Baicalein Inhibits Stx1 and 2 of EHE: Effects of Baicalein on the Cytotoxicity, Production, and Secretion of Shiga Toxins of Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
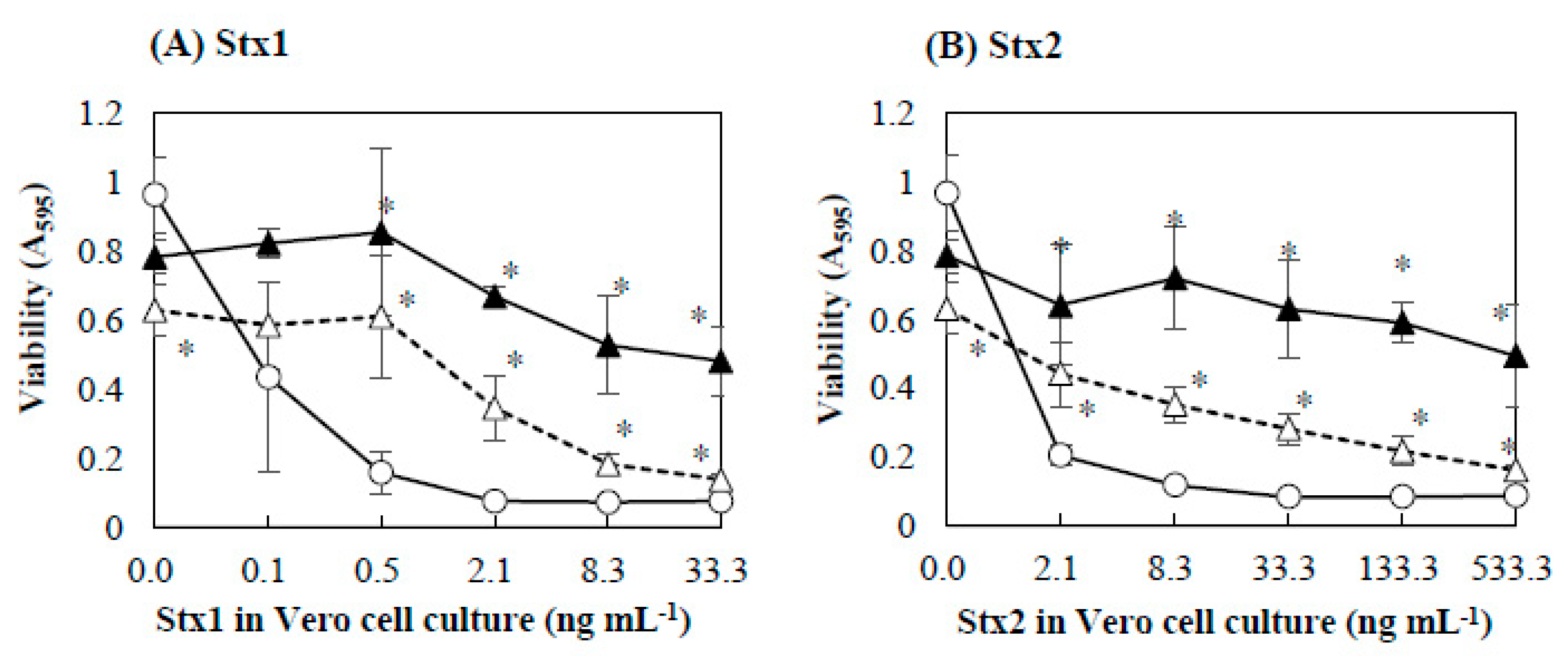
2.1. Effects of Baicalein on the Cytotoxicity of Stx
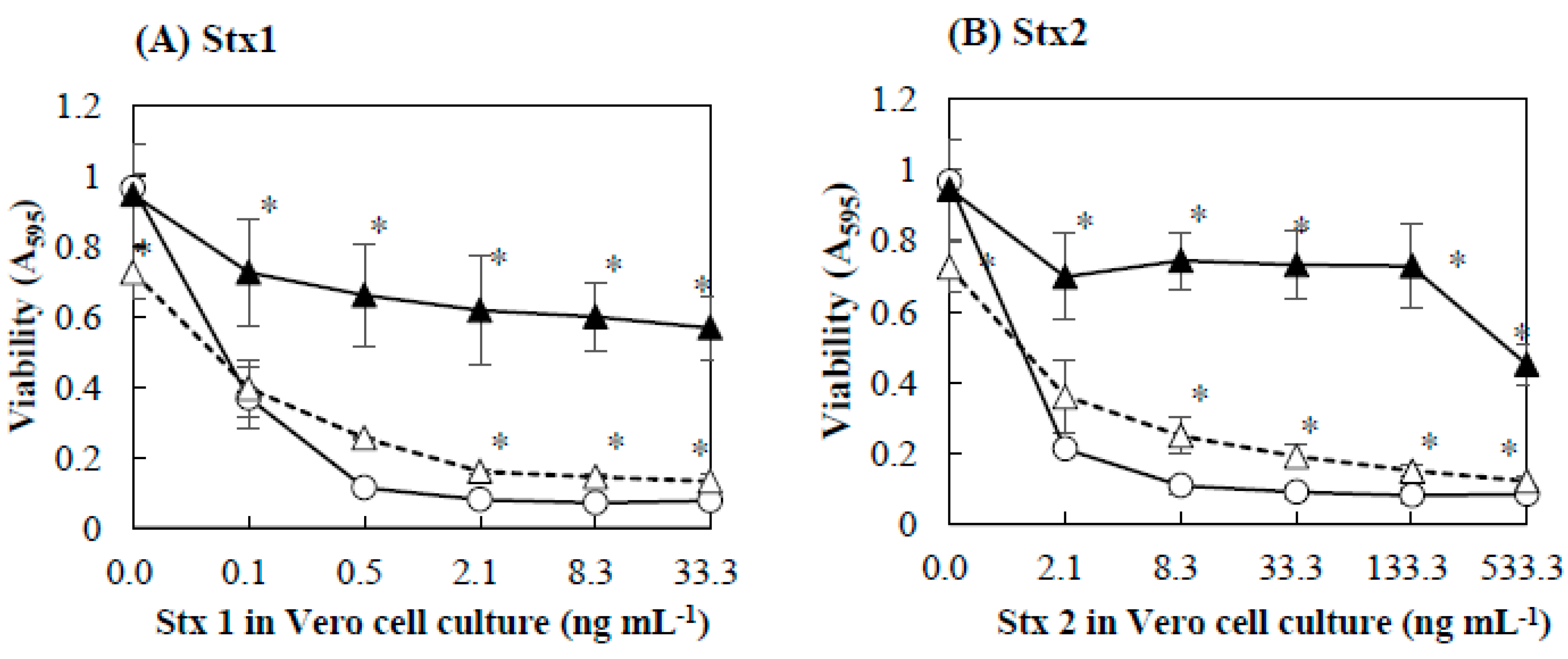
2.2. Protective Effect of Baicalein on Vero Cells against Stx
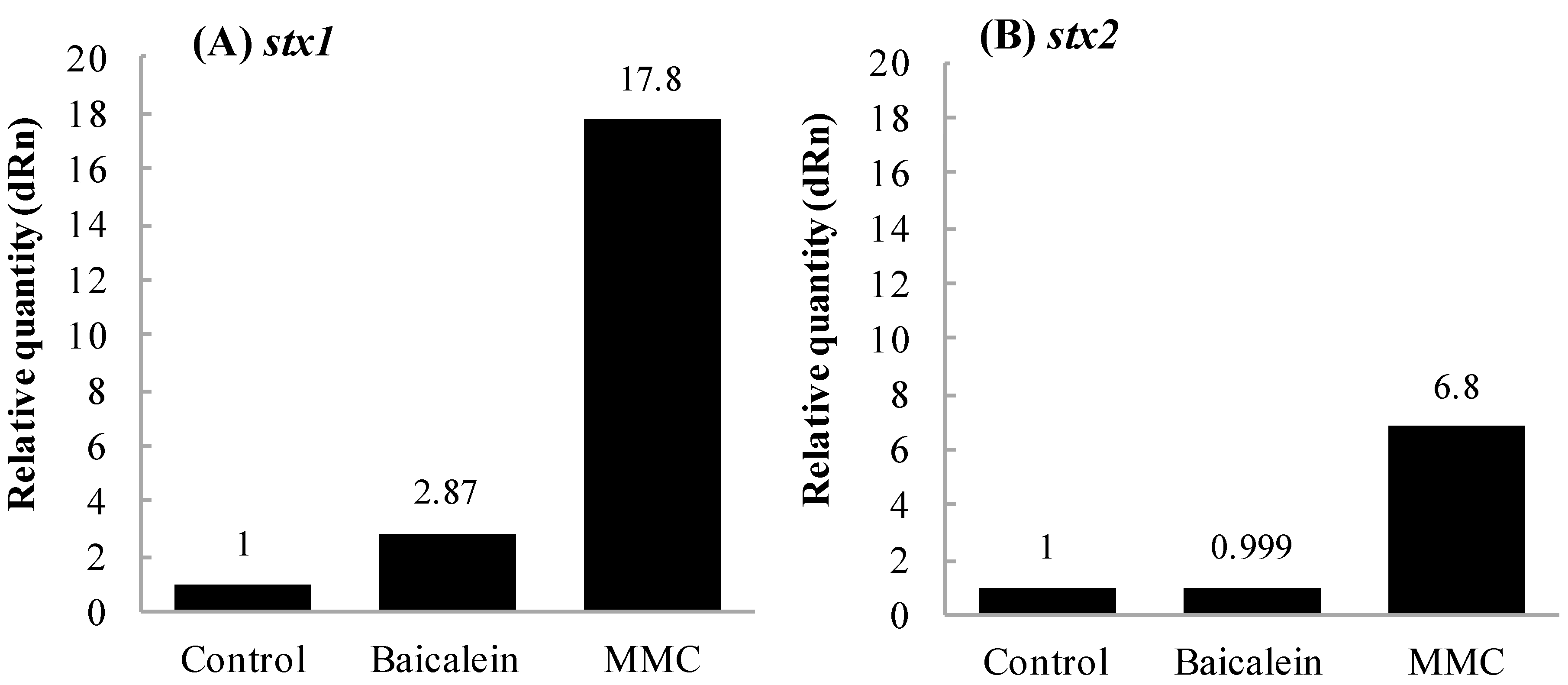
2.3. Effects of Baicalein on Production of Stx by EHEC
2.4. Interaction of Baicalein with Stx1B and Stx2B Pentamers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and methods
4.1. Analysis of Interaction between StxB Pentamers and Natural Products
4.2. Preparation of Stx1 and Stx2
4.3. Determination of Stx-inhibitory Activity of Baicalein
4.4. Determination of Protective Effect of Baicalein on Vero cells against Stx
4.5. Determination of Transcription of Stx, Production and Secretion of StxF
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croxen, M.A.; Finlay, B.B. Molecular mechanisms of Escherichia coli pathogenicity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 142–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steil, D.; Schepers, C.-L.; Pohlentz, G.; Legros, N.; Runde, J.; Humpf, H.-U.; Karch, H.; Müthing, J. Shiga toxin glycosphingolipid receptors of Vero-B4 kidney epithelial cells and their membrane microdomain lipid environment. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 2322–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müthing, J.; Meisen, I.; Zhang, W.; Bielaszewska, M.; Mormann, M.; Bauerfeind, R.; Schmidt, M.A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Karch, H. Promiscuous Shiga toxin 2e and its intimate relationship to Forssman. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Tesh, V.L. Roles of shiga toxins in immunopathology. Toxins 2019, 11, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtz, L.R.; Neill, M.A.; Tarr, P.I. Acute Bloody Diarrhea: A Medical emergency for patients of all ages. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.E.; Wilker, P.R.; Reiter, P.L.; Hedican, E.B.; Bender, J.B.; Hedberg, C.W. Antibiotic treatment of Escherichia coli O157 infection and the risk of hemolytic uremic syndrome, Minnesota. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 31, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agger, M.; Scheutz, F.; Villumsen, S.; Mølbak, K.; Petersen, A.M. Antibiotic treatment of verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli (VTEC) infection: A systematic review and a proposal. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 2440–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarr, P.I.; Gordon, C.A.; Chandler, W.L. Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli and haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet. Elsevier Ltd. 2005, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroi, M.; Takahashi, N.; Harada, T.; Kawamori, F.; Iida, N.; Kanda, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Ohashi, N.; Hara-Kudo, Y.; Masuda, T. Serotype, Shiga toxin (Stx) type, and antimicrobial resistance of Stx-producing Escherichia coli isolated from humans in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan (2003–2007). Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 65, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Morinaga, N.; Iwamarul, Y.; Yahiro, K.; Tagashira, M.; Moss, J.; Noda, M. Differential activities of plant polyphenols on the binding and internalization of cholera toxin in vero cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 23303–23309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiñones, B.; Massey, S.; Friedman, M.; Swimley, M.S.; Teter, K. Novel cell-based method to detect shiga toxin 2 from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and inhibitors of toxin activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Hong, Y.H.; Jang, S.I.; Lillehoj, E.P.; Ionescu, C.; Mazuranok, L.; Bravo, D. In vitro effects of plant and mushroom extracts on immunological function of chicken lymphocytes and macrophages. Br. Poult. Sci. 2010, 51, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doughari, J.H.; Human, I.S.; Bennade, S.; Ndakidemi, P.A. Phytochemicals as chemotherapeutic agents and antioxidants: Possible solution to the control of antibiotic resistant verocytotoxin producing bacteria. J. Med. Plants Res. 2009, 3, 839–848. [Google Scholar]
- Sanhueza, L.; Melo, R.; Montero, R.; Maisey, K.; Mendoza, L.; Wilkens, M. Synergistic interactions between phenolic compounds identified in grape pomace extract with antibiotics of different classes against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, T.; Toyofuku, S.; Tachiki, N.; Kimura, E.; Zhou, T.; Ozawa, T.; Nakayamab, M.; Shigemuneb, N.; Shimatanib, K.; Tokudab, H.; et al. Specific inhibition of cytotoxicity of Shiga-like toxin 1 of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli by gallocatechin gallate and epigallocatechin gallate. Food Control 2014, 42, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M.E.; Fujinaga, M.; Cherney, M.M.; Melton-Celsa, A.R.; Twiddy, E.M.; O’Brien, A.D.; James, M.N.G. Structure of Shiga toxin type 2 (Stx2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 27511–27517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, P.E.; Boodhoo, A.; Tyrrell, G.J.; Brunton, J.L.; Read, R.J. Crystal structure of the cell-binding B oligomer of verotoxin-1 from E. coli. Nature 1992, 355, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, K.; Nakane, H.; Fukushima, M.; Chermann, J.C.; Barré-Sinoussi, F. Differential inhibitory effects of various flavonoids on the activities of reverse transcriptase and cellular DNA and RNA polymerases. Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 190, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishige, K.; Schubert, D.S.Y. Flavonoids protect neuronal cells from oxidative stress by three distinct mechanisms. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.A.; Attele, A.S.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, C.S. Anti-HIV activity of medicinal herbs: Usage and potential development. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2001, 29, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.Y.; Dai, B.D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Xu, Y.G.; Cao, Y.B.; Gao, P.H.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Jiang, Y.Y. In vitro activity of baicalein against Candida albicans biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agent. 2008, 32, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntz, S.; Wenzel, U.; Daniel, H. Comparative analysis of the effects of flavonoids on proliferation, cytotoxicity, and apoptosis in human colon cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Nutr. 1999, 38, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pidgeon, G.P.; Kandouz, M.; Meram, A.; Honn, K.V. Mechanisms controlling cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis after 12-lipoxygenase inhibition in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2721–2727. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van, L.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.R.; Jin, G.; Arai, K.; Lo, E.H. Baicalein and 12/15-lipoxygenase in the ischemic brain. Stroke 2006, 37, 3014–3018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Otsuyama, K.I.; Liu, S.; Abroun, S.; Ishikawa, H.; Tsuyama, N.; Obata, M.; Li, F.-J.; Zheng, X.; Maki, Y. Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria radix from Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang (HLJDT), leads to suppression of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human myeloma cells. Blood 2005, 105, 3312–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.-I.; Su, W.-C.; Liu, H.-F. Baicalein induces cancer cell death and proliferation retardation by the inhibition of CDC2 kinase and survivin associated with opposite role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and AKT. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z.-S.; Fawcett, J.P. Mechanism of CYP2C9 inhibition by flavones and flavonols. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Niu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.M.; Deng, X.M. Baicalin inhibits the lethality of ricin in mice by inducing protein oligomerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 12899–12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, W.; Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Dong, J.; Deng, X.M. Baicalin protects mice from lethal infection by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chiu, Y.W.; Lin, T.H.; Huang, W.S.; Teng, C.Y.; Liou, Y.S.; Kuo, W.H. Baicalein inhibits the migration and invasive properties of human hepatoma cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 255, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.C.; Piao, M.J.; Fernando, P.M.D.J.; Han, X.; Hewage, S.R.K.M.; Park, J.E.; Ko, M.S.; Jung, U.; Kim, I.G.; Hyun, J.W. Baicalein protects human skin cells against ultraviolet B-induced oxidative stress. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cariddi, L.N.; Sabini, M.C.; Escobar, F.M.; Montironi, I.; Mañas, F.; Iglesias, D.; Comini, L.R.; Sabini, L.I.; Dalcero, A.M. Polyphenols as possible bioprotectors against cytotoxicity and DNA damage induced by ochratoxin A. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, G.L.; Lu, Y.; Hardes, K.; Strehlow, B.; Levesque, C.; Lindberg, I.; Sandvig, K.; Bakowsky, U.; Day, R.; Garten, W. Highly potent inhibitors of proprotein convertase furin as potential drugs for treatment of infectious diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21992–22003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavaliauskiene, S.; Dyvelingelem, A.B.; Skotland, T.; Sandvig, K. Protection against shiga toxins. Toxins 2017, 9, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertell, K. A review of toxicity and use and handling considerations for guanidine, guanidine hydrochloride, and urea. Pac. Northwest. Natl. Lab. 2006, 15747. [Google Scholar]
- Tangtavorn, N.; Yospaiboon, Y.; Ratanapakorn, T.; Sinawat, S.; Sanguansak, T.; Bhoomibunchoo, C.; Laovirojjanakul, W. Incidence of and risk factors for chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine retinopathy in Thai rheumatologic patients. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 10, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Song, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Sun, R. Synergistic effects of baicalein with cefotaxime against Klebsiella pneumoniae through inhibiting CTX-M-1 gene expression. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konowalchuk, J.; Dickie, N.; Stavric, S.; Speirs, J.I. Comparative studies of five heat-labile toxic products of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1978, 22, 644–6448. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, P.L.; Acheson, D.W.K.; Matthew, K.; Wagner, P.L.; Acheson, D.W.K. Human neutrophils and their products induce Shiga toxin production by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergholz, T.M.; Wick, L.M.; Qi, W.; Riordan, J.T.; Ouellette, L.M.; Whittam, T.S. Global transcriptional response of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to growth transitions in glucose minimal medium. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neely, M.N.; Friedman, D.I. Functional and genetic analysis of regulatory regions of coliphage H- 19B: Location of shiga-like toxin and lysis genes suggest a role for phage functions in toxin release. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, P.L.; Livny, J.; Neely, M.N.; Acheson, D.W.K.; Friedman, D.I.; Waldor, M.K. Bacteriophage control of Shiga toxin 1 production and release by Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 44, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, B.-Y.; Zhou, L.; Xie, K.-P.; Wang, Y.-J.; Xie, M.-J. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of baicalein. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2012, 47, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Yuk, H.G.; Marshall, D.L. Adaptation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to pH alters membrane lipid composition, verotoxin secretion, and resistance to simulated gastric fluid acid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3500–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; He, M.; Zang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, T.; Pan, S.; Xu, X.Y. A structure-activity relationship study of flavonoids as inhibitors of Escherichia coli by membrane interaction effect. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 2751–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinda, B.; Dinda, S.; DasSharma, S.; Banik, R.; Chakraborty, A.; Dinda, M. Therapeutic potentials of baicalin and its aglycone, baicalein against inflammatory disorders. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 131, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Hölscher, C. Therapeutic potential of baicalein in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Ojha, S. Therapeutic potential of baicalein in Parkinson’s disease: Focus on inhibition of α-synuclein oligomerization and aggregation. Synucleins Biochem. Role Dis. 2019, 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, B.P.; Silva, S.; Mesches, M.H.; Wilson, S.; Jia, Q. Safety evaluation of a combination, defined extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and Acacia catechu. J. Food Biochem. 2007, 31, 797–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Bruccoleri, R.E.; Olafson, B.D.; States, D.J.; Swaminathan, S.; Karplus, M. CHARMM: A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 1983, 4, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ID | Name | MW | Interaction with Stx2B Pentamers Obtained by the Docking Model | Structure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Hydrogen Bond | Intramolecular Energy (cal/mol) | ||||
