Multilevel Analysis of Factors Associated with Wasting and Underweight among Children Under-Five Years in Nigeria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ethics
3. Method
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Dependent Variables
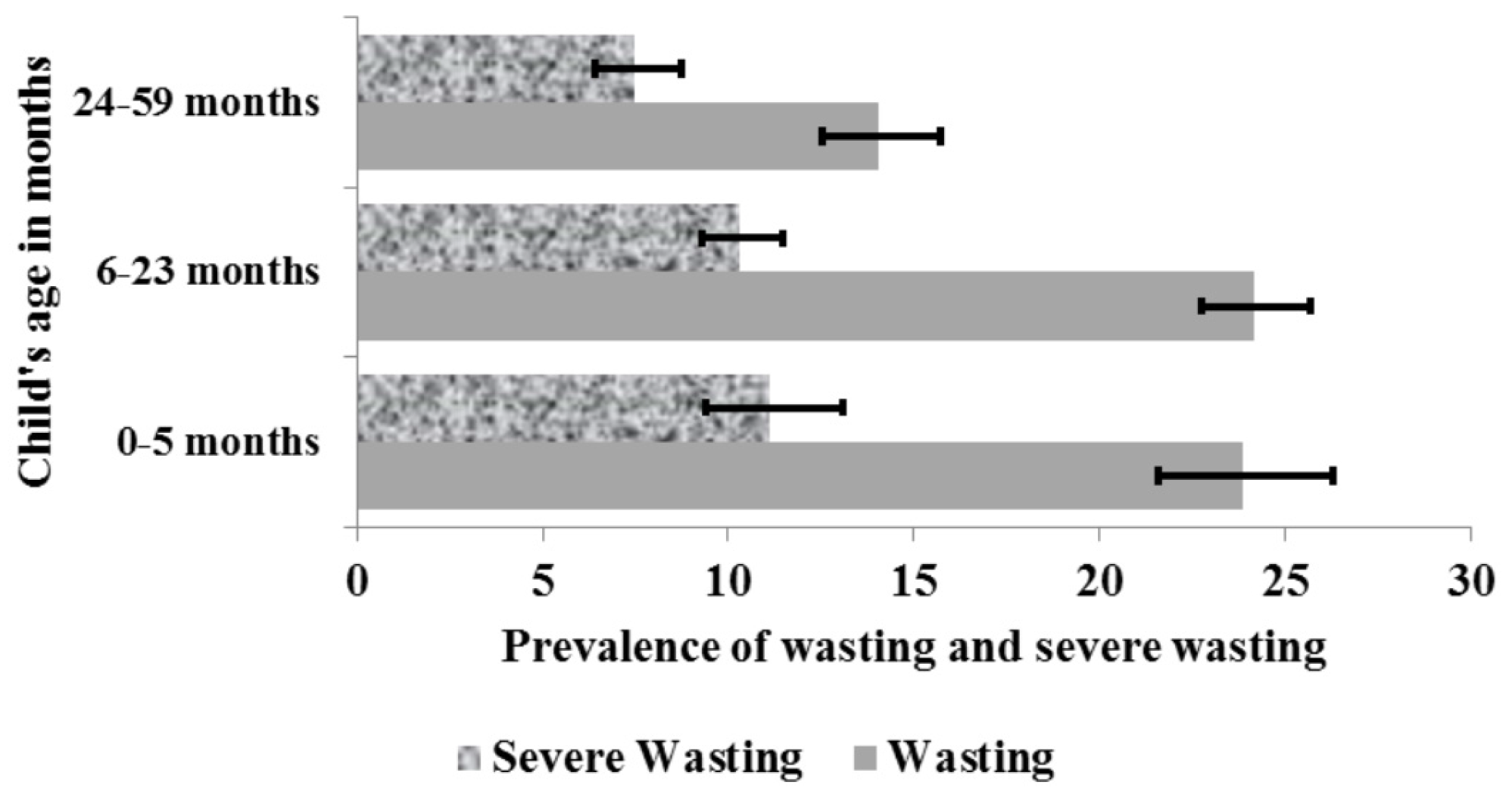
3.2.1. Wasting and Severe Wasting (Weight-for-Height)
3.2.2. Underweight and Severe Underweight (Weight-for-Age)
3.3. Independent Variables
Adopted from UNICEF Conceptual Framework (2013)
3.4. Statistical Analysis
- Undernutrition; Category 0 (not wasted/not underweight (>−2 SD)) and category 1 (wasted/underweight (>−3 SD)).
