Sensing the Deadliest Toxin: Technologies for Botulinum Neurotoxin Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Molecular Mechanism of BoNT Action
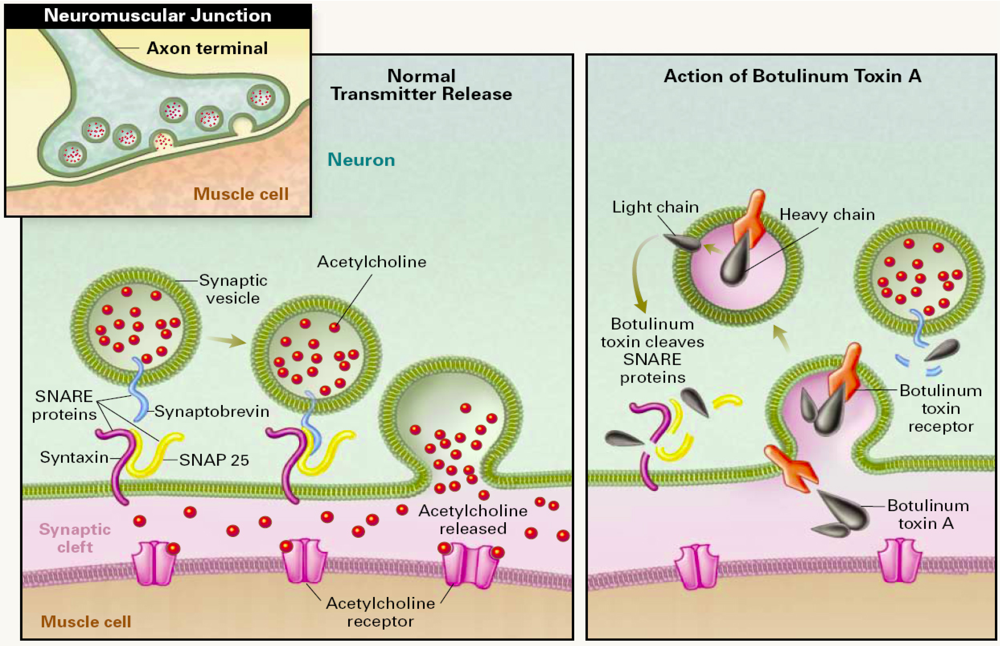
1.2. Botulism
2. BoNT Detection
3. Mouse Lethality Assay
3.1. Variations of Mouse Bioassay
4. In Vitro Methods of BoNT Detection
5. ELISA
5.1. Alternative ELISA Formats
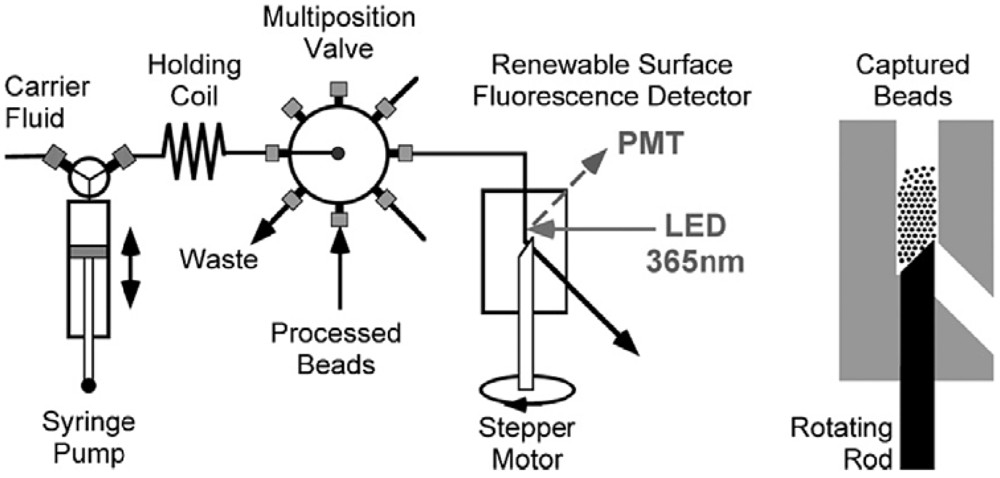
6. Flow Cytometric Assays
7. Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay
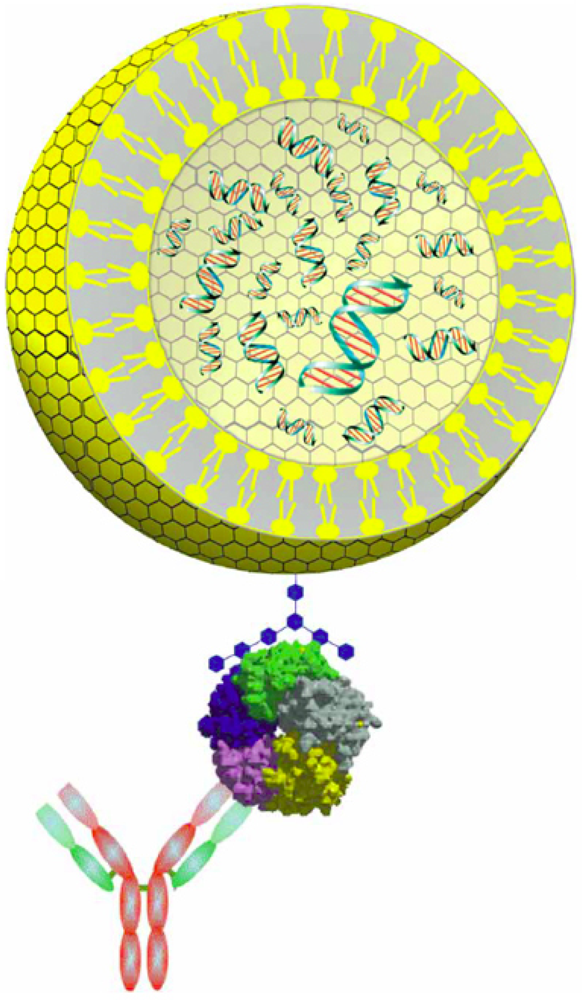
8. Immuno-PCR
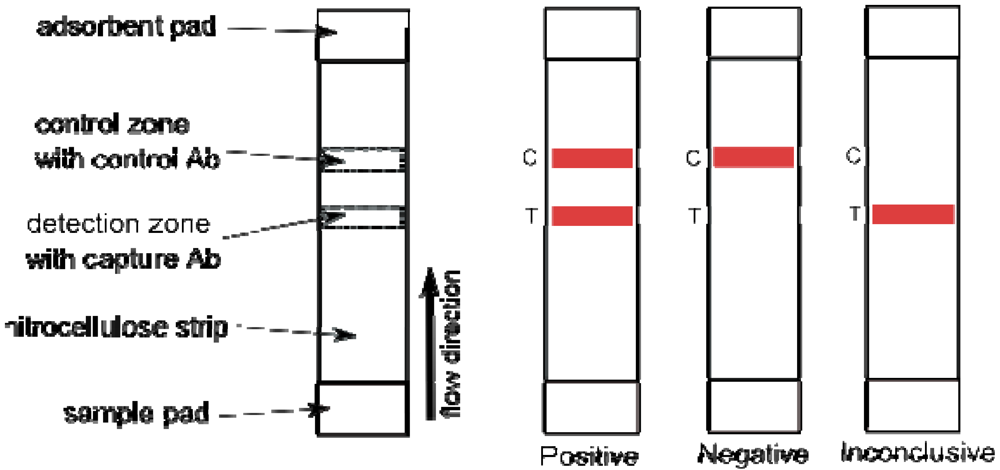
9. Lateral Flow Tests
10. Biosensors
11. Endopeptidase Activity Based Assays
12. Fluorescence Endopeptidase Assays
13. FRET Endopeptidase Assays
13.1. FRET Assays with Immunocapture
14. Immunodetection of Cleavage Product
15. Endopep-MS
16. Emerging in Vitro Assays and Technologies
17. Cell Based Assays
18. Summary and Outlook
| Method | Detection limit | Analysis time | Multiplex | Automation | Matrix interference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse lethality assay | 1 MLD50(20 pg/mL BoNT/A) | 4-6 days | no | no | low |
| ELISA | 5 pg/mL-2 ng/mL | 5-6 hours | limited | limited | manageable |
| Flow cytometric assay | 50 pg/mL-20 ng/mL | 4 hours | yes | yes | manageable |
| Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay | 5 pg/mL - 50 ng/mL | 1 hour | limited | limited | manageable |
| Immuno-PCR | 1-5 pg/mL | 6-9 hours | limited | no | manageable |
| Liposome-PCR | 0.02 fg/mL | 7-9 hours | limited | no | N/A |
| Lateral flow test | 5-50 ng/mL | 15 min | no | - | high |
| Biosensor (evanescence wave based) | 150 pg/mL-200 ng/mL | 10 min | yes | yes | low |
| Fluorescence endopeptidase assay | 3 pg/mL | 3 hours | no | on-chip | high |
