Microcystin Contamination in Irrigation Water and Health Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Microcystins
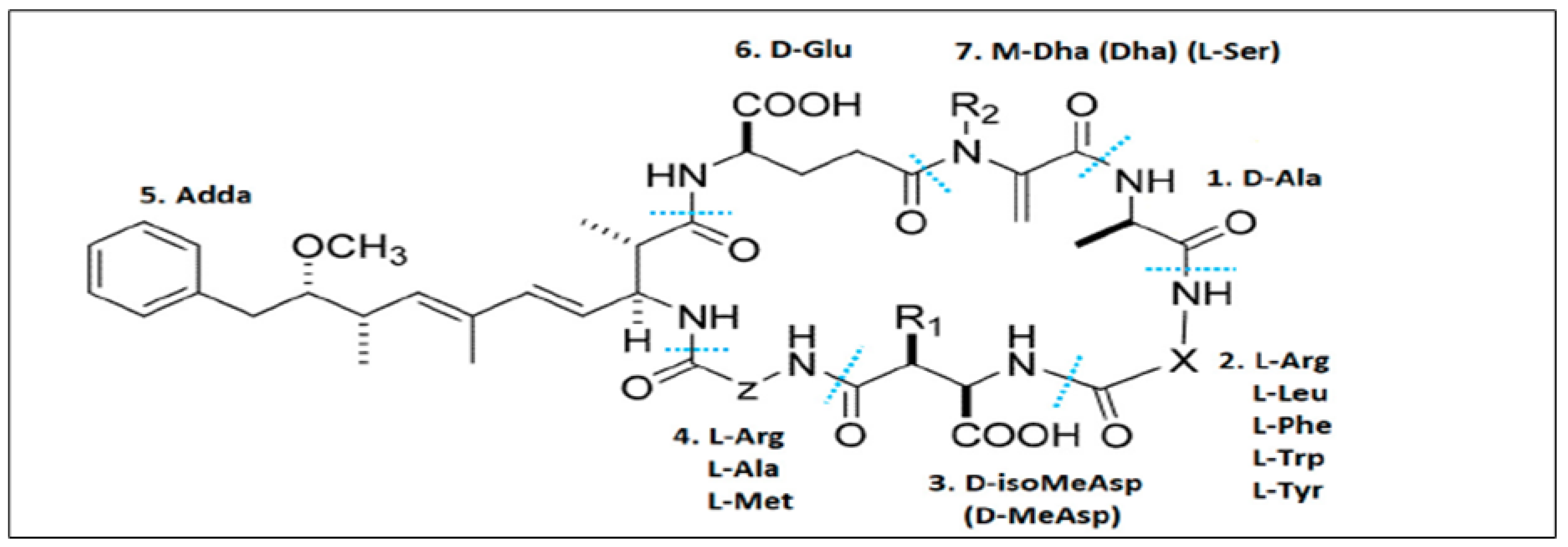
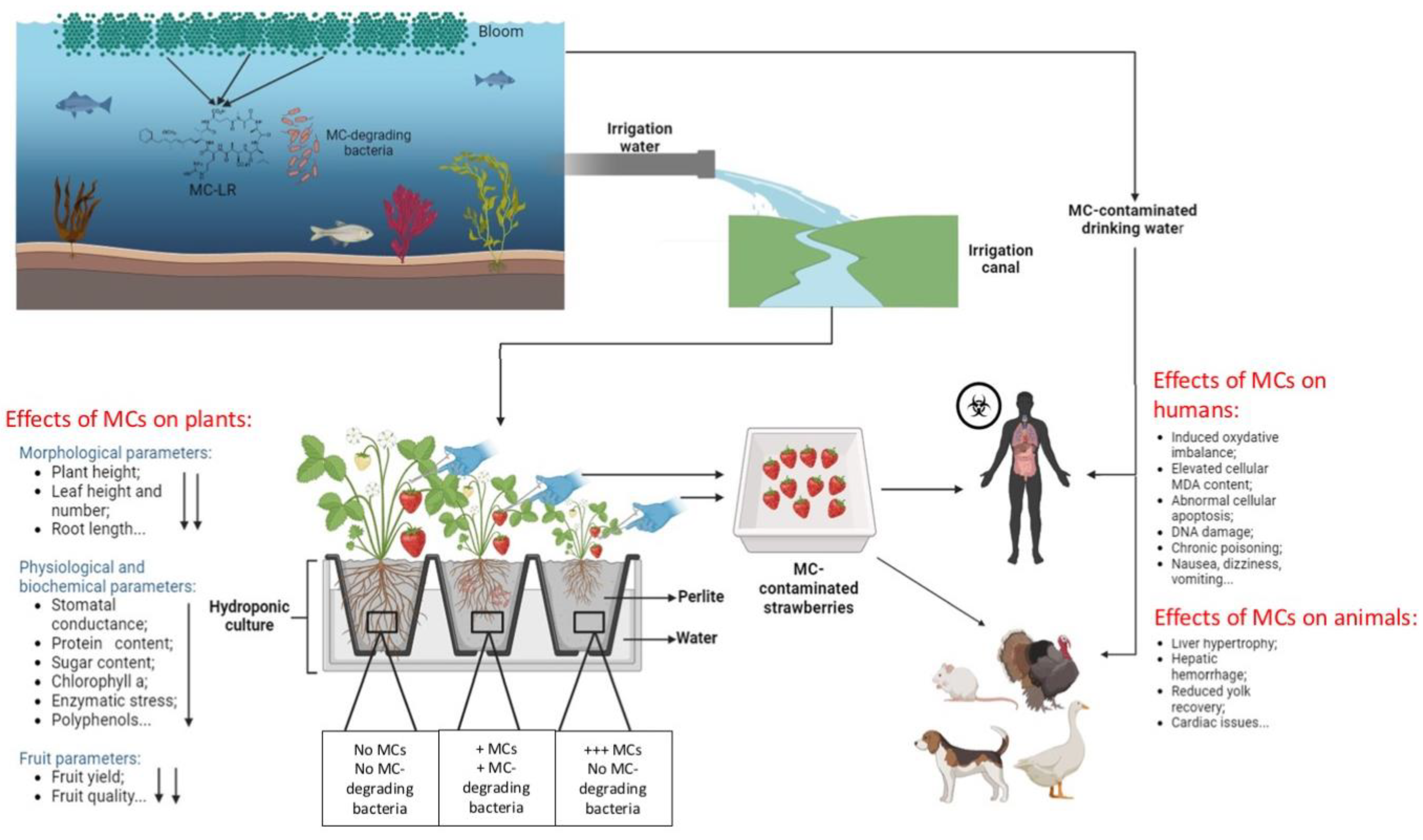
3. Emergence and Persistence of MCs in Irrigation Water
4. Phytotoxicity of MC on Crops in Hydroponic Systems
| Plant Species | Toxin | Growth Stage | Exposure Time (Days) | Applied Concentration (μg/L) | Phytotoxicity on Plant | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spinacia oleracea | MC-LR | Plants | 21 | 50 | (-) leaf FW | [66] |
| Cucumis sativus | MCt | Seedlings | 7 | 5 | (+) H2O2, O2-, MDA | [71] |
| Seedlings/flowering /fruiting | 7 | 1–1000 | (-) stem diameter, plant height, leaf area, root DW, leaf number, shoot DW, yield | [72] | ||
| Lactuca sativa | MC-LR (P) | Plants | 10 | 1–100 | (-) leaf biomass, root biomass | [73] |
| Seedlings | 14 | 5–1000 | (-) root length, total FW, shoot length | [74] | ||
| Vicia faba | MCt | Seedlings | 48 | 10–100 | (-) shoot DW, root DW, nodule number, and DW | [75] |
| Oryza sativa | MCt | Seedlings | 7 | 5–500 | (-) plant height, shoot DW, root length, root DW; (+) membrane permeability | [76] |
| Oryza sativa | MCt | Seedlings | 7 | 1-3000 | (+) root biomass, (-) stem biomass, leaf biomass, grains per panicle, grain weight per panicle, root biomass, setting percentage | [68] |
| Oryza sativa | MCt | Seedlings | 7 | 1–100 | (+) root surface area, shoot height; (-) shoot height, root surface area | [67] |
| Oryza sativa | MCt | Seedlings | 7 | 1–3000 | (-) stem dry weight, leaf DW, net photosynthetic rate, root DW | [77] |
| Oryza sativa | MCt | Seedlings | 7 | 5–10 | (+) H2O2, O2-, MDA; (-) RGR | [71] |
| Oryza sativa | MCt | Seedlings | 7 | 10–1000 | (-) root surface area, plant height, filled grains per panicle, panicle weight, seed setting rate, soluble protein, sugar, and starch in the grain | [78] |
| Oryza sativa | MCt | Booting | 7 | 10–1000 | ||
| Oryza sativa | MCt | Filling | 7 | 10–1000 | ||
| Oryza sativa | MCt | Seedlings | 21 | 10 | (+) Phosphorus content in shoots and roots, root and shoot DW; (-) root DW | [69] |
| Oryza sativa | MCt | Seedlings | 30 | 5–500 | (-) root length, root surface area, root dry weight, surface area and volume, root volume, lateral root number, crown root number | [71] |
5. Bioaccumulation of MCs in Tissues of Plants in Hydroponic Systems
6. Transfer and Fate of MCs in the Terrestrial Food Chain
7. Effects of MCs on Domestic/Wild/Aquatic Animals and Human Health Risks
8. Conceptual Diagram of MC Fate in a Terrestrial Food Chain
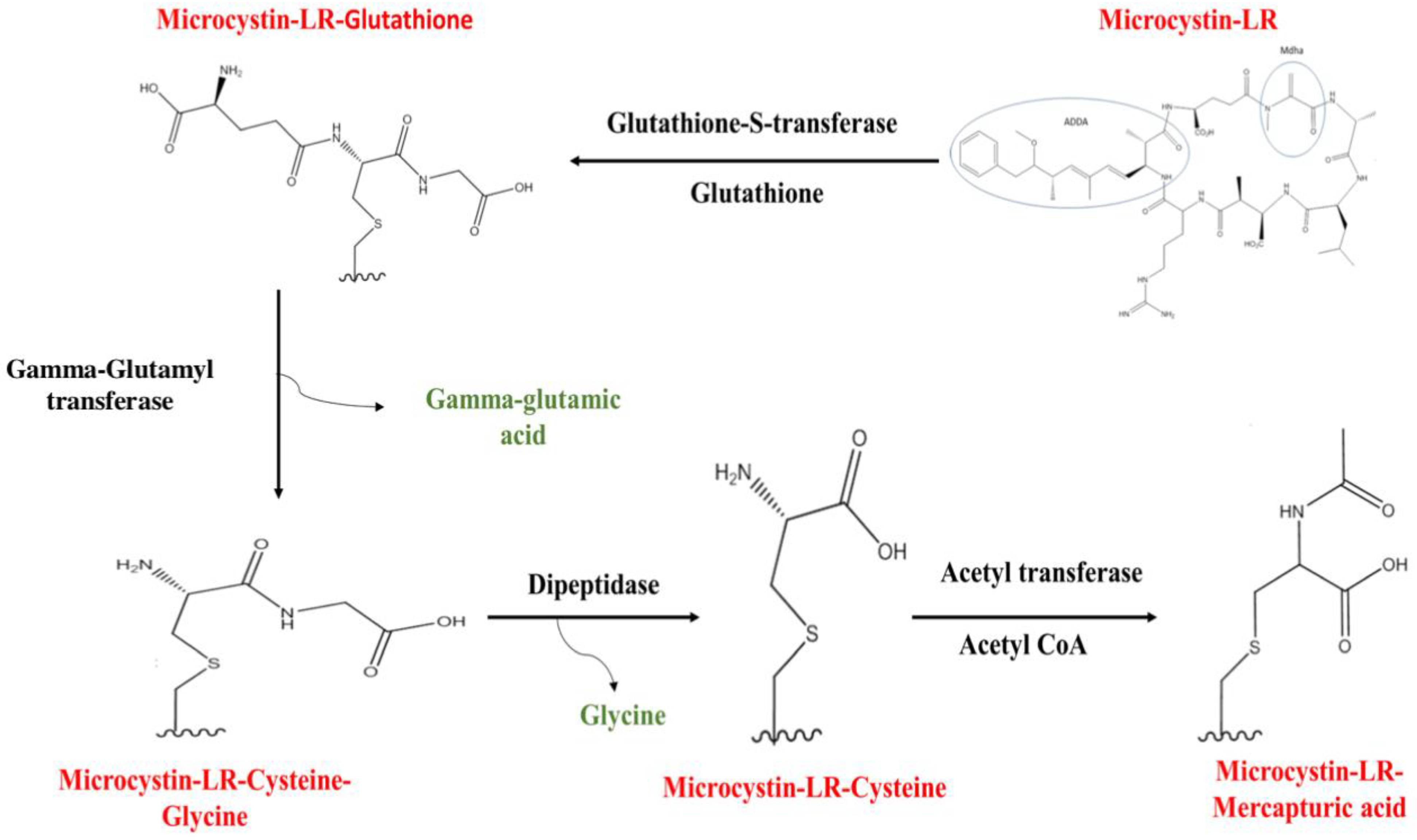
9. Depuration through the Conjugation of MCs
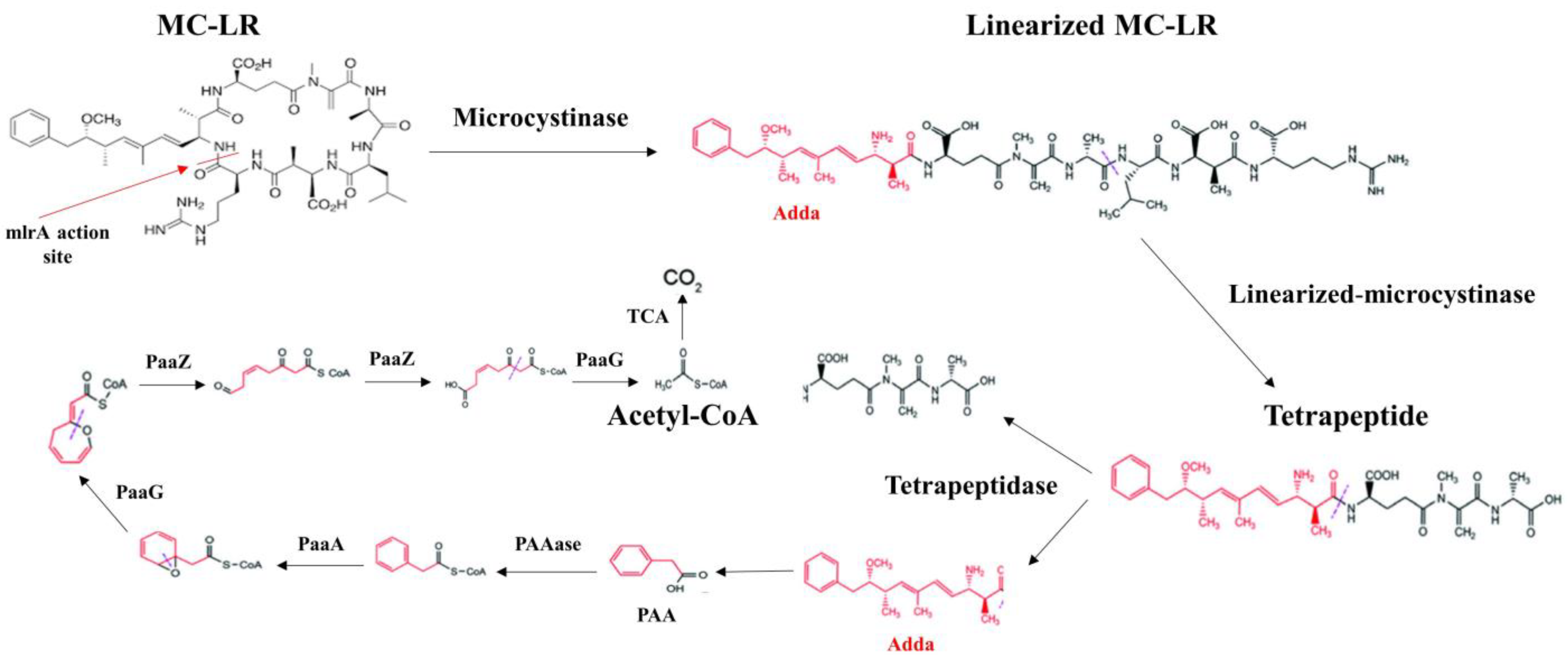
10. Approaching the Bacterial Enzymatic Biodegradation of MCs
11. Conclusions and Research Requirements
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Madamwar, D.; Incharoensakdi, A. Bloom dynamics of cyanobacteria and their toxins: Environmental health impacts and mitigation strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Duelling ‘CyanoHABs’: Unravelling the environmental drivers controlling dominance and succession among diazotrophic and non-N2-fixing harmful cyanobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamastra, L.; Balderacchi, M.; Trevisan, M. Inclusion of emerging organic contaminants in groundwater monitoring plans. MethodsX 2016, 3, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Steinman, A.D.; Wan, X.; Xie, L. Bioaccumulation of microcystin congeners in soil-plant system and human health risk assessment: A field study from Lake Taihu region of China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khalloufi, F.; Oufdou, K.; Lahrouni, M.; El Ghazali, I.; Saqrane, S.; Vasconcelos, V.; Oudra, B. Allelopatic effects of cyanobacteria extracts containing microcystins on Medicago sativa-Rhizobia symbiosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqrane, S.; Ghazali, I.E.; Oudra, B.; Bouarab, L.; Vasconcelos, V. Effects of cyanobacteria producing microcystins on seed germination and seedling growth of several agricultural plants. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2008, 43, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo Bittencourt-Oliveira, M.; Cordeiro-Araújo, M.K.; Chia, M.A.; de Toledo Arruda-Neto, J.D.; de Oliveira, Ê.T.; dos Santos, F. Lettuce irrigated with contaminated water: Photosynthetic effects, antioxidative response and bioaccumulation of microcystin congeners. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jiang, X.; Manubolu, M.; Riedl, K.; Ludsin, S.A.; Martin, J.F.; Lee, J. Fresh produce and their soils accumulate cyanotoxins from irrigation water: Implications for public health and food security. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, Q.; Ding, Q.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. A novel and native microcystin-degrading bacterium of Sphingopyxis sp. isolated from lake Taihu. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2011: Warning about the Dangers of Tobacco; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; ISBN 9244564262. [Google Scholar]
