










| Data-I | Data-II | Data-III | Data-IV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | 76,502 | 57,680 | 33,340 | 7974 |
| RMSEs | 2.3814 | 1.7890 | 1.1673 | 0.4795 |
| MSSIM | 0.0209 | 0.0503 | 0.1111 | 0.2816 |
| Data-I | Data-II | Data-III | Data-IV | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filtering Methods | # | RMSEs | MSSIM | # | RMSEs | MSSIM | # | RMSEs | MSSIM | # | RMSEs | MSSIM |
| Haar | 23 | 0.1115 | 0.6774 | 0 | 0.0222 | 0.8232 | 0 | 0.0094 | 0.8828 | 0 | 0.0037 | 0.9265 |
| Db2 | 34 | 0.1273 | 0.6609 | 0 | 0.0249 | 0.8164 | 0 | 0.0102 | 0.8781 | 0 | 0.0040 | 0.9236 |
| Db4 | 27 | 0.1138 | 0.6774 | 0 | 0.0231 | 0.8222 | 0 | 0.0096 | 0.8821 | 0 | 0.0038 | 0.9254 |
| Db6 | 30 | 0.1186 | 0.6722 | 0 | 0.0241 | 0.8191 | 0 | 0.0099 | 0.8802 | 0 | 0.0039 | 0.9233 |
| Bior1.3 | 19 | 0.1074 | 0.6828 | 0 | 0.0219 | 0.8244 | 0 | 0.0093 | 0.8834 | 0 | 0.0037 | 0.9261 |
| Bior1.5 | 19 | 0.1059 | 0.6854 | 0 | 0.0219 | 0.8246 | 0 | 0.0092 | 0.8828 | 0 | 0.0037 | 0.9255 |
| Data-V | Data-VI | Data-VII | |
|---|---|---|---|
| # | 42,863 | 54,673 | 51,599 |
| metric Q | 0.0964 | 0.0596 | 0.0445 |
| Data-V | Data-VI | Data-VII | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Metric Q | # | Metric Q | # | Metric Q | |
| Haar | 219 | 7.6778 | 228 | 6.5505 | 313 | 6.0949 |
| Db2 | 243 | 7.4972 | 222 | 6.5601 | 293 | 6.0813 |
| Db4 | 307 | 7.0544 | 249 | 6.4012 | 315 | 6.0873 |
| Db6 | 309 | 7.0296 | 233 | 6.4854 | 317 | 6.1029 |
| Bior1.3 | 328 | 6.8942 | 266 | 6.3551 | 312 | 6.0660 |
| Bior1.5 | 267 | 6.3835 | 304 | 6.0703 | 322 | 6.0596 |
| Data-I | Data-II | Data-III | Data-IV | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filtering Methods | # | RMSEs | MSSIM | # | RMSEs | MSSIM | # | RMSEs | MSSIM | # | RMSEs | MSSIM |
| Goldstein | 43,145 | 1.5159 | 0.0299 | 4077 | 0.4093 | 0.1243 | 472 | 0.1917 | 0.4354 | 71 | 0.1601 | 0.6853 |
| WInPF | 3943 | 0.7911 | 0.2127 | 1081 | 0.2500 | 0.4385 | 143 | 0.0875 | 0.6338 | 23 | 0.0325 | 0.7972 |
| PLOW | 889 | 0.3277 | 0.4441 | 38 | 0.0635 | 0.6919 | 0 | 0.0167 | 0.8317 | 0 | 0.0083 | 0.8759 |
| BM3D | 1184 | 0.2420 | 0.4215 | 22 | 0.0606 | 0.6639 | 0 | 0.0135 | 0.8518 | 0 | 0.0044 | 0.9160 |
| NlHoSVD | 93 | 0.2089 | 0.6345 | 0 | 0.0374 | 0.8300 | 0 | 0.0152 | 0.8913 | 0 | 0.0052 | 0.9351 |
| Filtering Methods | # | Metric Q | Computational Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interferogram of Data-VII | 51,599 | 0.0445 | - |
| Goldstein | 21,043 | 1.7703 | 0.2 |
| WInPF | 3279 | 2.0228 | 0.4 |
| Modified PLOW | 2066 | 4.9825 | 650.8 s |
| BM3D | 659 | 5.8600 | 303.1 s |
| NlHoSVD | 346 | 5.8994 | 665.8 s |
| Our method | 322 | 6.0596 | 546.0 s |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, D.; Lv, X.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Qian, J. A Sparsity-Based InSAR Phase Denoising Algorithm Using Nonlocal Wavelet Shrinkage. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8100830
Fang D, Lv X, Wang Y, Lin X, Qian J. A Sparsity-Based InSAR Phase Denoising Algorithm Using Nonlocal Wavelet Shrinkage. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(10):830. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8100830
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Dongsheng, Xiaolei Lv, Yong Wang, Xue Lin, and Jiang Qian. 2016. "A Sparsity-Based InSAR Phase Denoising Algorithm Using Nonlocal Wavelet Shrinkage" Remote Sensing 8, no. 10: 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8100830
APA StyleFang, D., Lv, X., Wang, Y., Lin, X., & Qian, J. (2016). A Sparsity-Based InSAR Phase Denoising Algorithm Using Nonlocal Wavelet Shrinkage. Remote Sensing, 8(10), 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8100830