SHP2, SOCS3 and PIAS3 Expression Patterns in Medulloblastomas: Relevance to STAT3 Activation and Resveratrol-Suppressed STAT3 Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Medulloblastoma Specimens and Microarray Construction
2.2. Tissue Microarray-Based Immunohistochemical Staining
2.3. Cell Culture and Resveratrol Treatments
2.4. Immunocytochemical Staining
2.5. Protein Preparation and Western Blotting
2.6. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
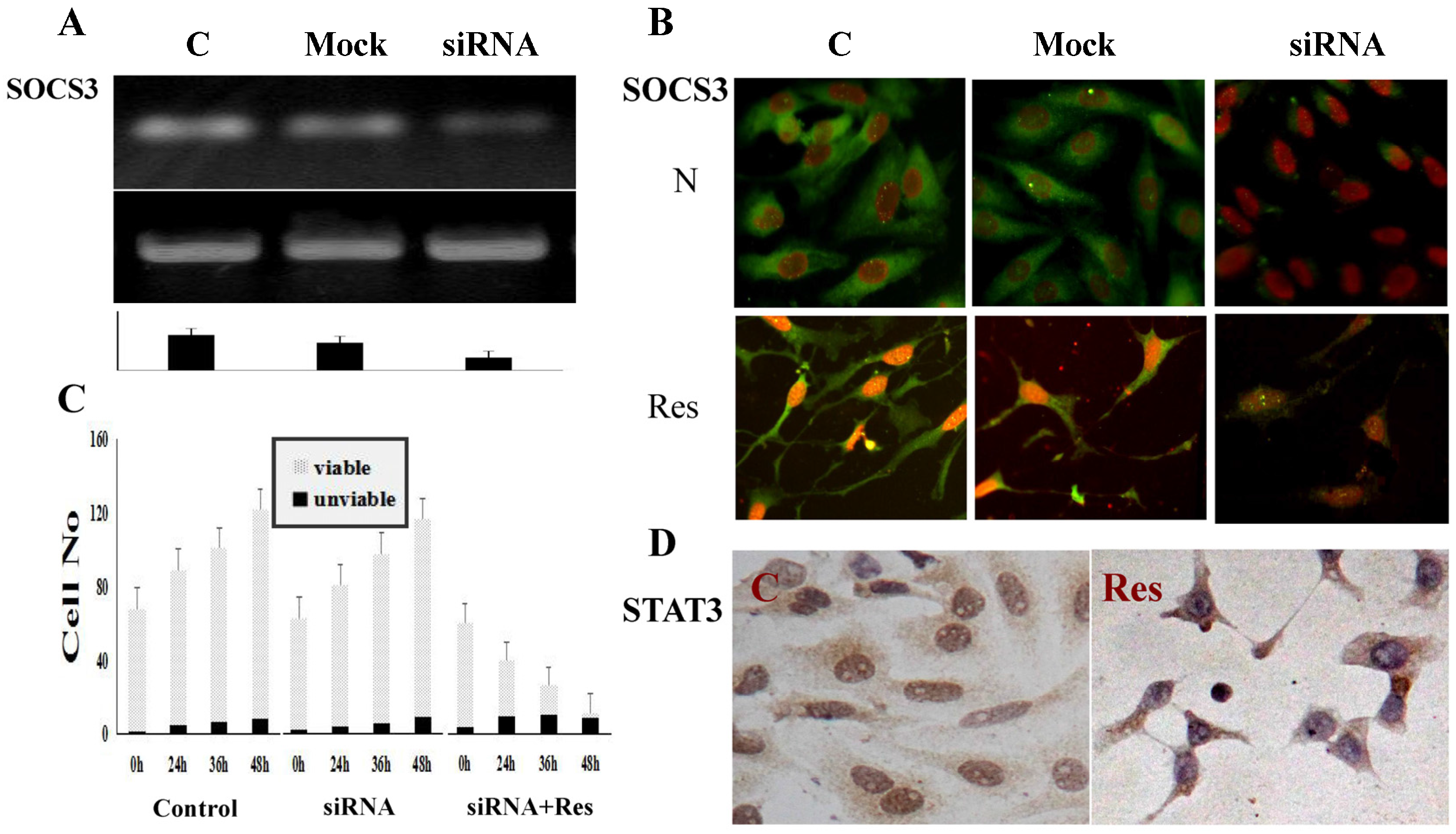
2.7. siRNA Knockdown of SOCS3 Expression
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Frequent STAT3 Activation in Medulloblastomas
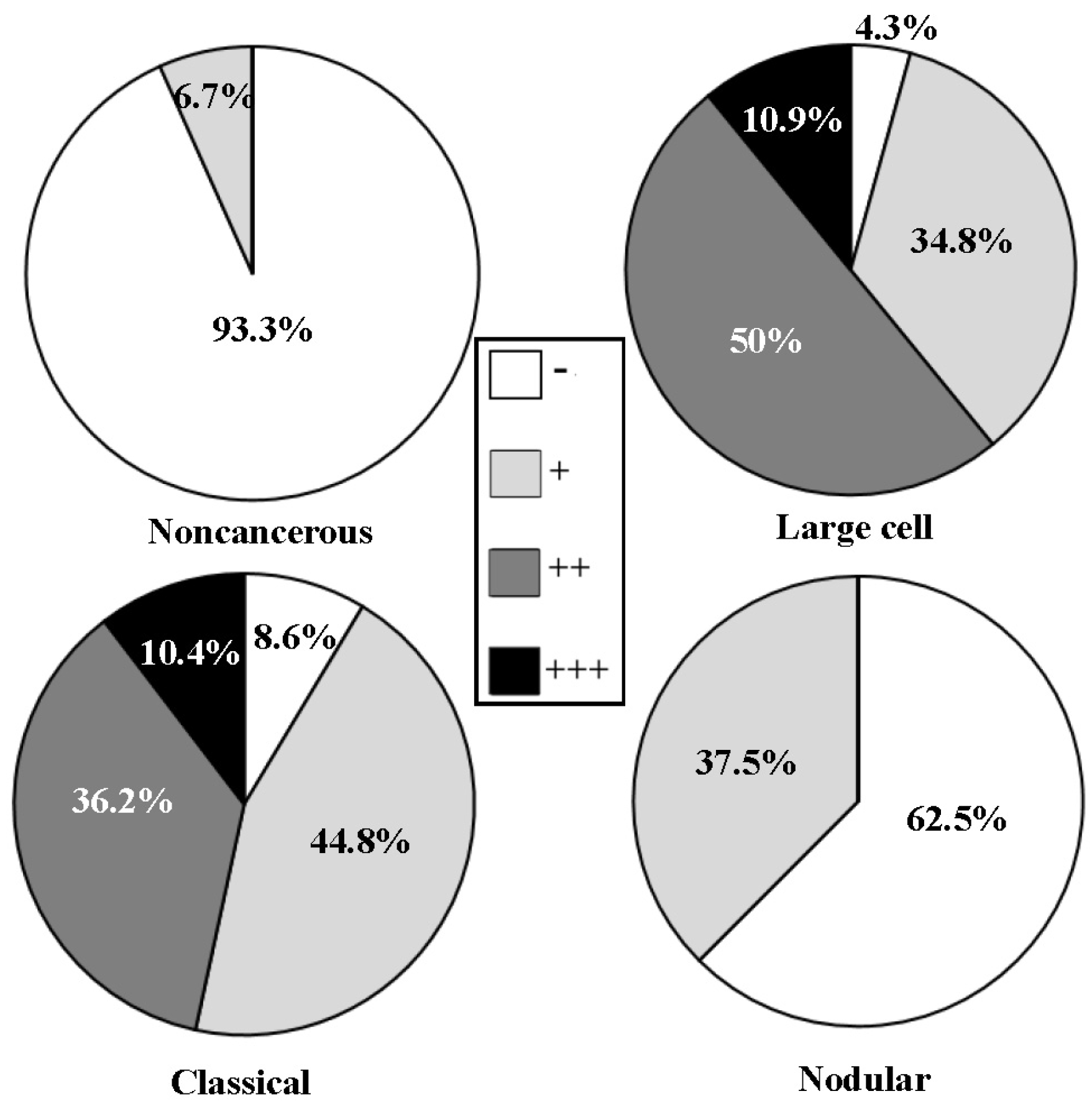
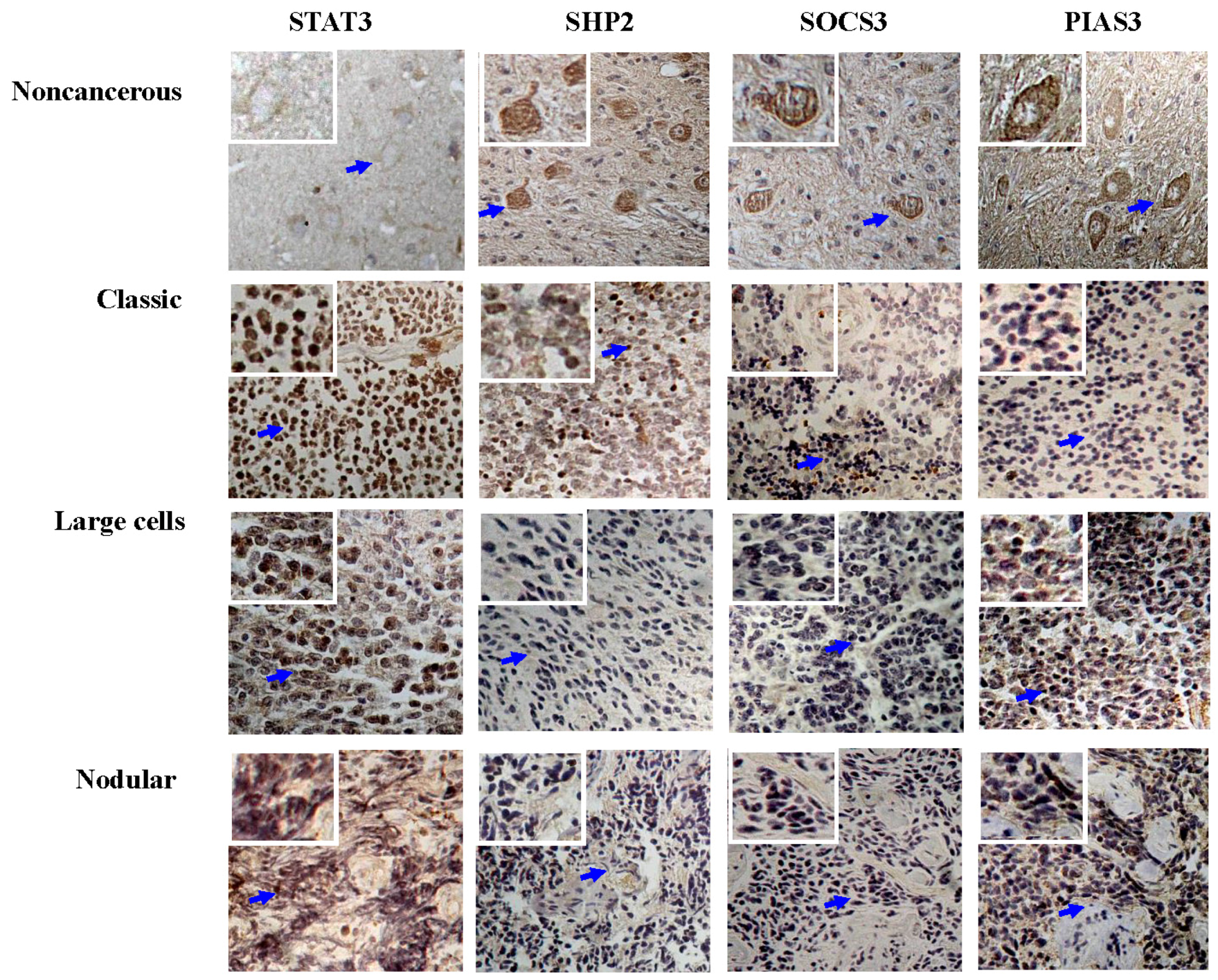
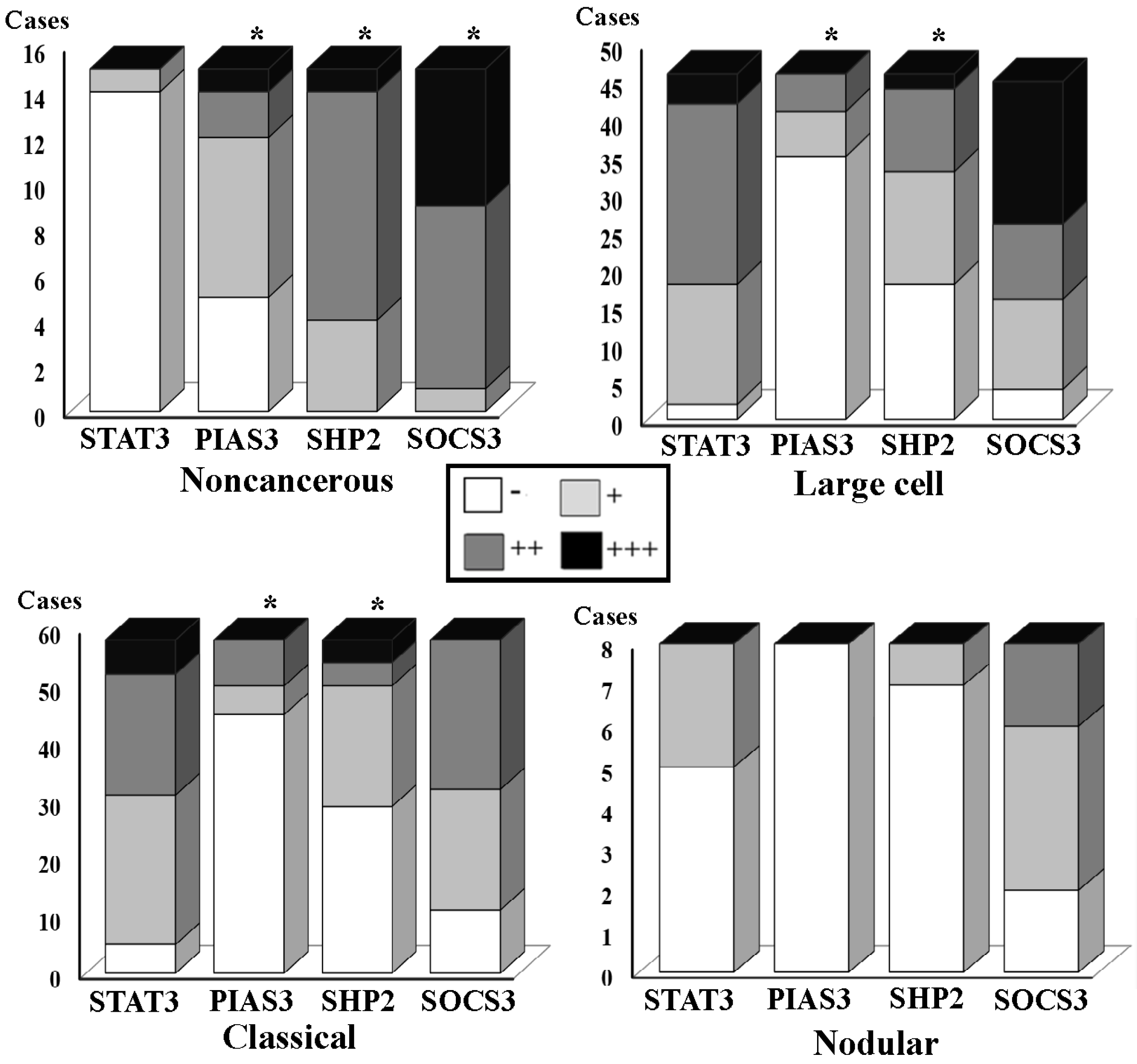
3.2. Differential SHP2, SOCS3 and PIAS3 Expression Patterns
3.3. STAT3 Activation and SOCS3 and PIAS3 Down-Regulation
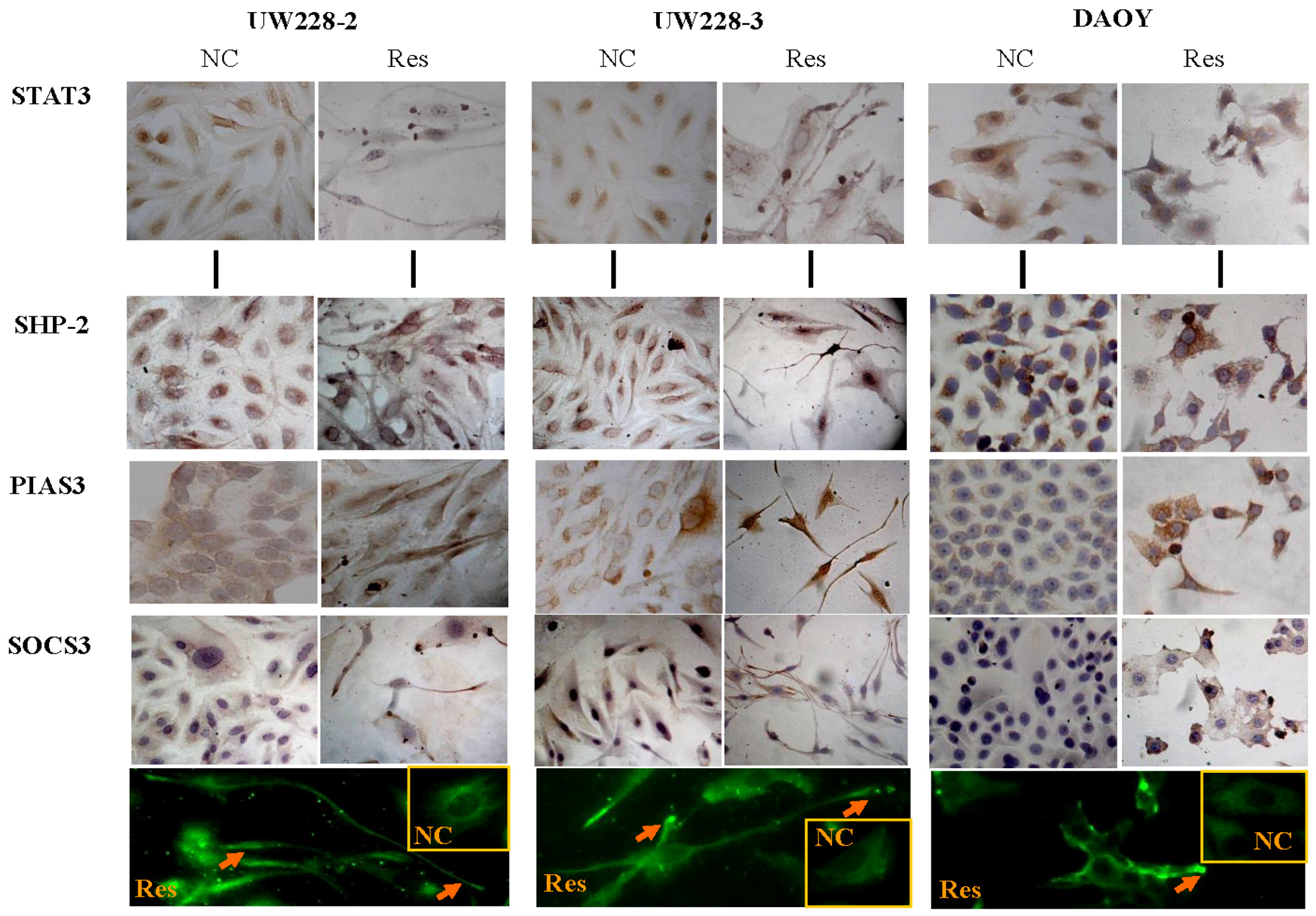
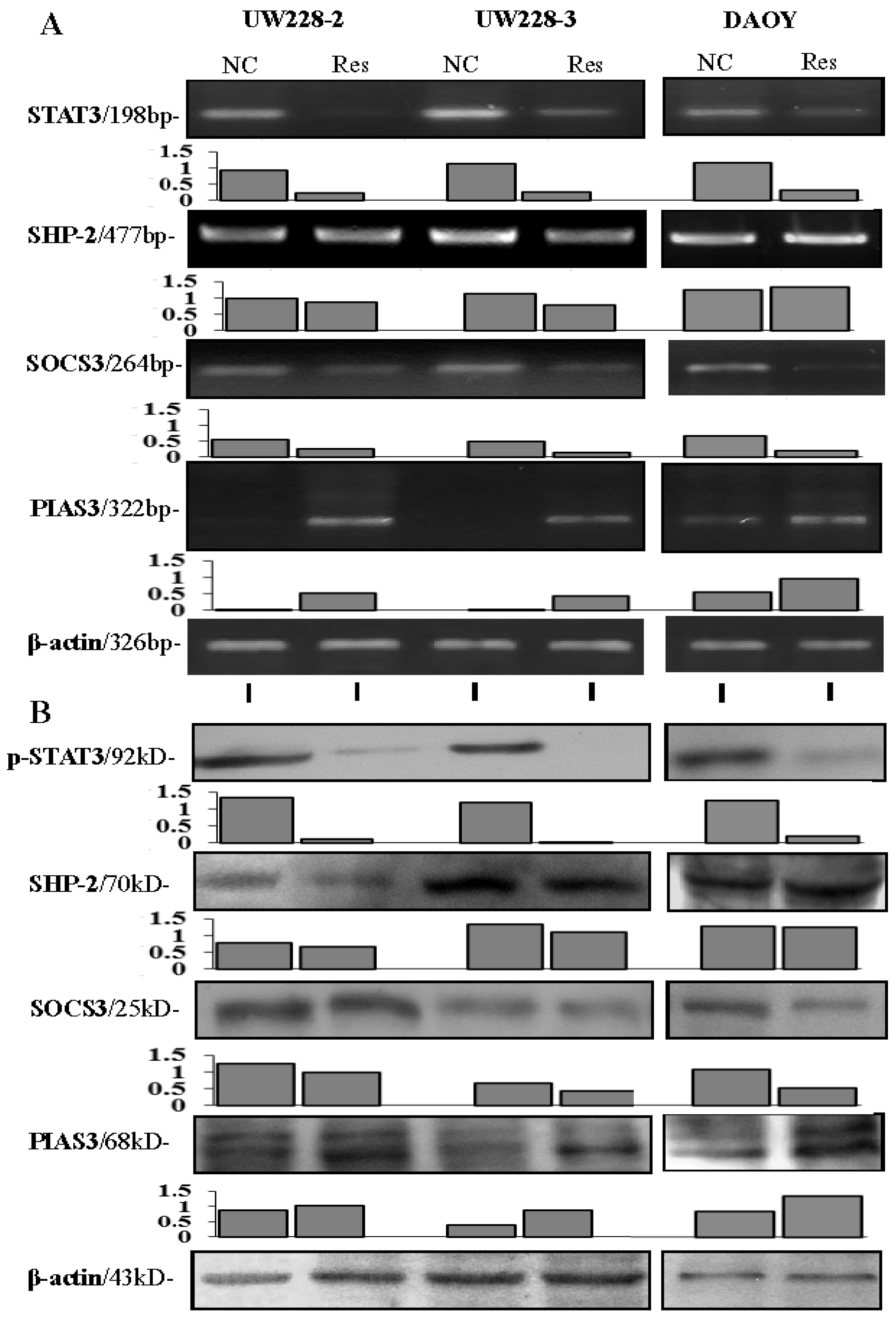
3.4. Inhibited STAT3 Signaling in Resveratrol-Suppressed Cells
3.5. Differential Responses of PIAS3, SOCS3 and SHP2 to Resveratrol
3.6. SOCS3 Knockdown Caused Process Shortening
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottardo, N.G.; Hansford, J.R.; McGlade, J.P.; Alvaro, F.; Ashley, D.M.; Bailey, S.; Baker, D.L.; Bourdeaut, F.; Cho, Y.; Clay, M.; et al. Medulloblastoma down under 2013: A report from the third annual meeting of the International Medulloblastoma Working Group. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Bouffet, E.; Faria, C.C.; Perreault, S.; Cho, Y.J.; Shih, D.J.; Lu, B.; Dubuc, A.M.; Northcott, P.A.; et al. Recurrence patterns across medulloblastoma subgroups: An integrated clinical and molecular analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.R.