Cytotoxic Activity and Antiproliferative Effects of Crude Skin Secretion from Physalaemus nattereri (Anura: Leptodactylidae) on in vitro Melanoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
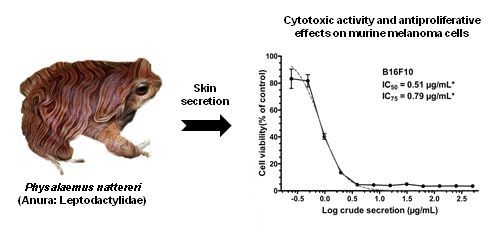
2.1. P. nattereri Crude Secretion Decreased Cell Viability in a Dose-Dependent Manner

2.2. Crude Skin Secretion Induced Changes in Cell Morphology

2.3. Crude Skin Secretion Induced Slight Changes in Cell Size and Granularity
2.4. Crude Skin Secretion Caused Alterations in Melanoma Cell Plasma Membrane


2.5. Crude Skin Secretion Reduced Mitochondrial Membrane Potential of Melanoma Cells

2.6. Crude Skin Secretion Induced Slight Changes in Cell Cycle Pattern of Melanoma Cells

2.7. Liquid Chromatographic Fractionation of P. nattereri Crude Skin Secretion, Antiproliferative, Hemolytic and Antibacterial Screenings, and Mass Spectrometry Analysis