- Severe undernutrition; Category 0 (not severely wasted/not severely underweight (>−2 SD)) and category 1 (severely wasted/severely underweight (>−3 SD)).
4. Results
5. Multivariate Analysis
5.1. Factors Associated with Wasting and Severe Wasting
5.2. Factors Associated with Underweight and Severe Underweight
6. Discussion
Policy Implications
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Guideline: Updates on the Management of Severe Acute Malnutrition in Infants and CHILDREN; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- The United Nations Children’s Fund; World Health Organization; World Bank. UNICEF, WHO—The World Bank Child Malnutrition Database: Estimates for 2015 and Launch of Interactive Data Dashboards; The United Nations Children’s Fund: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- National Population Commission (NPC); ICF International. Nigeria Demographic and Health Survey 2013; National Population Commission: Abuja, Nigeria; ICF International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunlesi, T.A.; Ayeni, V.A.; Fetuga, B.M.; Adekanmbi, A.F. Severe acute malnutrition in a population of hospitalized under-five Nigerian children. Niger. Postgrad. Med. J. 2015, 22, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balogun, T.B.; Yakubu, A.M. Recent illness, feeding practices and father’s education as determinants of nutritional status among preschool children in a rural Nigerian community. J. Trop. Paediatr. 2015, 61, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idris, S.H.; Popoola-Zakariyya, B.; Sambo, M.N.; Sufyan, M.B.; Abubakar, A. Nutritional status and pattern of infant feeding practices among children under-five in a rural community of north-western Nigeria. Int. Q. Community Health Educ. 2013, 33, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Maternal, Infant and Young Child Nutrition: Draft Comprehensive Implementation Plan. In Proceedings of the Sixth-Fifth World Health Assembly, Geneva, Switzerland, 21–26 May 2012.
- De Onis, M. WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Filmer, D.; Pritchett, L.H. Estimating wealth effects without expenditure Data—Or tears: An application to educational enrolments in states of India. Demography 2001, 38, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Progress on Drinking-Water and Sanitation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 6 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rabe-Hesketh, S.; Skrondal, A. Multilevel modelling of complex survey data. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 2006, 169, 805–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Children’s Fund. Improving Child Nutrition: The Achievable Imperative for Global Progress; United Nations Children’s Fund: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Agho, K.E.; Dibley, M.J.; Odiase, J.I.; Ogbonmwan, S.M. Determinants of exclusive breastfeeding in Nigeria. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2011, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbo, F.A.; Page, A.; Idoko, J.; Claudio, F.; Agho, K.E. Trends in complementary feeding indicators in Nigeria, 2003–2013. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issaka, A.I.; Agho, K.E.; Page, A.N.; Burns, P.L.; Stevens, G.J.; Dibley, M.J. Determinants of suboptimal complementary feeding practices among children aged 6–23 months in four anglophone West African countries. Matern. Child Nutr. 2015, 11 (Suppl. 1), 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Complementary Feeding of Young Children in Developing Countries: A Review of Current Scientific Knowledge; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998; p. 230. [Google Scholar]
