Characterization of Fumonisin A-Series by High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
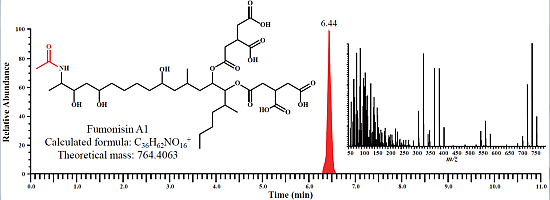
2.1. Determination of Fumonisins by an LC-Orbitrap
| Factor | FB1 | FB2 | FB3 | Compound I | Compound II | Compound III |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured mass (m/z) | 722.3973 | 706.4020 | 706.4015 | 764.4059 | 748.4123 | 748.4118 |
| Calculated formula | C34H60NO15+ | C34H60NO14+ | C34H60NO14+ | C36H62NO16+ | C36H62NO15+ | C36H62NO15+ |
| Theoretical mass (m/z) | 722.3958 | 706.4008 | 706.4008 | 764.4063 | 748.4114 | 748.4114 |
| Mass error (ppm) | 1.59 | 1.21 | 0.66 | −0.48 | 1.20 | 0.54 |

2.2. Characterization of the Fragment Ions for FB1, FB2, and FB3

| ID | FB1 | FB2 | FB3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Mass (m/z) | Calculated Formula [M + H]+ | Mass Error (ppm) | Measured Mass (m/z) | Calculated Formula [M + H]+ | Mass Error (ppm) | Measured Mass (m/z) | Calculated Formula [M + H]+ | Mass Error (ppm) | |
| 1 | 74.0601 | C3H8NO | 1.17 | 74.0601 | C3H8NO | 1.17 | |||
| 2 | 159.0290 | C6H7O5 | 1.40 | 159.0290 | C6H7O5 | 0.92 | 159.0290 | C6H7O5 | 1.21 |
| 3 | 170.1540 | C10H20NO | 0.39 | ||||||
| 4 | 186.1492 | C10H20NO2 | 1.77 | ||||||
| 5 | 220.2059 | C15H26N | -0.35 | 220.2058 | C15H26N | −1.03 | |||
| 6 | 236.2013 | C15H26NO | 1.77 | ||||||
| 7 | 238.2168 | C15H28NO | 0.96 | 238.2167 | C15H28NO | 0.56 | |||
| 8 | 254.2118 | C15H28NO2 | 1.44 | ||||||
| 9 | 256.2276 | C15H30NO2 | 1.93 | 256.2272 | C15H30NO2 | 0.26 | |||
| 10 | 272.2226 | C15H30NO3 | 0.88 | ||||||
| 11 | 316.3001 | C22H38N | 0.83 | ||||||
| 12 | 318.3157 | C22H40N | 0.65 | 318.3158 | C22H40N | 0.85 | |||
| 13 | 334.3106 | C22H40NO | 0.59 | ||||||
| 14 | 336.3263 | C22H42NO | 0.51 | 336.3262 | C22H42NO | 0.42 | |||
| 15 | 352.3213 | C22H42NO2 | 0.72 | ||||||
| 16 | 354.3369 | C22H44NO2 | 0.56 | 354.3369 | C22H44NO2 | 0.56 | |||
| 17 | 370.3318 | C22H44NO3 | 0.58 | ||||||
| 18 | 492.3330 | C28H46NO6 | 2.18 | ||||||
| 19 | 494.3478 | C28H48NO6 | 0.27 | 494.3480 | C28H48NO6 | 0.76 | |||
| 20 | 510.3431 | C28H48NO7 | 1.14 | ||||||
| 21 | 512.3592 | C28H50NO7 | 1.98 | 512.3593 | C28H50NO7 | 2.10 | |||
| 22 | 528.3538 | C28H50NO8 | 1.38 | ||||||
| 23 | 530.3693 | C28H52NO8 | 0.98 | 530.3691 | C28H52NO8 | 0.63 | |||
| 24 | 546.3630 | C28H52NO9 | −1.13 | ||||||
