Materials, Mechanics, and Patterning Techniques for Elastomer-Based Stretchable Conductors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Elastomers as the Substrate or Supporting Matrix
2.2. Electrical Conductors
2.2.1. Bulk Metal Films and Tracks
2.2.2. Metallic Nanowires
2.2.3. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials
2.2.4. Conductive Polymers
2.2.5. Liquid Metals and Ionic Liquids
3. Mechanics of the Stretchable Conductive Structure
3.1. Blending
3.2. Conductors in Microchannels
3.3. Stretchable Network on/Embedded in Elastomers
3.4. Geometry Design
3.5. Buckling
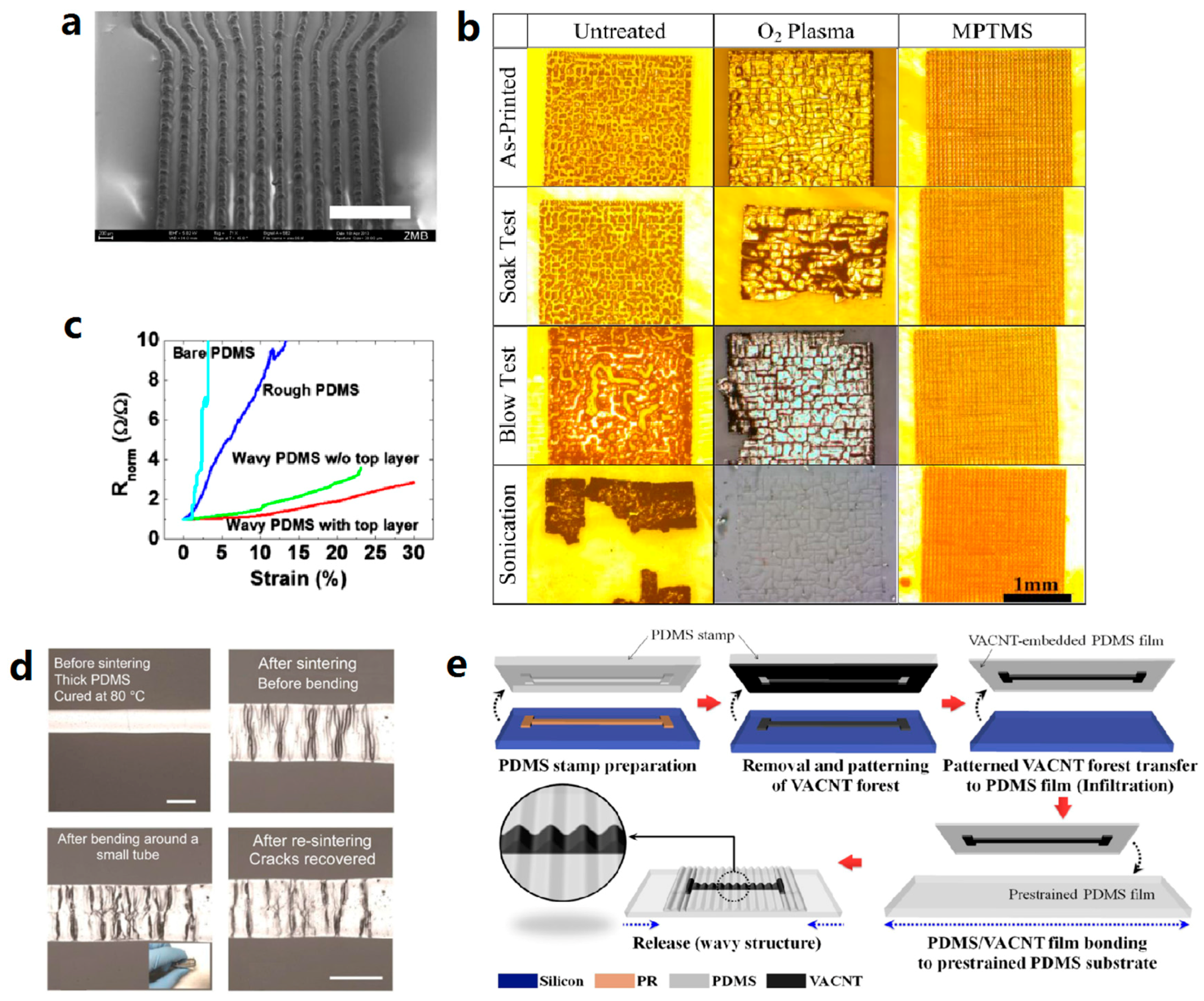
3.6. Out-of-Plane Design
3.7. Designs in Substrate
4. Patterning Techniques
4.1. Lithography
4.2. Stencil/Screen Printing
4.3. Direct Printing
4.4. Transfer Printing
5. Applicable Devices
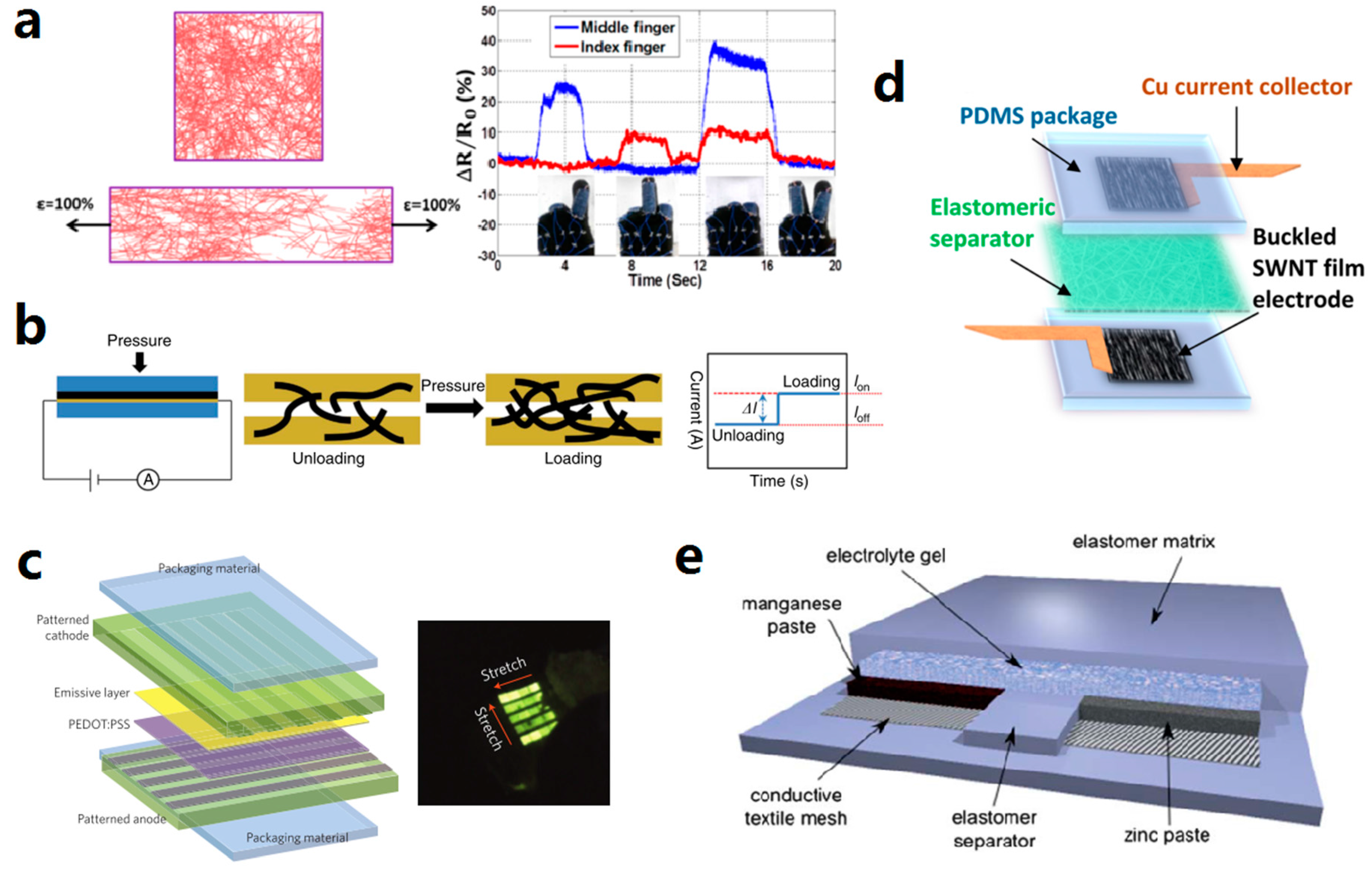
5.1. Sensors
5.2. Light-Emitting Circuits
5.3. Transistors
5.4. Energy Devices
6. Summary and Outlook
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowden, N.; Brittain, S.; Evans, A.G.; Hutchinson, J.W.; Whitesides, G.M. Spontaneous formation of ordered structures in thin films of metals supported on an elastomeric polymer. Nature 1998, 393, 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Liao, F.; Molesa, S.; Redinger, D.; Subramanian, V. Plastic-compatible low resistance printable gold nanoparticle conductors for flexible electronics. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, G412–G417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, A.; Ahnood, A.; Cole, M.T.; Lee, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Hiralal, P.; Bonaccorso, F.; Hasan, T.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Dyadyusha, A.; et al. Flexible electronics: The next ubiquitous platform. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 1486–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.A.; Someya, T.; Huang, Y. Materials and mechanics for stretchable electronics. Science 2010, 327, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, S.; Bauer, S. Materials for stretchable electronics. MRS Bull. 2012, 37, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Park, J.; Jeong, U. Design of conductive composite elastomers for stretchable electronics. Nano Today 2014, 9, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, W.-Y.; Huang, W. Stretchable thin-film electrodes for flexible electronics with high deformability and stretchability. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3349–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterial-enabled stretchable conductors: Strategies, materials and devices. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1480–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J. Stretchable thin film materials: Fabrication, application and mechanics. J. Electron. Packag. 2016, 138, 020801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoul, D.; Hu, W.; Gao, M.; Mehta, V.; Pei, Q. Recent advances in stretchable and transparent electronic materials. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1500407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.D.; Elias, A.L.; Chung, H.-J. Flexible electronics under strain: A review of mechanical characterization and durability enhancement strategies. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 2771–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacour, S.P.; Wagner, S.; Huang, Z.; Suo, Z. Stretchable gold conductors on elastomeric substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 2404–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.S.; Tien, J.; Chen, C.S. High-conductivity elastomeric electronics. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, J.; Fritz, G.; Kumar, P.; Lewis, P.; Miller, M.; Dineen, A.; Gray, C. Electrical characterization of traditional and aerosol jet printed conductors under tensile strain. MRS Adv. 2016, 1, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Gu, H.; Lin, W.; Yuen, M.M.; Wong, C.P.; Xiong, M.; Gao, B. Silver nanowires: From scalable synthesis to recyclable foldable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3052–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Vosguerichian, M.; Bao, Z. A review of fabrication and applications of carbon nanotube film-based flexible electronics. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1727–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pease, R.F.; Chou, S.Y. Lithography and other patterning techniques for future electronics. Proc. IEEE 2008, 96, 248–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lu, N.; Ma, R.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, R.-H.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Won, S.M.; Tao, H.; Islam, A.; et al. Epidermal electronics. Science 2011, 333, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larmagnac, A.; Eggenberger, S.; Janossy, H.; Vörös, J. Stretchable electronics based on Ag-PDMS composites. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Zhu, Y. Wearable multifunctional sensors using printed stretchable conductors made of silver nanowires. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Myers, A.C.; Adams, J.J.; Zhu, Y. Stretchable and reversibly deformable radio frequency antennas based on silver nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 4248–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-T.; Lee, D.; Sherry, A.; Grigoropoulos, C.P. Rapid selective metal patterning on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) fabricated by capillarity-assisted laser direct write. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 095018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, J.; Bao, B.; Wang, S.; He, M.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y. Fabrication of bendable circuits on a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) surface by inkjet printing semi-wrapped structures. Materials 2016, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Lee, J.; Song, H.; Kim, S.; Jeong, J.; Hong, Y. Inkjet-printed stretchable silver electrode on wave structured elastomeric substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 153110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Li, G.; Xu, K.; Tien, N.C.; Roberts, R.C.; Li, D. Inkjet-printed microelectrodes on PDMS as biosensors for functionalized microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Ren, X.; Kim, J.W.; Noh, H. Direct inkjet printing of micro-scale silver electrodes on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchip. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 115010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-K.; Kim, B.J.; Jang, H.; Yoon, S.C.; Lee, C.; Hong, B.H.; Rogers, J.A.; Cho, J.H.; Ahn, J.-H. Stretchable graphene transistors with printed dielectrics and gate electrodes. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4642–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Chang, Y.-H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. Conductive-on-demand: Tailorable polyimide/carbon nanotube nanocomposite thin film by dual-material aerosol jet printing. Carbon 2016, 98, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aga, R.; Jordan, C.; Aga, R.S.; Bartsch, C.M.; Heckman, E.M. Metal electrode work function modification using aerosol jet printing. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2014, 35, 1124–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, T.; Park, J.G.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.-M.; Wang, B. Conductivity enhancement of aerosol-jet printed electronics by using silver nanoparticles ink with carbon nanotubes. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 96, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.P.; Minev, I.; Graz, I.M.; Lacour, S.P. Microstructured silicone substrate for printable and stretchable metallic films. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4279–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, A.; Bowen, A.M.; Huang, Y.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Rogers, J.A. Transfer printing techniques for materials assembly and micro/nanodevice fabrication. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5284–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meitl, M.A.; Zhu, Z.-T.; Kumar, V.; Lee, K.J.; Feng, X.; Huang, Y.Y.; Adesida, I.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Rogers, J.A. Transfer printing by kinetic control of adhesion to an elastomeric stamp. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.-L.; Willett, R.L.; Baldwin, K.W.; Rogers, J.A. Interfacial chemistries for nanoscale transfer printing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 7654–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Kim, D.-H.; Lu, N.; Su, Y.; Kang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. Mechanics of epidermal electronics. J. Appl. Mech. 2012, 79, 031022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Cho, K.W.; Cho, H.R.; Wang, L.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.E.; Hyeon, T.; Lu, N.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, D.-H. Stretchable and transparent biointerface using cell-sheet-graphene hybrid for electrophysiology and therapy of skeletal muscle. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3207–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Leduc, C.; Ravussin, Y.; Li, S.; Davis, E.N.; Song, B.; Li, D.; Xu, K.; Accili, D.; Wang, Q.; et al. A differential dielectric affinity glucose sensor. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Lee, P.S. Stretchable energy storage and conversion devices. Small 2014, 10, 3443–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Wang, S. Theory for Stretchable Interconnects. In Stretchable Electronics; Someya, T., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Yeo, J.; Hong, S.; Nam, K.H.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.S.; Ko, S.H. Highly stretchable and highly conductive metal electrode by very long metal nanowire percolation network. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3326–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Hayamizu, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yomogida, Y.; Izadi-Najafabadi, A.; Futaba, D.N.; Hata, K. A stretchable carbon nanotube strain sensor for human-motion detection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Wavy ribbons of carbon nanotubes for stretchable conductors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, F. Buckling of aligned carbon nanotubes as stretchable conductors: A new manufacturing strategy. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Li, J.; Luan, P.; Dong, H.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Tu, M.; Zeng, Q.; Zhou, W.; Xie, S. Highly transparent and conductive stretchable conductors based on hierarchical reticulate single-walled carbon nanotube architecture. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 5238–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, U.H.; Jeong, D.-W.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, J.-M. Elastomer-infiltrated vertically aligned carbon nanotube film-based wavy-configured stretchable conductors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12909–12914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Shi, D.; Wang, E.; Zhang, G. Super-elastic graphene ripples for flexible strain sensors. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3645–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Li, X.; Zang, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K.; Wu, D.; Zhu, H. Wearable and highly sensitive graphene strain sensors for human motion monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4666–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Terentjev, E.M. Tailoring the electrical properties of carbon nanotube-polymer composites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 4062–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.S.; West, K.; Hassager, O.; Larsen, N.B. Highly stretchable and conductive polymer material made from poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) and polyurethane elastomers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3069–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Peng, S.; Liu, L.; Wen, W.; Sheng, P. Characterizing and patterning of PDMS-based conducting composites. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Nuñez-Flores, R.; Jia, W.; Wang, J. All-printed stretchable electrochemical devices. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3060–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, M.; Li, X.; Kim, C.; Hashimoto, M.; Wiley, B.J.; Ham, D.; Whitesides, G.M. Stretchable microfluidic radiofrequency antennas. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2749–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Hong, S.Y.; Lim, Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Zi, G.; Ha, J.S. Design and fabrication of novel stretchable device arrays on a deformable polymer substrate with embedded liquid-metal interconnections. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6580–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Wu, J.; Shi, M.; Yoon, J.; Park, S.-I.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. Stretchable GaAs photovoltaics with designs that enable high areal coverage. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohra, A.; Filiatrault, H.L.; Amyotte, S.D.; Carmichael, R.S.; Suhan, N.D.; Siegers, C.; Ferrari, L.; Davidson, G.J.E.; Carmichael, T.B. Reinventing butyl rubber for stretchable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 5222–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Kong, G.W.; Seo, J.H.; Ma, Y.; Jang, K.-I.; Fan, J.A.; Mao, S.; Chen, Q.; Li, D.; et al. Epidermal radio frequency electronics for wireless power transfer. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2016, 2, 16052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gu, T.; Wei, B. Dynamic and galvanic stability of stretchable supercapacitors. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6366–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Masarapu, C.; Rong, J.; Wei, B.; Jiang, H. Stretchable supercapacitors based on buckled single-walled carbon nanotube macrofilms. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4793–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Niu, X.; Zhao, R.; Pei, Q. Elastomeric transparent capacitive sensors based on an interpenetrating composite of silver nanowires and polyurethane. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 083303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Ghaffari, R.; Lu, N.; Rogers, J.A. Flexible and stretchable electronics for biointegrated devices. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. Mechanics and designs of stretchable bioelectronics. In Stretchable Bioelectronics for Medical Devices and Systems; Rogers, J.A., Ghaffari, R., Kim, D.-H., Eds.; Springer: Zug, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.N.; Park, C.; Whitesides, G.M. Solvent compatibility of poly(dimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6544–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, G.; Pecora, A.; Maiolo, L. Polysilicon thin-film transistors on polymer substrates. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2012, 15, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangla, R.; Gallaire, F.; Baroud, C.N. Microchannel deformations due to solvent-induced PDMS swelling. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.P.; Crosby, A.J. Fabricating microlens arrays by surface wrinkling. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3238–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.P.; Crosby, A.J. Spontaneous formation of stable aligned wrinkling patterns. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, A.; Fleischman, A.J.; Roy, S. Characterization of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) properties for biomedical micro/nanosystems. Biomed. Microdevices 2005, 7, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodas, D.; Khan-Malek, C. Hydrophilization and hydrophobic recovery of PDMS by oxygen plasma and chemical treatment-An SEM investigation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Roberts, R.C.; Tien, N.C.; Li, D. Inkjet Printed Silver Patterning on PDMS to Fabricate Microelectrodes for Microfluidic Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Sensors, Valencia, Spain, 2–5 November 2014; pp. 1100–1103.
- Efimenko, K.; Rackaitis, M.; Manias, E.; Vaziri, A.; Mahadevan, L.; Genzer, J. Nested self-similar wrinkling patterns in skins. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipomi, D.J.; Lee, J.A.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Bolander, J.A.; Bao, Z. Electronic properties of transparent conductive films of PEDOT:PSS on stretchable substrates. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huck, W.T.S.; Bowden, N.; Onck, P.; Pardoen, T.; Hutchinson, J.W.; Whitesides, G.M. Ordering of spontaneously formed buckles on planar surfaces. Langmuir 2000, 16, 3497–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft lithography. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1998, 28, 153–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Ham, J.; Lee, J.; Hong, S.; Han, S.; Suh, Y.D.; Lee, S.E.; Yeo, J.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, D.; et al. Highly stretchable or transparent conductor fabrication by a hierarchical multiscale hybrid nanocomposite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5671–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.Y.; Kim, K.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.T.; Han, C.-S. Highly conductive and stretchable Ag nanowire/carbon nanotube hybrid conductors. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 285203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.K.; Oh, J.; Lima, M.; Kozlov, M.E.; Kim, S.J.; Baughman, R.H. Elastomeric conductive composites based on carbon nanotube forests. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2663–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, N.; Pandya, S.; Liu, C. Multi-walled carbon nanotube filled conductive elastomers: Materials and application to micro transducers. In Proceedings of the 19th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Istanbul, Turkey, 22–26 January 2006; pp. 246–249.
- Ma, Z.; Su, B.; Gong, S.; Wang, Y.; Yap, L.W.; Simon, G.P.; Cheng, W. Liquid-wetting-solid strategy To fabricate stretchable sensors for human-motion detection. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Im, J.; Shin, M.; Min, Y.; Park, J.; Cho, H.; Park, S.; Shim, M.-B.; Jeon, S.; Chung, D.-Y.; et al. Highly stretchable electric circuits from a composite material of silver nanoparticles and elastomeric fibres. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Song, L.; Luan, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, X.; Tu, M.; Yang, F.; et al. Super-stretchable, transparent carbon nanotube-based capacitive strain sensors for human motion detection. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Cheng, H.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Ouyang, S.-C.; Kong, G.-W.; Yu, C.; et al. Epidermal impedance sensing sheets for precision hydration assessment and spatial mapping. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 2848–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Niu, X.; Li, L.; Yun, S.; Yu, Z.; Pei, Q. Intrinsically stretchable transparent electrodes based on silver-nanowire–crosslinked-polyacrylate composites. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 344002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettlgruber, G.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Siket, C.M.; Moser, R.; Graz, I.M.; Schwödiauer, R.; Bauer, S. Intrinsically stretchable and rechargeable batteries for self-powered stretchable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5505–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltenbrunner, M.; Kettlgruber, G.; Siket, C.; Schwödiauer, R.; Bauer, S. Arrays of ultracompliant electrochemical dry gel cells for stretchable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2065–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zang, J.; Rathmell, A.R.; Zhao, X.; Wiley, B.J. Reversible sliding in networks of nanowires. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2381–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, K.-Y.; Oh, Y.; Rho, J.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, H.R.; Baik, S. Highly conductive, printable and stretchable composite films of carbon nanotubes and silver. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecoflex® Series—Smooth-On. Available online: https://www.smooth-on.com/tb/files/ECOFLEX_SERIES_TB.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2016).
- Dragon Skin® Series—Smooth-On. Available online: https://www.smooth-on.com/tb/files/DRAGON_SKIN_SERIES_TB.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2016).
- Solaris®—Smooth-On. Available online: https://www.smooth-on.com/tb/files/Solaris_TB.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2016).
- VHBTM Tape Specialty Tapes—3M.com. Available online: http://multimedia.3m.com/mws/media/986695O/3m-vhb-tape-specialty-tapes.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2016).
- Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR)—Romac. Available online: http://www.romac.com/Submittals/RUBBER/NBR-SUB.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2016).