- Mwangome, M.; Prentice, A.; Plugge, E.; Nweneka, C. Determinants of appropriate child health and nutrition practices among women in rural Gambia. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2010, 28, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, T.; Pittore, K. Report of the WINNN-ORIE Nutrition Stakeholders Engagement Event, 29 April 2014, Abuja; Operational Research and Impact Evaluation: Northern Region, Nigeria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kandala, N.B.; Madungu, T.P.; Emina, J.B.; Nzita, K.P.; Cappuccio, F.P. Malnutrition among children under the age of five in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC): Does geographic location matter? BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabale, G.A.; Sharma, M.K. Determinants of Wasting Among Under-Five Children in Ethiopia: (A Multilevel Logistic Regression Model Approach). Int. J. Stat. Med. Res. 2014, 3, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitolo, M.R.; Gama, C.M.; Bortolini, G.A.; Campagnolo, P.D.; Drachler, M.D.L. Some risk factors associated with overweight, stunting and wasting among children under 5 years old. J. Pediatr. 2008, 84, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, S.F.; Hashmi, S.K. Consanguinity among the risk factors for underweight in children under five: A study from Rural Sindh. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2009, 21, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lesiapeto, M.S.; Smuts, C.M.; Hanekom, S.M.; Du Plessis, J.; Faber, M. Risk factors of poor anthropometric status in children under five years of age living in rural districts of the Eastern Cape and KwaZulu-Natal provinces, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 23, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.K.; Banu, B.; Khanom, K.; Ali, L.; Thapa, N.; Stray-Pedersen, B.; Devkota, B. Changing trends on the place of delivery: Why do Nepali women give birth at home? Reprod. Health 2012, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, M.; Gubhaju, B. Women’s Status, Household Structure and the Utilization of Maternal Health Services in Nepal: Even primary-leve1 education can significantly increase the chances of a woman using maternal health care from a modem health facility. Asia-Pac. Popul. J. 2001, 16, 23–44. [Google Scholar]
- Black, R.E.; Victora, C.G.; Walker, S.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Christian, P.; de Onis, M.; Uauy, R. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet 2013, 382, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, M.; Wondaferash, M.; Taha, M.; Dube, L. Prevalence of undernutrition and associated factors among children aged between six to fifty nine months in Bule Hora district, South Ethiopia. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masibo, P.K.; Makoka, D. Trends and determinants of undernutrition among young Kenyan children: Kenya Demographic and Health Survey; 1993, 1998, 2003 and 2008–2009. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiye, F.; Chama, C.; Chitah, B.; Jonsson, D. Determinants of child nutritional status in Zambia: An analysis of a national survey. Zamb. Soc. Sci. J. 2010, 1, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Kavosi, E.; Hassanzadeh Rostami, Z.; Kavosi, Z.; Nasihatkon, A.; Moghadami, M.; Heidari, M. Prevalence and determinants of under-nutrition among children under six: A cross-sectional survey in Fars province, Iran. Int. J. Health Policy Manag. 