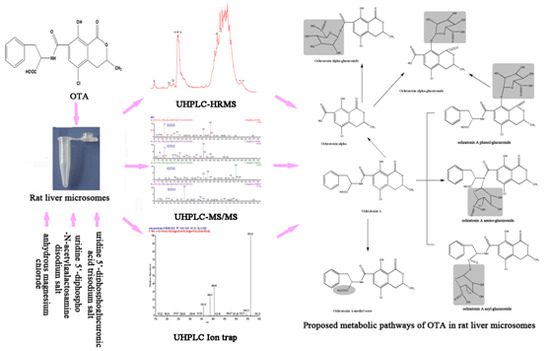
In Vitro Glucuronidation of Ochratoxin A by Rat Liver Microsomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
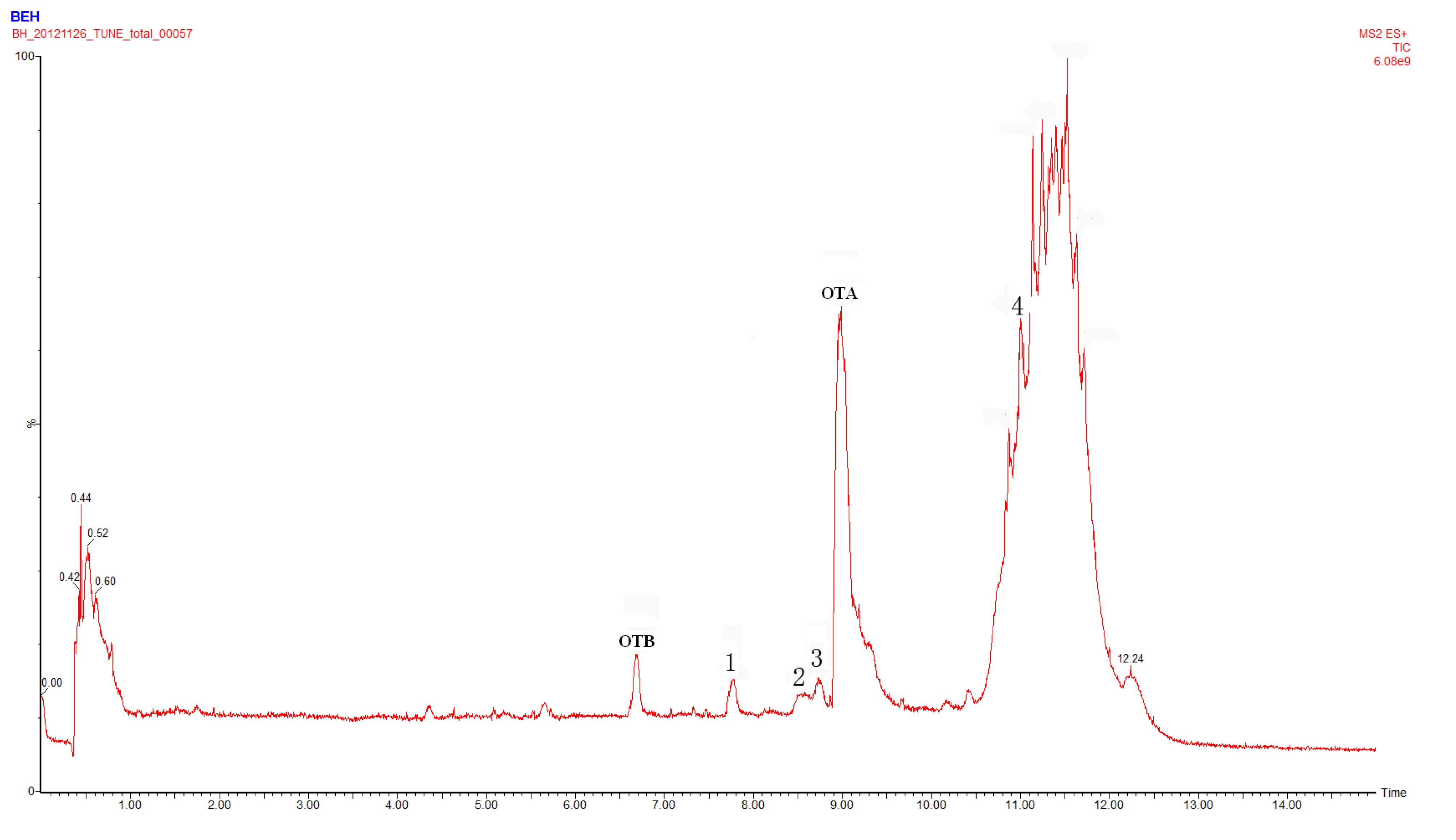
2.1. Compound 1
| Compound | Polarity | Ion formula | Observed m/z (Da) | Calculated m/z (Da) | Mass error (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | + | C26 H27 O12 N Cl | 580.12042 | 580.12219 | −0.59 |
| 1-3 | − | C26 H25 O12 N Cl | 578.10812 | 578.10651 | 2.14 |
| 4 | + | C21 H21 O6 N Cl | 418.10428 | 418.10574 | −0.91 |
| 4 | − | C21 H19 O6 N Cl | 416.09120 | 416.09009 | 1.66 |

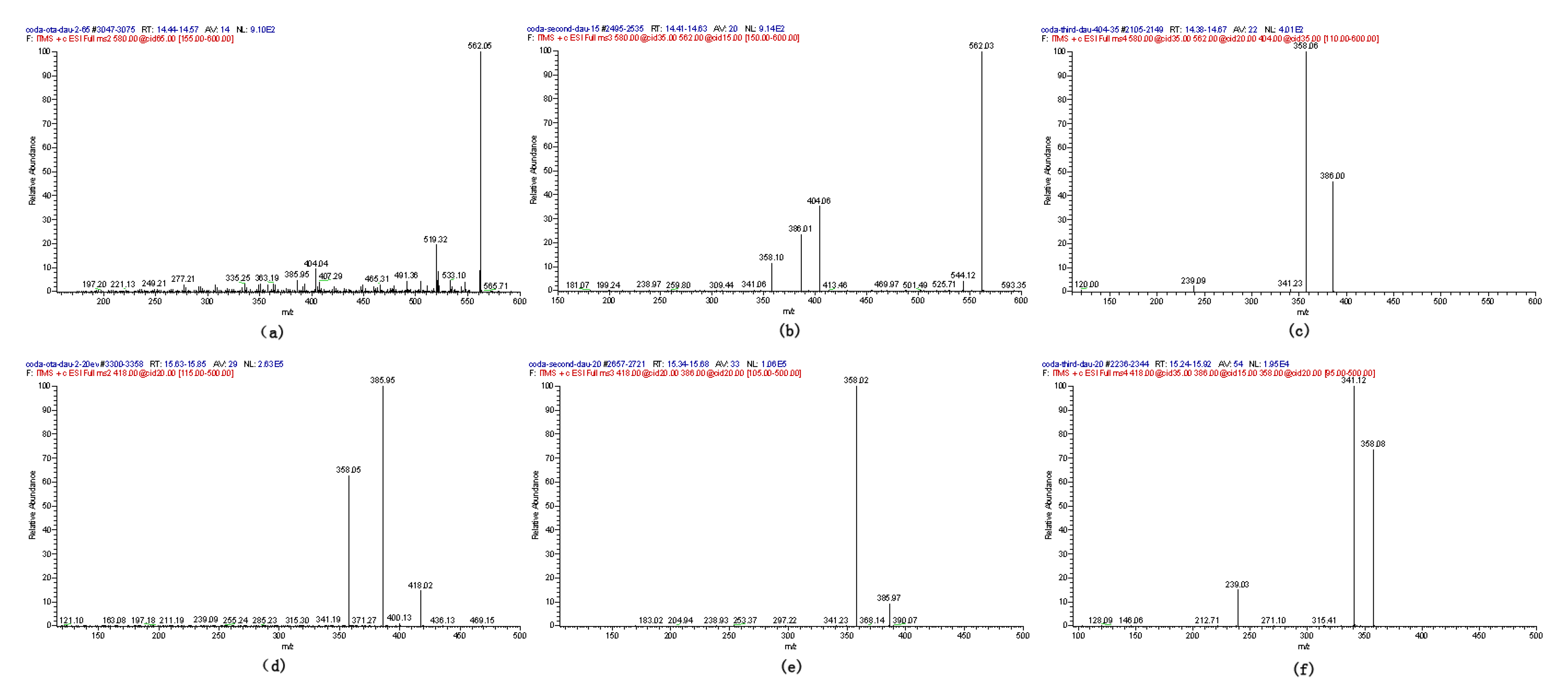
2.2. Compounds 2 and 3
2.3. Acylic, Phenolic and Amino Glucuronides

| Names | Precursor ion (m/z) | Primary product ion (m/z) | Collision energy (eV) | Secondary product ion (m/z) | Collision energy (eV) | Ionization mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound 1–3 | 580 | 358 | 20 | 239 | 38 | ESI+ |
| OTA methyl ester | 418 | 358 | 18 | 239 | 32 | ESI+ |
| OTα | 257 | 221 | 20 | 102 | 40 | ESI+ |
2.4. Identification of Compound 4
2.5. Identification of OTα
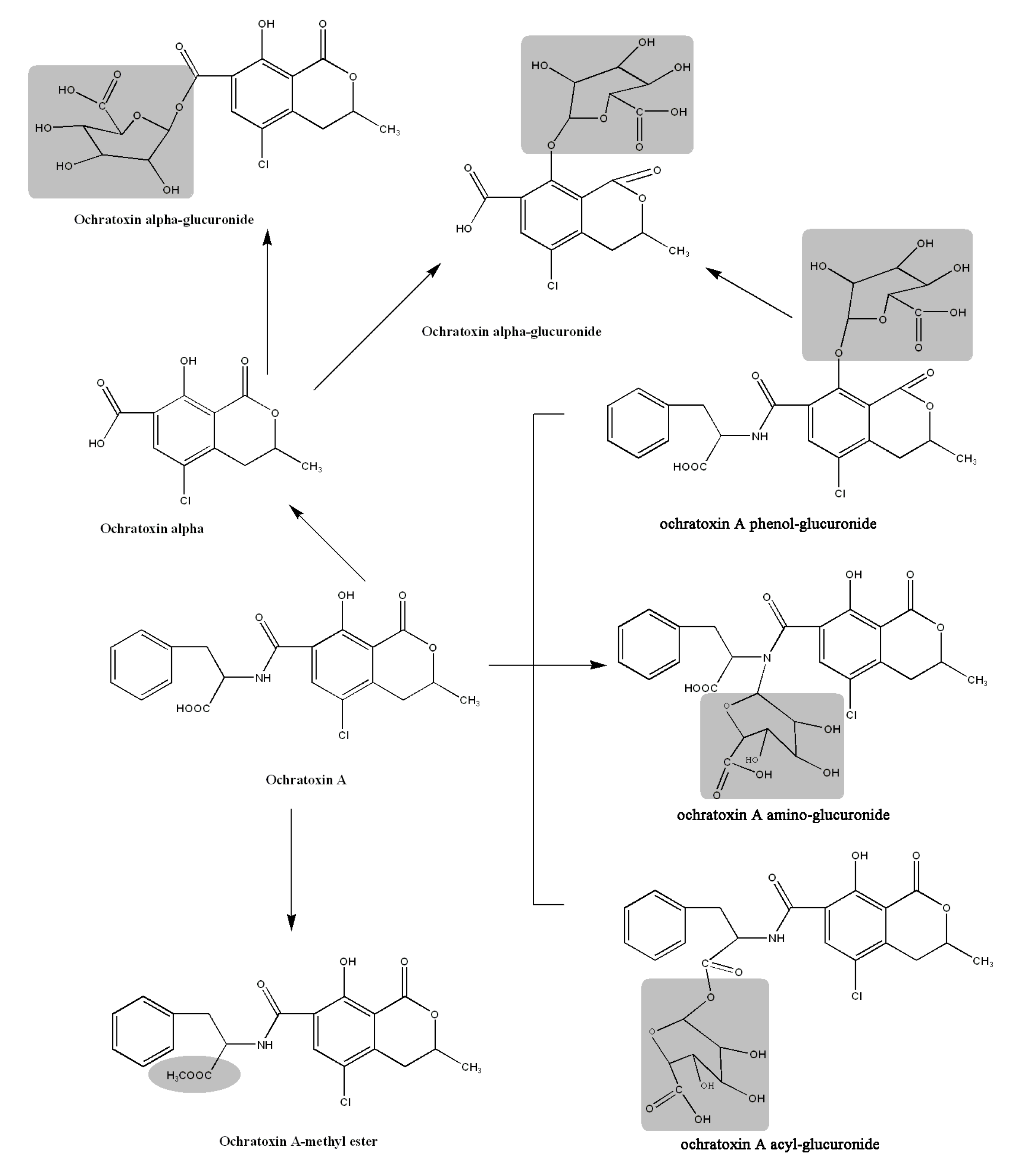
2.6. Proposed Metabolic Pathways
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. UHPLC-MS/MS Analysis
3.3. UHPLC-Orbitrap-HRMS Analysis
3.4. LC-Ion-Trap Analysis
3.5. Model Reactions
3.6. Hydrolysis of the Glucuronides
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizzo, I.; Vedoya, G.; Maurutto, S.; Haidukowski, M.; Varsavsky, E. Assessment of toxigenic fungi on Argentinean medicinal herbs. Microbiol. Res. 2004, 159, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrecht-Pflumio, S.; Chassat, T.; Dirheimer, G.; Marzin, D. Genotoxicity of ochratoxin A by Salmonella mutagenicity test after bioactivation by mouse kidney microsomes. Mutat. Res. 1999, 446, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, J.E. Carcinogenicity of ochratoxin A in experimental animals. IARC Sci. Publ. 1991, 229–244. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliano, N.; Donne, I.D.; Torri, C.; Migliori, M.; Grizzi, F.; Milzani, A.; Filippi, C.; Annoni, G.; Colombo, P.; Costa, F.; et al. Early cytotoxic effects of ochratoxin A in rat liver: A morphological, biochemical and molecular study. Toxicology 2006, 225, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, N.; Torri, C.; Donetti, E.; Grizzi, F.; Costa, F.; Bertelli, A.A.; Migliori, M.; Filippi, C.; Bedoni, M.; Panichi, V.; Giovannini, L.; Gioia, M. Ochratoxin