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Hemann, M.T. Understanding resistance to combination chemotherapy. Drug Resist. Updates 2012, 15, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, M.C.; Kusters, J.M.; Gidding, C.E.; Schieving, J.H.; van Lindert, E.J.; Kaanders, J.H.; Janssens, G.O. Acute toxicity profile of craniospinal irradiation with intensity-modulated radiation therapy in children with medulloblastoma: A prospective analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Jove, V.; Xin, H.; Hedvat, M.; Van Meter, T.E.; Yu, H. Sunitinib induces apoptosis and growth arrest of medulloblastoma tumor cells by inhibiting STAT3 and AKT signaling pathways. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, D.W.; Dalton, J.; Kocak, M.; Nicholson, S.L.; Fraga, C.; Neale, G.; Kenney, A.M.; Brat, D.J.; Perry, A.; Yong, W.H.; et al. Medulloblastoma: Clinicopathological correlates of SHH, WNT, and non-SHH/WNT molecular subgroups. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 121, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatton, B.A.; Villavicencio, E.H.; Pritchard, J.; LeBlanc, M.; Hansen, S.; Ulrich, M.; Ditzler, S.; Pullar, B.; Stroud, M.R.; Olson, J.M. Notch signaling is not essential in sonic hedgehog-activated medulloblastoma. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3865–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Bid, H.K.; Jou, D.; Wu, X.; Yu, W.; Li, C.; Houghton, P.J.; Lin, J. A novel small molecular STAT3 inhibitor, LY5, inhibits cell viability, cell migration, and angiogenesis in medulloblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 3418–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.