2014, 3, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.; Ausman, L.M.; Agho, K.E. Determinants of stunting and severe stunting among under-fives: Evidence from the 2011 Nepal Demographic and Health Survey. BMC Paediatr. 2014, 14, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Chowdhury, S.; Hossain, D. Acute malnutrition in Bangladeshi children: Levels and determinants. Asia-Pac. J. Public Health 2009, 21, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Characteristics | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Community Level Factors | ||
| Type of residence | ||
| Urban | 9067 | 37.0 |
| Rural | 15,465 | 63.0 |
| Geopolitical Zones | ||
| North Central | 3562 | 14.5 |
| North East | 4086 | 16.7 |
| North West | 8506 | 34.7 |
| South East | 2284 | 9.3 |
| South West | 2372 | 9.7 |
| South South | 3722 | 15.2 |
| Socio-demographic factors | ||
| Wealth Index | ||
| Poorest | 5378 | 21.9 |
| Poor | 5383 | 21.9 |
| Middle | 4711 | 19.2 |
| Rich | 4598 | 18.7 |
| Richest | 4462 | 18.2 |
| Mother’s working status | ||
| Non-working | 16,151 | 97.1 |
| Working (past 12 months) | 485 | 2.9 |
| Maternal education | ||
| No education | 11,378 | 46.4 |
| Primary | 4933 | 20.1 |
| Secondary and above | 8221 | 33.5 |
| Father’s occupation | ||
| Non agriculture | 20,237 | 82.5 |
| Agriculture | 1024 | 4.2 |
| Not working | 3271 | 13.3 |
| Father’s education | ||
| No education | 8870 | 37.0 |
| Primary | 4640 | 19.4 |
| Secondary and above | 10,447 | 43.6 |
| Marital status | ||
| Currently married | 23,592 | 97.6 |
| Formerly married (Divorce/Separated/Widow) | 579 | 2.4 |
| Mother’s literacy | ||
| Can’t read at all | 14,029 | 57.5 |
| Can read | 10,386 | 42.5 |
| Environmental factor | ||
| Source of drinking water | ||
| Protected | 13,878 | 56.6 |
| Unprotected | 10,653 | 43.4 |
| Media factors | ||
| Reading newspaper | ||
| Yes | 3589 | 14.7 |
| No | 20,793 | 85.3 |
| Listening to radio | ||
| Yes | 15,135 | 61.9 |
| No | 9314 | 38.1 |
| Watching TV | ||
| Yes | 11,690 | 47.9 |
| No | 12,732 | 52.1 |
| Proximate determinants | ||
| Maternal factors | ||
| Mother’s age | ||
| 15–24 years | 5780 | 23.6 |
| 25–34 years | 12,424 | 50.6 |
| 35–49 years | 6328 | 25.8 |
| Mother’s age at birth | ||
| <20 years | 3325 | 13.6 |
| 20–29 years | 12,878 | 52.5 |
| 30–39 years | 7161 | 29.2 |
| 40 and above | 1168 | 4.8 |
| Delivery factors | ||
| Type of delivery assistance | ||
| Health professional | 10,399 | 42.8 |
| Traditional birth attendant | 4938 | 20.3 |
| Relatives and other untrained personnel | 5856 | 24.1 |
| No one | 3113 | 12.8 |
| Place of delivery | ||
| Home | 15,065 | 61.4 |
| Health facility | 9467 | 38.6 |
| Mode of delivery | ||
| Non-caesarean | 23,734 | 97.8 |
| Caesarean | 523 | 2.2 |
| Combined Place and mode of delivery | ||
| Non-caesarean and Home delivery | 15,065 | 62.1 |
| Non-caesarean & Health facility | 8669 | 35.7 |
| Caesarean & Health facility | 523 | 2.2 |
| Pre/post-delivery factors | ||
| Antenatal clinic visits | ||
| None | 5177 | 32.8 |
| 1–3 | 1954 | 12.4 |
| 4+ | 8674 | 54.9 |
| Timing of postnatal check-up | ||
| No postnatal check-up | 19,243 | 78.4 |
| 0–2 days | 3748 | 15.3 |
| Delayed | 1541 | 6.3 |
| Currently breastfeeding | ||
| Yes | 13,950 | 56.9 |
| No | 10,582 | 43.1 |
| Duration of breastfeeding | ||
| up to 12 months | 5376 | 22.3 |
| >12 months | 18,792 | 77.8 |
| Child factors | ||
| Birth order | ||
| First-born | 4641 | 19.0 |
| 2nd–4th | 11,327 | 46.2 |
