Impact of Early Nutrition on Body Composition in Children Aged 9.5 Years Born with Extremely Low Birth Weight
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Measurement of Nutritional Intake
2.3. Measurement of Auxological Parameters
2.4. Measurement of Body Composition
2.5. Biochemical Analyses
2.6. Definitions
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth from Birth until 9.5 Years of Age
3.2. Relationship between Early Postnatal Nutrition and Auxological Parameters
3.3. Association between Auxological Parameters and Body Composition at 9.5 Years of Age
3.4. Influence of Early Postnatal Nutrition on Body Composition at 9.5 Years of Age
3.5. Nutritional Intake and Metabolic Parameters at 9.5 Years of Age
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hovi, P.; Andersson, S.; Eriksson, J.G.; Järvenpää, A.L.; Strang-Karlsson, S.; Mäkitie, O.; Kajantie, E. Glucose regulation in young adults with very low birth weight. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, M.; Fall, C.H.; Osmond, C.; Barker, D.J. Birth weight, weight at one year, and left ventricular mass in adult life. Br. Heart J. 1995, 73, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkhof, G.F.; Willemsen, R.H.; Leunissen, R.W.; Breukhoven, P.E.; Hokken-Koelega, A.C. Health profile of young adults born preterm: Negative effects of rapid weight gain in early life. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 4498–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hack, M. Young adult outcomes of very-low-birth-weight children. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2006, 11, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velkoska, E.; Cole, T.J.; Dean, R.G.; Burrell, L.M.; Morris, M.J. Early undernutrition leads to long-lasting reductions in body weight and adiposity whereas increased intake increases cardiac fibrosis in male rats. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierrat, V.; Marchand-Martin, L.; Guemas, I.; Matis, J.; Burguet, A.; Picaud, J.C.; Fresson, J.; Alberge, C.; Marret, S.; Roze, J.C.; et al. Height at 2 and 5 years of age in children born very preterm: The EPIPAGE study. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2011, 96, F348–F354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, R.J.; Ainsworth, S.B.; Fenton, A.C. Postnatal growth retardation: A universal problem in preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2004, 89, F428–F430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiler, A.; Woelfle, J.; Stutte, S.; Schreiner, F.; Bartmann, P.; Gohlke, B. Postnatal nutrition in extremely low birth weight infants and its impact on growth until the age of 6 years. Acta Paediatr. 2014, 103, e61–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euser, A.M.; Finken, M.J.; Keijzer-Veen, M.G.; Hille, E.T.; Wit, J.M.; Dekker, F.W. Dutch POPS-19 Collaborative Study Group. Associations between prenatal and infancy weight gain and BMI, fat mass, and fat distribution in young adulthood: A prospective cohort study in males and females born very preterm. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Jong, M.; Lafeber, H.N.; Cranendonk, A.; Van Weissenbruch, M.M. Components of the metabolic syndrome in early childhood in very-low-birth-weight infants. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2014, 81, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stutte, S.; Woelfle, J.; Born, M.; Bartmann, P.; Gohlke, B.C. Bone maturation in extremely low birth weight infants in relation to birth weight and endocrine parameters. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, M.; Schneider, K.T.; Jährig, K. Analysis of a 1992 birth sample in Germany.1: New percentile values of the body weight of newborn infants (German). Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 1996, 56, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanussen, M.; Thiel, C.; Tscharntke, V.; Von Büren, E. Synthetische Referenzwerte für Körpergröße. Deutsche Normalwerte (Basis 1993) für alle Altersstufen zwischen 0 und 20 Jahren (German). Kinder- und Jugendarzt 1999, 30, 488–493. [Google Scholar]
- Kromeyer-Hauschild, K.; Wabitsch, M.; Kunze, D.; Geller, F.; Geiß, H.C.; Hesse, V.; Von Hippel, A.; Jaeger, U.; Johnsen, D.; Korte, W.; et al. Perzentile für den Body- mass-Index für das Kindes- und Jugendalter unter Heranziehung verschiedener deutscher Stichproben. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 2001, 149, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerver, W.J.M.; De Bruin, R. Paediatric Morphometrics, 1st ed.; Universitaire Pers Maastricht: Maastricht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Agostoni, C.; Buonocore, G.; Carnielli, V.P.; De Curtis, M.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.D.; Fusch, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; et al. Enteral nutrient supply for preterm infants: Commentary from the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkola, K.; Ritari, N.; Tommiska, V.; Salokorpi, T.; Lehtonen, L.; Tammela, O.; Pääkkönen, L.; Olsen, P.; Korkman, M.; Fellman, V. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 5 years of age of a national cohort of extremely low birth weight infants who were born in 1996–1997. Pediatrics 2005, 116, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormack, B.E.; Bloomfield, F.H. Increased protein intake decreases postnatal growth faltering in ELBW babies. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2013, 98, F399–F404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, E.B.; Morley, R.; Lucas, A. Early diet and general cognitive outcome at adolescence in children born at or below 30 weeks gestation. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, I.S.; Ness, A.R.; Steer, C.D.; Wells, J.C.; Emmett, P.M.; Reilly, J.R.; Tobias, J.; Smith, G.D. Associations of size at birth and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry measures of lean and fat mass at age 9 to 10 years of age. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singhal, A.; Wells, J.; Cole, T.J.; Fewtrell, M.; Lucas, A. Programming of lean body mass: A link between birth weight, obesity and cardiovascular disease? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.W.; Faber, B.; Callanan, C.; Ford, G.W.; Davis, N.M. Extremely low birth weight and body size in early adulthood. Arch. Dis. Child 2004, 89, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, C.; Westerberg, A.C.; Rønnestad, A.; Nakstad, B.; Veierød, M.B.; Drevon, C.A.; Iversen, P.O. Growth and nutrient intake among very-low-birth-weight infants fed fortified human milk during hospitalisation. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, B.; Celik, I.; Jauch, K.W.; Koller, M.; Kopp, J.B.; Verwied-Jorky, S. Leitlinie parenterale Ernährung der DGEM. Aktuel. Ernähr. Med. 2007, 32 (Suppl. S1), S72–S88. [Google Scholar]
- Ridout, E.; Melara, D.; Rottinghaus, S.; Thureen, P.J. Blood urea nitrogen concentration as a marker of amino-acid intolerance in neonates with birthweight less than 1250 g. J. Perinatol. 2005, 25, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenkranz, R.A. Early nutritional support and outcomes in ELBW infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poindexter, B.B.; Langer, J.C.; Dusick, A.M.; Ehrenkranz, R.A. Early provision of parenteral amino acids in extremely low birth weight infants: Relation to growth and neurodevelopmental outcome. J. Pediatr. 2006, 148, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premji, S.S.; Fenton, T.R.; Sauve, R.S. Higher versus lower protein intake in formula-fed low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.C.; Treleaven, P.; Cole, T.J. BMI compared with 3-dimensional body shape: The UK National Sizing Survey. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garnett, S.P.; Cowell, C.T.; Baur, L.A.; Fay, R.A.; Lee, J.; Coakley, J.; Boulton, T.J. Abdominal fat and birth size in healthy prepubertal children. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| n | Mean Weight SDS | Mean Height SDS | Mean BMI SDS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Range) | (Range) | (Range) | ||
| at birth (mean GA 27.2 wks) | 61 | −0.88 | −0.80 | |
| (−2.60 to 0.44) | (−2.49 to 0.25) | |||
| at discharge (mean GA 40.3 wks) | 52 | −2.16 | −3.00 | |
| (−3.88 to 0.05) | (−5.19 to 1.22) | |||
| 0.5 yrs | 61 | −0.95 * | −6.56 | −1.49 |
| (−3.15 to 1.25) | (−13.9 to 2.45) | (−5.31 to 1.64) | ||
| 1 yr | 61 | −1.04 | −2.28 * | −1.85 |
| (−3.77 to 1.31) | (−5.9 to 0.03) | (−4.83 to 1.01) | ||
| 2 yrs | 61 | −1.03 | −0.94 * | −1.76 |
| (−4.03 to 0.78) | (−3.97 to 1.75) | (−5.81 to 1.76) | ||
| 4 yrs | 61 | −1.29 | −1.13 | −1.71 |
| (−3.41 to 1.23) | (−3.06 to 0.21) | (−6.5 to 1.54) | ||
| 5.7 yrs (4.5–7.7) | 61 | −1.29 | −0.97 | −1.36 |
| (−4.45 to 1.04) | (−3.71 to 0.9) | (−4.55 to 1.29) | ||
| 9.5 yrs (7.9–11.9) | 39 | −0.75 | −0.23 | −0.85 |
| (−3.56 to 1.76) | (−2.26 to 1.57) | (−3.71 to 1.88) |
| Regression Coefficients (ß) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent Variable | Sex b | Birth Weight c | Early Macronutrient Intake | Weight Dev d | Pubertal Stage e | R2corr. | ||
| Carb. | Protein | Fat | ||||||
| Lean body mass (g) | −0.479 p = 0.003 | 0.476 p = 0.004 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | 0.44 F = 11.11 p < 0.001 |
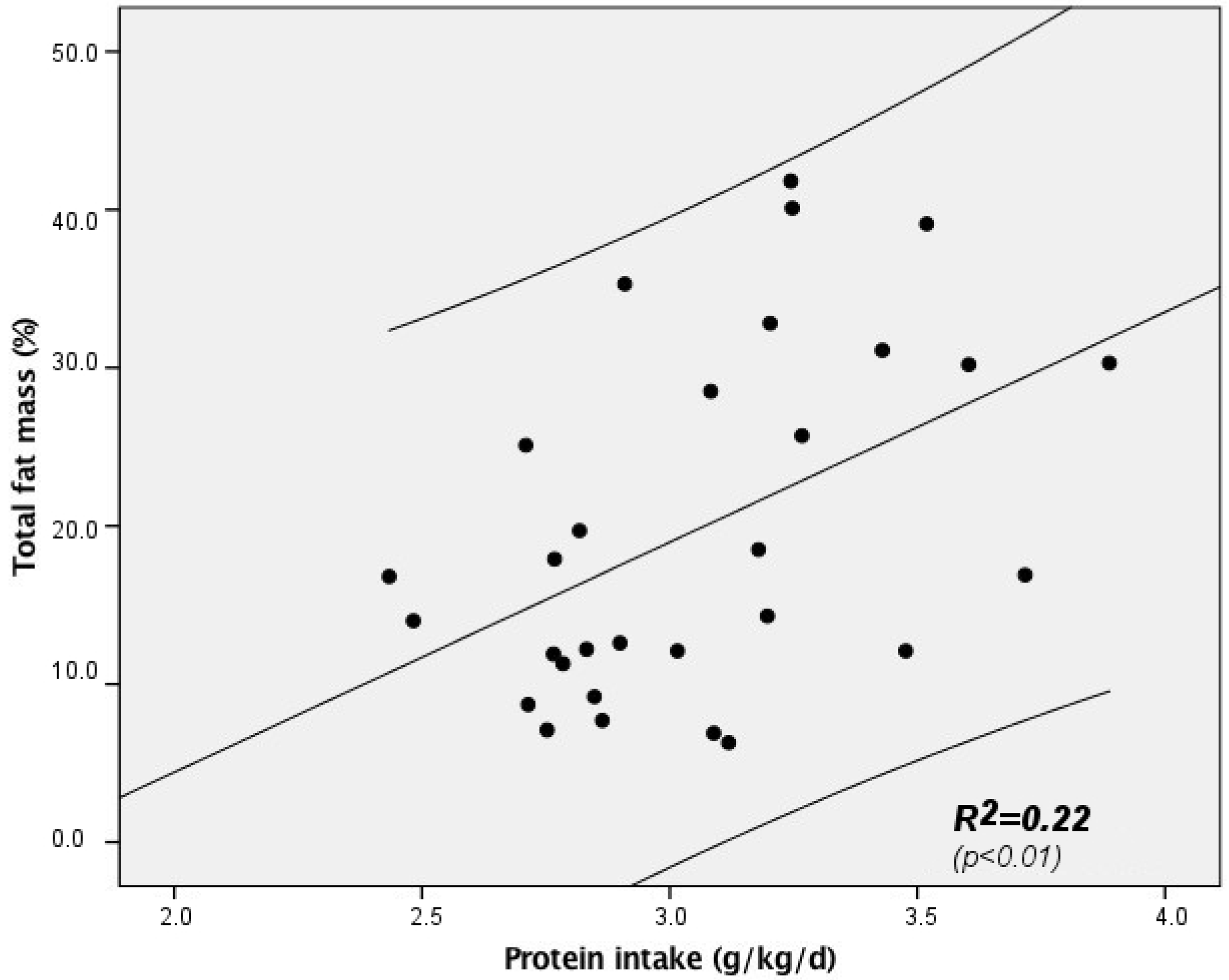