3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Collection of Specimens and Skin Secretion
4.2. Cell Treatment
4.3. Cell Viability Assay (MTT)
4.4. Investigation of the Mechanism of Action of P. nattereri Crude Skin Secretion on Melanoma Cells
4.4.1. Cell Morphology Analysis
4.4.2. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide Staining
4.4.3. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Liquid Chromatographic Fractionation of P. nattereri Crude Skin Secretion, Antiproliferative, Hemolytic and Antibacterial Screenings, and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Cancer Institute. What You Need to Know about Melanoma and Other Skin Cancers; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010.
- Thompson, J.F.; Scolyer, R.A.; Kefford, R.F. Cutaneous melanoma. Lancet 2005, 365, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subik, K.; Lee, J.F.; Baxter, L.; Strzepek, T.; Costello, D.; Crowley, P.; Xing, L.; Hung, M.C.; Bonfiglio, T.; Hicks, D.G.; et al. The expression patterns of ER, PR, HER2, CK5/6, EGFR, Ki-67 and AR by immunohistochemical analysis in breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer: Basic Clin. Res. 2010, 4, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Pukala, T.L.; Bowie, J.H.; Maselli, V.M.; Musgrave, I.F.; Tyler, M.J. Host-Defence peptides from the glandular secretions of amphibians: Structure and activity. Nat. Product Rep. 2006, 23, 368–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.V.R.; Shahani, S.K.; Meherji, P.K. Spermicidal activity of magainins: In vitro and in vivo studies. Contraception 1996, 53, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.V.R.; Yedery, R.D.; Aranha, C. Antimicrobial peptides: Premises and promises. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 24, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krugliak, M.; Feder, R.; Zolotarev, V.Y.; Gaidukov, L.; Dagan, A.; Ginsburg, H.; Mor, A. Antimalarial activities of dermaseptin S4 derivatives. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangoni, M.L.; Papo, N.; Saugar, J.M.; Barra, D.; Shai, Y.; Simmaco, M.; Rivas, L. Effect of natural L- to D-amino acid conversion on the organization, membrane binding, and biological function of the antimicrobial peptides bombinins H. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 4266–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi-Mattos, R.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Jared, C. The inguinal macroglands of the frog Physalaemus nattereri (Leptodactylidae): Structure, toxic secretion and relationship with deimatic behaviour. J. Zool. 2005, 266, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogawa, T.; Kamano, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Pettit, G.R. Isolation and structure of five new cancer cell growth inhibitory bufadienolides from the Chinese traditional drug Ch’an Su. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Guo, D.A. Analysis of bufadienolides in the Chinese drug ChanSu by high-performance liquid chromatography with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X. Systematic screening and characterization of novel bufadienolides from toad skin using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, R.C.; Jared, C. Cutaneous granular glands and amphibian venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A: Physiol. 1995, 111, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, B.T. The natural history of amphibian skin secretions, their normal functioning and potential medical applications. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1997, 72, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zoggel, H.; Hamma-Kourbali, Y.; Galanth, C.; Ladram, A.; Nicolas, P.; Courty, J.; Amiche, M.; Delbé, J. Antitumor and angiostatic peptides from frog skin secretions. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libério, M.S.; Joanitti, G.A.; Fontes, W.; Castro, M.S. Anticancer peptides and proteins: A panoramic view. Protein Pept. Lett. 2013, 20, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, J.S.; Hoskin, D.W. Cationic antimicrobial peptides as novel cytotoxic agents for cancer treatment. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2006, 15, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Quispe, C.; Theoduloz, C.; de Sousa, P.T., Jr.; Parizotto, C. Antiproliferative activity and new argininyl bufadienolide esters from the “cururú” toad Rhinella (Bufo) schneideri. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, F.; Li, A.; Zhao, L.; Xu, H.; Inagaki, Y.; Wang, D.; Cui, X.; Gao, B.; Kokudo, N.; Nakata, M.; et al. Cinobufacini, an aqueous extract from Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor, induces apoptosis through a mitochondria-mediated pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, B.; Gomes, A.; Debnath, A.; Saha, A.; Biswas, A.K.; Dasgupta, S.C.; Gomes, A. Antiproliferative, cytotoxic and apoptogenic activity of Indian toad (Bufo melanostictus, Schneider) skin extract on U937 and K562 cells. Toxicon 2006, 48, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, P.M.P.; Lima, D.J.B.; Debiasi, B.W.; Soares, B.M.; da Conceição Machado, K.; da Costa Noronhaf, J.; de Jesus Rodriguese, D.; Sinhorin, A.P.; Pessoa, C.; Vieira Júnior, G.M. Antiproliferative activity of Rhinella marina and Rhaebo guttatus venom extracts from Southern Amazon. Toxicon 2013, 72, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciani, J.M.; de-Sá-Júnior, P.L.; Ferreira, A.K.; Pereira, A.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Jared, C.; Pimenta, D.C. Cytotoxic and antiproliferative effects of crude amphibian skin secretions on breast tumor cells. Biomed. Prev. Nutr. 2013, 3, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Nakaya, K.; Yoshida, T.; Kuroiwa, Y. Induction by bufalin of differentiation of human leukemia cells HL60, U937, and ML1 toward macrophage/monocyte-like cells and its potent synergistic effect on the differentiation of human leukemia cells in combination with other inducers. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 4634–4641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cunha-Filho, G.A.; Resck, I.S.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; Pessoa, C.O.; Moraes, M.O.; Ferreira, J.R.; Rodrigues, F.A.; dos Santos, M.L. Cytotoxic profile of natural and some modified bufadienolides from toad Rhinella schneideri parotoid gland secretion. Toxicon 2010, 56, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.