-J.; Wu, M.-L.; Li, H.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Kong, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Inhibition of STAT3 expression and signaling in resveratrol-differentiated medulloblastoma cells. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phromnoi, K.; Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Kannappan, R.; Reuter, S.; Limtrakul, P.; Aggarwal, B.B. Dihydroxypentamethoxyflavone down-regulates constitutive and inducible signal transducers and activators of transcription-3 through the induction of tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siveen, K.S.; Nguyen, A.H.; Lee, J.H.; Li, F.; Singh, S.S.; Kumar, A.P.; Low, G.; Jha, S.; Tergaonkar, V.; Ahn, K.S.; et al. Negative regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 signalling cascade by lupeol inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabir, S.; Kluge, A.; Dowlati, A. The association and nuclear translocation of PIAS3-STAT3 complex is ligand and time dependent. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.N.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Luo, X.; Fang, D.F.; Chen, Y.; Pan, X.; Man, J.H.; Xia, Q.; Jin, B.F.; et al. CUEDC2 (CUE Domain-containing 2) and SOCS3 (Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling 3) cooperate to negatively regulate janus kinase 1/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Kim, J.H.; Li, F.; Qu, A.; Gavrilova, O.; Shah, Y.M.; Gonzalez, F.J. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α regulates a SOCS3-STAT3-adiponectin signal transduction pathway in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3844–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.M.