| FRET endopeptidase assay | 60 pg/mL-40 ng/mL | 3 hours | no | no | high |
| FRET endopeptidase assay with immunoseparation | 1 fg/mL | 2.5 hours | no | no | low |
| Immuno-detection of cleavage product | 40 fg/mL-200 pg/mL | 6 hours | limited | no | high |
| Endopep-MS | 0.4-6 pg/mL | 3-4 hours | yes | yes | high |
| Cell based assay | 1-10 ng/mL | 2-3 days | no | no | low |
Acknowledgements
References
- Schantz, E.J.; Johnson, E.A. Properties and use of botulinum toxin and other microbial neurotoxins in medicine. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 80–99. [Google Scholar]
- Dembek, Z.F.; Smith, L.A.; Rusnak, J.M. Botulism: Cause, effects, diagnosis, clinical and laboratory identification, and treatment modalities. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2007, 1, 122–134. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, G.; Matteoli, M.; Montecucco, C. Neurotoxins affecting neuroexocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 717–766. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, H.D.; Sharma, S.K. Clostridium botulinum: A bug with beauty and weapon. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 31, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Inglesby, T.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Ascher, M.S.; Eitzen, E.; Fine, A.D.; Hauer, J.; Layton, M.; Lillibridge, S.; Osterholm, M.T.; O'Toole, T.; Parker, G.; Perl, T.M.; Russell, P.K.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Tonat, K. Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. JAMA 2001, 285, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar]
- CDC Bioterrorism Agents/Disease. Available online: http://www.bt.cdc.gov/agent/agentlist-category.asp/ (Accessed on 7 January 2010).