-Y.; Huang, W.J.; Kan, S.-F.; Wang, P.S. Effects of bufalin and cinobufagin on the proliferation of androgen dependent and independent prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2003, 54, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boleti, A.P.; Ventura, C.A.; Justo, G.Z.; Silva, R.A.; de Sousa, A.C.; Ferreira, C.V.; Yano, T.; Macedo, M.L. Pouterin, a novel potential cytotoxic lectin-like protein with apoptosis-inducing activity in tumorigenic mammalian cells. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, S.S.; Bang, Y.J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, B.J. In vitro activities of native and designed peptide antibiotics against drug sensitive and resistant tumor cell lines. Peptides 2003, 24, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, M.; Robertson, J.D.; Gogvadze, V.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Orrenius, S. Cytochrome c release from mitochondria proceeds by a two-step process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Azevedo, R.A.; Figueiredo, C.R.; Ferreira, A.K.; Matsuo, A.L.; Massaoka, M.H.; Girola, N.; Auada, A.V.V.; Farias, C.F.; Pasqualoto, K.F.M.; Rodrigues, C.P.; et al. Mastoparan induces apoptosis in B16F10-Nex2 melanoma cells via the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway and displays antitumor activity in vivo. Peptides 2015, 68, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano, M.; Moreno, S. Regulation of CDK/cyclin complexes during the cell cycle. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Rishi, A.K.; Dawson, M.I.; Tschang, R.; Farhana, L.; Boyanapalli, M.; Reichert, U.; Shroot, B.; Van Buren, E.C.; Fontana, J.A. S-Phase arrest and apoptosis induced in normal mammary epithelial cells by a novel retinoid. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Teraishi, F.; Davis, J.J.; Jacob, D.; Fang, B. Induction of S-phase arrest and p21 overexpression by a small molecule 2[[3-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)propyl] amino]ethanol in correlation with activation of ERK. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4984–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enback, J.; Laakkonen, P. Tumour-homing peptides: Tools for targeting, imaging and destruction. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.S.; Thorne, S.H.; Bartlett, D.L. Oncolytic virotherapy: molecular targets in tumor-selective replication and carrier cell-mediated delivery of oncolytic viruses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1785, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, J.W.; Spande, T.F.; Garraffo, H.M. Alkaloids from amphibian skin: a tabulation of over eight-hundred compounds. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1556–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honorato, C.T.M. Análise peptidômica da secreção cutânea do anuro Eupemphix nattereri com ênfase na prospecção de peptídeos antimicrobianos. Master’s thesis, Universidade de Brasília, Brasília, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, E.A. Estrutura gênica, indução, expressão e processamento de peptídeos bioativos isolados a partir da secreção cutânea de Phyllomedusa azurea e Physalaemus nattereri. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Brasília, Brasília, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Libério, M.S.; Joanitti, G.A.; Azevedo, R.B.; Cilli, E.M.; Zanotta, L.C.; Nascimento, A.C.; Sousa, M.V.; Pires Júnior, O.R.; Fontes, W.; Castro, M.S. Anti-Proliferative and cytotoxic activity of pentadactylin isolated from Leptodactylus labyrinthicus on melanoma cells. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, H.-B.; Li, S.; Tian, L.-L.; Shang, D.-J. Antitumor effects and cell selectivity of temporin-1CEa, an antimicrobial peptide from the skin secretions of the Chinese brown frog (Rana chensinensis). Biochimie 2012, 94, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, I.; Scorciapino, M.A.; Manzo, G.; Casu, M.; Rinaldi, A.C.; Attoub, S.; Mechkarska, M.; Conlon, J.M. Conformational analysis and cytotoxic activities of the frog skin host-defense peptide, hymenochirin-1Pa. Peptides 2014, 61, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadidi, M.; Sioud, M. Selective targeting of cancer cells using synthetic peptides. Drug Resist. Updat. 2003, 6, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronot, X.; Benel, L.; Adolphe, M.; Mounolou, J.C. Mitochondrial analysis in living cells: The use of rhodamine 123 and flow cytometry. Biol. Cell 1986, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardi, C.; Nicoletti, I. Analysis of apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, M.S.; Ferreira, T.C.; Cilli, E.M.; Crusca, J.; Mendes-Giannini, M.J.S.; Sebben, A.; Ricart, C.A.; Sousa, M.V.; Fontes, W. Hylin a1, the first cytolytic peptide isolated from the arboreal South American frog Hypsiboas albopunctatus (“spotted treefrog”). Peptides 2009, 30, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, A.C.e.; Márquez, C.A.P.; Azevedo, R.B.; Joanitti, G.A.; Júnior, O.R.P.; Fontes, W.; Castro, M.S. Cytotoxic Activity and Antiproliferative Effects of Crude Skin Secretion from Physalaemus nattereri (Anura: Leptodactylidae) on in vitro Melanoma Cells. Toxins 2015, 7, 3989-4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7103989
Carvalho ACe, Márquez CAP, Azevedo RB, Joanitti GA, Júnior ORP, Fontes W, Castro MS. Cytotoxic Activity and Antiproliferative Effects of Crude Skin Secretion from Physalaemus nattereri (Anura: Leptodactylidae) on in vitro Melanoma Cells. Toxins. 2015; 7(10):3989-4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7103989
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Andréa Cruz e, César Augusto Prías Márquez, Ricardo Bentes Azevedo, Graziella Anselmo Joanitti, Osmindo Rodrigues Pires Júnior, Wagner Fontes, and Mariana S. Castro. 2015. "Cytotoxic Activity and Antiproliferative Effects of Crude Skin Secretion from Physalaemus nattereri (Anura: Leptodactylidae) on in vitro Melanoma Cells" Toxins 7, no. 10: 3989-4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7103989
APA StyleCarvalho, A. C. e., Márquez, C. A. P., Azevedo, R. B., Joanitti, G. A., Júnior, O. R. P., Fontes, W., & Castro, M. S. (2015). Cytotoxic Activity and Antiproliferative Effects of Crude Skin Secretion from Physalaemus nattereri (Anura: Leptodactylidae) on in vitro Melanoma Cells. Toxins, 7(10), 3989-4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7103989