| 5 or more | 8564 | 34.9 |
| Preceding birth interval | ||
| No previous birth | 4641 | 19.0 |
| <24 months | 4326 | 17.7 |
| >24 months | 15,520 | 63.4 |
| Sex of child | ||
| Male | 12,193 | 49.7 |
| Female | 12,339 | 50.3 |
| Perceived birth size | ||
| Small | 3385 | 14.0 |
| Average | 10,052 | 41.5 |
| Large | 10,759 | 44.5 |
| Child’s age in months | ||
| 0–5 | 2238 | 9.3 |
| 6–23 | 7876 | 32.8 |
| 24–59 | 13,915 | 57.9 |
| Child had diarrhoea recently | ||
| No | 21,885 | 89.3 |
| Yes | 2556 | 10.4 |
| Child had fever in last two weeks | ||
| No | 21,251 | 86.6 |
| Yes | 3153 | 12.9 |
| Characteristics | Wasted Children 0–59 Months | Severely Wasted Children 0–59 Months | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted Odd Ratio (95% CI) | p | Adjusted Odd Ratio (95% CI) | p | Unadjusted Odd Ratio (95% CI) | p | Adjusted Odd Ratio (95% CI) | p | |
| Community Level Factors | ||||||||
| Type of residence | ||||||||
| Urban | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Rural | 1.05 (0.86, 1.28) | 0.641 | 0.72 (0.59, 0.89) | 0.001 | 1.07 (0.81, 1.41) | 0.641 | 0.71 (0.55, 0.93) | 0.013 |
| Geopolitical Zones | ||||||||
| North Central | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| North East | 1.73 (1.38, 2.17) | <0.001 | 1.51 (1.19, 1.91) | 0.001 | 2.07 (1.46, 2.94) | <0.001 | 1.87 (1.31, 2.66) | 0.001 |
| North West | 2.59 (2.09, 3.22) | <0.001 | 2.42 (1.93, 3.03) | <0.001 | 3.60 (2.62, 4.95) | <0.001 | 3.17 (2.28, 4.40) | <0.001 |
| South East | 0.98 (0.77, 1.23) | 0.837 | 0.81 (0.63, 1.05) | 0.112 | 0.91 (0.63, 1.32) | 0.613 | 0.69 (0.47, 1.04) | 0.074 |
| South West | 0.92 (0.72, 1.16) | 0.473 | 0.88 (0.69, 1.12) | 0.285 | 0.82 (0.56, 1.21) | 0.316 | 0.75 (0.51, 1.10) | 0.143 |
| South South | 0.78 (0.62, 0.98) | 0.031 | 0.67 (0.52, 0.85) | 0.001 | 0.61 (0.42, 0.87) | 0.007 | 0.49 (0.33, 0.71) | <0.001 |
| Socio-demographic factors | ||||||||
| Mother’s education | ||||||||
| No education | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Primary | 0.65 (0.57, 0.74) | <0.001 | 0.90 (0.78, 1.04) | 0.160 | 0.53 (0.44, 0.63) | <0.001 | 0.81 (0.66, 0.98) | 0.002 |
| Secondary and above | 0.54 (0.47, 0.62) | <0.001 | 0.79 (0.67, 0.94) | 0.007 | 0.47 (0.38, 0.58) | <0.001 | 0.74 (0.58, 0.94) | 0.014 |
| Father’s education | ||||||||
| No education | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Primary | 0.67 (0.58, 0.76) | <0.001 | 0.89 (0.77, 1.03) | 0.120 | 0.57 (0.47, 0.70) | <0.001 | 0.84 (0.68, 1.03) | 0.095 |
| Secondary and above | 0.57 (0.50, 0.65) | <0.001 | 0.77 (0.67, 0.88) | <0.001 | 0.47 (0.39, 0.58) | <0.001 | 0.65 (0.53, 0.79) | <0.001 |
| Watching TV | ||||||||
| Yes | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| No | 1.28 (1.13, 1.46) | <0.001 | 0.78 (0.68, 0.88) | <0.001 | 1.30 (1.08, 1.57) | 0.005 | 0.68 (0.56, 0.82) | <0.001 |
| Proximate determinants | ||||||||
| Maternal factors | ||||||||
| Mother’s BMI | ||||||||
| <18.5 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| 18.5–25 | 0.66 (0.56, 0.78) | <0.001 | 0.76 (0.64, 0.90) | 0.002 | 0.73 (0.59, 0.91) | 0.005 | ||
| 25+ | 0.48 (0.39, 0.59) | <0.001 | 0.68 (0.56, 0.83) | <0.001 | 0.56 (0.43, 0.74) | <0.001 | ||
| Delivery factors | ||||||||
| Type of delivery assistance | ||||||||
| No one | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| Traditional birth attendant | 1.85 (1.59, 2.15) | <0.001 | 1.39 (1.11, 1.73) | 0.004 | 2.25 (1.79, 2.82) | <0.001 | ||
| Relatives or other | 1.77 (1.53, 2.05) | <0.001 | 1.44 (1.14, 1.80) | 0.002 | 2.08 (1.74, 2.49) | <0.001 | ||