- Kostrzewa, R.M.; Segura-Aguilar, J. Botulinum neurotoxin: Evolution from poison, to research tool-onto medicinal therapeutic and future pharmaceutical panacea. Neurotox. Res. 2007, 12, 275–290. [Google Scholar]
- Savino, P.J.; Maus, M. Botulinum toxin therapy. Neurol. Clin. 1991, 9, 205–224. [Google Scholar]
- Eubanks, L.M.; Dickerson, T.J. Investigating novel therapeutic targets and molecular mechanisms to treat botulinum neurotoxin A intoxication. Future Microbiol. 2007, 2, 677–687. [Google Scholar]
- Oguma, K.; Fujinaga, Y.; Inoue, K. Structure and function of Clostridium botulinum toxins. Microbiol. Immunol. 1995, 39, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, L.L. Identification of the major steps in botulinum toxin action. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 167–193. [Google Scholar]
- Rummel, A.; Hafner, K.; Mahrhold, S.; Darashchonak, N.; Holt, M.; Jahn, R.; Beermann, S.; Karnath, T.; Bigalke, H.; Binz, T. Botulinum neurotoxins C, E and F bind gangliosides via a conserved binding site prior to stimulation-dependent uptake with botulinum neurotoxin F utilising the three isoforms of SV2 as second receptor. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1942–1954. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Yeh, F.; Tepp, W.H.; Dean, C.; Johnson, E.A.; Janz, R.; Chapman, E.R. SV2 is the protein receptor for botulinum neurotoxin A. Science 2006, 312, 592–596. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.; Mushrush, D.J.; Lacy, D.B.; Montal, M. Botulinum neurotoxin devoid of receptor binding domain translocates active protease. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, 245. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.; Montal, M. Single molecule detection of intermediates during botulinum neurotoxin translocation across membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10447–10452. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, G.; Benfenati, F.; Poulain, B.; Rossetto, O.; Polverino de Laureto, P.; DasGupta, B.R.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature 1992, 359, 832–835. [Google Scholar]
- Breidenbach, M.A.; Brunger, A.T. Substrate recognition strategy for botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Nature 2004, 432, 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Blasi, J.; Chapman, E.R.; Link, E.; Binz, T.; Yamasaki, S.; Decamilli, P.; Sudhof, T.C.; Niemann, H.; Jahn, R. Botulinum neurotoxin A selectively cleaves the synaptic protein SNAP-25. Nature 1993, 365, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, L.P. Stroke, spasticity, and botulinum toxin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 382–383. [Google Scholar]
- Sobel, J.; Tucker, N.; Sulka, A.; McLaughlin, J.; Maslanka, S. Foodborne botulism in the United States, 1990-2000. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004 , 10, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.G.; Spilke, C.E.; Denton, M.; Jamieson, S. Clostridium botulinum: An increasing complication of heroin misuse. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2005, 12, 251–252. [Google Scholar]
- Kongsaengdao, S.; Samintarapanya, K.; Rusmeechan, S.; Wongsa, A.; Pothirat, C.; Permpikul, C.; Pongpakdee, S.; Puavilai, W.; Kateruttanakul, P.; Phengtham, U.; Panjapornpon, K.; Janma, J.; Piyavechviratana, K.; Sithinamsuwan, P.; Deesomchok, A.; Tongyoo, S.; Vilaichone, W.; Boonyapisit, K.; Mayotarn, S.; Piya-Isragul, B.; Rattanaphon, A.; Intalapaporn, P.; Dusitanond, P.; Harnsomburana, P.; Laowittawas, W.; Chairangsaris, P.; Suwantamee, J.; Wongmek, W.; Ratanarat, R.; Poompichate, A.; Panyadilok, H.; Sutcharitchan, N.; Chuesuwan, A.; Oranrigsupau, P.; Sutthapas, C.; Tanprawate, S.; Lorsuwansiri, J.; Phattana, N. An outbreak of botulism in Thailand: Clinical manifestations and management of severe respiratory failure. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.; Singh, B.R.; Sharma, S. Botulism diagnostics: From clinical symptoms to in vitro assays. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 33, 109–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom, M.; Korkeala, H. Laboratory diagnostics of botulism. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 298–314. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K.; Whiting, R.C. Methods for detection of Clostridium botulinum toxin in foods. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, H.M.; Lilly, T.J. Clostridium botulinum. In Bacteriological analytical manual, 8th ed; US Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, J.L. Comparison of amplified ELISA and mouse bioassay procedures for determination of botulinal toxins A, B, E, and F. J. AOAC Int. 2001 , 84, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solberg, M.; Post, L.S.; Furgang, D.; Graham, C. Bovine serum eliminates rapid nonspecific toxic reactions during bioassay of stored fish for Clostridium botulinum toxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 644–649. [Google Scholar]
- Dezfulian, M.; Bartlett, J.G. Detection of Clostridium botulinum type B toxin in the presence of a lethal substance interfering with toxin neutralization. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1985, 3, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, M.; Kameyama, S.; Sakaguchi, G. Assay in mice for low levels of Clostridium botulinum toxin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1990, 11, 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Sesardic, D.; McLellan, K.; Ekong, T.A.; Das, R.G. Refinement and validation of an alternative bioassay for potency testing of therapeutic botulinum type A toxin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1996, 78, 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Boroff, D.A.; Fleck, U. Statistical analysis of a rapid in vivo method for the titration of the toxin of Clostridium botulinum. J. Bacteriol. 