| 25 | 668.3648 | C34H54NO12 | 1.04 | ||||||
| 26 | 670.3806 | C34H56NO12 | 1.27 | 670.3789 | C34H56NO12 | −1.27 | |||
| 27 | 686.3731 | C34H56NO13 | −2.29 | ||||||
| 28 | 688.3909 | C34H58NO13 | 0.87 | 688.3903 | C34H58NO13 | −0.01 | |||
| 29 | 704.3867 | C34H58NO14 | 2.18 | ||||||
| 30 | 706.4016 | C34H60NO14 | 1.02 | 706.4016 | C34H60NO14 | 1.10 | |||
| 31 | 722.3966 | C34H60NO15 | 1.11 | ||||||
2.3. Analysis of Fragment Ions for Compounds I, II, and III

| ID | Compound I | Compound II | Compound III | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Mass (m/z) | Calculated Formula [M + H]+ | Mass Error (ppm) | Measured Mass (m/z) | Calculated Formula [M + H]+ | Mass Error (ppm) | Measured Mass (m/z) | Calculated Formula [M + H]+ | Mass Error (ppm) | |
| 0' | 60.0444 | C2H6NO | 0.21 | 60.0445 | C2H6NO | 1.42 | 60.0444 | C2H6NO | 0.72 |
| 1 | 74.0601 | C3H8NO | 0.25 | 74.0601 | C3H8NO | 0.97 | |||
| 1’ | 116.0706 | C5H10NO2 | −0.35 | 116.0707 | C5H10NO2 | 0.70 | |||
| 2 | 159.0288 | C6H7O5 | −0.04 | 159.0289 | C6H7O5 | 0.53 | 159.0289 | C6H7O5 | 0.44 |
| 3 | 170.1541 | C10H20NO | 0.75 | ||||||
| 3' | 212.1646 | C12H22NO2 | 0.21 | ||||||
| 4' | 228.1594 | C12H22NO3 | −0.13 | ||||||
| 5 | 220.2060 | C15H26N | 0.29 | 220.2061 | C15H26N | 0.42 | |||
| 5' | 262.2168 | C17H28NO | 0.99 | ||||||
| 6 | 236.2003 | C15H26NO | −2.38 | ||||||
| 6' | 278.2114 | C17H28NO2 | −0.20 | ||||||
| 7 | 238.2167 | C15H28NO | 0.84 | 238.2164 | C15H28NO | −0.78 | |||
| 7' | 280.2264 | C17H30NO2 | −2.70 | 280.2274 | C17H30NO2 | 0.89 | |||
| 8' | 296.2205 | C17H30NO3 | −2.07 | ||||||
| 11 | 316.2997 | C22H38N | −0.61 | ||||||
| 11' | 358.3106 | C24H40NO | 0.39 | ||||||
| 12 | 318.3156 | C22H40N | 0.08 | 318.3155 | C22H40N | −0.02 | |||
| 12' | 360.3261 | C24H42NO | −0.12 | 360.3260 | C24H42NO | −0.37 | |||
| 13 | 334.3102 | C22H40NO | −0.78 | ||||||
| 13' | 376.3208 | C24H42NO2 | −0.46 | ||||||
| 14 | 336.3261 | C22H42NO | 0.15 | 336.3260 | C22H42NO | −0.21 | |||
| 14' | 378.3367 | C24H44NO2 | 0.12 | 378.3367 | C24H44NO2 | 0.12 | |||
| 15 | 352.3202 | C22H42NO2 | −2.40 | ||||||
| 15' | 394.3315 | C24H44NO3 | −0.07 | ||||||
| 16 | 354.3371 | C22H44NO2 | 1.34 | ||||||
| 16' | 396.3475 | C24H46NO3 | 0.64 | 396.3473 | C24H46NO3 | 0.25 | |||
| 17' | 412.3418 | C24H46NO4 | −0.75 | ||||||
| 18' | 534.3431 | C30H48NO7 | 1.14 | ||||||