| Health professional | 1.84 (1.55, 2.19) | <0.001 | 1.11 (0.88, 1.41) | 0.367 | 2.39 (1.88, 3.04) | <0.001 | ||
| Combined Place/mode of delivery | ||||||||
| Home delivery | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Health facility with non-caesarean | 0.59 (0.52, 0.67) | <0.001 | 1.12 (0.92, 1.37) | 0.254 | 0.47 (0.39, 0.57) | <0.001 | 0.79 (0.65, 0.96) | 0.017 |
| Health facility with caesarean | 0.31 (0.20, 0.46) | <0.001 | 0.61 (0.39, 0.94) | 0.025 | 0.24 (0.14, 0.43) | <0.001 | 0.44 (0.24, 0.79) | 0.007 |
| Child factors | ||||||||
| Sex of child | ||||||||
| Male | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Female | 0.88 (0.81, 0.95) | 0.001 | 0.83 (0.77, 0.89) | <0.001 | 0.85 (0.76, 0.94) | 0.002 | 0.79 (0.71, 0.88) | <0.001 |
| Perceived birth size | ||||||||
| Small | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Average | 0.76 (0.66, 0.87) | <0.001 | 0.85 (0.74, 0.97) | 0.017 | 0.72 (0.60, 0.85) | <0.001 | 0.81 (0.68, 0.96) | 0.018 |
| Large | 0.60 (0.52, 0.69) | <0.001 | 0.66 (0.57, 0.76) | <0.001 | 0.57 (0.48, 0.67) | <0.001 | 0.64 (0.53, 0.77) | <0.001 |
| Child had fever in last two weeks | ||||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| Yes | 1.07 (0.94, 1.21) | 0.312 | 1.18 (1.06, 1.32) | 0.003 | 0.81 (0.68, 0.98) | 0.028 | ||
| Child’s age in months | 0.98 (0.98, 0.98) | <0.001 | 0.98 (0.98, 0.98) | <0.001 | 0.99 (0.98, 0.99) | <0.001 | 0.98 (0.98, 0.99) | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Underweight Children 0–59 Months | Severely Underweight Children 0–59 Months | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted Odd Ratio (OR) (95% CI) | p | Adjusted Odd Ratio (AOR) (95% CI) | p | Unadjusted Odd Ratio (OR) (95% CI) | p | Adjusted Odd Ratio (AOR) (95% CI) | p | |
| Community Level Factors | ||||||||
| Geopolitical Zones | ||||||||
| North Central | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| North East | 1.97 (1.58, 2.45) | <0.001 | 1.44 (1.17, 1.78) | 0.001 | 1.85 (1.34, 2.56) | <0.001 | 1.48 (1.06, 2.06) | 0.021 |
| North West | 3.94 (3.20, 4.84) | <0.001 | 3.22 (2.58, 4.01) | <0.001 | 4.37 (3.19, 5.98) | <0.001 | 3.82 (2.72, 5.35) | <0.001 |
| South East | 0.52 (0.39, 0.67) | <0.001 | 0.47 (0.36, 0.59) | <0.001 | 0.38 (0.24, 0.58) | <0.001 | 0.32 (0.21, 0.49) | <0.001 |
| South West | 0.64 (0.51, 0.81) | <0.001 | 0.64 (0.51, 0.79) | <0.001 | 0.49 (0.32, 0.75) | 0.001 | 0.48 (0.32, 0.73) | 0.001 |
| South South | 0.73 (0.58, 0.93) | 0.011 | 0.76 (0.60, 0.96) | 0.022 | 0.53 (0.35, 0.80) | 0.003 | 0.52 (0.34, 0.78) | 0.002 |
| Socio-demographic factors | ||||||||
| Mother’s education | ||||||||
| No education | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| Primary | 0.48 (0.43, 0.54) | <0.001 | 0.89 (0.79, 1.01) | 0.062 | 0.49 (0.41, 0.58) | <0.001 | ||
| Secondary and higher | 0.29 (0.26, 0.35) | <0.001 | 0.74 (0.62, 0.87) | <0.001 | 0.28 (0.21, 0.36) | <0.001 | ||
| Father’s education | ||||||||
| No Education | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Primary | 0.56 (0.49, 0.63) | <0.001 | 0.96 (0.85, 1.08) | 0.500 | 0.62 (0.52, 0.74) | <0.001 | 1.14 (0.95, 1.36) | 0.153 |
| Secondary and higher | 0.38 (0.33, 0.43) | <0.001 | 0.78 (0.69, 0.88) | <0.001 | 0.38 (0.31, 0.46) | <0.001 | 0.85 (0.71, 1.03) | 0.103 |
| Proximate determinants | ||||||||
| Maternal factors | ||||||||
| Mother’s BMI | ||||||||
| <18.5 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| 18.5–25 | 0.56 (0.48, 0.66) | <0.001 | 0.67 (0.57, 0.78) | <0.001 | 0.64 (0.53, 0.78) | <0.001 | 0.78 (0.63, 0.95) | 0.015 |