1966, 92, 1580–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Torii, Y.; Goto, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Ishida, S.; Harakawa, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Kaji, R.; Kozaki, S.; Ginnaga, A. Quantitative determination of biological activity of botulinum toxins utilizing compound muscle action potentials (CMAP), and comparison of neuromuscular transmission blockage and muscle flaccidity among toxins. Toxicon 2009, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, R.E.; Deshpande, S.S.; Smith, T. Comparison of in vivo and in vitro mouse bioassays for botulinum toxin antagonists. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1999, 19, S29–S33. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, M.; Scovill, J.; Parker, G.; Lebeda, F.J.; Piotrowski, J.; Deshpande, S.S. Antagonism of botulinum toxin-induced muscle weakness by 3,4-diaminopyridine in rat phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm preparations. Toxicon 1995, 33, 527–537. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, S.S.; Sheridan, R.E.; Adler, M. A study of zinc-dependent metalloendopeptidase inhibitors as pharmacological antagonists in botulinum neurotoxin poisoning. Toxicon 1995, 33, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Scarlatos, A.; Welt, B.A.; Cooper, B.Y.; Archer, D.; DeMarse, T.; Chau, K.V. Methods for detecting botulinum toxin with applicability to screening foods against biological terrorist attacks. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, R121–R130. [Google Scholar]
- Boroff, D.A.; Chu-Chen, G. Radioimmunoassay for type A toxin of Clostridium botulinum. Appl. Microbiol. 1973, 25, 545–549. [Google Scholar]
- Ashton, A.C.; Crowther, J.S.; Dolly, J.O. A sensitive and useful radioimmunoassay for neurotoxin and its haemagglutinin complex from Clostridium botulinum. Toxicon 1985, 23, 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, H.M.; Brenner, K.; Angelotti, R.; Hall, H.E. Serological studies of types A, B, and E botulinal toxins by passive hemagglutination and bentonite flocculation. J. Bacteriol. 1966, 91, 967–974. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, J.L.; Hamdy, M.K.; Zapatka, F.A.; Hebert, W.O. Immunodiffusion method for detection of type A Clostridium botulinum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1981, 42, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, C.A.; Anderson, A.W. Rapid detection and quantitative estimation of type A botulinum toxin by electroimmunodiffusion. Infect. Immun. 1971, 4, 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mestrandrea, L.W. Rapid detection of Clostridium botulinum toxin by capillary tube diffusion. Appl. Microbiol. 1974, 27, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Vermilyea, B.L.; Walker, H.W.; Ayres, J.C. Detection of botulinal toxins by immunodiffusion. Appl. Microbiol. 1968, 16, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Notermans, S.; Dufrenne, J.; Schothorst, M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Clostridium botulinum toxin type A. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1978, 31, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kozaki, S.; Dufrenne, J.; Hagenaars, A.M.; Notermans, S. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of Clostridium botulinum type B toxin. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1979, 32, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Notermans, S.; Dufrenne, J.; Kozaki, S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Clostridium botulinum type E toxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1979, 37, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Stanker, L.H.; Merrill, P.; Scotcher, M.C.; Cheng, L.W. Development and partial characterization of high-affinity monoclonal antibodies for botulinum toxin type A and their use in analysis of milk by sandwich ELISA. J. Immunol. Methods. 2008, 336, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, M.A.; Rivera, V.R.; Neal, D. Development of sensitive colorimetric capture ELISAs for Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin serotypes E and F. Toxicon 2002, 40, 797–802. [Google Scholar]
- Volland, H.; Lamourette, P.; Nevers, M.C.; Mazuet, C.; Ezan, E.; Neuburger, L.M.; Popoff, M.; Creminon, C. A sensitive sandwich enzyme immunoassay for free or complexed Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type A. J. Immunol. Methods. 2008, 330, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Szilagyi, M.; Rivera, V.R.; Neal, D.; Merrill, G.A.; Poli, M.A. Development of sensitive colorimetric capture elisas for Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin serotypes A and B. Toxicon 2000, 38, 381–389. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, J.L.; Eliasberg, S.J.; Harrison, M.A.; Edmonds, P. Detection of preformed type A botulinal toxin in hash brown potatoes by using the mouse bioasssay and a modified ELISA test. J. AOAC Int. 2001, 84, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, J.L.; Maslanka, S.; Johnson, E.; Goodnough, M. Detection of botulinal neurotoxins A, B, E, and F by amplified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.L.; Eliasberg, S.J.; Edmonds, P.; Harrison, M.A. Comparison of the mouse bioassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay procedures for the detection of type A botulinal toxin in food. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Doellgast, G.J.; Triscott, M.X.; Beard, G.A.; Bottoms, J.D.; Cheng, T.; Roh, B.H.; Roman, M.G.; Hall, P.A.; Brown, J.E. Sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins A, B, and E using signal amplification via enzyme-linked coagulation assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar]