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Xu, X.X.; Qu, X.J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.Z.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y. Resveratrol inhibits the invasion of glioblastoma-initiating cells via down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4383–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.H.; Li, H.; Sun, X.X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Wu, M.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, C.; Kong, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Metabolic patterns and biotransformation activities of resveratrol in human glioblastoma cells: Relevance with therapeutic efficacies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.L.; Li, H.; Yu, L.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Kong, Q.Y.; Song, X.; Shu, X.H.; Liu, J. Short-term resveratrol exposure causes in vitro and in vivo growth inhibition and apoptosis of bladder cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.H.; Wang, L.L.; Li, H.; Song, X.; Shi, S.; Gu, J.Y.; Wu, M.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Kong, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Diffusion efficiency and bioavailability of resveratrol administered to rat brain by different routes: Therapeutic implications. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.H.; Li, H.; Sun, Z.; Wu, M.L.; Ma, J.X.; Wang, J.M.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Fu, Y.S.; Chen, X.Y.; et al. Identification of metabolic pattern and bioactive form of resveratrol inhuman medulloblastoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Liu, N.; Chen, X.Y.; Wu, M.L.; Zhang, K.L.; Kong, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Correlative analyses of notch signaling with resveratrol-induced differentiation and apoptosis of human medulloblastoma cells. Neurosci Lett. 2008, 438, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Li, H.; Wu, M.L.; Fan, S.H.; Wang, Q.; Shu, X.H.; Kong, Q.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Liu, J. Inhibition of NF-κB signaling commits resveratrol-treated medulloblastoma cells to apoptosis without neuronal differentiation. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2011, 104, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.Y.; Kong, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Cytopathological evaluations combined RNA and protein analyses on defined cell regions using single frozen tissue block. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Dong, X.; Gong, F.; Su, N.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.T.; Liu, J.L.; Xue, J.H.; Ji2, S.P.; Zhang, Z.W. Promotion of erythropoietic differentiation in hematopoietic stem cells by SOCS3 knock-down. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.S.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.X.; Yang, X.H.; Wu, M.L.; Zhang, K.L.; Kong, Q.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, N.N.; et al. CRABP-II methylation: A critical determinant of retinoic acid resistance of medulloblastoma cells. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, D. Classifying the medulloblastoma: Insights from morphology and molecular genetics. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2002, 1, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Epigenetic background of neuronal fate determination. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 87, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherry, M.M.; Reeves, A.; Wu, J.K.; Cochran, B.H. STAT3 is required for proliferation and maintenance of multipotency in glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2383–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xie, J. A role for transcription factor STAT3 signaling in oncogene smoothened-driven carcinogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38356–38366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, T.J.; Aguilera, D.; Castellino, R.C. The rationale for targeted therapies in medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Barrueco, R.; Yu, J.; Saucedo-Cuevas, L.P.; Olivan, M.; Llobet-Navas, D.; Putcha, P.; Castro, V.; Murga-Penas, E.M.; Collazo-Lorduy, A.; Castillo-Martin, M.; et al. Inhibition of the autocrine IL-6–JAK2–STAT3–calprotectin axis as targeted therapy for HR−/HER2+ breast cancers. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1631–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Tseng, S.C.; Zhang, M.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Tighe, S.; Lu, W.J.; Zhu, Y.T. LIF-JAK1-STAT3 signaling delays contact inhibition of human corneal endothelial cells. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.W.; Gang, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, H. Expression of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) as an autocrinal growth factor in human medulloblastomas. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 125, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Cimica, V.; Reich, N.C. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 inhibits breast tumor kinase activation of STAT3. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 20904–20912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Williams, P.R.; He, Z. SOCS3: A common target for neuronal protection and axon regeneration after spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 263, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer Sequences | Annealing Temperature | Product Size | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHP-2 | F: 5′-CGAGTGATTGTCATGACAACG-3′ | 56 °C | 477 bp | [16] |
| R: 5′-TGCTTCTGTCTGGACCATCC-3′ | ||||
| SOCS3 | F: 5′-GAGCCCCCTCCTTCCCCTCGC-3′ | 56 °C | 264 bp | [21] |
| R: 5′-GGTCCAGGAACTCCCGAATG-3′ | ||||
| PIAS3 | F: 5′-ACGCTGTTGGCCCCTGGCAC-3′ | 56 °C | 411 bp | [22] |
| R: 5′-GGGGCTCGGCCCCATTCTTGG-3′ | ||||
| β-actin | F: 5′-GCATGGAGTCCTGTGGCAT-3′ | 58 °C | 326 bp | [17] |
| R: 5′-CTAGAAGCATTTGGGGTGG-3′ |
| n | p-STAT3 | p | p-SHP2 | p | SOCS3 | p | PIAS3 | p | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| − | + | ≥++ | − | + | ≥++ | − | + | ≥++ | − | + | ≥++ | ||||||
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | ||||||
| Noncancerous | 15 | 14 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 11 | 0 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 7 | 3 | ||||
| (93.3) | (6.7) | (0.0) | (0.0) | (26.7) | (73.3) | (0.0 | (6.7) | (93.3) | (33.3) | (46.7) | (20.0) | ||||||
| MB | 112 | 12 | 45 | 55 | 0.000 # | 54 | 36 | 22 | 0.000 # | 17 | 37 | 58 | 0.003 # | 88 | 11 | 13 | 0.001 # |
| (10.7) | (40.2) | (49.1) | (48.2) | (32.1) | (19.7) | (15.2) | (33.0) | (51.8) | (78.6) | (9.8) | (11.6) | ||||||
| Large | 46 | 2 | 16 | 28 | 0.000 * | 18 | 15 | 13 | 0.001 * | 4 | 12 | 30 | 0.000 * | 35 | 6 | 5 | 0.000 * |
| (4.3) | (34.8) | (60.9) | (39.1) | (32.6) | (28.3) | (8.7) | (26.1) | (65.2) | (76.1) | (13.0) | (10.9) | ||||||