- Poste, A.E.; Ozersky, T. Invasive dreissenid mussels and round gobies: A benthic pathway for the trophic transfer of microcystin. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2159–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, N.J.; Dodson, J.; Tassone, S.J.; Bukaveckas, P.A.; Bulluck, L.P. Biotransport of algal toxins to riparian food webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10007–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woller-Skar, M.M.; Jones, D.N.; Luttenton, M.R.; Russell, A.L. Microcystin detected in little brown bats (Myotis lucifugus). Am. Midl. Nat. 2015, 174, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoti, M.I.; Edokpayi, J.; Mutileni, N.; Durowoju, O.; Munyai, F.L. Cyanotoxins in groundwater; occurrence, potential sources, health impacts and knowledge gap for public health. Toxicon 2023, 226, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, C.; Churro, C.; Dias, E. Risk levels of toxic cyanobacteria in Portuguese recreational freshwaters. Toxins 2017, 9, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welten, R.D.; Meneely, J.P.; Chevallier, O.P.; Kosek, V.; Greer, B.; Hajšlová, J.; Elliott, C.T. Oral microcystin-LR does not cause hepatotoxicity in pigs: Is the risk of microcystin-LR overestimated? Expo. Health 2020, 12, 775–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, C.-L.; Li, D.-W.; Li, H.-Y.; Li, R.-M.; Yang, W.-D. Microcystin-LR exposure interfered maintenance of colonic microenvironmental homeostasis in rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 173, 113611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odriozola, E.; Ballabene, N.; Salamanco, A. Poisoning in cattle caused by blue-green algae. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 1984, 16, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Puschner, B.; Galey, F.D.; Johnson, B.; Dickie, C.W.; Vondy, M.; Francis, T.; Holstege, D.M. Blue-green algae toxicosis in cattle. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1998, 213, 1605–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Merwe, D.; Sebbag, L.; Nietfeld, J.C.; Aubel, M.T.; Foss, A.; Carney, E. Investigation of a Microcystis aeruginosa cyanobacterial freshwater harmful algal bloom associated with acute microcystin toxicosis in a dog. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Merwe, K.; Van Dijk, H.; Zon, R. Eye movements as an indicator of situation awareness in a flight simulator experiment. Int. J. Aviat. Psychol. 2012, 22, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masango, C.A. Indigenous traditional knowledge protection: Prospects in South Africa’s intellectual property framework? South Afr. J. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 76, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Andicoberry, C.; García-Viliada, L.; Lopez-Rodas, V.; Costas, E. Catastrophic mortality of flamingos in a Spanish national park caused by cyanobacteria. Vet. Rec. 2002, 151, 706. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, C. Ozonation of microcystins: Kinetics and toxicity decrease. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6427–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandermann Jr, H. Plant metabolism of xenobiotics. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1992, 17, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.S.; Singh, M.; Aggrawal, P.; Laxmi, A. Glucose and auxin signaling interaction in controlling Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings root growth and development. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hoffmann, V. Goûter le Monde. Une Histoire Culturelle du Goût à L’époque Moderne; Peter Lang: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2013; ISBN 2875741160. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, N. Uptake, Metabolism, and Detoxification of Sulfur. In Air Pollution and Plant Biotechnology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; p. 179. [Google Scholar]
- Manage, P.M.; Edwards, C.; Singh, B.K.; Lawton, L.A. Isolation and identification of novel microcystin-degrading bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6924–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.J.; Orr, P.T. Release and degradation of microcystin following algicide treatment of a Microcystis aeruginosa bloom in a recreational lake, as determined by HPLC and protein phosphatase inhibition assay. Water Res. 1994, 28, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kultschar, B.; Llewellyn, C. Secondary Metabolites in Cyanobacteria. In Secondary Metabolites—Sources and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Puddick, J.; Prinsep, M.R.; Wood, S.A.; Kaufononga, S.A.F.; Cary, S.C.; Hamilton, D.P. High levels of structural diversity observed in microcystins from Microcystis CAWBG11 and characterization of six new microcystin congeners. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5372–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeg, J.-P. Microcystines: Intoxication des animaux domestiques et sécurité des aliments d’origine animale. Rev. Med. Vet. 2007, 1, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Botes, D.P.; Kruger, H.; Viljoen, C.C. Isolation and characterization of four toxins from the blue-green alga, Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxicon 1982, 20, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivonen, K. Effects of light, temperature, nitrate, orthophosphate, and bacteria on growth of and hepatotoxin production by Oscillatoria agardhii strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 2658–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivonen, K.; Namikoshi, M.; Evans, W.R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Sun, F.; Rouhiainen, L.; Luukkainen, R.; Rinehart, K.L. Isolation and characterization of a variety of microcystins from seven strains of the cyanobacterial genus Anabaena. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkainen, R.; Sivonen, K.; Namikoshi, M.; Färdig, M.; Rinehart, K.L.; Niemelä, S.I. Isolation and identification of eight microcystins from thirteen Oscillatoria agardhii strains and structure of a new microcystin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 2204–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Boyer, G.L. Health impacts from cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Implications for the North American Great Lakes. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Massey, I.Y.; Feng, H.; Yang, F. A Review of Cardiovascular To xicity of Microcystins. Toxins 2019, 11, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Wang, P.; Jia, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, X.; Wang, Y. A review on factors affecting microcystins production by algae in aquatic environments. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X. Current research scenario for biological effect of exogenous factors on microcystin synthesis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 26190–26201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoof, L.; Jaakkola, S.; Važić, T.; Häggqvist, K.; Kirkkala, T.; Ventelä, A.-M.; Kirkkala, T.; Svirčev, Z.; Meriluoto, J. Elimination of cyanobacteria and microcystins in irrigation water—Effects of hydrogen peroxide treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8638–8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghazali, I.; Saqrane, S.; Saker, M.; Youness, O.; Oudra, B.; Vasconcelos, V.; Del Campo, F.F. Caractérisation biochimique et moléculaire d’efflorescences à cyanobactéries toxiques dans le réservoir Lalla Takerkoust (Maroc). Rev. Sci. L’eau 2011, 24, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rushford, C.A.; North, R.L.; Miller, G.L. Detection of cyanotoxins in irrigation water and potential impact on putting green health. Int. Turfgrass Soc. Res. J. 2022, 14, 994–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; El-Sharouny, H.M.; Ali, W.S.M. Microcystin production in benthic mats of cyanobacteria in the Nile River and irrigation canals, Egypt. Toxicon 2006, 47, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Cyanobacterial Toxins: Microcystins; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.; Kawan, A.; Zhang, X. Sex-dependent effects of microcystin-LR on hypothalamic-pituitary-gonad axis and gametogenesis of adult zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crush, J.R.; Briggs, L.R.; Sprosen, J.M.; Nichols, S.N. Effect of irrigation with lake water containing microcystins on microcystin content and growth of ryegrass, clover, rape, and lettuce. Environ. Toxicol. Int. J. 2008, 23, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Al Shehri, A.M. Microcystin-producing blooms of Anabaenopsis arnoldi in a potable mountain lake in Saudi Arabia. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levizou, E.; Papadimitriou, T.; Papavasileiou, E.; Papadimitriou, N.; Kormas, K.A. Root vegetables bioaccumulate microcystins-LR in a developmental stage-dependent manner under realistic exposure scenario: The case of carrot and radish. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 240, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Li, Y.-W.; Liu, B.-L.; Zhao, H.-M.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Mo, C.-H.; Wong, M.-H.; Li, Q.X. High ecological and human health risks from microcystins in vegetable fields in southern China. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoumalakou, E.; Papadimitriou, T.; Berillis, P.; Kormas, K.A.; Levizou, E. Spray irrigation with microcystins-rich water affects plant performance from the microscopic to the functional level and food safety of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Han, L. Hourly remote sensing monitoring of harmful algal blooms (HABs) in Taihu Lake based on GOCI images. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 35958–35970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifirò, G.; Barbaro, E.; Gambaro, A.; Vita, V.; Clausi, M.T.; Franchino, C.; Palumbo, M.P.; Floridi, F.; De Pace, R. Quantitative determination by screening ELISA and HPLC-MS/MS of microcystins LR, LY, LA, YR, RR, LF, LW, and nodularin in the water of Occhito lake and crops. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7699–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, M.; Karas, P.A.; Vasileiadis, S.; Zafiriadis, I.; Papadimitriou, T.; Levizou, E.; Kormas, K.; Karpouzas, D.G. Irrigation of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) with microcystin-enriched water holds low risk for plants and their associated rhizopheric and epiphytic microbiome. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, A.; Alzain, M.N.; Alzamel, N.M.; Loutfy, N. Accumulation of microcystin from Oscillatoria limnetica Lemmermann and Microcystis aeruginosa (Kützing) in two leafy green vegetable crop plants Lactuca sativa L. and Eruca sativa. Plants 2022, 11, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewickrama, M.M.; Manage, P.M. Accumulation of Microcystin-LR in grains of two rice varieties (Oryza sativa L.) and a leafy vegetable, Ipomoea aquatica. Toxins 2019, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douma, M.; Loudiki, M.; Oudra, B.; Mouhri, K.; Ouahid, Y.; del Campo, F.F. Taxonomic diversity and toxicological assessment of Cyanobacteria in Moroccan inland waters. Rev. Sci. L’eau 2009, 22, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudra, B.; Loudiki, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Sabour, B.; Sbiyyaa, B.; Oufdou, K.; Mezrioui, N. Detection and quantification of microcystins from cyanobacteria strains isolated from reservoirs and ponds in Morocco. Environ. Toxicol. Int. J. 2002, 17, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboal, M.; Puig, M. Intracellular and dissolved microcystin in reservoirs of the river Segura basin, Murcia, SE Spain. Toxicon 2005, 45, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haida, M.; El Khalloufi, F.; Mugani, R.; Redouane, E.M.; Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Oudra, B. Effects of Irrigation with Microcystin-Containing Water on Growth, Physiology, and Antioxidant Defense in Strawberry Fragaria vulgaris under Hydroponic Culture. Toxins 2022, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Gu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Johnson, D.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Tian, H.; Huang, Y. Self-assembled BiVO4 mesocrystals for efficient photocatalytic decontamination of microcystin-LR. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Rediske, R.R.; Yao, L.; Xie, L. Effect of microcystins on root growth, oxidative response, and exudation of rice (Oryza sativa). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 149, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llana-Ruiz-Cabello, M.; Jos, A.; Cameán, A.; Oliveira, F.; Barreiro, A.; Machado, J.; Azevedo, J.; Pinto, E.; Almeida, A.; Campos, A. Analysis of the Use of Cylindrospermopsin and/or Microcystin-Contaminated Water in the Growth, Mineral Content, and Contamination of Spinacia oleracea and Lactuca sativa. Toxins 2019, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Liu, H. Response of hormone in rice seedlings to irrigation contaminated with cyanobacterial extract containing microcystins. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Jin, S.; Min, Y.; Yang, J. Combined effects of microcystin and nitrite on the growth, lipid peroxidation, and antioxidant responses of the freshwater rotifer Brachionus calycif lorus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 192, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Gu, J.-D.; Tie, B.; Yao, B.; Shao, J. Interactive effects of cadmium and Microcystis aeruginosa (cyanobacterium) on the growth, antioxidative responses and accumulation of cadmium and microcystins in rice seedlings. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1588–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lu, X.; Min, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J. Interactive effects of microcystin and ammonia on the reproductive performance and phenotypic traits of the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Liang, C. Responses of antioxidative enzymes and gene expression in Oryza sativa L and Cucumis sativus L seedlings to microcystins stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ren, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, C. Effect of irrigation with microcystins-contaminated water on growth and fruit quality of Cucumis sativus L. and the health risk. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 204, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; Campos, A.; Azevedo, J.; Barreiro, A.; Planchon, S.; Renaut, J.; Vasconcelos, V. Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) leaf-proteome profiles after exposure to cylindrospermopsin and a microcystin-LR/cylindrospermopsin mixture: A concentration-dependent response. Phytochemistry 2015, 110, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Steinman, A.D.; Wan, X.; Xie, L. Combined toxicity of microcystin-LR and copper on lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Chemosphere 2018, 206, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahrouni, M.; Oufdou, K.; Khalloufi, F.E.; Pajuelo, E.; Oudra, B. Impact of cyanobacterial toxins (microcystins) on growth and root development of in vitro Vicia faba cultures. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2015, 12, 2028–9324. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Steinman, A.D.; Yao, L.; Xie, L. Increment of root membrane permeability caused by microcystins result in more elements uptake in rice (Oryza sativa). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Wang, W. Response and recovery of rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings to irrigation with microcystin-contaminated water. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4573–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Ma, X.; Liu, H. Effect of microcystins at different rice growth stages on its yield, quality, and safety. Environ. Sci. Pollut.Res. 2020, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrovic, S.M.; Allis, O.