| Fat Mass (%) | NS | NS | NS | 0.515 p = 0.006 | NS | NS | NS | 0.24 F = 9.05 p < 0.01 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | NS | NS | −0.336 p = 0.038 | −0.531 p = 0.002 | NS | NS | NS | 0.41 F = 10.15 p = 0.001 |
| Fasting Insulin f (mU/L) | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | 0.559 p = 0.008 | NS | 0.28 F = 8.64 p < 0.01 |
| Total Fat Mass (%) | Abdominal Fat Mass (%) | Hip Fat Mass (%) | Lean Body Mass (g) | Triceps Skinfold (SDS) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein intake (g/kg/day) | r = 0.481 | r = 0.488 | r = 0.443 | r = 0.299 | r = 0.381 |
| p = 0.007 | p = 0.006 | p = 0.014 | p = 0.108 | p = 0.05 | |
| Lipid intake (g/kg/day) | r = 0.275 | r = 0.157 | r = 0.247 | r = −0.006 | r = 0.230 |
| p = 0.141 | p = 0.406 | p = 0.189 | p = 0.975 | p = 0.248 | |
| Carb. Intake (g/kg/day) | r = −0.036 | r = 0.027 | r = −0.093 | r = −0.138 | r = 0.117 |
| p = 0.849 | p = 0.888 | p = 0.624 | p = 0.468 | p = 0.562 | |
| Energy intake (kcal/kg/day) | r = 0.371 | r = 0.332 | r = 0.319 | r = −0.004 | r = 0.342 |
| p = 0.043 | p = 0.073 | p = 0.086 | p = 0.984 | p = 0.08 |
| Protein Intake | Carbohydrate Intake | Lipid Intake | Energy Intake | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/kg/day) | (g/kg/day) | (g/kg/day) | (kcal/kg/day) | |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | −0.445 | −0.417 | −0.188 | −0.393 |
| p = 0.014 | p = 0.022 | p = 0.320 | p = 0.032 | |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 0.143 | −0.029 | −0.081 | −0.077 |
| p = 0.450 | p = 0.879 | p = 0.670 | p = 0.722 | |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | −0.056 | −0.336 | −0.169 | −0.327 |
| p = 0.768 | p = 0.070 | p = 0.371 | p = 0.078 | |
| Fasting insulin (mU/L) | 0.581 | 0.155 | 0.077 | 0.232 |
| p = 0.003 | p = 0.469 | p = 0.722 | p = 0.274 | |
| HOMA index | 0.566 | 0.152 | 0.073 | 0.230 |
| p = 0.003 | p = 0.468 | p = 0.728 | p = 0.269 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stutte, S.; Gohlke, B.; Peiler, A.; Schreiner, F.; Born, M.; Bartmann, P.; Woelfle, J. Impact of Early Nutrition on Body Composition in Children Aged 9.5 Years Born with Extremely Low Birth Weight. Nutrients 2017, 9, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9020124
Stutte S, Gohlke B, Peiler A, Schreiner F, Born M, Bartmann P, Woelfle J. Impact of Early Nutrition on Body Composition in Children Aged 9.5 Years Born with Extremely Low Birth Weight. Nutrients. 2017; 9(2):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9020124
Chicago/Turabian StyleStutte, Sonja, Bettina Gohlke, Annika Peiler, Felix Schreiner, Mark Born, Peter Bartmann, and Joachim Woelfle. 2017. "Impact of Early Nutrition on Body Composition in Children Aged 9.5 Years Born with Extremely Low Birth Weight" Nutrients 9, no. 2: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9020124
APA StyleStutte, S., Gohlke, B., Peiler, A., Schreiner, F., Born, M., Bartmann, P., & Woelfle, J. (2017). Impact of Early Nutrition on Body Composition in Children Aged 9.5 Years Born with Extremely Low Birth Weight. Nutrients, 9(2), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9020124





