Dietary Patterns are Associated with Leukocyte LINE-1 Methylation in Women: A Cross-Sectional Study in Southern Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. LINE-1 Methylation Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dietary Patterns of Study Population
3.2. Correlations between Food Intake and LINE-1 Methylation
3.3. Association between Dietary Patterns and LINE-1 Methylation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sales, N.M.; Pelegrini, P.B.; Goersch, M.C. Nutrigenomics: Definitions and advances of this new science. J. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 2014, 202759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.W.; Claycombe, K.J.; Martinez, J.A.; Friso, S.; Schalinske, K.L. Nutritional epigenomics: A portal to disease prevention. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddington, C.H. Preliminary Notes on the Development of the Wings in Normal and Mutant Strains of Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1939, 25, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milagro, F.I.; Campión, J.; Cordero, P.; Goyenechea, E.; Gómez-Uriz, A.M.; Abete, I.; Zulet, M.A.; Martínez, J.A. A dual epigenomic approach for the search of obesity biomarkers: DNA methylation in relation to diet-induced weight loss. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, S.; Olek, A. Diabetes: A candidate disease for efficient DNA methylation profiling. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2440S–2443S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Erickson, S.W.; MacLeod, S.L.; Cleves, M.A.; Hu, P.; Karim, M.A.; Hobbs, C.A. Maternal genome-wide DNA methylation patterns and congenital heart defects. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langemeijer, S.M.; Kuiper, R.P.; Berends, M.; Knops, R.; Aslanyan, M.G.; Massop, M.; Stevens-Linders, E.; van Hoogen, P.; van Kessel, A.G.; Raymakers, R.A.; et al. Acquired mutations in TET2 are common in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auclair, G.; Weber, M. Mechanisms of DNA methylation and demethylation in mammals. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.D.; Qu, J.H.; Chang, X.J.; Lu, Y.Y.; Bai, W.L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.X.; An, L.J.; Wang, C.P.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Hypomethylation of long interspersed nuclear element-1 promoter is associated with poor outcomes for curative resected hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.M.; Bird, A. DNA methylation landscapes: Provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.S.; Estécio, M.R.; Doshi, K.; Kondo, Y.; Tajara, E.H.; Issa, J.P. A simple method for estimating global DNA methylation using bisulfite PCR of repetitive DNA elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.D.; Kim, J. Global DNA hypomethylation in peripheral blood leukocytes as a biomarker for cancer risk: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchitta, M.; Quattrocchi, A.; Maugeri, A.; Vinciguerra, M.; Agodi, A. LINE-1 hypomethylation in blood and tissue samples as an epigenetic marker for cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccarelli, A.; Rienstra, M.; Benjamin, E.J. Cardiovascular epigenetics: Basic concepts and results from animal and human studies. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2010, 3, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agodi, A.; Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Basile, G.; Zamboni, M.; Bernardini, G.; Corona, D.; Veroux, M. Unveiling the Role of DNA Methylation in Kidney Transplantation: Novel Perspectives toward Biomarker Identification. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1602539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kutateladze, T.G. Diet and the epigenome. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, H.H.; Baccarelli, A.A. Environmental epigenetics: From novelty to scientific discipline. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, T.P.; Moreno, F.S.; Ross, S.A. Targeting the epigenome with bioactive food components for cancer prevention. J. Nutrigenet. Nutr. 2011, 4, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, E.; Kuijsten, A.; Dofková, M.; Mistura, L.; D’Addezio, L.; Turrini, A.; Dubuisson, C.; Favret, S.; Havard, S.; Trolle, E.; et al. Geographic and socioeconomic diversity of food and nutrient intakes: A comparison of four European countries. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agodi, A.; Barchitta, M.; Quattrocchi, A.; Maugeri, A.; Canto, C.; Marchese, A.E.; Vinciguerra, M. Low fruit consumption and folate deficiency are associated with LINE-1 hypomethylation in women of a cancer-free population. Genes Nutr. 2015, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, A.; Mazzone, M.G.; Giuliano, F.; Vinciguerra, M.; Basile, G.; Barchitta, M.; Agodi, A. Curcumin Modulates DNA Methyltransferase Functions in a Cellular Model of Diabetic Retinopathy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 5407482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Mazzone, M.G.; Giuliano, F.; Basile, G.; Agodi, A. Resveratrol Modulates SIRT1 and DNMT Functions and Restores LINE-1 Methylation Levels in ARPE-19 Cells under Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.F.; Morabia, A.; Carroll, J.; Gonzalez, K.; Fulda, K.; Kaur, M.; Vishwanatha, J.K.; Santella, R.M.; Cardarelli, R. Dietary patterns are associated with levels of global genomic DNA methylation in a cancer-free population. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Barone, G.; Mazzoleni, P.; Catalfo, A.; De Guidi, G.; Iemmolo, M.G.; Crimi, N.; Agodi, A. Mediterranean Diet and Particulate Matter Exposure Are Associated with LINE-1 Methylation: Results from a Cross-Sectional Study in Women. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Physical Status: The Use and Interpretation of Anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee; Tech. Rep. Ser. No. 854; World Health Organ.: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995; pp. 1–452. [Google Scholar]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; La Rosa, M.C.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Favara, G.; Panella, M.; Cianci, A.; Agodi, A. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Vitamin D Receptor Gene Affect Birth Weight and the Risk of Preterm Birth: Results from the “Mamma & Bambino” Cohort and A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1172. [Google Scholar]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Agrifoglio, O.; Scalisi, A.; Agodi, A. The Association of Dietary Patterns with High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Infection and Cervical Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study in Italy. Nutrients 2018, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.; Stampfer, M.J. Total energy intake: Implications for epidemiologic analyses. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 124, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agodi, A.; Maugeri, A.; Kunzova, S.; Sochor, O.; Bauerova, H.; Kiacova, N.; Barchitta, M.; Vinciguerra, M. Association of Dietary Patterns with Metabolic Syndrome: Results from the Kardiovize Brno 2030 Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Favara, G.; La Rosa, M.C.; La Mastra, C.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Agodi, A. Maternal Dietary Patterns Are Associated with Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index and Gestational Weight Gain: Results from the “Mamma & Bambino” Cohort. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1308. [Google Scholar]
- Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Agrifoglio, O.; Favara, G.; La Mastra, C.; La Rosa, M.C.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Panella, M.; Cianci, A.; Agodi, A. The impact of social determinants and lifestyles on dietary patterns during pregnancy: Evidence from the “Mamma & Bambino” study. Ann. Ig. Med. Prev. Comunita 2019, 31, 31–89. [Google Scholar]
- Kurdyukov, S.; Bullock, M. DNA Methylation Analysis: Choosing the Right Method. Biology 2016, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchitta, M.; Quattrocchi, A.; Maugeri, A.; Canto, C.; La Rosa, N.; Cantarella, M.A.; Spampinato, G.; Scalisi, A.; Agodi, A. LINE-1 hypermethylation in white blood cell DNA is associated with high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Fallico, M.; Castellino, N.; Reibaldi, M.; Agodi, A. Characterization of SIRT1/DNMTs Functions and LINE-1 Methylation in Patients with Age-Related Macular Degeneration. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, W.A. L1 retrotransposons in human cancers. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2006, 2006, 83672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotkin, R.K.; Martienssen, R. Transposable elements and the epigenetic regulation of the genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.S.; Power, B.E.; Molloy, P.L. DNA hypomethylation and human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1775, 138–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filkowski, J.N.; Ilnytskyy, Y.; Tamminga, J.; Koturbash, I.; Golubov, A.; Bagnyukova, T.; Pogribny, I.P.; Kovalchuk, O. Hypomethylation and genome instability in the germline of exposed parents and their progeny is associated with altered miRNA expression. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Agrifoglio, O.; Agodi, A. The Role of miRNAs as Biomarkers for Pregnancy Outcomes: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 8067972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura-Calixto, F.; Goñi, I. Definition of the Mediterranean diet based on bioactive compounds. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H. Dietary bioactive compounds and their health implications. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78 (Suppl. S1), A18–A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rocha, C.; Pérez-Mojica, J.E.; León, S.Z.; Cervantes-Paz, B.; Tristán-Flores, F.E.; Rodríguez-Ríos, D.; Molina-Torres, J.; Ramírez-Chávez, E.; Alvarado-Caudillo, Y.; Carmona, F.J.; et al. Associations between whole peripheral blood fatty acids and DNA methylation in humans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beck, S.; Rakyan, V.K. The methylome: Approaches for global DNA methylation profiling. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakyan, V.K.; Down, T.A.; Balding, D.J.; Beck, S. Epigenome-wide association studies for common human diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shim, J.S.; Oh, K.; Kim, H.C. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiologic studies. Epidemiol. Health 2014, 36, e2014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agodi, A.; Barchitta, M.; Valenti, G.; Marzagalli, R.; Frontini, V.; Marchese, A.E. Increase in the prevalence of the MTHFR 677 TT polymorphism in women born since 1959: Potential implications for folate requirements. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidemann, C.; Scheidt-Nave, C.; Richter, A.; Mensink, G.B. Dietary patterns are associated with cardiometabolic risk factors in a representative study population of German adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbaresko, J.; Siegert, S.; Koch, M.; Aits, I.; Lieb, W.; Nikolaus, S.; Laudes, M.; Jacobs, G.; Nöthlings, U. Comparison of two exploratory dietary patterns in association with the metabolic syndrome in a Northern German population. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliga, E.; Kozieł, D.; Cieśla, E.; Rębak, D.; Głuszek, S. Dietary Patterns in Relation to Metabolic Syndrome among Adults in Poland: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, A.; Dallongeville, J.; Haas, B.; Ruidavets, J.B.; Amouyel, P.; Ferrières, J.; Simon, C.; Arveiler, D. Sedentary behaviour, physical activity and dietary patterns are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 2012, 38, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, H.H.; Marsit, C.J.; Kelsey, K.T. Global methylation in exposure biology and translational medical science. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nüsgen, N.; Goering, W.; Dauksa, A.; Biswas, A.; Jamil, M.A.; Dimitriou, I.; Sharma, A.; Singer, H.; Fimmers, R.; Fröhlich, H.; et al. Inter-locus as well as intra-locus heterogeneity in LINE-1 promoter methylation in common human cancers suggests selective demethylation pressure at specific CpGs. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koestler, D.C.; Christensen, B.; Karagas, M.R.; Marsit, C.J.; Langevin, S.M.; Kelsey, K.T.; Wiencke, J.K.; Houseman, E.A. Blood-based profiles of DNA methylation predict the underlying distribution of cell types: A validation analysis. Epigenetics 2013, 8, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantini, L.; Bonzini, M.; Tripodi, A.; Angelici, L.; Nordio, F.; Cantone, L.; Apostoli, P.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Baccarelli, A.A. Blood hypomethylation of inflammatory genes mediates the effects of metal-rich airborne pollutants on blood coagulation. Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 70, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.Z.; Hou, L.; Bollati, V.; Tarantini, L.; Marinelli, B.; Cantone, L.; Yang, A.S.; Vokonas, P.; Lissowska, J.; Fustinoni, S.; et al. Predictors of global methylation levels in blood DNA of healthy subjects: A combined analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agodi, A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M. The link between MTHFR C677T polymorphism, folate metabolism and global DNA methylation: A literature review. In Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) in Health and Disease; Evans, R., Ed.; Nova Biomedical: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 71–82. [Google Scholar]
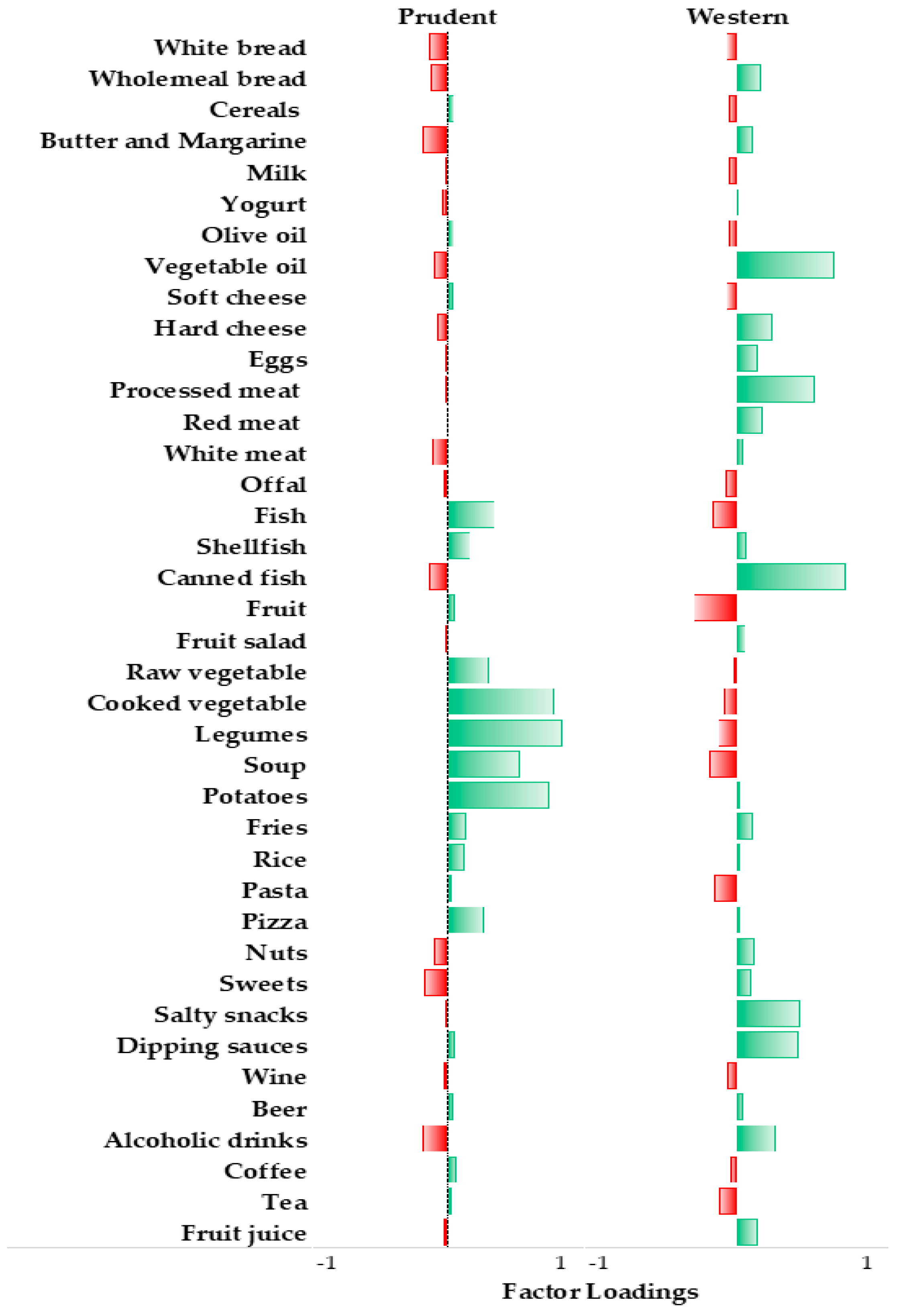


| Characteristics | Prudent | Western | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Tertile | 2nd Tertile | 3rd Tertile | p-Value | 1st Tertile | 2nd Tertile | 3rd Tertile | p-Value | |
| Age, years | 32.0 (19.0) | 35.0 (19.0) | 46.0 (34.0) | <0.001 | 41.0 (34.0) | 40.0 (24.0) | 30.0 (17.0) | <0.001 |
| Educational level | ||||||||
| Low | 34.5% | 18.8% | 23.3% | 0.049 | 24.1% | 23.1% | 29.3% | 0.832 |
| Medium | 37.9% | 53.8% | 50.9% | 47.4% | 49.6% | 45.7% | ||
| High | 27.6% | 27.4% | 25.9% | 28.4% | 27.4% | 25.0% | ||
| Employment status (% unemployed) | 62.1% | 47.0% | 53.4% | 0.069 | 53.4% | 55.6% | 53.4% | 0.933 |
| Smoking status | ||||||||
| Never smokers | 67.8% | 69.2% | 62.6% | 0.757 | 63.5% | 65.5% | 70.7% | 0.011 |
| Former smokers | 11.3% | 13.7% | 14.8% | 14.8% | 19.8% | 5.2% | ||
| Current smokers | 20.9% | 17.1% | 22.6% | 21.7% | 14.7% | 24.1% | ||
| Use of folic acid supplement (% users) | 19.0% | 18.8% | 7.8% | 0.024 | 19.8% | 16.2% | 9.5% | 0.083 |