| NP-000438 | Rhododendrol | 166.22 | 3 | <2 |  |
| NP-000814 | Acerogenin G | 298.38 | 3 | <1 | 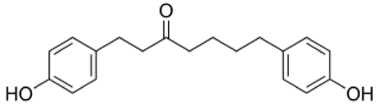 |
| NP-001362 | Esculetin | 178.14 | 4 | <2 | 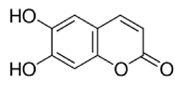 |
| NP-003423 | N-caffeoyltyramine | 299.32 | 4 | <2 | 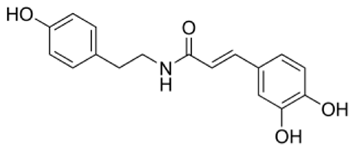 |
| NP-003587 | Thymol | 150.22 | 0 | <2 |  |
| NP-003729 | Baicalein | 270.24 | 2 | <1 | 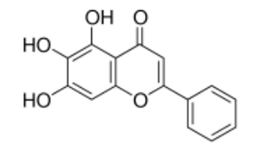 |
| NP-003855 | [6]-Gingerol | 294.39 | 2 | <1 | 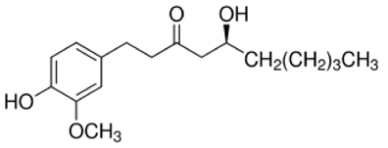 |
| Samples | Stx Concentration (ng/mL) ** | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Baicalein | Mitomycin C | ||
| Stx1 | Extracellular | 400 | 400 | 1600 |
| Intracellular | 50 | 50 | ND | |
| Stx2 | Extracellular | 200 | 200 | 204800 |
| Intracellular | 3 | 3 | ND | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinh, P.T.; Shinohara, Y.; Yamada, A.; Duc, H.M.; Nakayama, M.; Ozawa, T.; Sato, J.; Masuda, Y.; Honjoh, K.-I.; Miyamoto, T. Baicalein Inhibits Stx1 and 2 of EHE: Effects of Baicalein on the Cytotoxicity, Production, and Secretion of Shiga Toxins of Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Toxins 2019, 11, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090505
Vinh PT, Shinohara Y, Yamada A, Duc HM, Nakayama M, Ozawa T, Sato J, Masuda Y, Honjoh K-I, Miyamoto T. Baicalein Inhibits Stx1 and 2 of EHE: Effects of Baicalein on the Cytotoxicity, Production, and Secretion of Shiga Toxins of Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Toxins. 2019; 11(9):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090505
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinh, Pham Thi, Yui Shinohara, Akifumi Yamada, Hoang Minh Duc, Motokazu Nakayama, Tadahiro Ozawa, Jun Sato, Yoshimitsu Masuda, Ken-Ichi Honjoh, and Takahisa Miyamoto. 2019. "Baicalein Inhibits Stx1 and 2 of EHE: Effects of Baicalein on the Cytotoxicity, Production, and Secretion of Shiga Toxins of Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli" Toxins 11, no. 9: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090505
APA StyleVinh, P. T., Shinohara, Y., Yamada, A., Duc, H. M., Nakayama, M., Ozawa, T., Sato, J., Masuda, Y., Honjoh, K.-I., & Miyamoto, T. (2019). Baicalein Inhibits Stx1 and 2 of EHE: Effects of Baicalein on the Cytotoxicity, Production, and Secretion of Shiga Toxins of Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Toxins, 11(9), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090505




