Region-of-Interest Extraction Based on Local–Global Contrast Analysis and Intra-Spectrum Information Distribution Estimation for Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Well-defined boundaries: Accurate ROIs are conducive to image compression, image registration and change detection. This problem can be solved by superpixel segmentation since superpixels usually maintain much boundary information.
- (2)
- Complete ROIs without inner holes: In remote sensing images, because of the complex texture information in ROIs, there is a high likelihood of obtaining ROIs with inner holes. However, applications such as image compression and image registration need all of the information for ROIs.
- (3)
- No interference outside of the ROIs: Some interference is often detected when we extract ROIs. For example, when ROIs are residential areas from high-resolution remote sensing images, shades of mountains and discontinuous roads are easily detected interference.
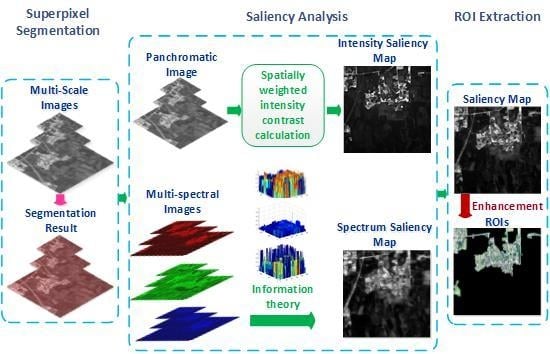
2. Methodology
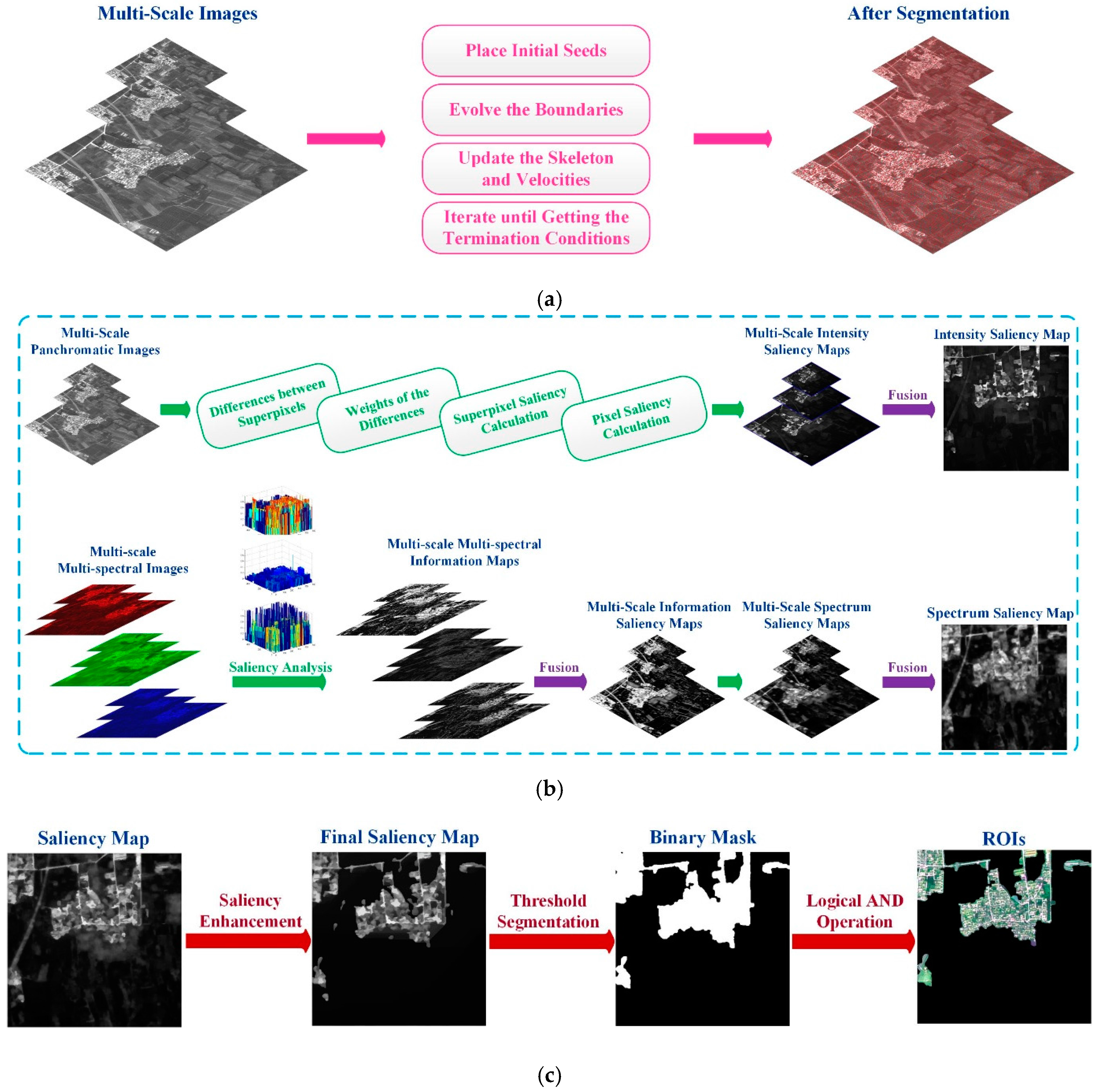
2.1. Superpixel Segmentation
2.2. Saliency Analysis
2.2.1. Local–Global Contrast Analysis
2.2.2. Intra-Spectrum Information Distribution Estimation
2.2.3. Anti-Noise Properties
2.3. Saliency Enhancement and ROI Extraction
3. Experiments and Discussion
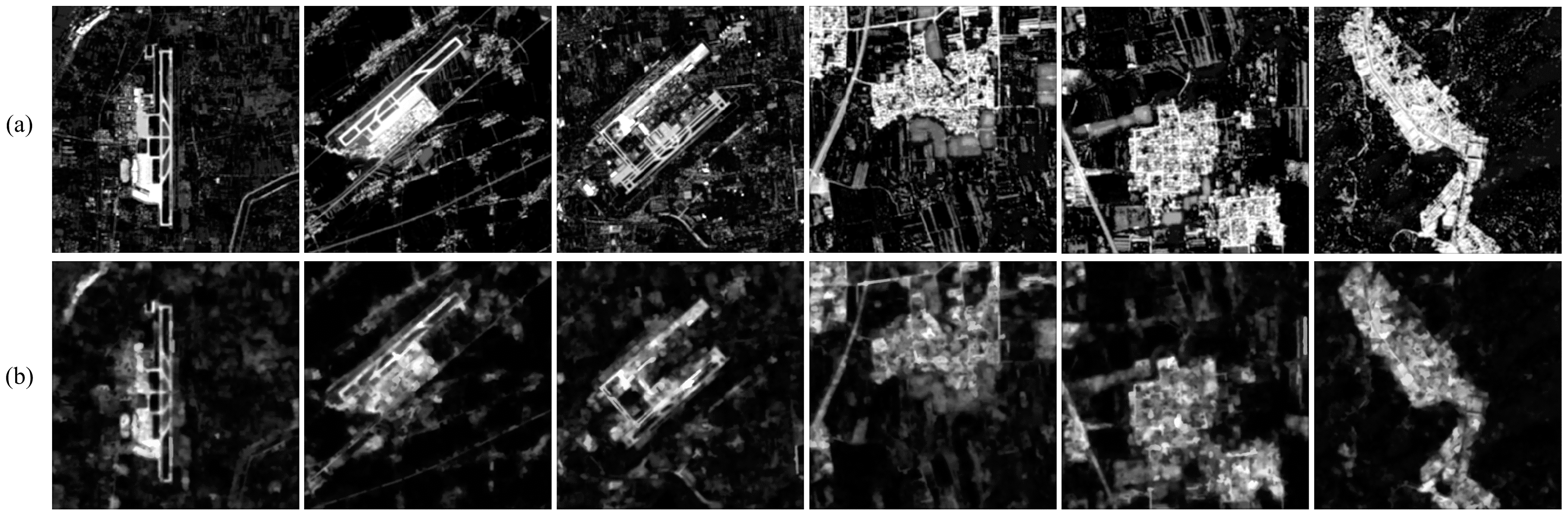
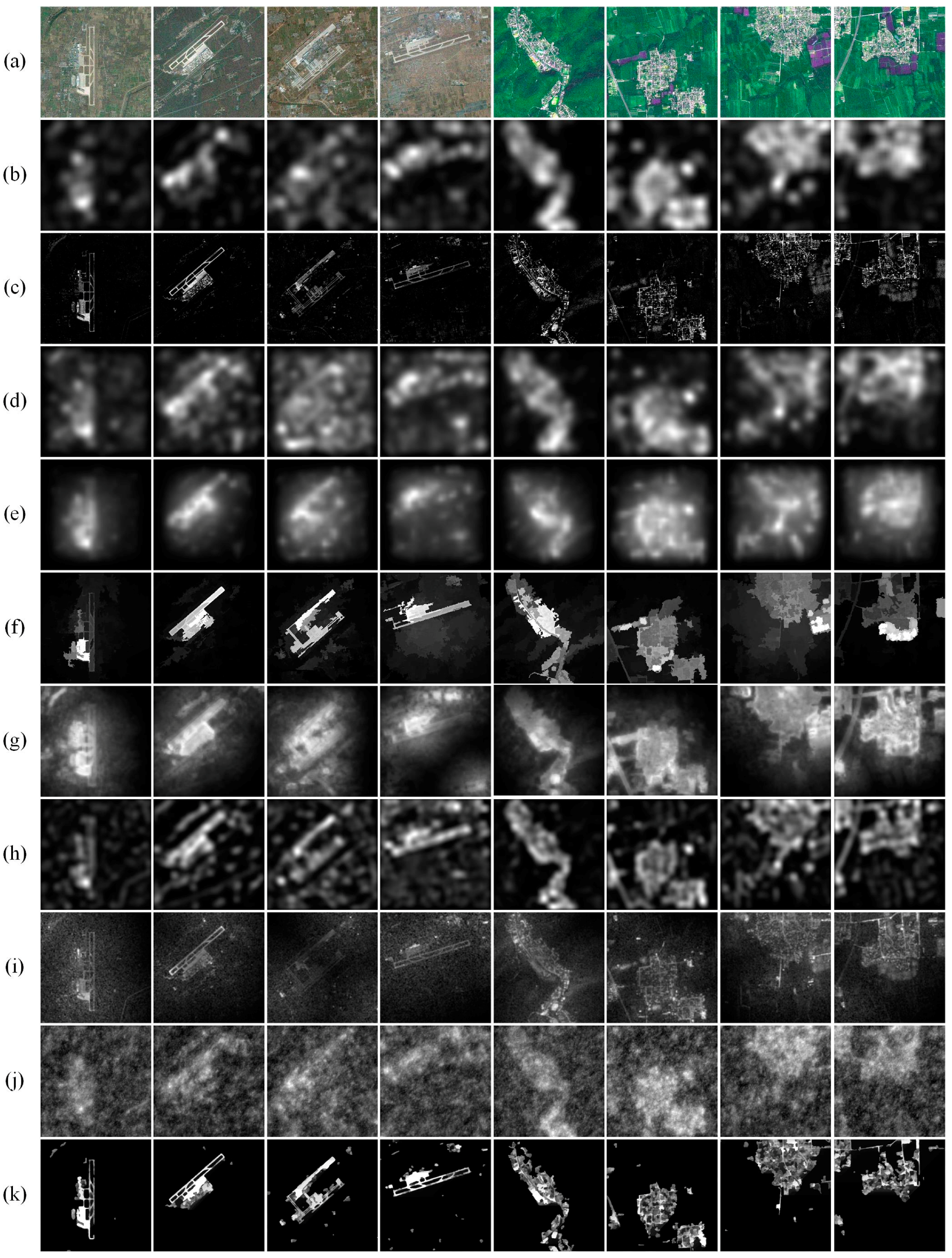
3.1. ROI Detection in Noise-Free Images
3.1.1. Qualitative Comparisons
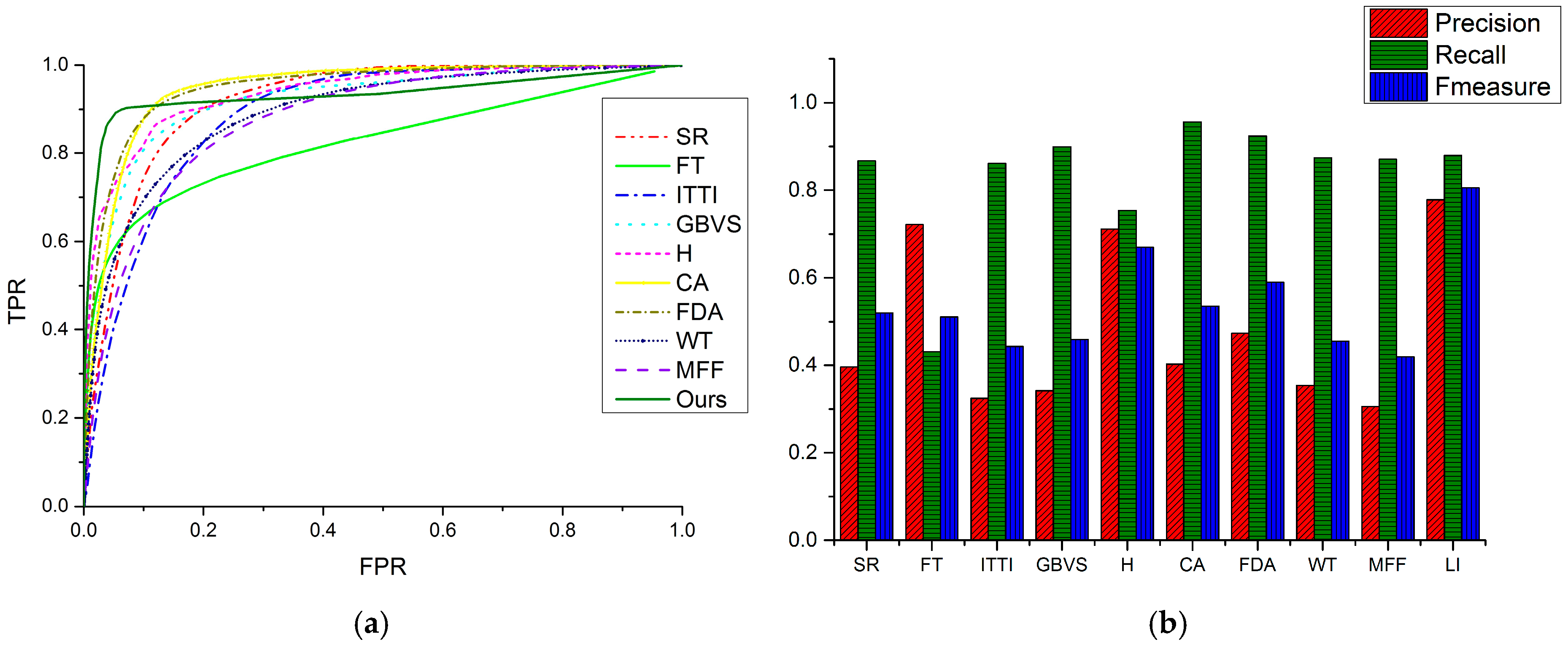
3.1.2. Quantitative Comparisons
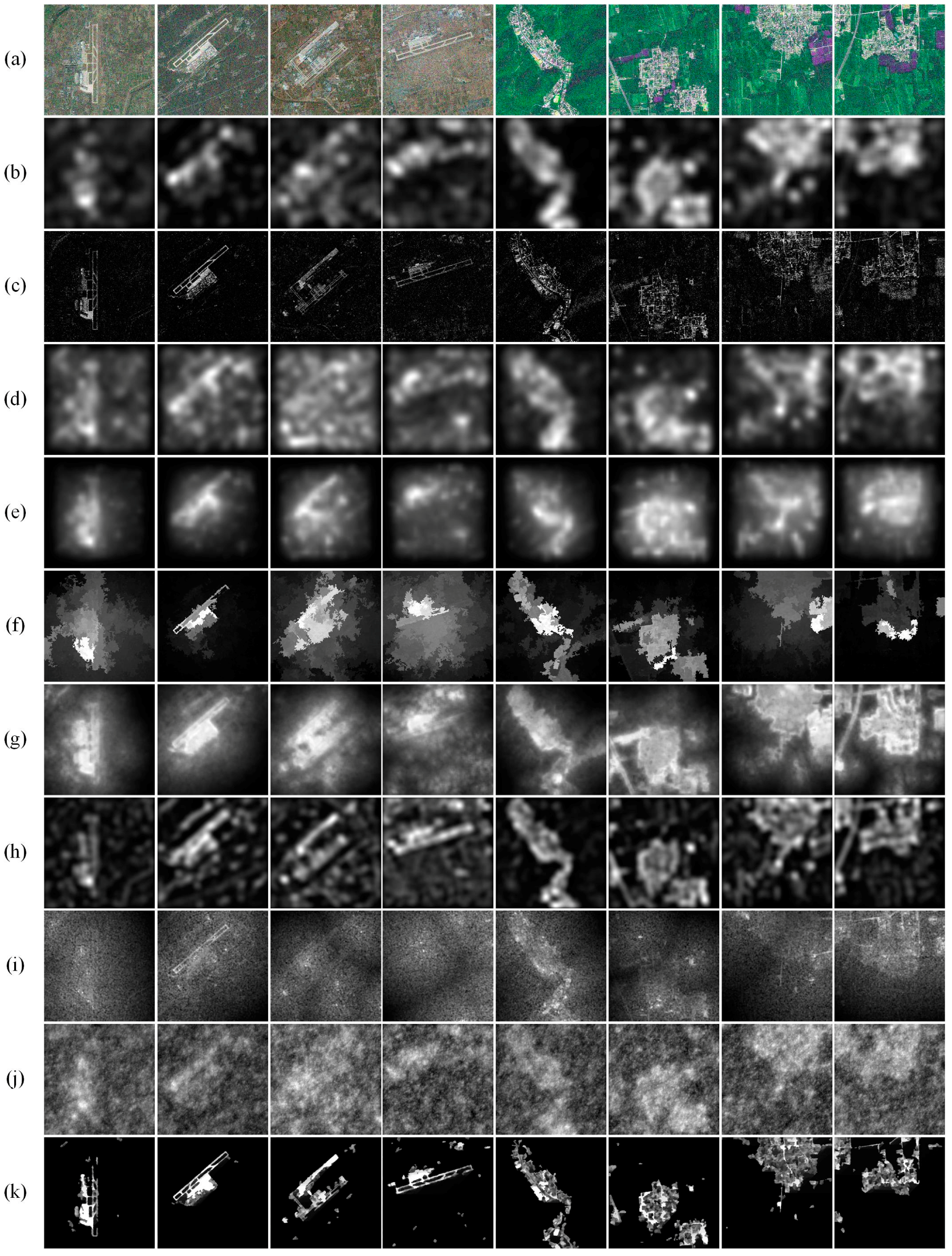
3.2. ROI Detection in Noisy Images
3.2.1. Qualitative Comparisons
3.2.2. Quantitative Comparisons
3.3. Additional Discussions