- Doellgast, G.J.; Beard, G.A.; Bottoms, J.D.; Cheng, T.; Roh, B.H.; Roman, M.G.; Hall, P.A.; Triscott, M.X. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and enzyme-linked coagulation assay for detection of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins A, B, and E and solution-phase complexes with dual-label antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, M.G.; Humber, J.Y.; Hall, P.A.; Reddy, N.R.; Solomon, H.M.; Triscott, M.X.; Beard, G.A.; Bottoms, J.D.; Cheng, T.; Doellgast, G.J. Amplified immunoassay ELISA-ELCA for measuring Clostridium-botulinum type-E neurotoxin in fish fillets. J. Food Prot. 1994, 57, 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.J.; Lou, J.; Geren, I.N.; Forsyth, C.M.; Tsai, R.; Laporte, S.L.; Tepp, W.H.; Bradshaw, M.; Johnson, E.A.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. Sequence variation within botulinum neurotoxin serotypes impacts antibody binding and neutralization. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5450–5457. [Google Scholar]
- Ekong, T.A.; McLellan, K.; Sesardic, D. Immunological detection of Clostridium botulinum toxin type A in therapeutic preparations. J. Immunol. Methods. 1995, 180, 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, J.L.; Crawford, R.G. Detection of type a botulinal toxin-producing organisms subcultured from cheese using an amplified ELISA system. J. Rapid. Methods. Autom. Microbiol. 1998, 6, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Dezfulian, M.; Bartlett, J.G. Detection of Clostridium botulinum type A toxin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with antibodies produced in immunologically tolerant animals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1984, 19, 645–648. [Google Scholar]
- Dezfulian, M.; Bartlett, J.G. Selective isolation and rapid identification of Clostridium-botulinum type-A and type-B by toxin detection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 21, 231–233. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K.; Ferreira, J.L.; Eblen, B.S.; Whiting, R.C. Detection of type A, B, E, and F Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins in foods by using an amplified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with digoxigenin-labeled antibodies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, M.D.; Meng, J.H.; Kimsey, P. An ELISA for detection of botulinal toxin type-A, type-B, and type-E in inoculated food samples. J. Food Prot. 1993, 56, 856–861. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, A.; Dezfulian, M. Rapid identification of Clostridium botulinum and botulinal toxin in food. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 1997, 42, 149–151. [Google Scholar]
- Dezfulian, M.; Hatheway, C.L.; Yolken, R.H.; Bartlett, J.G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Clostridium botulinum type A and type B toxins in stool samples of infants with botulism. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1984, 20, 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Zhou, B.; Kim, Y.; Janda, K.D. A cyclic peptide-polymer probe for the detection of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Toxicon 2006, 47, 901–908. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Harrison, S.H.; Schoeniger, J.S. Gangliosides as receptors for biological toxins: Development of sensitive fluoroimmunoassays using ganglioside-bearing liposomes. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 6019–6024. [Google Scholar]
- Fishman, P.H.; Pacuszka, T.; Orlandi, P.A. Gangliosides as receptors for bacterial enterotoxins. Adv. Lipid Res. 1993, 25, 165–187. [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren, J.; Elwing, H.; Fredman, P.; Strannegard, O.; Svennerholm, L. Gangliosides as receptors for bacterial toxins and Sendai virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1980, 125, 453–470. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, M.; Iwamori, M.; Nagai, Y. Interaction between Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin and gangliosides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1980, 628, 328–335. [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark, P.; Dupuy, J.; Imamura, A.; Kiso, M.; Stevens, R.C. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type A in complex with the cell surface co-receptor GT1b-insight into the toxin-neuron interaction. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, M.G.; Grate, J.W.; Tyler, A.; Ozanich, R.M.; Miller, K.D.; Lou, J.; Marks, J.D.; Bruckner-Lea, C.J. Quantum dot immunoassays in renewable surface column and 96-well plate formats for the fluorescence detection of botulinum neurotoxin using high-affinity antibodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Grate, J.W.; Warner, M.G.; Ozanich, R.M., Jr.; Miller, K.D.; Colburn, H.A.; Dockendorff, B.; Antolick, K.C.; Anheier, N.C., Jr.; Lind, M.A.; Lou, J.; Marks, J.D.; Bruckner-Lea, C.J. Renewable surface fluorescence sandwich immunoassay biosensor for rapid sensitive botulinum toxin detection in an automated fluidic format. Analyst 2009, 134, 987–996. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.; Hara, C.A.; Knize, M.G.; Hwang, M.H.; Venkateswaran, K.S.; Wheeler, E.K.; Bell, P.M.; Renzi, R.F.; Fruetel, J.A.; Bailey, C.G. Magnetic bead based immunoassay for autonomous detection of toxins. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8416–8423. [Google Scholar]
- Varnum, S.M.; Warner, M.G.; Dockendorff, B.; Anheier, N.C., Jr.; Lou, J.; Marks, J.D.; Smith, L.A.; Feldhaus, M.J.; Grate, J.W.; Bruckner-Lea, C.J. Enzyme-amplified protein microarray and a fluidic renewable surface fluorescence immunoassay for botulinum neurotoxin detection using high-affinity recombinant antibodies. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2006, 570, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Ozanich, R.M., Jr.; Bruckner-Lea, C.J.; Warner, M.G.; Miller, K.; Antolick, K.C.; Marks, J.D.; Lou, J.; Grate, J.W. Rapid multiplexed flow cytometric assay for botulinum neurotoxin detection using an automated fluidic microbead-trapping flow cell for enhanced sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5783–5793. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, G.P.; Taitt, C.R. Amplification of microsphere-based microarrays using catalyzed reporter deposition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 324–328. [Google Scholar]
- Pauly, D.; Kirchner, S.; Stoermann, B.; Schreiber, T.; Kaulfuss, S.; Schade, R.; Zbinden, R.; Avondet, M.A.; Dorner, M.B.; Dorner, B.G. Simultaneous quantification of five bacterial and plant toxins from complex matrices using a multiplexed fluorescent magnetic suspension assay. Analyst 2009, 134, 2028–2039. [Google Scholar]
