Rank-Based Methods for Selection of Landscape Metrics for Land Cover Pattern Change Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Selection of Pattern Metrics for Land Cover Change Identification
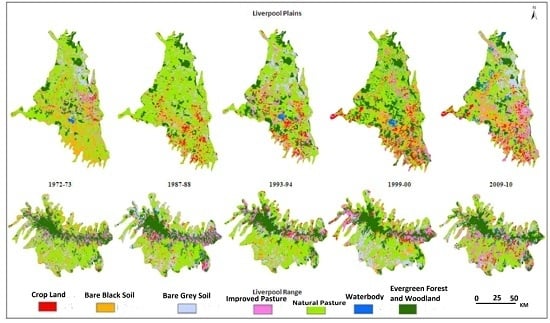
2. Study Area

3. Methods
3.1. Land Cover Classification

| Code | Name | Type | Rank * | Code | Name | Type | Rank * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP | Number of patches | Area | 10 | NCA | Number of core areas | Interior | 25 |
| CA | Class area (ha) | Area | 21 | TCA | Total core area (ha) | Interior | 19 |
| LPI | Largest patch index | Area | 13 | CORE_MN | Mean core area per patch (ha) | Interior | 1 |
| AREA_MN | Mean patch size (ha) | Area | 22 | CORE_SD | Patch core area standard deviation (ha) | Interior | 26 |
| AREA_SD | Patch size standard deviation (ha) | Area | 15 | CORE_CV | Patch core area coefficient of variation (%) | Interior | 27 |
| Area_CV | Patch size coefficient of variation (%) | Area | 23 | ENN_MN | Mean nearest neighbor distance (m) | Isolation | 6 |
| TE | Total edge (m) | Edge | 9 | PROX_MN | Mean proximity index | Isolation | 16 |
| MPE | Mean patch edge (m) | Edge | 24 | PR | Patch richness | Heterogeneity | 5 |
| PAR_AM | Mean perimeter/area ratio | Shape | 6 | SHDI | Shannon’s diversity index | Heterogeneity | 3 |
| LSI | Landscape shape index | Shape | 17 | SHEI | Shannon’s evenness index | Heterogeneity | 3 |
| SHAPE_MN | Mean shape index | Shape | 12 | MSIDI | Modified Simpson’s diversity index | Heterogeneity | 2 |
| SHAPE_AW | Area-weighted mean patch fractal dimension | Shape | 8 | IJI | Interspersion and juxtaposition index (%) | Heterogeneity | 18 |
| FRAC | Fractal dimension | Shape | 11 | AI | Aggregation index (%) | Heterogeneity | 28 |
| FRAC_MN | Mean patch fractal dimension | Shape | 12 | CONTAG | Contagion index | Dispersion | 7 |
| FRAC_AW | Area-weighted mean patch fractal dimension | Shape | 8 | COHESION | Patch cohesion index | Connectivity | 14 |
3.2. Capability of Metrics to Capture Change in Landscape Pattern
3.3. Sensitivity of Metrics to Spatial Resolution of Remote Sensing Data
3.4. Sensitivity of Metrics to Number of Classes
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Cluster Analysis