| Total energy intake, kcal | 1693.0 (3581.0) | 1940.0 (614.0) | 2142.0 (563.0) | <0.001 | 2028.0 (682.0) | 1781.0 (2610.0) | 2065.0 (744.0) | 0.001 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 23.3 (6.8) | 23.9 (5.8) | 24.1 (23.0) | 0.971 | 23.0 (4.8) | 25.0 (5.7) | 23.0 (8.1) | 0.067 |
| Body mass index categories | ||||||||
| Underweight | 3.5% | 6.9% | 5.2% | 0.403 | 3.5% | 2.6% | 9.6% | 0.002 |
| Normal weight | 60.9% | 50.9% | 53.0% | 65.2% | 47.9% | 51.8% | ||
| Overweight | 19.1% | 28.4% | 29.6% | 21.7% | 35.9% | 19.3% | ||
| Obese | 16.5% | 13.8% | 12.2% | 9.6% | 13.7% | 19.3% | ||
| Regression Model | LINE-1 Methylation | 1st Tertile | 2nd Tertile | 3rd Tertile | p-Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (SE) | p-Value | β (SE) | p-Value | ||||
| Model 1 | CpG site 1 | Ref. | 0.001 (0.002) | 0.599 | 0.008 (0.002) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| CpG site 2 | Ref. | 0.009 (0.010) | 0.348 | 0.011 (0.009) | 0.234 | 0.233 | |
| CpG site 3 | Ref. | 0.011 (0.007) | 0.120 | 0.019 (0.006) | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| Average | Ref. | 0.006 (0.005) | 0.263 | 0.012 (0.005) | 0.017 | 0.017 | |
| Model 2 | CpG site 1 | Ref. | 0.001 (0.002) | 0.990 | 0.009 (0.003) | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| CpG site 2 | Ref. | 0.015 (0.004) | 0.001 | 0.030 (0.005) | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| CpG site 3 | Ref. | 0.016 (0.003) | <0.001 | 0.034 (0.003) | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Average | Ref. | 0.009 (0.002) | <0.001 | 0.022 (0.003) | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Regression Model | LINE-1 Methylation | 1st Tertile | 2nd Tertile | 3rd Tertile | p-Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (SE) | p-Value | β (SE) | p-Value | ||||
| Model 1 | CpG site 1 | Ref. | 0.001 (0.002) | 0.828 | −0.003 (0.002) | 0.276 | 0.262 |
| CpG site 2 | Ref. | −0.009 (0.008) | 0.310 | −0.002 (0.009) | 0.838 | 0.835 | |
| CpG site 3 | Ref. | −0.008 (0.006) | 0.202 | −0.002 (0.007) | 0.753 | 0.743 | |
| Average | Ref. | −0.005 (0.005) | 0.316 | −0.002 (0.005) | 0.702 | 0.690 | |
| Model 2 | CpG site 1 | Ref. | 0.002 (0.002) | 0.523 | −0.001 (0.003) | 0.676 | 0.760 |
| CpG site 2 | Ref. | 0.005 (0.005) | 0.282 | −0.003 (0.005) | 0.549 | 0.837 | |
| CpG site 3 | Ref. | 0.007 (0.004) | 0.067 | −0.001 (0.004) | 0.834 | 0.705 | |
| Average | Ref. | 0.004 (0.003) | 0.101 | −0.001 (0.003) | 0.647 | 0.986 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Favara, G.; La Rosa, M.C.; La Mastra, C.; Quattrocchi, A.; Agodi, A. Dietary Patterns are Associated with Leukocyte LINE-1 Methylation in Women: A Cross-Sectional Study in Southern Italy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081843
Barchitta M, Maugeri A, Magnano San Lio R, Favara G, La Rosa MC, La Mastra C, Quattrocchi A, Agodi A. Dietary Patterns are Associated with Leukocyte LINE-1 Methylation in Women: A Cross-Sectional Study in Southern Italy. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081843
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarchitta, Martina, Andrea Maugeri, Roberta Magnano San Lio, Giuliana Favara, Maria Clara La Rosa, Claudia La Mastra, Annalisa Quattrocchi, and Antonella Agodi. 2019. "Dietary Patterns are Associated with Leukocyte LINE-1 Methylation in Women: A Cross-Sectional Study in Southern Italy" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081843
APA StyleBarchitta, M., Maugeri, A., Magnano San Lio, R., Favara, G., La Rosa, M. C., La Mastra, C., Quattrocchi, A., & Agodi, A. (2019). Dietary Patterns are Associated with Leukocyte LINE-1 Methylation in Women: A Cross-Sectional Study in Southern Italy. Nutrients, 11(8), 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081843







