Temporal Changes of Protein Composition in Breast Milk of Chinese Urban Mothers and Impact of Caesarean Section Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Ethical and Legal Considerations
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Sample Characteristics
2.6. Milk Sample Processing before Analyses
2.7. Measurement of Major Breast Milk Proteins
2.7.1. Sample Preparation
2.7.2. Method Validation
2.8. Measurement of Selected Breast Milk Immune Factors
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subject Characteristics
3.2. Major Breast Milk Proteins
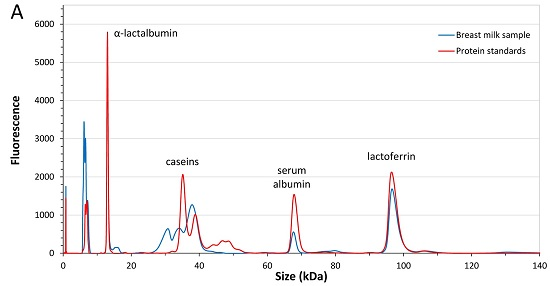
3.2.1. Analytical Method Performance
3.2.2. Analysis of Major Breast Milk Proteins
3.3. Breast Milk Immune Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Major Breast Milk Proteins
4.2. Breast Milk Immune Factors
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vorbach, C.; Capecchi, M.R.; Penninger, J.M. Evolution of the mammary gland from the innate immune system? Bioessays 2006, 28, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonnerdal, B. Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1537S–1543S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lonnerdal, B. Bioactive proteins in breast milk. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2013, 49 (Suppl. 1), 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striker, G.A.; Casanova, L.D.; Nagao, A.T. Influence of type of delivery on A, G and M immunoglobulin concentration in maternal colostrum. J. Pediatr. 2004, 80, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.L.; Weber, D.; Phinney, B.S.; Smilowitz, J.T.; Hinde, K.; Lonnerdal, B.; Korf, I.; Lemay, D.G. Comparative proteomics of human and macaque milk reveals species-specific nutrition during postnatal development. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2143–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, A. Constituents of human milk. Food Nutr. Bull. 1996, 17, 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa, T.J.; Pezo, A.; Cruz, K.; Chea-Woo, E.; Cleary, T.G. Clinical studies of lactoferrin in children. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakansson, A.P.; Roche-Hakansson, H.; Mossberg, A.K.; Svanborg, C. Apoptosis-like death in bacteria induced by hamlet, a human milk lipid-protein complex. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakansson, A.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Orrenius, S.; Sabharwal, H.; Svanborg, C. Apoptosis induced by a human milk protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8064–8068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Lonnerdal, B. Bioactive peptides derived from human milk proteins—Mechanisms of action. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, D.C.; Guerrero, A.; Khaldi, N.; Borghese, R.; Bhandari, A.; Underwood, M.A.; Lebrilla, C.B.; German, J.B.; Barile, D. A peptidomic analysis of human milk digestion in the infant stomach reveals protein-specific degradation patterns. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandtzaeg, P. The mucosal immune system and its integration with the mammary glands. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, S8–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.B.; Karlsson, S. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 knockout mice. A mutation in one cytokine gene causes a dramatic inflammatory disease. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Planchon, S.M.; Martins, C.A.; Guerrant, R.L.; Roche, J.K. Regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier function by tgf-beta 1. Evidence for its role in abrogating the effect of a T cell cytokine. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 5730–5739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.D.; Hirokawa, M.; Horwitz, D.A. The role of transforming growth factor beta in the generation of suppression: An interaction between CD8+ T and NK cells. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 1937–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathias, A.; Pais, B.; Favre, L.; Benyacoub, J.; Corthesy, B. Role of secretory IgA in the mucosal sensing of commensal bacteria. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogier, E.W.; Frantz, A.L.; Bruno, M.E.; Wedlund, L.; Cohen, D.A.; Stromberg, A.J.; Kaetzel, C.S. Secretory antibodies in breast milk promote long-term intestinal homeostasis by regulating the gut microbiota and host gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3074–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonnerdal, B.; Forsum, E.; Hambraeus, L. A longitudinal study of the protein, nitrogen, and lactose contents of human milk from swedish well-nourished mothers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1976, 29, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jensen, R.G. Handbook of Milk Composition; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, S.; Yoshida, M.; Ichijo, M.; Ishizaka, S.; Tsujii, T. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) in human milk. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1993, 94, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Karmaus, W.; Davis, S.; Gangur, V. Immune markers in breast milk and fetal and maternal body fluids: A systematic review of perinatal concentrations. J. Hum. Lact. 2011, 27, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, J.; Rushing, J. Cesarean versus vaginal delivery: Long-term infant outcomes and the hygiene hypothesis. Clin. Perinatol. 2011, 38, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penders, J.; Gerhold, K.; Thijs, C.; Zimmermann, K.; Wahn, U.; Lau, S.; Hamelmann, E. New insights into the hygiene hypothesis in allergic diseases: Mediation of sibling and birth mode effects by the gut microbiota. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevelsted, A.; Stokholm, J.; Bonnelykke, K.; Bisgaard, H. Cesarean section and chronic immune disorders. Pediatrics 2015, 135, e92–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, K.G.; Nommsen-Rivers, L.A.; Heinig, M.J.; Cohen, R.J. Risk factors for suboptimal infant breastfeeding behavior, delayed onset of lactation, and excess neonatal weight loss. Pediatrics 2003, 112, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, K.C.; Evans, R.G.; Royal, R.; Esterman, A.J.; James, S.L. Effect of caesarean section on breast milk transfer to the normal term newborn over the first week of life. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2003, 88, F380–F382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulski, J.K.; Smith, M.; Hartmann, P.E. Normal and caesarian section delivery and the initiation of lactation in women. Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 1981, 59, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellerstein, S.; Feldman, S.; Duan, T. China’s 50% caesarean delivery rate: Is it too high? BJOG 2015, 122, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, Y.; You, L.; Ma, D.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, P. Breast milk macronutrient composition and the associated factors in urban chinese mothers. Chin. Med. J. 2014, 127, 1721–1725. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anema, S.G. The use of “lab-on-a-chip” microfluidic sds electrophoresis technology for the separation and quantification of milk proteins. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, S.; De Castro, C.; Bénet, T.; Hou, Y.; Sun, H.; Thakkar, S.; Vinyes-Pares, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P. Temporal change of the content of 10 oligosaccharides in the milk of chinese urban mothers. Nutrients 2016, 8, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barwick, V.J.; Ellison, S.L.; Lucking, C.L.; Burn, M.J. Experimental studies of uncertainties associated with chromatographic techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 918, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velona, T.; Abbiati, L.; Beretta, B.; Gaiaschi, A.; Flauto, U.; Tagliabue, P.; Galli, C.L.; Restani, P. Protein profiles in breast milk from mothers delivering term and preterm babies. Pediatr. Res. 1999, 45, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, C.; Lonnerdal, B. Human-milk proteins: Analysis of casein and casein subunits by anion-exchange chromatography, gel electrophoresis, and specific staining methods. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, I.M.P.L. Chromatographic separation and quantification of major human milk proteins. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2007, 30, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, M.; Beddis, K.; Black, J.; Henderson, H.; Nair, A.; Wheeler, T. Effect of gestation length on the levels of five innate defence proteins in human milk. Early Hum. Dev. 2015, 91, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.; Petrova, A. Biologically active breast milk proteins in association with very preterm delivery and stage of lactation. J. Perinatol. 2011, 31, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Santaella, M.; Mira-Pascual, L.; Martinez-Arias, E.; Khodayar-Pardo, P.; Ros, G.; Martinez-Costa, C. Longitudinal study of cytokine expression, lipid profile and neuronal growth factors in human breast milk from term and preterm deliveries. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8577–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altendorfer, I.; König, S.; Braukmann, A.; Saenger, T.; Bleck, E.; Vordenbäumen, S.; Kubiak, A.; Schneider, M.; Jose, J. Quantification of αs1-casein in breast milk using a targeted mass spectrometry-based approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 103, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonnerdal, B. Infant formula and infant nutrition: Bioactive proteins of human milk and implications for composition of infant formulas. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 712S–717S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonnerdal, B.; Lien, E.L. Nutritional and physiologic significance of alpha-lactalbumin in infants. Nutr. Rev. 2003, 61, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, E.; Scicchitano, F.; Citraro, R.; Aiello, R.; Camastra, C.; Mainardi, P.; Chimirri, S.; Perucca, E.; Donato, G.; De Sarro, G. Protective activity of alpha-lactoalbumin (ALAC), a whey protein rich in tryptophan, in rodent models of epileptogenesis. Neuroscience 2012, 226, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelleher, S.L.; Chatterton, D.; Nielsen, K.; Lonnerdal, B. Glycomacropeptide and alpha-lactalbumin supplementation of infant formula affects growth and nutritional status in infant rhesus monkeys. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruck, W.M.; Kelleher, S.L.; Gibson, G.R.; Nielsen, K.E.; Chatterton, D.E.; Lonnerdal, B. Rrna probes used to quantify the effects of glycomacropeptide and alpha-lactalbumin supplementation on the predominant groups of intestinal bacteria of infant rhesus monkeys challenged with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2003, 37, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, D.; Adelman, A.S.; Zhuang, W.; Rai, G.P.; Boettcher, J.; Lonnerdal, B. Longitudinal changes in lactoferrin concentrations in human milk: A global systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, C.; Lonnerdal, B. Re-evaluation of the whey protein/casein ratio of human milk. Acta Paediatr. 1992, 81, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonnerdal, B.; Adkins, Y. Developmental changes in breast milk protein composition during lactation. In Development of the Gastrointestinal Tract; Sanderson, R., Walker, W., Eds.; B.C. Decker Inc.: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 1999; pp. 227–244. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, A.S.; Garza, C.; Nichols, B.L.; Goldblum, R.M. Immunologic factors in human milk during the first year of lactation. J. Pediatr. 1982, 100, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, J.S.; Bryan, D.L.; James, M.J.; Gibson, R.A. Cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, TGF-β1, and TGF-β2) and prostaglandin E2 in human milk during the first three months postpartum. Pediatr. Res. 1999, 46, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oddy, W.H.; Halonen, M.; Martinez, F.D.; Lohman, I.C.; Stern, D.A.; Kurzius-Spencer, M.; Guerra, S.; Wright, A.L. Tgf-beta in human milk is associated with wheeze in infancy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urwin, H.J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Song, P.; Man, Q.; Meng, L.; Froyland, L.; Miles, E.A.; et al. Immune factors and fatty acid composition in human milk from river/lake, coastal and inland regions of China. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, V.P.; Punnonen, J.; de Vries, J.E. Transforming growth factor-beta directs iga switching in human B cells. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Kalliomaki, M.; Ouwehand, A.; Arvilommi, H.; Kero, P.; Isolauri, E. Transforming growth factor-beta in breast milk: A potential regulator of atopic disease at an early age. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penttila, I.A. Milk-derived transforming growth factor-beta and the infant immune response. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, S21–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stam, J.; Sauer, P.J.; Boehm, G. Can we define an infant’s need from the composition of human milk? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 521S–528S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Study Population | 5–11 Days | 12–30 Days | 1–2 Months | 2–4 Months | 4–8 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 90) | (n = 90) | (n = 90) | (n = 90) | (n = 90) | |
| Mother | |||||
| Age (years), Mean (SD) | 27 (4) | 27 (3) | 28 (4) | 27 (4) | 26 (4) |
| Height (cm), Mean (SD) | 160 (4) | 160 (5) | 161 (5) | 161 (5) | 159 (5) |
| Weight (kg), Mean (SD) | 60.7 (8.7) | 60.8 (7.9) | 61.9 (8.9) | 58.4 (8.3) | 56.2 (8.1) |
| BMI (kg/m2), Mean (SD) | 23.7 (3.3) | 23.7 (2.8) | 23.9 (3.1) | 22.5 (2.9) | 22.2 (3.1) |
| Gestational weight gain (kg), Mean (SD) | 16.7 (7.4) | 16.2 (6.0) | 15.9 (5.7) | 15.9 (5.9) | 14.9 (7.6) |
| Postpartum weight loss (kg), Mean (SD) | 9.1 (6.1) | 8.6 (5.3) | 9.8 (4.0) | 10.0 (6.2) | 10.6 (5.9) |
| Caesarean delivery, N (%) | 39 (42) | 43 (48) | 53 (59) | 35 (39) | 35 (38) |
| Infant | |||||
| Males, N (%) | 51 (57) | 48 (53) | 48 (53) | 54 (60) | 43 (48) |
| Gestational age at birth (weeks), Mean (SD) | 39.3 (1.2) | 39.2 (1.3) | 39.2 (1.6) | 39.4 (1.3) | 39.5 (1.5) |
| Proteins | 5–11 Days | 12–30 Days | 1–2 Months | 2–4 Months | 4–8 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 90) | (n = 90) | (n = 90) | (n = 90) | (n = 90) | |
| Major breast milk proteins | |||||
| α-lactalbumin (g/L), Median (IQR) | 3.27 (0.60) | 3.16 (0.55) | 2.84 a (0.55) | 2.53 a (0.47) | 2.28 a (0.63) |
| Lactoferrin (g/L), Median (IQR) | 3.30 (2.11) | 1.86 a (0.89) | 1.24 a (0.53) | 1.15 (0.46) | 1.17 (0.47) |
| Serum albumin (g/L), Median (IQR) | 0.48 (0.14) | 0.48 (0.14) | 0.42 (0.09) | 0.44 (0.10) | 0.42 (0.08) |
| Total caseins (g/L), Median (IQR) | 5.84 (3.17) | 6.57 a (2.15) | 6.24 (2.25) | 5.79 a (1.69) | 5.60 (1.73) |
| Immune factors | |||||
| IgA (mg/L), Median (IQR) | 1148 (1022) | 615 a (494) | 553 a (232) | 557 (312) | 564 (337) |
| IgM (mg/L), Median (IQR) | 117 (168) | 47 a (47) | 35 a (31) | 35 (29) | 25 a (25) |
| IgG (mg/L), Median (IQR) | 22 (13) | 23 (12) | 20 (14) | 24 (15) | 23 (14) |
| TGF-β1 (ng/L), Median (IQR) | 1258 (1305) | 685 a (482) | 600 (356) | 598 (379) | 659 (410) |
| TGF-β2 (ng/L), Median (IQR) | 5286 (10,444) | 2322 a (3100) | 1877 a (1890) | 1920 a (2112) | 2311 b (2868) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Affolter, M.; Garcia-Rodenas, C.L.; Vinyes-Pares, G.; Jenni, R.; Roggero, I.; Avanti-Nigro, O.; De Castro, C.A.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; et al. Temporal Changes of Protein Composition in Breast Milk of Chinese Urban Mothers and Impact of Caesarean Section Delivery. Nutrients 2016, 8, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8080504
Affolter M, Garcia-Rodenas CL, Vinyes-Pares G, Jenni R, Roggero I, Avanti-Nigro O, De Castro CA, Zhao A, Zhang Y, Wang P, et al. Temporal Changes of Protein Composition in Breast Milk of Chinese Urban Mothers and Impact of Caesarean Section Delivery. Nutrients. 2016; 8(8):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8080504
Chicago/Turabian StyleAffolter, Michael, Clara L. Garcia-Rodenas, Gerard Vinyes-Pares, Rosemarie Jenni, Iris Roggero, Ornella Avanti-Nigro, Carlos Antonio De Castro, Ai Zhao, Yumei Zhang, Peiyu Wang, and et al. 2016. "Temporal Changes of Protein Composition in Breast Milk of Chinese Urban Mothers and Impact of Caesarean Section Delivery" Nutrients 8, no. 8: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8080504
APA StyleAffolter, M., Garcia-Rodenas, C. L., Vinyes-Pares, G., Jenni, R., Roggero, I., Avanti-Nigro, O., De Castro, C. A., Zhao, A., Zhang, Y., Wang, P., Thakkar, S. K., & Favre, L. (2016). Temporal Changes of Protein Composition in Breast Milk of Chinese Urban Mothers and Impact of Caesarean Section Delivery. Nutrients, 8(8), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8080504