4.2. Analysis of β and γ-Scores of Metrics to Capture Landscape Pattern Change


4.3. Sensitivity of Metrics to Spatial Resolution of Remote Sensing Data

4.4. Sensitivity of Metrics to Thematic Changes


4.5. Selection of Landscape Metrics
4.6. Change Analysis Using the Two Study Sites


5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Read, J.; Lam, N.S. Spatial methods for characterising land cover and detecting land-cover changes for the tropics. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2457–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Romme, W.H.; Crist, M.; Roworth, E. Cumulative effects of roads and logging on landscape structure in the San Juan Mountains, Colorado (USA). Landsc. Ecol. 2001, 16, 327–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimgruber, P.; Mcshea, W.J.; Schnell, G.D. Effects of scale and logging on landscape structure in a forest mosaic. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2002, 74, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnot, C.; Fisher, P.F.; Wadsworth, R.; Wellens, J. Landscape metrics with ecotones: Pattern under uncertainty. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, J.A.; Martinko, E.A.; Price, K.P. Landscape structure analysis of Kansas at three scales. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2000, 52, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, D.O. Forest fragmentation in Loudoun County, Virginia, USA evaluated with multitemporal Landsat imagery. Landsc. Ecol. 2001, 16, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.J.; Cameron, G.N. Analysis of landscape patterns in coastal wetlands of Galveston Bay, Texas (USA). Landsc. Ecol. 2001, 16, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botequilha Leitão, A.; Ahern, J. Applying landscape ecological concepts and metrics in sustainable landscape planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2002, 59, 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergel, S.E. Spatial and non-spatial factors: When do they affect landscape indicators of watershed loading? Landsc. Ecol. 2005, 20, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, J. Use and misuse of landscape indices. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; Gardner, R.H.; O’Neill, R.V. Landscape Ecology in Theory and Practice; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Cunningham, R.B.; Donnelly, C.F.; Lesslie, R. On the use of landscape surrogates as ecological indicators in fragmented forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 159, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Marks, B.J. Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure; Gen. Tech. Rep. PNW-GTR-351; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rempel, R.S.; Carr, A.; Elkie, P.C. Patch Analyst User’s Manual: A Tool for Quantifying Landscape Structure; Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources, Boreal Science, Northwest Science & Technology: Thunder Bay, ON, Canada, 1999.
- Crews-Meyer, K.A. Characterizing landscape dynamism using pane-pattern metrics. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Cumming, S.; Vervier, P. Statistical models of landscape pattern metrics, with applications to regional scale dynamic forest simulations. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanfield, B.J.; Bliss, J.C.; Spies, T.A. Land ownership and landscape structure: A spatial analysis of sixty-six Oregon (USA) Coast Range watersheds. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riitters, K.H.; O’neill, R.; Hunsaker, C.; Wickham, J.D.; Yankee, D.; Timmins, S.; Jones, K.; Jackson, B. A factor analysis of landscape pattern and structure metrics. Landsc. Ecol. 1995, 10, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, D.H.; Riitters, K.; Orvis, K. A multi-scale analysis of landscape statistics. Landsc. Ecol. 1997, 12, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlpine, C.A.; Eyre, T.J. Testing landscape metrics as indicators of habitat loss and fragmentation in continuous eucalypt forests (Queensland, Australia). Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honnay, O.; Piessens, K.; van Landuyt, W.; Hermy, M.; Gulinck, H. Satellite based land use and landscape complexity indices as predictors for regional plant species diversity. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 63, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.; de Aranzabal, I.; Aguilera, P.; Rescia, A.; Pineda, F. Relationship between landscape typology and socioeconomic structure: Scenarios of change in Spanish cultural landscapes. Ecol. Model. 2003, 168, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, E.J. Quantifying landscape spatial pattern: What is the state of the art? Ecosystems 1998, 1, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, J.; Stehman, S.; Sohl, T.; Loveland, T. Detecting trends in landscape pattern metrics over a 20-year period using a sampling-based monitoring programme. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civco, D.L.; Hurd, J.D.; Wilson, E.H.; Arnold, C.L.; Prisloe, M.P. Quantifying and describing urbanizing landscapes in the Northeast United States. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Frohn, R.C. Remote Sensing for Landscape Ecology: New Metric Indicators for Monitoring, Modeling, and Assessment of Ecosystems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- DeClercq, E.M.; Vandemoortele, F.; DeWulf, R.R. A method for the selection of relevant pattern indices for monitoring of spatial forest cover pattern at a regional scale. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2006, 8, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.M.; Langford, W.T.; Jones, S.D.; Bekessy, S.A. Are landscape ecologists addressing uncertainty in their remote sensing data? Landsc. Ecol. 2012, 27, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.; Krummel, J.; Gardner, R.; Sugihara, G.; Jackson, B.; DeAngelis, D.; Milne, B.; Turner, M.; Zygmunt, B.; Christensen, S.; et al. Indices of landscape pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 1988, 1, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, J. Response to Bissonette JA and Storch I. 2002: “Fragmentation: Is the message clear?”