A-induced renal cortex fibrosis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: molecular mechanisms of ochratoxin A-injury and potential effects of red wine. Mol. Med. 2005, 11, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. Ochratoxin A: An overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. An update on direct genotoxicity as a molecular mechanism of ochratoxin a carcinogenicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castegnaro, M.; Canadas, D.; Vrabcheva, T.; Petkova-Bocharova, T.; Chernozemsky, I.N.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Balkan endemic nephropathy: Role of ochratoxins A through biomarkers. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Petkova-Bocharova, T.; Chernozemsky, I.N.; Castegnaro, M. Balkan endemic nephropathy and associated urinary tract tumours: A review on aetiological causes and the potential role of mycotoxins. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Tozlovanu, M.; Manderville, R.; Peraica, M.; Castegnaro, M.; Stefanovic, V. New molecular and field evidences for the implication of mycotoxins but not aristolochic acid in human nephropathy and urinary tract tumor. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Ochratoxin A and aristolochic acid involvement in nephropathies and associated urothelial tract tumours. Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 2009, 60, 465–483. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Monograph on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risk to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 82, pp. 171–300. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Regulation (EC). No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. 2001; 466. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Opinion of the Scientific Panel on contaminants in the food chain [CONTAM] related to ochratoxin A in food. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Milićević Dragan, R.; Jurić Verica, B.; Vuković Dubravka, Z.; Mandić Miodrag, M.; Baltić Tatjana, M. Residue of ochratoxin A in swine tissues: Risk assessment. Arch. Oncol. 2009, 17, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.C.; Pena, A.; Lino, C.M. Human ochratoxin a biomarkers—From exposure to effect. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2011, 41, 187–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malir, F.; Ostry, V.