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. Bioaccumulation and harmful effects of microcystin-LR in the aquatic plants Lemna minor and Wolffia arrhiza and the filamentous alga Chladophora fracta. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbel, S.; Bouaïcha, N.; Mougin, C. Dynamics of the toxic cyanobacterial microcystin-leucine-arginine peptide in agricultural soil. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO Chron. 2011, 38, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C.; Beattie, K.A.; Krause, E.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Codd, G.A. Uptake, effects, and metabolism of cyanobacterial toxins in the emergent reed plant Phragmites australis (cav.) trin. ex steud. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2001, 20, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Praena, D.; Campos, A.; Azevedo, J.; Neves, J.; Freitas, M.; Guzmán-Guillén, R.; Cameán, A.M.; Renaut, J.; Vasconcelos, V. Exposure of Lycopersicon esculentum to microcystin-LR: Effects in the leaf proteome and toxin translocation from water to leaves and fruits. Toxins 2014, 6, 1837–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Tsuji, K.; Watanabe, M.F.; Kondo, F. Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria—III. Effect of pH and temperature. Phycologia 1996, 35, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-X.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Wang, T.; Qin, W.; Xu, L.; Cheng, S.; Yang, L. Stimulation effect of microcystin-LR on matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 expression in mouse liver. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 199, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, K.; Watanuki, T.; Kondo, F.; Watanabe, M.F.; Suzuki, S.; Nakazawa, H.; Suzuki, M.; Uchida, H.; Harada, K.-I. Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria—II. Effect of UV light on decomposition and isomerization. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eynard, F.; Mez, K.; Walther, J.-L. Risk of cyanobacterial toxins in Riga waters (Latvia). Water Res. 2000, 34, 2979–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbel, S.; Mougin, C.; Bouaïcha, N. Cyanobacterial toxins: Modes of actions, fate in aquatic and soil ecosystems, phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation in agricultural crops. Chemosphere 2014, 96, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Zhang, D.; Ke, Z.; Yang, H. In situ studies on the bioaccumulation of microcystins in the phytoplanktivorous silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) stocked in Lake Taihu with dense toxic Microcystis blooms. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 1026–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haida, M.; Tamegart, L.; Mugani, R.; Essadki, Y.; Azevedo, J.; Araújo, M.J.; Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Gamrani, H.; Oudra, B. Tracing the fate of microcystins from irrigation water to food chains: Studies with Fragaria vulgaris and Meriones shawi. Toxicon 2023, 236, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, L.M.D.; Karlsson, K.M.; Meriluoto, J.A.O.; Kardinaal, E.; Visser, P.M.; Siewertsen, K.; Van Donk, E.; Ibelings, B.W. Assimilation and depuration of microcystin–LR by the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 69, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Park, H.-D. Determination of microcystins in fish tissues using HPLC with a rapid and efficient solid phase extraction. Aquaculture 2007, 271, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.d.S.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B. Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and effects on aquatic animals. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2729–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Deng, X.; Xie, P.; Chen, J.; Guo, L. Risk assessment of microcystins in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) from eight eutrophic lakes in China. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, E.; Petit, A.; Sanchez, W.; Paty, C.; Gerard, C.; Bormans, M. Evidence of trophic transfer of microcystins from the gastropod Lymnaea stagnalis to the fish Gasterosteus aculeatus. Harmful Algae 2014, 31, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toporowska, M.; Pawlik-Skowronska, B.; Kalinowska, R. Accumulation and effects of cyanobacterial microcystins and anatoxin-a on benthic larvae of Chironomus spp. (Diptera: Chironomidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2014, 111, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, P.T.; Jones, G.J.; Hunter, R.A.; Berger, K. Exposure of beef cattle to sub-clinical doses of Microcystis aeruginosa: Toxin bioaccumulation, physiological effects and human health risk assessment. Toxicon 2003, 41, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Xie, P.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Z. Simultaneous determination of microcystin contaminations in various vertebrates (fish, turtle, duck and water bird) from a large eutrophic Chinese lake, Lake Taihu, with toxic Microcystis blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woller-Skar, M.M.; Russell, A.L.; Gaskill, J.A.; Luttenton, M.R. Microcystin in multiple life stages of Hexagenia limbata, with implications for toxin transfer. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbrouck, C.; Kestemont, P. Effects of microcystins on fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2006, 25, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasri, H.; El Herry, S.; Bouaïcha, N. First reported case of turtle deaths during a toxic Microcystis spp. bloom in Lake Oubeira, Algeria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, K.; Gomes, A.; Calado, L.; Yasui, G.; Assis, D.; Henry, T.; Fonseca, A.; Pinto, E. Toxicity of cyanopeptides from two microcystis strains on larval development of Astyanax altiparanae. Toxins 2019, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Paerl, H.W.; Zhu, G.; Wu, T.; Li, W.; Shi, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Caruso, A.M. The role of tropical cyclones in stimulating cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms in hypertrophic Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaïcha, N.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; Labidi, Z.; Djabri, A.; Benayache, N.Y.; Nguyen-Quang, T. Structural diversity, characterization and toxicology of microcystins. Toxins 2019, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ying, F.; Chen, Y.; Han, X. Microcystin (-LR) affects hormones level of male mice by damaging hypothalamic-pituitary system. Toxicon 2012, 59, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiwaki-Matsushima, R.; Ohta, T.; Nishiwaki, S.; Suganuma, M.; Kohyama, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Carmichael, W.W.; Fujiki, H. Liver tumor promotion by the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin-LR. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1992, 118, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, N.; Shen, J.; Ye, M. Degradation and detoxification of microcystin-LR in drinking water by sequential use of UV and ozone. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1897–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Z.; Zhang, F.-Q.; Li, C.-F.; Yi, D.; Fu, X.-L.; Cui, L.-X. A cyanobacterial toxin, microcystin-LR, induces apoptosis of sertoli cells by changing the expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2011, 224, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Xie, P.; Zhang, X.; Tang, R.; Gao, Y.; Li, D.; Li, L. In vivo studies on the immunotoxic effects of microcystins on rabbit. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 27, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briand, J.-F.; Jacquet, S.; Bernard, C.; Humbert, J.-F. Health hazards for terrestrial vertebrates from toxic cyanobacteria in surface water ecosystems. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, I.; Seawright, A.A.; Shaw, G.R. Cyanobacterial poisoning in livestock, wild mammals and birds—An overview. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 613–637. [Google Scholar]
- Mez, K.; Beattie, K.A.; Codd, G.A.; Hanselmann, K.; Hauser, B.; Naegeli, H.; Preisig, H.R. Identification of a microcystin in benthic cyanobacteria linked to cattle deaths on alpine pastures in Switzerland. Eur. J. Phycol. 1997, 32, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbis, C.R.; Waldron, D.L.; Mitchell, G.F.; Anderson, J.W.; McCauley, I. Recovery of hepatic function and latent mortalities in sheep exposed to the blue-green alga Microcystis aeruginosa. Vet. Rec. 1995, 137, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Rueckert, A.; Hamilton, D.P.; Cary, S.C.; Dietrich, D.R. Switching toxin production on and off: Intermittent microcystin synthesis in a Microcystis bloom. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2011, 3, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soll, M.P.; Williams, M.C. Mortality of white rhinoceros (Ceratotherium simum) suspected to be associated with the blue-green alga Microcystis aeruginosa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1985, 56, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Huang, F.; Massey, I.Y.; Wen, C.; Zheng, S.; Xu, S.; Yang, F. Effects of microcystin-LR on the microstructure and inflammation-related factors of jejunum in mice. Toxins 2019, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yi, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.; Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F.; Tian, L. A review of nephrotoxicity of microcystins. Toxins 2020, 12, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, W.J.; Altheimer, S.; Cattori, V.; Meier, P.J.; Dietrich, D.R.; Hagenbuch, B. Organic anion transporting polypeptides expressed in liver and brain mediate uptake of microcystin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F.; Ding, Z.; Yang, S.; Guo, J.; Al-Osman, M.; Kamegni, R.B.; Zeng, W. Exposure routes and health effects of microcystins on animals and humans: A mini-review. Toxicon 2018, 151, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobac, D.; Tokodi, N.; Lujić, J.; Marinović, Z.; Subakov-Simić, G.; Dulić, T.; Važić, T.; Nybom, S.; Meriluoto, J.; Codd, G.A. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in fishponds and their effects on fish tissue. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badar, M.; Batool, F.; Khan, S.S.; Khokhar, I.; Qamar, M.K.; Yasir, C. Effects of microcystins toxins contaminated drinking water on hepatic problems in animals (cows and buffalos) and toxins removal chemical method. Buffalo Bull. 2017, 36, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Guo, J.; Huang, F.; Massey, I.Y.; Huang, R.; Li, Y.; Wen, C.; Ding, P.; Zeng, W.; Liang, G. Removal of microcystin-LR by a novel native effective bacterial community designated as YFMCD4 isolated from Lake Taihu. Toxins 2018, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piyathilaka, M.; Pathmalal, M.M.; Tennekoon, K.H.; De Silva, B.; Samarakoon, S.R.; Chanthirika, S. Microcystin-LR-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human embryonic kidney and human kidney adenocarcinoma cell lines. Microbiology 2015, 161, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubickova, B.; Babica, P.; Hilscherová, K.; Šindlerová, L. Effects of cyanobacterial toxins on the human gastrointestinal tract and the mucosal innate immune system. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xie, P.; Guo, L.; Li, L.; Miyabara, Y.; Park, H. Organ distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in freshwater fish at different trophic levels from the eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China. Environ. Toxicol. Int. J. 2005, 20, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giblin, S.M.; Larson, J.H.; King, J.D. Environmental drivers of cyanobacterial abundance and cyanotoxin production in backwaters of the Upper Mississippi River. River Res. Appl. 2022, 38, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Barrios, C.A.; Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S. Bioaccumulation of microcystins in seston, zooplankton and fish: A case study in Lake Zumpango, Mexico. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, M.; Xiao, B.; Gu, P. Transmission of microcystins in natural systems and resource processes: A review of potential risks to humans health. Toxins 2023, 15, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, N.P.E. Role of metabolism in chemecal toxicity. In Cytochromes P450 Metabolic and Toxicological Aspects; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Manahan, S.E. Toxicological Chemistry and Biochemistry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; ISBN 1420032127. [Google Scholar]
- Lilja, H.; Jeppsson, J.-O.; Kristensson, H. Evaluation of serum gamma-glutamyltransferase by electrofocusing, and variations in isoform patterns. Clin. Chem. 1983, 29, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.R.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Boyer, G.L. The fate of microcystins in the environment and challenges for monitoring. Toxins 2014, 6, 3354–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivonen, K.; Jones, G. Cyanobacterial toxins. Toxic Cyanobacteria. Water A Guide Their Health Conseq. Monit. Manag. 1999, 1, 43–112. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.C.; Lee, A.K.; Yates, R.S.; Liang, S.; Rochelle, P.A. Analysis of microcystins in drinking water by ELISA and LC/MS/MS. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2017, 109, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Okano, K.; Park, H.-D.; Itayama, T.; Inamori, Y.; Neilan, B.A.; Burns, B.P.; Sugiura, N. Detection and sequencing of the microcystin LR-degrading gene, mlrA, from new bacteria isolated from Japanese lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 229, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Jones, G.J.; Blakeley, R.L.; Jones, A.; Negri, A.P.; Riddles, P. Enzymatic pathway for the bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin LR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4086–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamri, S.A. Biodegradation of microcystin by a new Bacillus sp. isolated from a Saudi freshwater lake. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 6552–6559. [Google Scholar]
- Lawton, L.A.; Welgamage, A.; Manage, P.M.; Edwards, C. Novel bacterial strains for the removal of microcystins from drinking water. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemes, G.A.F.; Kist, L.W.; Bogo, M.R.; Yunes, J.S. Biodegradation of [D-Leu1] microcystin-LR by a bacterium isolated from sediment of Patos Lagoon estuary, Brazil. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idroos, F.S.; De Silva, B.; Manage, P.M. Biodegradation of microcystin analogues by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolated from Beira Lake Sri Lanka. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2017, 45, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Huang, F.; Feng, H.; Wei, J.; Massey, I.Y.; Liang, G.; Zhang, F.; Yin, L.; Kacew, S.; Zhang, X. A complete route for biodegradation of potentially carcinogenic cyanotoxin microcystin-LR in a novel indigenous bacterium. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F. A mini review on microcystins and bacterial degradation. Toxins 2020, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briand, E.; Humbert, J.; Tambosco, K.; Bormans, M.; Gerwick, W.H. Role of bacteria in the production and degradation of Microcystis cyanopeptides. Microbiologyopen 2016, 5, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, D.G.; Riddles, P.; Jones, G.J.; Smith, W.; Blakeley, R.L. Characterisation of a gene cluster involved in bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin LR. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Liu, K.; Xu, K.; Sun, R.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. Further understanding of degradation pathways of microcystin-LR by an indigenous Sphingopyxis sp. in environmentally relevant pollution concentrations. Toxins 2018, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lakes/Reservoirs | Location | Cyanobacteria | Extracellular MCs (µg/L) | Intracellular MCs | Congeners | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hakanoa Lake | North Island, New Zealand | Microcystis aeruginosa; Anabaena cf. smithii | 2100 | ND | MC-RR, -LR, -FR, -WR, -LY, -AR, -LA, and YR | [50] |
| Köyliönjärvi Lake | southwest Finland | Microcystis spp. (M. wesenbergii, M. botrys and M. aeruginosa); Dolichospermumsp., and Aphanizomenon sp.; Planktothrix sp.; Aulacoseira ambigua and Cyclotella spp.; Planktolyngbya limnetica; | 0.12–0.28 | 0.97–2.4 µg/L | MC-RR, -LR, -YR, and -RR | [46] |
| Groundwater wells | Asir region, Saudi Arabia | Oscillatoria limnetica | 0.3–1.8 | 336 µg/g | MC-RR, -LR, and -YR | [51] |
| Karla Reservoir | Central Greece | Planktothrix cf. agardhii; Anabaena sp. | 1.5–33 | ND | MC-LR, and -RR | [52] |
| Dianchi Lake; Xingyun Lake | Yunnan province, China | ND | 0.117–46.7 | 0.062–514.6 µg/L | MC-RR, -LR, and -YR | [53] |
| Dashahe Reservoir | Jiangmen, Guangdong province, China | 0.016–3.1 | 0.594–450.7 µg/L | |||
| Karla Reservoir | Central Greece | ND | 3.8 | ND | MCt | [54] |
| Nile river | Egypt | Anabaena subcylindrica; Nostoc spongiaeforme; Plectonema boryanum; Phormidium corium; Aulacoseira ambigua and Cyclotella sp. | ND | 1.6–3.66 µg/L | MC-RR, and -YR | [47] |
| Lalla Takerkoust reservoir | Marrakech, Morocco | Microcystis aeruginosa Kütz | 60 | 3240 µg/g | MCt | [43] |
| Taihu Lake | Suzhou, China | Microcystis | 4.14 | 17.57 µg/L | MC-RR, -LR, and -YR | [55] |
| Occhito reservoir | Italy | ND | 0.18 µg/L | ND | MC-LR, -RR, -LA, -YR, -LY, -LF, and -LW | [56] |
| Karla Reservoir | Central Greece | Microcystis aeruginosa | 1.43–2.03 | ND | MC-LR, and -RR | [57] |
| Sources of irrigation water | Egypt | Oscillatoria limnetica and Microcystis aeruginosa | 45.04–600 | 58,000–87,000 µg/L | MC-LR, and -RR | [58] |
| Beira Lake | Sri Lanka | Microcystis aeruginosa | 180 | 340 µg/g | MC-LR | [59] |
| Irrigation heads; Irrigation intakes; Epilimnion of surface water sources | Missouri and Kansas, USA | ND | 8.53–8.65 | ND | ND | [46] |
| Mansour Eddahbi Reservoir | South of Ouarzazate city, Morocco | Microcystis aeruginosa Kütz; Pseudanabaena papillaterminata Kuk; and Oscillatoria sp. | ND | 64.4 μg/g | MC, -LR, -RR, -YR, -FR, and -WR | [60] |
| Lalla Takerkoust reservoir | Central regions of Morocco | Microcystis aeruginosa | ND | 2.2–944 µg/g | MC-LR | [61] |
| Reservoirs of the river Segura | Murcia, SE Spain | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae and Microcystis aeruginosa | 0.067–1.586 | ND | MC-RR, -LR, and -YR | [62] |
| Plants Species | Applied Concentration (μg/L) | Organs | Concentration Accumulated (µg/kg) | Exposure Time (Days) | EDIAdu/EDIchi (μg/kg) | BFA of MCs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactuca sativa | 5–2000 MC-LR (P) | Leaves | 700–1400 MC-LR FW | 14 | 0.43–0.86/0.28–0.56 | 140/0.7 | [74] |
| Cucumis sativus L. | 1–1000 CE FW MCt | Fruit | 2.87–29.64 MCt FW | 7 | 0.001–0.018/0.001–0.011 | 0.29 | [72] |
| Oryza sativa | 5–500 CE FW MCt | Roots | ≈7000–35,000 MCt FW | 30 | - | 1400/70 | [76] |
| Stems | ≈10,000–38,000 MCt FW | - | 2000/76 | ||||
| Leaves | ≈20,000–112,000 MCt FW | - | 4000/224 | ||||
| Oryza sativa | 1–3000 CE FW MCt | Roots | ≈20–275 MCt FW | 7 | - | 20/0.091 | [78] |
| Stems | ≈18–30 MCt FW | - | 18/0.01 | ||||
| Leaves | ≈22–230 MCt FW | - | 22/0.076 | ||||
| Oryza sativa | 9.79 CE FW MCt | Roots | ≈1.22 MCt FW | 21 | - | 0.12 | [69] |
| Leaves | ≈0.98 MCt FW | - | 0.1 | ||||
| Leaves | 1.55–6.59 MCt FW | 0.001/0.0005 | 1.55–0.32 | ||||
| Fruit | 1.04 MCt FW | 0–0.052 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haida, M.; El Khalloufi, F.; Mugani, R.; Essadki, Y.; Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Oudra, B. Microcystin Contamination in Irrigation Water and Health Risk. Toxins 2024, 16, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16040196
Haida M, El Khalloufi F, Mugani R, Essadki Y, Campos A, Vasconcelos V, Oudra B. Microcystin Contamination in Irrigation Water and Health Risk. Toxins. 2024; 16(4):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16040196
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaida, Mohammed, Fatima El Khalloufi, Richard Mugani, Yasser Essadki, Alexandre Campos, Vitor Vasconcelos, and Brahim Oudra. 2024. "Microcystin Contamination in Irrigation Water and Health Risk" Toxins 16, no. 4: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16040196
APA StyleHaida, M., El Khalloufi, F., Mugani, R., Essadki, Y., Campos, A., Vasconcelos, V., & Oudra, B. (2024). Microcystin Contamination in Irrigation Water and Health Risk. Toxins, 16(4), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16040196