- Lacour, S.P.; Jones, J.; Suo, Z.; Wagner, S. Design and performance of thin metal film interconnects for skin-like electronic circuits. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2004, 25, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacour, S.P.; Jones, J.; Wagner, S.; Li, T.; Suo, Z. Stretchable interconnects for elastic electronic surfaces. Proc. IEEE 2005, 93, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, W.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, J.; Ameen, A.; Shi, L.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Ma, R.; Jin, S.H.; Kang, Z.; et al. Multifunctional epidermal electronics printed directly onto the skin. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Ahn, J.-H.; Choi, W.M.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, T.-H.; Song, J.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.; Lu, C.; Rogers, J.A. Stretchable and foldable silicon integrated circuits. Science 2008, 320, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Rogers, J.A. Inorganic materials and assembly techniques for flexible and stretchable electronics. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenen, M.A.M.; Arning, V.; Thiem, H.; Steiger, J.; Anselmann, R. Printable electronics: Flexibility for the future. Phys. Status Solidi A 2009, 206, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelaer, J.; Smith, P.J.; Mager, D.; Soltman, D.; Volkman, S.K.; Subramanian, V.; Korvink, J.G.; Schubert, U.S. Printed electronics: The challenges involved in printing devices, interconnects, and contacts based on inorganic materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8446–8453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Jun, B.H.; Kim, T.H.; Joung, J. Direct synthesis and inkjetting of silver nanocrystals toward printed electronics. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Sluis, O.; Hsu, Y.Y.; Timmermans, P.H.M.; Gonzalez, M.; Hoefnagels, J.P.M. Stretching-induced interconnect delamination in stretchable electronic circuits. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 34008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.; Axisa, F.; Bulcke, M.V.; Brosteaux, D.; Vandevelde, B.; Vanfleteren, J. Design of metal interconnects for stretchable electronic circuits. Microelectron. Reliab. 2008, 48, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
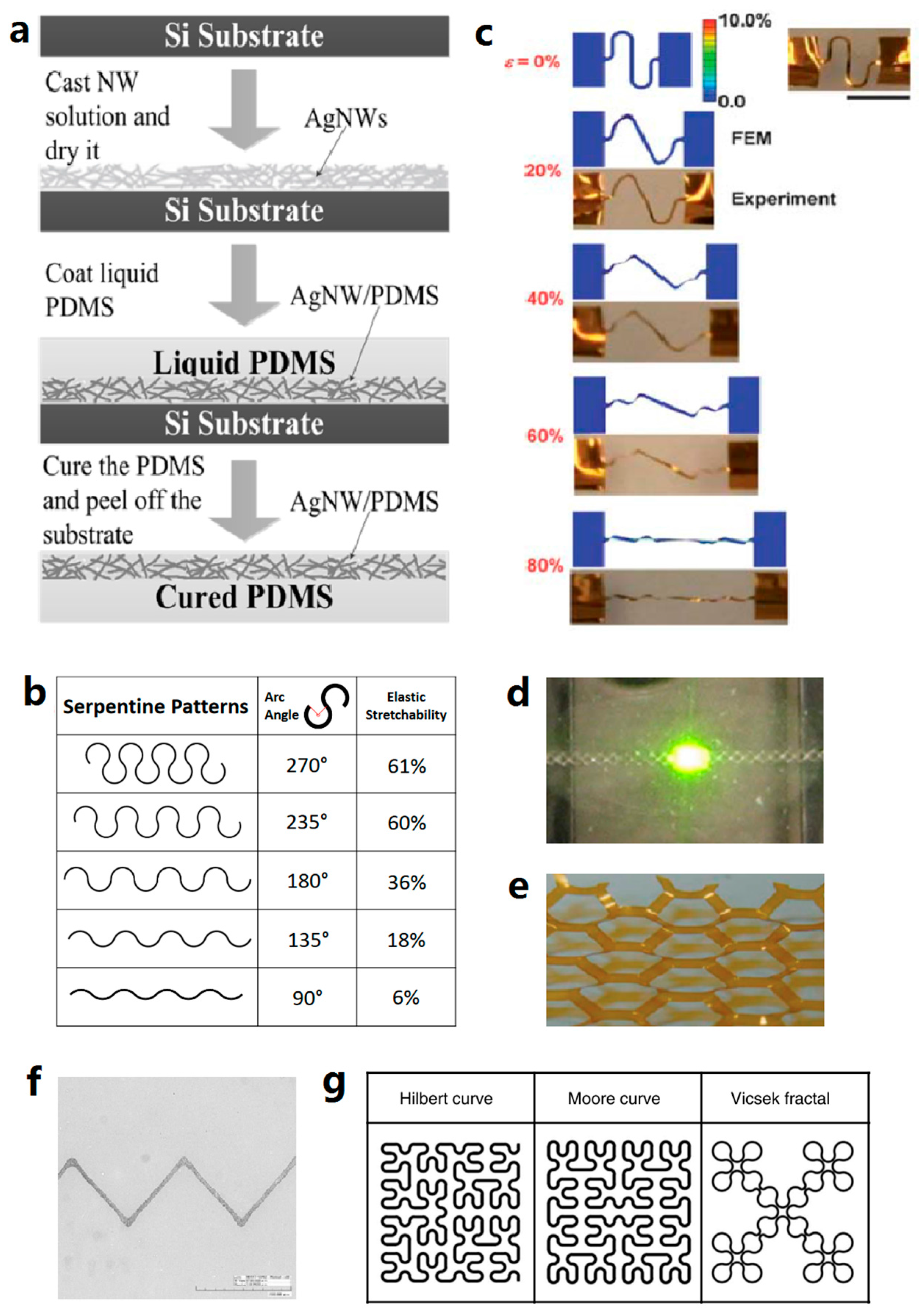
- Fan, J.A.; Yeo, W.-H.; Su, Y.; Hattori, Y.; Lee, W.; Jung, S.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, H.; Falgout, L.; et al. Fractal design concepts for stretchable electronics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.-Y.; Gonzalez, M.; Bossuyt, F.; Vanfleteren, J.; de Wolf, I. Polyimide-enhanced stretchable interconnects: Design, fabrication, and Characterization. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2011, 58, 2680–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
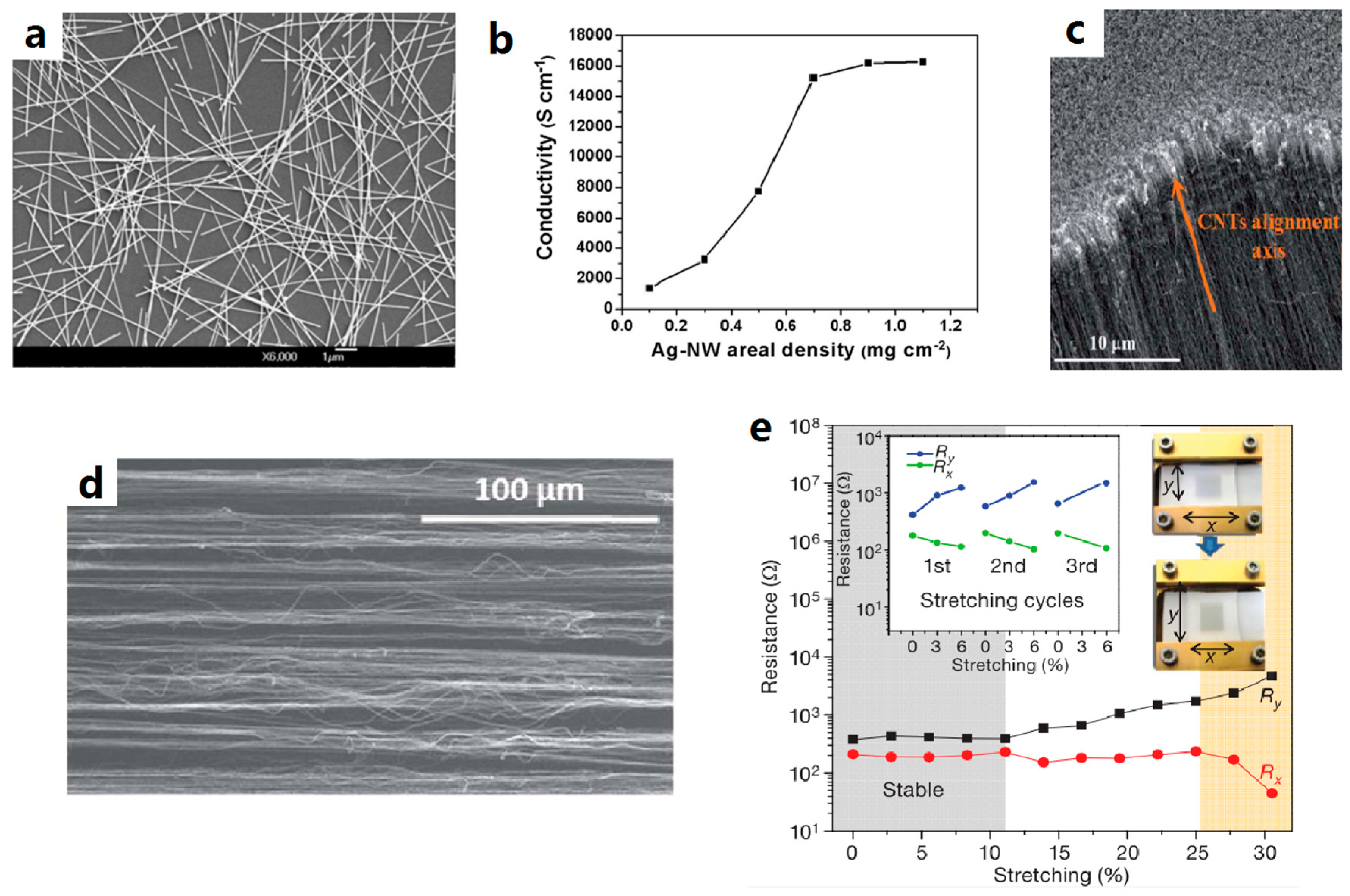
- Xu, F.; Zhu, Y. Highly conductive and stretchable silver nanowire conductors. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5117–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Hong, S.; Ham, J.; Yeo, J.; Lee, J.; Kang, B.; Lee, P.; Kwon, J.; Lee, S.S.; Yang, M.-Y.; et al. Fast plasmonic laser nanowelding for a Cu-nanowire percolation network for flexible transparent conductors and stretchable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5808–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Gu, M.; Cheng, W. Mechanically strong, optically transparent, giant metal superlattice nanomembranes from ultrathin gold nanowires. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, S.; Schwalb, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Si, J.; Shirinzadeh, B.; Cheng, W. A wearable and highly sensitive pressure sensor with ultrathin gold nanowires. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley, D.; Giusti, G.; Mayousse, C.; Celle, C.; Bellet, D.; Simonato, J.-P. Flexible transparent conductive materials based on silver nanowire networks: A review. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 452001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Peumans, P.; Cui, Y. Scalable coating and properties of transparent, flexible, silver nanowire electrodes. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2955–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, S.; Higgins, T.M.; Lyons, P.E.; Doherty, E.M.; Nirmalraj, P.N.; Blau, W.J.; Boland, J.J.; Coleman, J.N. Silver nanowire networks as flexible, transparent, conducting films: Extremely high DC to optical conductivity ratios. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjadi, M.; Pichitpajongkit, A.; Lee, S.; Ryu, S.; Park, I. Highly stretchable and sensitive strain sensor based on silver nanowire-elastomer nanocomposite. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5154–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, T.; Kim, W.S. Reversibly stretchable transparent conductive coatings of spray-deposited silver nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.-W.; Xiao, H.-M.; Fu, S.-Y. Wearable electronics of silver-nanowire/poly(dimethylsiloxane) nanocomposite for smart clothing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madaria, A.R.; Kumar, A.; Ishikawa, F.N.; Zhou, C. Uniform, highly conductive, and patterned transparent films of a percolating silver nanowire network on rigid and flexible substrates using a dry transfer technique. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, L.; Tong, K.; Ren, Z.; Hu, W.; Niu, X.; Chen, Y.; Pei, Q. Silver nanowire percolation network soldered with graphene oxide at room temperature and its application for fully stretchable polymer light-emitting diodes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1590–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-P.; Liao, Y.-C. Highly stretchable and conductive silver nanowire thin films formed by soldering nanomesh junctions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 19856–19860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamai, T. Electrical properties of conductive elastomer as electrical contact material. IEEE Trans. Compon. Hybrids Manuf. Technol. 1982, 5, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Zhao, Y.; Jang, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, K.S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kim, P.; Choi, J.-Y.; Hong, B.H. Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. Nature 2009, 457, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rwei, S.-P.; Ku, F.-H.; Cheng, K.-C. Dispersion of carbon black in a continuous phase: Electrical, rheological, and morphological studies. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2002, 280, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawski, M.; Pearse, J.D.; Smela, E. Elastomers filled with exfoliated graphite as compliant electrodes. Carbon 2010, 48, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekitani, T.; Noguchi, Y.; Hata, K.; Fukushima, T.; Aida, T.; Someya, T. A rubberlike stretchable active matrix using elastic conductors. Science 2008, 321, 1468–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Vural, M.; Islam, M.F. Single-walled carbon nanotube aerogel-based elastic conductors. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2865–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Bayram, Y.; Du, F.; Dai, L.; Volakis, J.L. Polymer-carbon nanotube sheets for conformal load bearing antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sheehan, C.J.; Zhai, J.; Zou, G.; Luo, H.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, Y.T.; Jia, Q.X. Polymer-embedded carbon nanotube ribbons for stretchable conductors. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3027–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Sun, Y.; Liu, P.; Lin, X.; Fan, S.; Jiang, K. Cross-stacked superaligned carbon nanotube films for transparent and stretchable conductors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2721–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; He, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Ji, C.; Shi, E.; Li, P.; Zhu, K.; Peng, Q.; et al. Super-stretchable spring-like carbon nanotube ropes. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2896–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cai, W.; An, J.; Kim, S.; Nah, J.; Yang, D.; Piner, R.; Velamakanni, A.; Jung, I.; Tutuc, E.; et al. Large-area synthesis of high quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils. Science 2009, 324, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Leow, W.R.; Zhu, B.; Yang, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Yin, S.; et al. Suspended wavy graphene microribbons for highly stretchable microsupercapacitors. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5559–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.-H.; Bae, M.-H.; Kim, D.G.; Cheng, H.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, D.-H.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Kim, H.-S.; et al. Stretchable, transparent graphene interconnects for arrays of microscale inorganic light emitting diodes on rubber substrates. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3881–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepúlveda, A.T.; Guzman de Villoria, R.; Viana, J.C.; Pontes, A.J.; Wardle, B.L.; Rocha, L.A. Full elastic constitutive relation of non-isotropic aligned-CNT/PDMS flexible nanocomposites. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4847–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ronning, F.; Gofryk, K.; Mara, N.A.; Haberkorn, N.; Zou, G.; Wang, H.; Lee, J.H.; Bauer, E.; McCleskey, T.M.; et al. Aligned carbon nanotubes sandwiched in epitaxial NbC film for enhanced superconductivity. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2268–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.; Lim, Y.; Jang, G.N.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.-J.; Park, H.; Hong, S.Y.; Lee, G.; Zi, G.; Ha, J.S. Stretchable patterned graphene gas sensor driven by integrated micro-supercapacitor array. Nano Energy 2016, 19, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Shirai, H.; Hirai, T. Wrinkled polypyrrole electrode for electroactive polymer actuators. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 4631–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, W.; Yue, Z.; Too, C.O.; Wallace, G.G. Buckled, stretchable polypyrrole electrodes for battery applications. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3580–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Shu, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Tao, X.-M. Fiber-based wearable electronics: A review of materials, fabrication, devices, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5310–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.-S. Conductive elastomers for stretchable electronics, sensors and energy harvesters. Polymers 2016, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savagatrup, S.; Chan, E.; Renteria-Garcia, S.M.; Printz, A.D.; Zaretski, A.V.; O’Connor, T.F.; Rodriquez, D.; Valle, E.; Lipomi, D.J. Plasticization of PEDOT:PSS by common additives for mechanically robust organic solar cells and wearable sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-Y.; Kang, H.-Y.; Gwon, S.H.; Choi, G.M.; Lim, S.-M.; Sun, J.-Y.; Joo, Y.-C. A Strain-Insensitive Stretchable Electronic Conductor: PEDOT:PSS/Acrylamide Organogels. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Zhong, M.; Wu, H.; Park, S.; Mohin, J.W.; Klosterman, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Bettinger, C.J. Elastomeric Conducting Polyaniline Formed Through Topological Control of Molecular Templates. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5991–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleau, E.; Reece, S.; Desai, S.C.; Smith, M.E.; Dickey, M.D. Self-healing stretchable wires for reconfigurable circuit wiring and 3D microfluidics. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, M.D.; Chiechi, R.C.; Larsen, R.J.; Weiss, E.A.; Weitz, D.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn): A liquid metal alloy for the formation of stable structures in microchannels at room temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, A.; Fassler, A.; Usiak, C.; Majidi, C. Liquid-phase gallium-indium alloy electronics with microcontact printing. Langmuir 2013, 29, 6194–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.W.; Moon, Y.G.; Seong, H.; Jung, S.W.; Oh, J.-Y.; Na, B.S.; Park, N.-M.; Lee, S.S.; Im, S.G.; Koo, J.B. Photolithography-based patterning of liquid metal interconnects for monolithically integrated stretchable circuits. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15459–15465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Son, C.; Ziaie, B. A multiaxial stretchable interconnect using liquid-alloy-filled elastomeric microchannels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 011904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Ohno, H.; Scrosati, B. Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, H.; Pan, T. Photopatternable conductive PDMS materials for microfabrication. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Cai, X.; Guo, Q.; Bian, B.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J. Direct pen writing of adhesive particle-free ultrahigh silver salt-loaded composite ink for stretchable circuits. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, D.C.; McDonald, J.C.; Schueller, O.J.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4974–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, A.C.; Bruzewicz, D.A.; Weibel, D.B.; Whitesides, G.M. Microsolidics: Fabrication of three-dimensional metallic microstructures in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Maleki, T.; Wei, P.; Ziaie, B. A biaxial stretchable interconnect with liquid-alloy-covered joints on elastomeric substrate. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2009, 18, 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Vohra, A.; Imin, P.; Imit, M.; Carmichael, R.S.; Meena, J.S.; Adronov, A.; Carmichael, T.B. Transparent, stretchable, and conductive SWNT films using supramolecular functionalization and layer-by-layer self-assembly. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 29254–29263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Someya, T.; Kato, Y.; Sekitani, T.; Iba, S.; Noguchi, Y.; Murase, Y.; Kawaguchi, H.; Sakurai, T. Conformable, flexible, large-area networks of pressure and thermal sensors with organic transistor active matrixes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12321–12325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Takei, K.; Gillies, A.G.; Fearing, R.S.; Javey, A. Carbon nanotube active-matrix backplanes for conformal electronics and sensors. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5408–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Fan, J.A.; Xu, S.; Song, Y.M.; Choi, K.-J.; Yeo, W.-H.; Lee, W.; Nazaar, S.N.; et al. Experimental and theoretical studies of serpentine microstructures bonded to prestrained elastomers for stretchable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-Y.; Gonzalez, M.; Bossuyt, F.; Axisa, F.; Vanfleteren, J.; de Wolf, I. The effects of encapsulation on deformation behavior and failure mechanisms of stretchable interconnects. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Fu, H.; Lee, J.; Su, J.; Hwang, K.-C.; Rogers, J.A.; Huang, Y. Buckling in serpentine microstructures and applications in elastomer-supported ultra-stretchable electronics with high areal coverage. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 8062–8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khang, D.-Y.; Jiang, H.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. A stretchable form of single-crystal silicon for high-performance electronics on rubber substrates. Science 2006, 311, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Jiang, H.; Choi, W.M.; Khang, D.Y.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. An analytical study of two-dimensional buckling of thin films on compliant substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 014303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khang, D.-Y.; Rogers, J.A.; Lee, H.H. Mechanical buckling: Mechanics, metrology, and stretchable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 19, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Song, J.; Choi, W.M.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, R.-H.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.Y.; Hwang, K.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. Materials and noncoplanar mesh designs for integrated circuits with linear elastic responses to extreme mechanical deformations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18675–18680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Li, T.; Suo, Z.; Vlassak, J.J. High ductility of a metal film adherent on a polymer substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 161910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.J.; Jeong, K.; Liu, G.L.; Lee, L.P. Microfabricated suspensions for electrical connections on the tunable elastomer membrane. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 6051–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, D.C.; Park, M.; Park, C.; Kim, B.; Xia, Y.; Hur, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Park, J.J.; Jeong, U. Ordered zigzag stripes of polymer gel/metal nanoparticle composites for highly stretchable conductive electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2946–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Moran-Mirabal, J. Highly bendable and stretchable electrodes based on micro/nanostructured gold films for flexible sensors and electronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1500345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Fosser, K.A.; Nuzzo, R.G. Fabrication of stable metallic patterns embedded in poly (dimethylsiloxane) and model applications in non-planar electronic and lab-on-a-chip device patterning. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cho, J.; Lee, J.; Huang, X.; Jia, L.; Fan, J.A.; Su, Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Stretchable batteries with self-similar serpentine interconnects and integrated wireless recharging systems. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Shin, W.-J.; Fan, J.A.; Liu, Z.; Lu, C.-J.; Kong, G.-W.; Chen, K.; Patnaik, D.; et al. Materials and designs for wireless epidermal sensors of hydration and strain. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3846–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, R.K.; Majidi, C.; Wood, R.J. Masked deposition of gallium-indium alloys for liquid-embedded elastomer conductors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5292–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skylar-Scott, M.A.; Gunasekaran, S.; Lewis, J.A. Laser-assisted direct ink writing of planar and 3D metal architectures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6137–6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, T.; Sowade, E.; Roscher, F.; Wiemer, M.; Gessner, T.; Baumann, R.R. Additive manufacturing technologies compared: Morphology of deposits of silver ink using inkjet and aerosol jet printing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.E.; Derby, B. Inkjet printing biomaterials for tissue engineering: Bioprinting. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 430–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatani, M.; Lu, Y.; Lee, K.-S.; Kim, H.-C.; Choi, J.-W. Direct-write stretchable sensors using single-walled carbon nanotube/polymer matrix. J. Electron. Packag. 2013, 135, 11009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichan, C.; Saikrajang, T.; Lomas, T.; Jomphoak, A.; Maturos, T.; Phokaratkul, D.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Tuantranont, A. Inkjet printing PEDOT:PSS using desktop inkjet printer. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, Pattaya, Chonburi, Thailand, 6–9 May 2009; Volume 1, pp. 465–468.