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Roubal, T. Ochratoxin A exposure biomarkers in the Czech Republic and comparison with foreign countries. Biomarkers 2012, 17, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, J.; Liao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Y.; De Saeger, S.; Wu, A. Combinatorial approach of LC-MS/MS and LC-TOF-MS for uncovering in vivo kinetics and biotransformation of ochratoxin A in rat. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 925, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Castegnaro, M. Further arguments in favour of direct covalent binding of Ochratoxin A (OTA) after metabolic biotransformation. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22 Suppl 1, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringot, D.; Chango, A.; Schneider, Y.J.; Larondelle, Y. Toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics of ochratoxin A, an update. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 159, 18–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucet-Marquis, V.; Pont, F.; Stormer, F.C.; Rizk, T.; Castegnaro, M.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Evidence of a new dechlorinated ochratoxin A derivative formed in opossum kidney cell cultures after pretreatment by modulators of glutathione pathways: correlation with DNA-adduct formation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Dohnal, V.; Huang, L.; Kuca, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Yuan, Z. Metabolic pathways of ochratoxin A. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manderville, R.A.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Bioactivation and DNA adduction as a rationale for ochratoxin A carcinogenesis. World Mycotoxin J. 2008, 1, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozlovanu, M.; Faucet-Marquis, V.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. Genotoxicity of the hydroquinone metabolite of ochratoxin A: structure-activity relationships for covalent DNA adduction. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozlovanu, M.; Canadas, D.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Frenette, C.; Paugh, R.J.; Manderville, R.A. Glutathione conjugates of ochratoxin A as biomarkers of exposure. Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 2012, 63, 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings-Gee, J.E.; Tozlovanu, M.; Manderville, R.; Miller, M.S.