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brinkmann, R. The Art and Science of Digital Compositing, 2nd ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: San Mateo, CA, USA, 1999; p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Qiu, B. Region-of-interest coding based on saliency detection and directional wavelet for remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, L. Joint Multi-Image Saliency Analysis for Region of Interest Detection in Optical Multispectral Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L. Airport target detection in remote sensing images: A new method based on two-way saliency. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Liu, J.; Sun, M.; Zeng, D.; Wang, X. A Hierarchical Maritime Target Detection Method for Optical Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, H.; Xia, G. Automatic Ship Detection in SAR Images Using Multi-Scale Heterogeneities and an A Contrario Decision. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7695–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Xia, G.; Hu, F.; Zhang, L. A Comparative Study of Sampling Analysis in the Scene Classification of Optical High-Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14988–15013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvor, D.; Durieux, L.; Andrés, S.; Laporte, M. Advances in geographic object-based image analysis with ontologies: A review of main contributions and limitations from a remote sensing perspective. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 82, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L. A hybrid object-oriented conditional random field classification framework for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7023–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, K. Global and local saliency analysis for the extraction of residential areas in high-spatial-resolution remote sensing image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 3750–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Koch, C. Learning saliency-based visual attention: A review. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borji, A.; Cheng, M.; Jiang, H.; Li, J. Salient object detection: A benchmark. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 5706–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, C.; Ullman, S. Shifts in selective visual attention: Towards the underlying neural circuitry. Hum. Neurobiol. 1985, 4, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C.; Niebur, E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goferman, S.; Zelnik-Manor, L.; Tal, A. Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Meur, O.; le Callet, P.; Barba, D.; Thoreau, D. A coherent computational approach to model bottom-up visual attention. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 802–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, H. Contrast-Based Image Attention Analysis by Using Fuzzy Growing. In Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2–8 November 2003; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 374–381. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Qiu, B. Region of interest extraction in remote sensing images by saliency analysis with the normal directional lifting wavelet transform. Neurocomputing 2016, 179, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, N.; Tsotsos, J. Saliency based on information maximization. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Zhang, G.; Mitra, N.J.; Huang, X.; Hu, S. Global contrast based salient region detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, L. Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 18–23 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Imamoglu, N.; Lin, W.; Fang, Y. A saliency detection model using low-level features based on wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2013, 15, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosin, P.L. A simple method for detecting salient regions. Pattern Recognit. 