- Jones, C.S.; Lu, X.; Renn, M.; Stroder, M.; Shih, W.-S. Aerosol-jet-printed, high-speed, flexible thin-film transistor made using single-walled carbon nanotube solution. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B́fahy, S.; Yunus, S.; Pardoen, T.; Bertrand, P.; Troosters, M. Stretchable helical gold conductor on silicone rubber microwire. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 141911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipomi, D.J.; Chong, H.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Mei, J.; Bao, Z. Toward mechanically robust and intrinsically stretchable organic solar cells: Evolution of photovoltaic properties with tensile strain. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 107, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.S.; Chang, W.-J.; Koo, Y.-M.; Bashir, R. Reliable fabrication method of transferable micron scale metal pattern for poly(dimethylsiloxane) metallization. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, D.R.; Zheng, X. Fabrication of nanowire electronics on nonconventional substrates by water-assisted transfer printing method. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3435–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Ci, L.; Gao, W.; Ajayan, P.M. Transfer printing of graphene using gold film. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Ahn, C.; Hyun, J.K.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, D.K.; Rogers, J.A.; Huang, Y.; Jeon, S. Three-dimensional nanonetworks for giant stretchability in dielectrics and conductors. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjadi, M.; Kyung, K.-U.; Park, I.; Sitti, M. Stretchable, skin-mountable, and wearable strain sensors and their potential applications: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1678–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannsfeld, S.C.B.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Stoltenberg, R.M.; Chen, C.V.H.-H.; Barman, S.; Muir, B.V.O.; Sokolov, A.N.; Reese, C.; Bao, Z. Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensors with microstructured rubber dielectric layers. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Jiang, H. A stretchable temperature sensor based on elastically buckled thin film devices on elastomeric substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 141912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.G.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, H.M.; Kim, T.; Choi, J.H.; Seo, D.K.; Yoo, J.-B.; Hong, S.-H.; Kang, T.J.; Kim, Y.H. Highly sensitive NO2 gas sensor based on ozone treated graphene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166–167, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, L.; Niu, X.; Yu, Z.; Pei, Q. Elastomeric polymer light-emitting devices and displays. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chortos, A.; Koleilat, G.I.; Pfattner, R.; Kong, D.; Lin, P.; Nur, R.; Lei, T.; Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Lai, Y.-C.; et al. Mechanically Durable and Highly Stretchable Transistors Employing Carbon Nanotube Semiconductor and Electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4441–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-S.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Choi, K.-H.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, D.-G.; Lee, D.-Y.; Nam, S.; et al. High-performance, transparent, and stretchable electrodes using graphene-metal nanowire hybrid structures. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2814–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.; Song, J.H.; Lim, G.-H.; Lim, B.; Park, J.-J.; Jeong, U. Highly stretchable polymer transistors consisting entirely of stretchable device components. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3706–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.Y.; Rondeau-Gagné, S.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Chortos, A.; Lissel, F.; Wang, G.-J.N.; Schroeder, B.C.; Kurosawa, T.; Lopez, J.; Katsumata, T.; et al. Intrinsically stretchable and healable semiconducting polymer for organic transistors. Nature 2016, 539, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Wei, B. Materials and structures for stretchable energy storage and conversion devices. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3592–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Peng, H.; Durstock, M.; Dai, L. High-performance transparent and stretchable all-solid supercapacitors based on highly aligned carbon nanotube sheets. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Yoo, J.-K.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, K.; Jung, Y.S. A stretchable polymer-carbon nanotube composite electrode for flexible lithium-ion batteries: Porosity engineering by controlled phase separation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipomi, D.J.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Bao, Z. Stretchable organic solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Deng, J.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Peng, H. Stretchable, wearable dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2643–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagdeviren, C.; Yang, B.D.; Su, Y.; Tran, P.L.; Joe, P.; Anderson, E.; Xia, J.; Doraiswamy, V.; Dehdashti, B.; Feng, X.; et al. Conformal piezoelectric energy harvesting and storage from motions of the heart, lung, and diaphragm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Kim, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Lisko, B.; Purohit, P.K.; McAlpine, M.C. Enhanced piezoelectricity and stretchability in energy harvesting devices fabricated from buckled PZT ribbons. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bito, J.; Hester, J.G.; Tentzeris, M.M. Ambient RF energy harvesting from a two-way talk radio for flexible wearable wireless sensor devices utilizing inkjet printing technologies. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 4533–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Bito, I.; Jeong, S.; Georgiadis, A.; Tentzeris, M.M. A flexible hybrid printed RF energy harvester utilizing catalyst-based copper printing technologies for far-field RF energy harvesting applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 May 2015; pp. 1–4.