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Schwartz, G.G. Ochratoxin A: In utero exposure in mice induces adducts in testicular DNA. Toxins 2010, 2, 1428–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maul, R.; Warth, B.; Kant, J.S.; Schebb, N.H.; Krska, R.; Koch, M.; Sulyok, M. Investigation of the hepatic glucuronidation pattern of the Fusarium mycotoxin deoxynivalenol in various species. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2715–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warth, B.; Sulyok, M.; Berthiller, F.; Schuhmacher, R.; Krska, R. New insights into the human metabolism of the Fusarium mycotoxins deoxynivalenol and zearalenone. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 220, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikula, H.; Weber, J.; Lexmuller, S.; Bichl, G.; Schwartz, H.; Varga, E.; Berthiller, F.; Hametner, C.; Krska, R.; Frohlich, J. Simultaneous preparation of alpha/beta-zearalenol glucosides and glucuronides. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 373, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, G.S.; Burger, H.M.; Gambacorta, L.; Gong, Y.Y.; Krska, R.; Rheeder, J.P.; Solfrizzo, M.; Srey, C.; Sulyok, M.; Visconti, A.; et al. Multiple mycotoxin exposure determined by urinary biomarkers in rural subsistence farmers in the former Transkei, South Africa. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warth, B.; Sulyok, M.; Fruhmann, P.; Mikula, H.; Berthiller, F.; Schuhmacher, R.; Hametner, C.; Abia, W.A.; Adam, G.; Frohlich, J.; et al. Development and validation of a rapid multi-biomarker liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method to assess human exposure to mycotoxins. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Marquardt, R.R.; Frohlich, A.A.; Vitti, T.G.; Crow, G. Pharmacokinetics of ochratoxin A and its metabolites in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1997, 145, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, I.; Valenta, H.; Rohr, K. Determination of ochratoxin A in bile of swine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 1995, 668, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross-Steinmeyer, K.; Weymann, J.; Hege, H.G.; Metzler, M. Metabolism and lack of DNA reactivity of the mycotoxin ochratoxin A in cultured rat and human primary hepatocytes. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2002, 50, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsch, T.; Humpf, H.U. HT-2 Toxin 4-glucuronide as new T-2 toxin metabolite: Enzymatic synthesis, analysis, and species specific formation of T-2 and HT-2 toxin glucuronides by rat, mouse, pig, and human liver microsomes. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2012, 60, 10170–10178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapolla, C.; Cangemi, G.; Barco, S.; Barbagallo, L.; Bugnone, D.; Maffia, A.; Melioli, G.; Profumo, A.; Benatti, U.; Damonte, G. Identification and structural characterization by LC-ESI-IONTRAP and LC-ESI-TOF of some metabolic conjugation products of homovanillic acid in urine of neuroblastoma patients. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Luan, L.; Ren, Y.; Wu, Y. Analysis of ochratoxin A and ochratoxin B in traditional Chinese medicines by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using [(13)C(20)]-ochratoxin A as an internal standard. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4365–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenette, C.; Paugh, R.J.; Tozlovanu, M.; Juzio, M.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. Structure-activity relationships for the fluorescence of ochratoxin A: Insight for detection of ochratoxin A metabolites. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 617, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjeba-Medjdoub, K.; Tozlovanu, M.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Frenette, C.; Paugh, R.J.; Manderville, R.A. Structure-activity relationships imply different mechanisms of action for ochratoxin A-mediated cytotoxicity and genotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggi, R.; Addison, R.S.; King, A.R.; Suthers, B.D.; Dickinson, R.G. Conjugation of desmethylnaproxen in the rat—A novel acyl glucuronide-sulfate diconjugate as a major biliary metabolite. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2002, 30, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Tallman, M.N.; Ali, S.Y.; Smith, P.C. UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 is the principal enzyme responsible for etoposide glucuronidation in human liver and intestinal microsomes: Structural characterization of phenolic and alcoholic glucuronides of etoposide and estimation of enzyme kinetics. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 371–380. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, K.; Nouri, P.; Kavetskaia, O. Challenges in the indirect quantitation of acyl-glucuronide metabolites of a cardiovascular drug from complex biological mixtures in the absence of reference standards. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, K.; Blaszkewicz, M.; Degen, G.H. Simultaneous analysis of ochratoxin A and its major metabolite ochratoxin alpha in plasma and urine for an advanced biomonitoring of the mycotoxin. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronel, M.B.; Marin, S.; Tarrago, M.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Ramos, A.J.; Sanchis, V. Ochratoxin A and its metabolite ochratoxin alpha in urine and assessment of the exposure of inhabitants of Lleida, Spain. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almela, L.; Rabe, V.; Sanchez, B.; Torrella, F.; Lopez-Perez, J.P.; Gabaldon, J.A.; Guardiola, L. Ochratoxin A in red paprika: relationship with the origin of the raw material. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Murphy, P.; Cunnick, J.; Hendrich, S. Synthesis and characterization of deoxynivalenol glucuronide: Its comparative immunotoxicity with deoxynivalenol. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Supplementary Files
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Z.; Tangni, E.K.; Di Mavungu, J.D.; Vanhaecke, L.; De Saeger, S.; Wu, A.; Callebaut, A. In Vitro Glucuronidation of Ochratoxin A by Rat Liver Microsomes. Toxins 2013, 5, 2671-2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5122671
Han Z, Tangni EK, Di Mavungu JD, Vanhaecke L, De Saeger S, Wu A, Callebaut A. In Vitro Glucuronidation of Ochratoxin A by Rat Liver Microsomes. Toxins. 2013; 5(12):2671-2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5122671
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Zheng, Emmanuel K. Tangni, José Diana Di Mavungu, Lynn Vanhaecke, Sarah De Saeger, Aibo Wu, and Alfons Callebaut. 2013. "In Vitro Glucuronidation of Ochratoxin A by Rat Liver Microsomes" Toxins 5, no. 12: 2671-2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5122671
APA StyleHan, Z., Tangni, E. K., Di Mavungu, J. D., Vanhaecke, L., De Saeger, S., Wu, A., & Callebaut, A. (2013). In Vitro Glucuronidation of Ochratoxin A by Rat Liver Microsomes. Toxins, 5(12), 2671-2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5122671