| 25+ | 0.30 (0.25, 0.37) | <0.001 | 0.52 (0.43, 0.63) | <0.001 | 0.35 (0.28, 0.46) | <0.001 | 0.66 (0.51, 0.84) | 0.001 |
| Delivery factors | ||||||||
| Combined Place/mode of delivery | ||||||||
| Home delivery | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Health facility with non-caesarean | 0.38 (0.33, 0.43) | <0.001 | 0.85 (0.76, 0.95) | <0.001 | 0.34 (0.28, 0.41) | <0.001 | 0.69 (0.52, 0.91) | 0.008 |
| Health facility with caesarean | 0.26 (0.18, 0.37) | <0.001 | 0.69 (0.48, 0.99) | 0.016 | 0.27 (0.16, 0.47) | <0.001 | 0.67 (0.33, 1.36) | 0.268 |
| Currently breastfeeding | ||||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| Yes | 0.85 (0.79, 0.92) | <0.001 | 0.89 (0.81, 0.97) | 0.007 | 0.84 (0.75, 0.95) | 0.005 | ||
| Duration of breastfeeding | ||||||||
| up to 12 months | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| >12 months | 1.36 (1.24, 1.49) | <0.001 | 1.61 (1.44, 1.80) | <0.001 | 1.22 (1.07, 1.38) | 0.002 | 1.91 (1.64, 2.23) | <0.001 |
| Child factors | ||||||||
| Preceding birth interval | ||||||||
| No previous birth | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| <24 months | 1.32 (1.18, 1.48) | <0.001 | 1.11 (0.98, 1.26) | 0.093 | 1.48 (1.23, 1.77) | <0.001 | 1.29 (1.06, 1.56) | 0.010 |
| >24 months | 1.16 (1.05, 1.27) | 0.002 | 0.97 (0.88, 1.07) | 0.513 | 1.25 (1.09, 1.44) | 0.002 | 1.04 (0.89, 1.19) | 0.620 |
| Sex of child | ||||||||
| Male | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Female | 0.86 (0.80, 0.92) | <0.001 | 0.79 (0.74, 0.85) | <0.001 | 0.86 (0.78, 0.95) | 0.002 | 0.79 (0.72, 0.88) | <0.001 |
| Perceived birth size | ||||||||
| Small | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Average | 0.72 (0.64, 0.82) | <0.001 | 0.87 (0.76, 0.99) | 0.044 | 0.66 (0.56, 0.77) | <0.001 | 0.78 (0.65, 0.93) | 0.005 |
| Large | 0.49 (0.43, 0.55) | <0.001 | 0.55 (0.48, 0.63) | <0.001 | 0.44 (0.37, 0.52) | <0.001 | 0.50 (0.41, 0.60) | <0.001 |
| Child had diarrhoea recently | ||||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 1.51 (1.35, 1.69) | <0.001 | 1.36 (1.21, 1.53) | <0.001 | 1.55 (1.34, 1.78) | <0.001 | 1.43 (1.24, 1.65) | <0.001 |
| Child had fever in last two weeks | ||||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 1.28 (1.15, 1.43) | <0.001 | 1.35 (1.21, 1.51) | <0.001 | 1.13 (0.96, 1.32) | 0.137 | 1.22 (1.03, 1.46) | 0.024 |
| Child’s age in months | 1.00 (1.00, 1.01) | 0.002 | 0.99 (0.99, 0.99) | 0.002 | 0.98 (0.98, 0.99) | <0.001 | ||
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akombi, B.J.; Agho, K.E.; Merom, D.; Hall, J.J.; Renzaho, A.M. Multilevel Analysis of Factors Associated with Wasting and Underweight among Children Under-Five Years in Nigeria. Nutrients 2017, 9, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9010044
Akombi BJ, Agho KE, Merom D, Hall JJ, Renzaho AM. Multilevel Analysis of Factors Associated with Wasting and Underweight among Children Under-Five Years in Nigeria. Nutrients. 2017; 9(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkombi, Blessing J., Kingsley E. Agho, Dafna Merom, John J. Hall, and Andre M. Renzaho. 2017. "Multilevel Analysis of Factors Associated with Wasting and Underweight among Children Under-Five Years in Nigeria" Nutrients 9, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9010044
APA StyleAkombi, B. J., Agho, K. E., Merom, D., Hall, J. J., & Renzaho, A. M. (2017). Multilevel Analysis of Factors Associated with Wasting and Underweight among Children Under-Five Years in Nigeria. Nutrients, 9(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9010044