- Lee, J.-H.; Ryu, H.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kwak, S.-S.; Yoon, H.-J.; Kim, T.-H.; Seung, W.; Kim, S.-W. Thermally induced strain-coupled highly stretchable and sensitive pyroelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Lin, L.; Niu, S.; Yang, P.K.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zi, Y.; Wang, J.; Liao, Q.; et al. Stretchable-rubber-based triboelectric nanogenerator and its application as self-powered body motion sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3688–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, W.; Harada, S.; Arie, T.; Akita, S.; Takei, K. Wearable, human-interactive, health-monitoring, wireless devices fabricated by macroscale printing techniques. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3299–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.M.; Ghaffar, F.A.; Park, S.I.; Rogers, J.A.; Shamim, A.; Hussain, M.M. Metal/polymer based stretchable antenna for constant frequency far-field communication in wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 6565–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chortos, A.; Liu, J.; Bao, Z. Pursuing prosthetic electronic skin. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, J.C.; Yap, H.K.; Xi, W.; Wang, Z.; Yeow, C.-H.; Lim, C.T. Flexible and stretchable strain sensing actuator for wearable soft robotic applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1, 1600018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Son, D.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.B.; Song, J.-K.; Choi, S.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.-H. Transparent and stretchable interactive human machine interface based on patterned graphene heterostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillborg, H.; Gedde, U.W. Hydrophobicity changes in silicone rubbers. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1999, 6, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassie, N.; Macfarlane, I.G. The thermal degradation of polysiloxanes-I. Poly(dimethylsiloxane). Eur. Polym. J. 1978, 14, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morra, M.; Occhiello, E.; Marola, R.; Garbassi, F.; Humphrey, P.; Johnson, D. On the aging of oxygen plasma-treated PDMS surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1990, 137, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Chung, H.-J.; Kim, K.; Lim, S.A.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Liu, Y.; Yeo, W.-H.; Kim, R.-H.; Kim, S.S.; et al. Immunologic and tissue biocompatibility of flexible/stretchable electronics and optoelectronics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Feng, X.; Huang, Y. Mechanics and thermal management of stretchable inorganic electronics. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Song, J. Recent advances on thermal analysis of stretchable electronics. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2016, 6, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.S.; Geim, A.K.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lin, T.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Chang, C.-Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, T.-Y.; Ye, B.-W.; Hsieh, Y.-P.; Su, W.-F.; et al. Stretchable organic memory: Toward learnable and digitized stretchable electronic applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-H.; Baek, D.H.; Choi, Y.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, S.-H. Wearable polyimide-PDMS electrodes for intrabody communication. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 25032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Maximum Strain (%) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDMS | 6.25 | 120–160 | 2.05 (strain < 40%) | [52,55] |
| Ecoflex® 00-30 | 1.38 | 900 | 0.07 (strain = 100%) | [87] |
| Polyurethane | 7.32 | 760 | 7.82 (initial) | [76] |
| IIR | 3.51 | 170 | 0.41 (strain < 40%) | [55] |
| POE fiber mat | - | >600 | - | [78] |
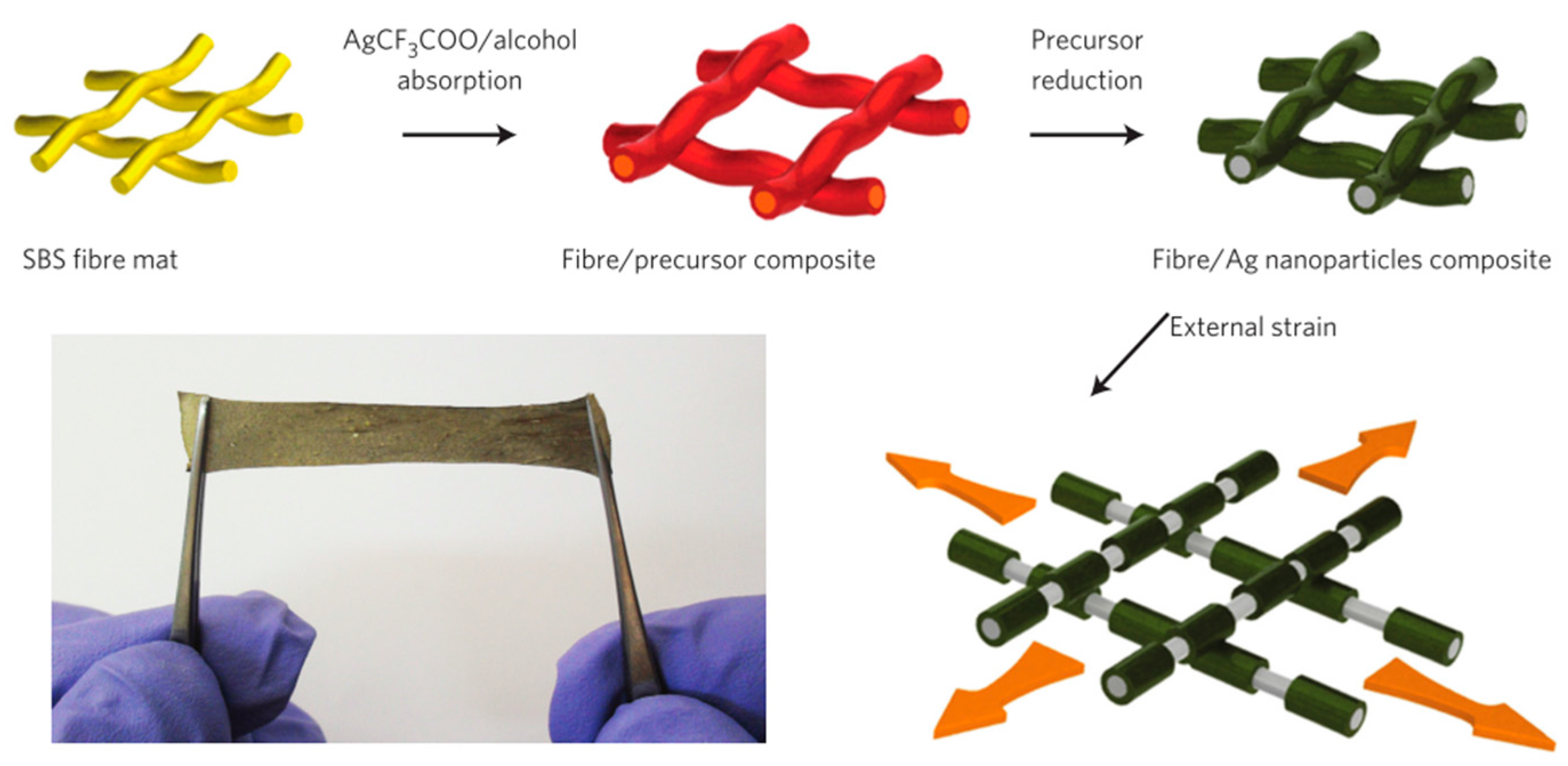
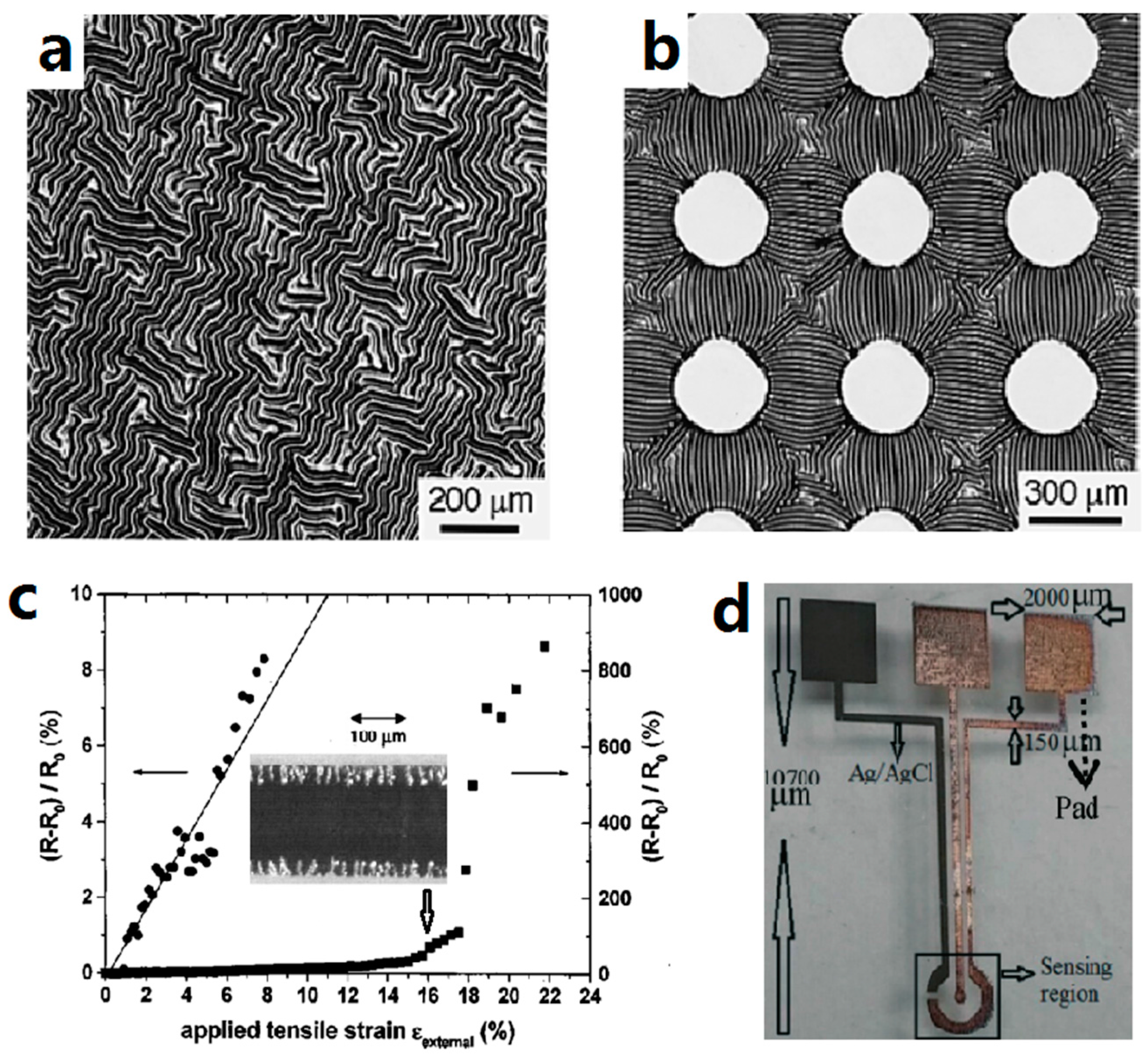
| SBS fiber mat | - | >530 | 0.47 (low strain) | [79] |
| Dragon Skin® 30 | 3.45 | 364 | 0.59 (strain = 100%) | [88] |
| Solaris | 1.24 | 290 | 0.17 (strain = 100%) | [89] |
| Acrylic elastomer (VHB 4910) | 0.69 | - | - | [90] |
| NBR | 10 | 250 | - | [91] |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Mahajan, B.K.; Shou, W.; Pan, H. Materials, Mechanics, and Patterning Techniques for Elastomer-Based Stretchable Conductors. Micromachines 2017, 8, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8010007
Yu X, Mahajan BK, Shou W, Pan H. Materials, Mechanics, and Patterning Techniques for Elastomer-Based Stretchable Conductors. Micromachines. 2017; 8(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xiaowei, Bikram K. Mahajan, Wan Shou, and Heng Pan. 2017. "Materials, Mechanics, and Patterning Techniques for Elastomer-Based Stretchable Conductors" Micromachines 8, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8010007
APA StyleYu, X., Mahajan, B. K., Shou, W., & Pan, H. (2017). Materials, Mechanics, and Patterning Techniques for Elastomer-Based Stretchable Conductors. Micromachines, 8(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8010007