- Gattomenking, D.L.; Yu, H.; Bruno, J.G.; Goode, M.T.; Miller, M.; Zulich, A.W. Sensitive detection of biotoxoids and bacterial spores using an immunomagnetic electrochemiluminescence sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, 501–507. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmo-Viret, V.; Attree, O.; Blanco-Gros, V.; Thullier, P. Comparison of electrochemiluminescence assay and ELISA for the detection of Clostridium botulinum type B neurotoxin. J. Immunol. Methods. 2005, 301, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, V.R.; Gamez, F.J.; Keener, W.K.; White, J.A.; Poli, M.A. Rapid detection of Clostridium botulinum toxins A, B, E, and F in clinical samples, selected food matrices, and buffer using paramagnetic bead-based electrochemiluminescence detection. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 353, 248–256. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, R.W.; Abbott, D. High-throughput enzyme-linked immunoabsorbant assay (ELISA) electrochemiluminescent detection of botulinum toxins in foods for food safety and defence purposes. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2008, 25, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, T.; Smith, C.L.; Cantor, C.R. Immuno-PCR: Very sensitive antigen detection by means of specific antibody-DNA conjugates. Science 1992, 258, 120–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Lai, S.C.; Huang, Y.Y.; Shalo, M.F. Detection of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type A using immuno-PCR. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 32, 321–325. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, H.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Tang, S.S.; Liu, H.W. A highly sensitive immuno-polymerase chain reaction assay for Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type A. Toxicon 2004, 43, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, J.T.; Xu, L.; Sheng, Z.M.; O'Leary, T.J. A liposome-PCR assay for the ultrasensitive detection of biological toxins. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 555–557. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, J.T.; Xu, L.; Sheng, Z.M.; He, J.; O'Leary, T.J. Liposome polymerase chain reaction assay for the sub-attomolar detection of cholera toxin and botulinum neurotoxin type A. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K.; Eblen, B.S.; Bull, R.L.; Burr, D.H.; Whiting, R.C. Evaluation of lateral-flow Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin detection kits for food analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3935–3941. [Google Scholar]
- Attree, O.; Guglielmo-Viret, V.; Gros, V.; Thullier, P. Development and comparison of two immunoassay formats for rapid detection of botulinum neurotoxin type A. J. Immunol. Methods. 2007, 325, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Gessler, F.; Pagel-Wieder, S.; Avondet, M.A.; Bohnel, H. Evaluation of lateral flow assays for the detection of botulinum neurotoxin type A and their application in laboratory diagnosis of botulism. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 57, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Chiao, D.J.; Wey, J.J.; Shyu, R.H.; Tang, S.S. Monoclonal antibody-based lateral flow assay for detection of botulinum neurotoxin type A. Hybridoma. (Larchmt). 2008, 27, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.M.; Cho, J.H.; Cho, I.H.; Paek, E.H.; Oh, H.B.; Kim, B.S.; Ryu, C.; Lee, K.; Kim, Y.K.; Paek, S.H. Plastic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA)-on-a-chip biosensor for botulinum neurotoxin A. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2007, 587, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chiao, D.J.; Shyu, R.H.; Hu, C.S.; Chiang, H.Y.; Tang, S.S. Colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic assay for detection of botulinum neurotoxin type B. J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 809, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn-Yoon, S.; DeCory, T.R.; Durst, R.A. Ganglioside-liposome immunoassay for the detection of botulinum toxin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Taitt, C.R.; Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Ngundi, M.M.; Ligler, F.S. Array Biosensor for Toxin Detection: Continued Advances. Sensors 2008, 8, 8361–8377. [Google Scholar]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Shubin, Y.S.; Delehanty, J.B.; Golden, J.P.; Taitt, C.R.; Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Ligler, F.S. Fluorescence-based array biosensors for detection of biohazards. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ogert, R.A.; Brown, J.E.; Singh, B.R.; Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Ligler, F.S. Detection of Clostridium botulinum toxin A using a fiber optic-based biosensor. Anal. Biochem. 1992, 205, 306–312. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Colston, J.T.; Chambers, J.P.; Rael, E.D.; Valdes, J.J. Detection of botulinum toxin using an evanescent wave immunosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1994, 9, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.R.; Silvia, M.A. Detection of botulinum neurotoxins using optical fiber-based biosensor. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1996, 391, 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe-Taitt, C.A.; Golden, J.P.; Feldstein, M.J.; Cras, J.J.; Hoffman, K.E.; Ligler, F.S. Array biosensor for detection of biohazards. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 14, 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Ligler, F.S.; Taitt, C.R.; Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Sapsford, K.E.; Shubin, Y.; Golden, J.P. Array biosensor for detection of toxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 377, 469–477. [Google Scholar]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Taitt, C.R.; Loo, N.; Ligler, F.S. Biosensor detection of botulinum toxoid A and staphylococcal enterotoxin B in food. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5590–5592. [Google Scholar]