| 19' | 536.3582 | C30H50NO7 | 0.08 | 536.3591 | C30H50NO7 | 1.66 | |||
| 20' | 552.3516 | C30H50NO8 | −2.67 | ||||||
| 21' | 554.3691 | C30H52NO8 | 0.72 | 554.3691 | C30H52NO8 | 0.61 | |||
| 22' | 570.3637 | C30H52NO9 | −0.02 | ||||||
| 23' | 572.3793 | C30H54NO9 | −0.06 | 572.3794 | C30H54NO9 | 0.15 | |||
| 24' | 588.3752 | C30H54NO10 | 1.63 | ||||||
| 25' | 710.3760 | C36H56NO13 | 2.00 | ||||||
| 26' | 712.3914 | C36H58NO13 | 1.53 | 712.3902 | C36H58NO13 | −0.10 | |||
| 27' | 728.3850 | C36H58NO14 | −0.32 | ||||||
| 28' | 730.4010 | C36H60NO14 | 0.23 | 730.4014 | C36H60NO14 | 0.82 | |||
| 29' | 746.3956 | C36H60NO15 | −0.24 | ||||||
| 30' | 748.4123 | C36H62NO15 | 1.20 | 748.4118 | C36H62NO15 | 0.54 | |||
| 31' | 764.4059 | C36H62NO16 | −0.48 | ||||||
2.4. Characterization of Compound I Using the FA1 Standard

2.5. Determination of FA1, FB1, FB2, and FB3 in MTC-9999E
| Validation item | FA1 | FB1 | FB2 | FB3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linearity (r) | 0.9987 | 0.9989 | 0.9995 | 0.9972 |
| Recovery (%) | 101.8 | 99.0 | 100.2 | 96.4 |
| Intraday-precision (%) | 5.3 | 9.0 | 5.0 | 10.8 |
| LOD (μg/kg) | 0.73 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.12 |
| LOQ (μg/kg) | 2.44 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 0.40 |
| Analytical level (mg/kg) | 4.2 | 28.6 | 8.9 | 2.0 |
| Acceptance limit (mg/kg) | - | 28.3 ± 7.6 | 7.1 ± 1.9 | 1.7 ± 0.5 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Sample, Chemicals, and Reagents
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. LC-Orbitrap MS Analysis
3.4. Synthesis of FA1 from FB1 and the Characterization of the Structures by NMR Analysis
3.5. Validation of the Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussein, H.S.; Brasel, J.M. Toxicity, metabolism, and impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. Toxicology 2001, 167, 101–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norred, W.P. Fumonisins-Mycotoxins prodused by Fusarium moniliforme. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1993, 38, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 82, pp. 301–366. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA regulatory guidance for mycotoxins. Available online: http://www.ngfa.org/wp-content/uploads/NGFAComplianceGuide-FDARegulatoryGuidanceforMycotoxins8-2011.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2014).