2009, 42, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, J.; Koch, C.; Perona, P. Graph-based visual saliency. Neural Inf. Proc. Syst. 2006, 19, 545–552. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Hemami, S.; Estrada, F.; Susstrunk, S. Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1597–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Yan, Q.; Xu, L.; Jia, J. Hierarchical image saliency detection on extended CSSD. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Mitra, N.; Huang, X.; Torr, P.; Hu, S. Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Malik, J. Learning a classification model for segmentation. In Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Levinshtein, A.; Stere, A.; Kutulakos, K.N.; Fleet, D.J.; Dickinson, S.J.; Siddiqi, K. TurboPixels: Fast superpixels using geometric flows. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 2290–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borji, A. What is a salient object? A dataset and a baseline model for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 742–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, L. A novel multiresolution spatiotemporal saliency detection model and its applications in image and video compression. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Pourazad, M.T.; Nasiopoulos, P. Human visual system-based saliency detection for high dynamic range content. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2016, 18, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Gao, S.; Li, C.; Li, Y. Efficient Color Boundary Detection with Color-Opponent Mechanisms. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–27 June 2013; pp. 2810–2817. [Google Scholar]
- Moan, S.L.; Mansouri, A.; Hardeberg, J.Y.; Voisin, Y. Saliency for spectral image analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2472–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, Q.; Chen, J. Multi-Image Saliency Analysis via Histogram and Spectral Feature Clustering for Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 2802–2806. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Fu, Y.; Xing, K.; Han, X. A Model of Target Recognition from Remote Sensing Images. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 3665–3670. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, K.; Li, H. Regions of interest detection in panchromatic remote sensing images based on multiscale feature fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4704–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, K. Region-of-interest extraction based on frequency domain analysis and salient region detection for remote sensing image. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo-Martín, C.; Lillo-Saavedra, M.; Menasalvas, E.; Fonseca-Luengo, D.; García-Pedrero, A.; Costumero, R. Local optimal scale in a hierarchical segmentation method for satellite images. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2016, 46, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pedrero, A.; Gonzalo-Martin, C.; Fonseca-Luengo, D.; Lillo-Saavedra, M. A GEOBIA methodology for fragmented agricultural landscapes. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 767–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, K.; Bouix, S.; Tannenbaum, A.; Zucker, S. Hamilton-jacobi skeletons. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 48, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzi, F.; Krahenb, P.; Pritch, Y. Saliency Filters: Contrast Based Filtering for Salient Region Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RL, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Lin, L.; Lu, J.; Li, C.; Shi, K. PISA: Pixelwise image saliency by aggregating complementary appearance contrast measures with edge-preserving coherence. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3019–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Du, B.; Soomro, N.Q. Region-of-interest detection via superpixel-to-pixel saliency analysis for remote sensing image. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1752–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R.; Ghinea, G.; Swaminathan, S. Salient region detection using patch level and region level image abstractions. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Wang, S. Region-of-Interest Extraction Based on Local–Global Contrast Analysis and Intra-Spectrum Information Distribution Estimation for Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060597
Zhang L, Wang S. Region-of-Interest Extraction Based on Local–Global Contrast Analysis and Intra-Spectrum Information Distribution Estimation for Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(6):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060597
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Libao, and Shiyi Wang. 2017. "Region-of-Interest Extraction Based on Local–Global Contrast Analysis and Intra-Spectrum Information Distribution Estimation for Remote Sensing Images" Remote Sensing 9, no. 6: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060597
APA StyleZhang, L., & Wang, S. (2017). Region-of-Interest Extraction Based on Local–Global Contrast Analysis and Intra-Spectrum Information Distribution Estimation for Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 9(6), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060597