—Lack of agreement on fragmentation metrics blurs correspondence between fragmentation experiments and predicted effects. Conserv. Ecol. 2003, 7, r6. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, J.D.; O’Neill, R.V.; Ritters, K.H.; Wade, T.G.; Jones, K.B. Sensitivity of selected landscape pattern metrics to land-cover misclassification and differences in land-cover composition. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Saura, S. Effects of minimum mapping unit on land cover data spatial configuration and composition. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 4853–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S. Effects of remote sensor spatial resolution and data aggregation on selected fragmentation indices. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; O’Neill, R.V.; Gardner, R.H.; Milne, B.T. Effects of changing spatial scale on the analysis of landscape pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 1989, 3, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Martinez-Millan, J. Sensitivity of landscape pattern metrics to map spatial extent. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Shen, W.; Sun, W.; Tueller, P.T. Empirical patterns of the effects of changing scale on landscape metrics. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 761–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: Scaling relations. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Jenerette, G.D.; Wu, J.; Gardner, R.H. Evaluating empirical scaling relations of pattern metrics with simulated landscapes. Ecography 2004, 27, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioregional Conservation Assessment Scoping Report (BCASR). Brigalow Belt South, NSW, Bioregional Conservation Assessment Scope Report, Western Regional Assessments Unit, NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service, Dabbo, NSW 2830, 2002. Available online: http//www.nsw.gov.au (accessed on 15 October 2014).
- Foody, G.M. Thematic map comparison: Evaluating the statistical significance of differences in classification accuracy. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Harshness in image classification accuracy assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3137–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Kumar, L. Independent two step thresholding of binary images in inter-annual land cover change/no-change identification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2013, 81, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Kumar, L. Binary images in seasonal land-cover change identification: A comparative study in parts of NSW, Australia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2162–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Oderwald, R.G.; Mead, R.A. Assessing Landsat classification accuracy using discrete multivariate analysis statistical techniques. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1983, 49, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principle and Practices, Mapping Science Series; Lewis Publications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rocchini, D.; Perry, G.L.W.; Salerno, M.; Maccherini, S.; Chiarucci, A. Landscape change and the dynamics of open formations in a natural reserve. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanddemoortele, F. Analyse Van Bosversnippering in Vlaanderen: Evaluatie Van Landschapsindices. Master’s Thesis, Ghent University, Gent, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Neel, M.C.; McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A. Behavior of class-level landscape metrics across gradients of class aggregation and area. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyantuyev, A.; Wu, J. Effects of thematic resolution on landscape pattern analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Reynolds, J.F. A new contagion index to quantify spatial patterns of landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 1993, 8, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.J.B.; Weaver, K.; Schnekenburger, F.; Perera, A.H. Sensitivity of landscape pattern indices to input data characteristics on real landscapes: Implications for their use in natural disturbance emulation. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressey, R.; Hager, T.; Ryan, K.; Schwarz, J.; Wall, S.; Ferrier, S.; Creaser, P. Using abiotic data for conservation assessments over extensive regions: Quantitative methods applied across New South Wales, Australia. Biol. Conserv. 2000, 96, 55–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Authority. NSW Environmental Protection Authority 2000, NSW State of the Environment Report 2000. Environmental Protection Authority, Sydney. Available online: http://www.epa.nsw.gov.au (accessed on 23 August 2014).
- Fang, S.; Wente, S.; Gertner, G.Z.; Wang, G.; Anderson, A. Uncertainty analysis of predicted disturbance from offroad vehicular traffic in complex landscapes at Fort Hood. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmel, Y.; Dean, D.J. Performance of a spatio-temporal error model for raster datasets under complex error patterns. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 5283–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sinha, P.; Kumar, L.; Reid, N. Rank-Based Methods for Selection of Landscape Metrics for Land Cover Pattern Change Detection. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020107
Sinha P, Kumar L, Reid N. Rank-Based Methods for Selection of Landscape Metrics for Land Cover Pattern Change Detection. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(2):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020107
Chicago/Turabian StyleSinha, Priyakant, Lalit Kumar, and Nick Reid. 2016. "Rank-Based Methods for Selection of Landscape Metrics for Land Cover Pattern Change Detection" Remote Sensing 8, no. 2: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020107
APA StyleSinha, P., Kumar, L., & Reid, N. (2016). Rank-Based Methods for Selection of Landscape Metrics for Land Cover Pattern Change Detection. Remote Sensing, 8(2), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020107