| Classic | 58 | 5 | 26 | 27 | 0.000 & | 29 | 21 | 8 | 0.001 & | 11 | 21 | 26 | 0.004 & | 45 | 5 | 8 | 0.000 & |
| (8.6) | (44.8) | (46.6) | (50.0) | (36.2) | (13.8) | (19.0) | (36.2) | (44.8) | (77.6) | (8.6) | (13.8) | ||||||
| Nodular | 8 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| (62.5) | (37.5) | (0.0) | (87.5) | (12.5) | (0.0) | (25.0) | (75.0) | (25.0) | (100) | (0.0) | (0.0) | ||||||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, P.; Yu, L.-J.; Huang, T.-M.; Song, X.; Kong, Q.-Y.; Dong, J.-L.; Li, P.-N.; Liu, J. SHP2, SOCS3 and PIAS3 Expression Patterns in Medulloblastomas: Relevance to STAT3 Activation and Resveratrol-Suppressed STAT3 Signaling. Nutrients 2017, 9, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9010003
Li C, Li H, Zhang P, Yu L-J, Huang T-M, Song X, Kong Q-Y, Dong J-L, Li P-N, Liu J. SHP2, SOCS3 and PIAS3 Expression Patterns in Medulloblastomas: Relevance to STAT3 Activation and Resveratrol-Suppressed STAT3 Signaling. Nutrients. 2017; 9(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Cong, Hong Li, Peng Zhang, Li-Jun Yu, Tian-Miao Huang, Xue Song, Qing-You Kong, Jian-Li Dong, Pei-Nan Li, and Jia Liu. 2017. "SHP2, SOCS3 and PIAS3 Expression Patterns in Medulloblastomas: Relevance to STAT3 Activation and Resveratrol-Suppressed STAT3 Signaling" Nutrients 9, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9010003
APA StyleLi, C., Li, H., Zhang, P., Yu, L.-J., Huang, T.-M., Song, X., Kong, Q.-Y., Dong, J.-L., Li, P.-N., & Liu, J. (2017). SHP2, SOCS3 and PIAS3 Expression Patterns in Medulloblastomas: Relevance to STAT3 Activation and Resveratrol-Suppressed STAT3 Signaling. Nutrients, 9(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9010003