- Kostov, Y.; Sergeev, N.; Wilson, S.; Herold, K.E.; Rasooly, A. A simple portable electroluminescence illumination-based CCD detector. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 503, 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Kulagina, N.V.; Anderson, G.P.; Ligler, F.S.; Shaffer, K.M.; Taitt, C.R. Antimicrobial peptides: New recognition molecules for detecting botulinum toxins. Sensors 2007, 7, 2808–2824. [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathy, R.; Padmanabhan, S.; Eric, Y.P.; Moochhala, S.; Lionel, L.K.; Ponnampalam, G. Rapid detection of botulinum neurotoxins A, B, E, and F by optical immunoassay. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 5432–5440. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.J.; Stafford, R.G.; Millard, C.B. High-throughput assays for botulinum neurotoxin proteolytic activity: Serotypes A, B, D, and F. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 296, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisk, M.L.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Beebe, D.J. Self-assembled peptide monolayers as a toxin sensing mechanism within arrayed microchannels. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2760–2767. [Google Scholar]
- Frisk, M.L.; Berthier, E.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Beebe, D.J. Bead-based microfluidic toxin sensor integrating evaporative signal amplification. Lab. Chip. 2008, 8, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar]
- Rasooly, R.; Stanker, L.H.; Carter, J.M.; Do, P.M.; Cheng, L.W.; He, X.; Brandon, D.L. Detection of botulinum neurotoxin-A activity in food by peptide cleavage assay. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 126, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Sun, S.; Francis, J.; Sharma, S.; Kostov, Y.; Rasooly, A. A fluorescence detection platform using spatial electroluminescent excitation for measuring botulinum neurotoxin A activity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 618–625. [Google Scholar]
- Bagramyan, K.; Barash, J.R.; Arnon, S.S.; Kalkum, M. Attomolar detection of botulinum toxin type A in complex biological matrices. PLoS One. 2008, 3, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Poras, H.; Ouimet, T.; Orng, S.V.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Popoff, M.R.; Roques, B.P. Detection and quantification of botulinum neurotoxin type a by a novel rapid in vitro fluorimetric assay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4382–4390. [Google Scholar]
- Rasooly, R.; Do, P.M. Development of an in vitro activity assay as an alternative to the mouse bioassay for Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type A. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4309–4313. [Google Scholar]
- Perpetuo, E.A.; Juliano, L.; Juliano, M.A.; Fratelli, F.; Prado, S.M.; Pimenta, D.C.; Lebrun, I. Enzymatic profiling of tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins based on vesicle-associated-membrane protein derived fluorogenic substrates. Protein Pept. Lett. 2008, 15, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Chapman, E.R. Using fluorescent sensors to detect botulinum neurotoxin activity in vitro and in living cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14701–14706. [Google Scholar]
- Parpura, V.; Chapman, E.R. Detection of botulinum toxins: Micromechanical and fluorescence-based sensors. Croat. Med. J. 2005, 46, 491–497. [Google Scholar]
- Pires-Alves, M.; Ho, M.; Aberle, K.K.; Janda, K.D.; Wilson, B.A. Tandem fluorescent proteins as enhanced FRET-based substrates for botulinum neurotoxin activity. Toxicon 2009, 53, 392–399. [Google Scholar]
- Hallis, B.; James, B.A.; Shone, C.C. Development of novel assays for botulinum type A and B neurotoxins based on their endopeptidase activities. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.G.; Ochiai, M.; Liu, Y.; Ekong, T.; Sesardic, D. Development of improved SNAP25 endopeptidase immuno-assays for botulinum type A and E toxins. J. Immunol. Methods. 2008, 329, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ekong, T.A.; Feavers, I.M.; Sesardic, D. Recombinant SNAP-25 is an effective substrate for Clostridium botulinum type A toxin endopeptidase activity in vitro. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3337–3347. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.G.; Liu, Y.; Sesardic, D. New highly specific botulinum type C1 endopeptidase immunoassays utilising SNAP25 or Syntaxin substrates. J. Immunol. Methods. 2009, 343, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kegel, B.; Behrensdorf-Nicol, H.A.; Bonifas, U.; Silberbach, K.; Klimek, J.; Kramer, B.; Weisser, K. An in vitro assay for detection of tetanus neurotoxin activity: Using antibodies for recognizing the proteolytically generated cleavage product. Toxicol. In Vitro. 2007, 21, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar]
- Wictome, M.; Newton, K.; Jameson, K.; Hallis, B.; Dunnigan, P.; Mackay, E.; Clarke, S.; Taylor, R.; Gaze, J.; Foster, K.; Shone, C. Development of an in vitro bioassay for Clostridium botulinum type B neurotoxin in foods that is more sensitive than the mouse bioassay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3787–3792. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, E.R.; Skipper, P.J.; Shone, C.C. An assay for botulinum toxin types A, B and F that requires both functional binding and catalytic activities within the neurotoxin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, A.E.; Moura, H.; Woolfitt, A.R.; Kalb, S.R.; McWilliams, L.G.; Pavlopoulos, A.; Schmidt, J.G.; Ashley, D.L.; Barr, J.R. From the mouse to the mass spectrometer: Detection and differentiation of the endoproteinase activities of botulinum neurotoxins A-G by mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3916–3924. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, J.R.; Moura, H.; Boyer, A.E.; Woolfitt, A.R.; Kalb, S.R.; Pavlopoulos, A.; McWilliams, L.G.; Schmidt, J.G.; Martinez, R.A.; Ashley, D.L. Botulinum neurotoxin detection and differentiation by mass spectrometry. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Kalb, S.R.; Moura, H.; Boyer, A.E.; McWilliams, L.G.; Pirkle, J.L.; Barr, J.R. The use of Endopep-MS for the detection of botulinum toxins A, B, E, and F in serum and stool samples. Anal. Biochem. 2006 , 351, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaunt, P.S.; Kalb, S.R.; Barr, J.R. Detection of botulinum type E toxin in channel catfish with visceral toxicosis syndrome using catfish bioassay and endopep mass spectrometry. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2007, 19, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Kalb, S.R.; Goodnough, M.C.; Malizio, C.J.; Pirkle, J.L.; Barr, J.R. Detection of botulinum neurotoxin A in a spiked milk sample with subtype identification through toxin proteomics. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6140–6146. [Google Scholar]
- Tombelli, S.; Mascini, M. Aptamers as molecular tools for bioanalytical methods. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2009, 11, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.; Ho, C.M. Aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for Botulinum neurotoxin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.; McBurnett, S.R.; Andrews, C.J.; Allman, A.M.; Bruno, J.G.; Kiel, J.L. Aptamer selection express: A novel method for rapid single-step selection and sensing of aptamers. J. Biomol. Tech. 2008, 19, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Ossandon, M.; Kostov, Y.; Rasooly, A. Lab-on-a-chip for botulinum neurotoxin a (BoNT-A) activity analysis. Lab. Chip. 2009, 9, 3275–3281. [Google Scholar]
- Mangru, S.; Bentz, B.L.; Davis, T.J.; Desai, N.; Stabile, P.J.; Schmidt, J.J.; Millard, C.B.; Bavari, S.; Kodukula, K. Integrated bioassays in microfluidic devices: Botulinum toxin assays. J. Biomol. Screen 2005, 10, 788–794. [Google Scholar]
- Moorthy, J.; Mensing, G.A.; Kim, D.; Mohanty, S.; Eddington, D.T.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Beebe, D.J. Microfluidic tectonics platform: A colorimetric, disposable botulinum toxin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay system. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Ladd, J.; Taylor, A.D.; Homola, J.; Jiang, S.Y. Detection of botulinum neurotoxins in buffer and honey using a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor. Sensor Actuat. B-Chem. 2008, 130, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Marconi, S.; Ferracci, G.; Berthomieu, M.; Kozaki, S.; Miquelis, R.; Boucraut, J.; Seagar, M.; Leveque, C. A protein chip membrane-capture assay for botulinum neurotoxin activity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 233, 439–446. [Google Scholar]
- Ferracci, G.; Miquelis, R.; Kozaki, S.; Seagar, M.; Leveque, C. Synaptic vesicle chips to assay botulinum neurotoxins. Biochem. J. 2005, 391, 659–666. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Chu, B.H.; Chen, K.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Lele, T.P.; Tseng, Y.; Pearton, S.J.; Ramage, J.; Hooten, D.; Dabiran, A.; Chow, P.P.; Ren, F. Botulinum toxin detection using AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Klaubert, B.; Vujtovic-Ockenga, N.; Wermter, R.; Schad, K.; von Meyer, L. Determination of botulinum toxins after peptic sample pre-treatment by multidimensional nanoscale liquid chromatography and nano-electrospray ion-trap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life. Sci. 2009, 877, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.P.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; Cui, Z.Q.; Zhou, Y.F.; Zhang, X.E. Micellar electrokinetic chromatography and laser induced fluorescence detection of botulinum neurotoxin type A activity using a dual-labelled substrate. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2008, 88, 947–956. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Montana, V.; Chapman, E.R.; Mohideen, U.; Parpura, V. Botulinum toxin type B micromechanosensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13621–13625. [Google Scholar]
- Peruski, A.H.; Johnson, L.H. 3rd; Peruski, L.F. Rapid and sensitive detection of biological warfare agents using time-resolved fluorescence assays. J. Immunol. Methods. 2002, 263, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyagarajan, B.; Krivitskaya, N.; Potian, J.G.; Hognason, K.; Garcia, C.C.; McArdle, J.J. Capsaicin protects mouse neuromuscular junctions from the neuroparalytic effects of botulinum neurotoxin a. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 331, 361–371. [Google Scholar]
- Scarlatos, A.; Cadotte, A.J.; DeMarse, T.B.; Welt, B.A. Cortical networks grown on microelectrode arrays as a biosensor for botulinum toxin. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, E129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Boldt, G.E.; Eubanks, L.M.; Janda, K.D. Identification of a botulinum neurotoxin A protease inhibitor displaying efficacy in a cellular model. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2006, 3063–3065. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Supplementary Files
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Čapek, P.; Dickerson, T.J. Sensing the Deadliest Toxin: Technologies for Botulinum Neurotoxin Detection. Toxins 2010, 2, 24-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2010024
Čapek P, Dickerson TJ. Sensing the Deadliest Toxin: Technologies for Botulinum Neurotoxin Detection. Toxins. 2010; 2(1):24-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleČapek, Petr, and Tobin J. Dickerson. 2010. "Sensing the Deadliest Toxin: Technologies for Botulinum Neurotoxin Detection" Toxins 2, no. 1: 24-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2010024
APA StyleČapek, P., & Dickerson, T. J. (2010). Sensing the Deadliest Toxin: Technologies for Botulinum Neurotoxin Detection. Toxins, 2(1), 24-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2010024