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in food-stuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, L364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzaro, I.; Falavigna, C.; Dall’Asta, C.; Proctor, R.H.; Galaverna, G.; Battilani, P. Fumonisin B, A and C profile and masking in Fusarium verticillioides strains on fumonisin-inducing and maize-based media. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 159, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, S.M.; Eppley, R.M.; Mazzola, E.P.; Hadden, C.E.; Shockcor, J.P.; Crouch, R.C.; Martin, G.E. Identification of an N-acetyl keto derivative of fumonisin B1 in corn cultures of Fusarium proliferatum. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, S.M.; Plattner, R.D. Fumonisin composition in cultures of Fusarium moniliforme, Fusarium proliferatum, and Fusarium nygami. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheeder, J.P.; Marasas, W.F.O.; Vismer, H.F. Production of fumonisin analogs by Fusarium species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2101–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewram, V.; Mshicileli, N.; Shephard, G.S.; Vismer, H.F.; Rheeder, J.P.; Lee, Y.-W.; Leslie, J.F.; Marasas, W.F.O. Production of fumonisin B and C analogues by several Fusarium species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4861–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzaro, I.; Falavigna, C.; Galaverna, G.; Dall’Asta, C.; Battilani, P. Cornmeal and starch influence the dynamic of fumonisin B, A and C production and masking in Fusarium verticillioides and F. proliferatum. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 166, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Westhuizen, L.; Shephard, G.S.; Snyman, S.D.; Abel, S.; Swanevelder, S.; Gelderblom, W.C.A. Inhibition of sphingolipid biosynthesis in rat primary hepatocyte cultures by fumonisin B1 and other structurally related compounds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.K.; Shier, W.T.; Seo, J.A.; Lee, Y.W.; Musser, S.M. Phytotoxicity and cytotoxicity of the fumonisin C and P series of mycotoxins from Fusarium spp. fungi. Toxicon 1998, 36, 2033–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songsermsakul, P.; Razzazi-Fazeli, E. A review of recent trends in applications of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for determination of mycotoxins. J. Liq. Chrom. Relat. Technol. 2008, 31, 1641–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubert, J.; Soler, C.; Marín, R.; James, K.J.; Mañes, J. Mass spectgrometry strategies for mycotoxins analysis in Europian beers. Food Control 2013, 30, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herebian, D.; Zühlke, S.; Lamshöft, M.; Spiteller, M. Multi-Mycotoxin analysis in complex biological matrices using LC-ESI/MS: Experimental study using triple stage quadrupole and LTQ-Orbitrap. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Sakamoto, S.; Sago, Y.; Nagashima, H. Detection of type A trichothecene di-glucosides produced in corn by high-resolution liquid chromatography-orbitrap mass spectrometry. Toxins 2013, 5, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariasova, M.; Vaclavikova, M.; Lacina, O.; Vaclavik, L.; Hajslova, J. Deoxynivalenol oligoglycosides: “Masked” Fusarium toxins occurring in malt, beer, and breadstuff. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9280–9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.; Lattanzio, V.M.; Schena, R.; Visconti, A.; Pascale, M. Use of liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry for isolation and characterization of hydrolyzed fumonisins and relevant analysis in maize-based products. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 49, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson, M.; Klejnstrup, M.L.; Phipps, R.K.; Nielsen, K.F.; Frisvad, J.C.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Larsen, T.O. Isolation and NMR characterization of fumonisin B2 and a new fumonisin B6 from Aspergillus niger. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, J.; Iida, J.; Nagatomi, Y.; Mochizuki, N. Minimization of carryover for high-throughput liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry analysis of 14 mycotoxins in corn grits. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas Shier, W.; Abbas, H.K.; Badria, F.A. Complete structures of the sphingosine analog mycotoxin fumonisin B1 and ALL toxin TA: Absolute configuration of the side chains. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 1571–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.C.; Dutcher, J.D. Separation of acetylated neomycins B and C by paper chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 836–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamura, M.; Mochizuki, N.; Nagatomi, Y.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K. Characterization of Fumonisin A-Series by High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2014, 6, 2580-2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6082580
Tamura M, Mochizuki N, Nagatomi Y, Toriba A, Hayakawa K. Characterization of Fumonisin A-Series by High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Toxins. 2014; 6(8):2580-2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6082580
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamura, Masayoshi, Naoki Mochizuki, Yasushi Nagatomi, Akira Toriba, and Kazuichi Hayakawa. 2014. "Characterization of Fumonisin A-Series by High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry" Toxins 6, no. 8: 2580-2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6082580
APA StyleTamura, M., Mochizuki, N., Nagatomi, Y., Toriba, A., & Hayakawa, K. (2014). Characterization of Fumonisin A-Series by High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Toxins, 6(8), 2580-2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6082580