Hydroformylation of 1-Hexene over Rh/Nano-Oxide Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalytic Activity of Supported Catalysts
| Product composition (mol%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalyst/run | Rh a (wt%) | Rh b (wt%) | BET surface area (m2/g) | Conversion% | Hexene% | Hexene isomers% | Total aldehydes% | n/Ic | TON d | TOF (h−1) |
| 1 | Rh/TiO2 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 15 | - | 100 | - | Traces | - | - | - |
| 2 | Rh/nano-TiO2 | 0.60 | 0.46 | 23 | 52 | 48 | 17 | 34 | 1.6 | 17.8 | 0.74 |
| 3 | Rh/SiO2 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 2 | - | 100 | - | Traces | - | - | - |
| 4 | Rh/nano-SiO2 | 0.47 | 0.22 | 78 | 100 | - | 23 | 77 | 1.0 | 43.8 | 1.82 |
| 5 | Rh/ZnO | 0.94 | 0.31 | 8 | 100 | - | 24 | 76 | 1.1 | 21.9 | 0.91 |
| 6 | Rh/ZnO (the first recycle run) | 0.31 | - | - | 10 | 90 | 3 | 7 | 0.6 | 6.9 | 0.29 |
| 7 | Rh/nano-ZnO | 0.83 | 0.67 | 12 | 100 | - | 4 | 96 | 0.8 | 24.8 | 1.03 |
| 8 | Rh/nano-ZnO (the first recycle run) | 0.67 | 0.66 | - | 98 | 2 | 31 | 67 | 1.5 | 31.2 | 1.30 |
| 9 | nano-ZnO | - | - | - | - | 100 | - | - | - | - | - |
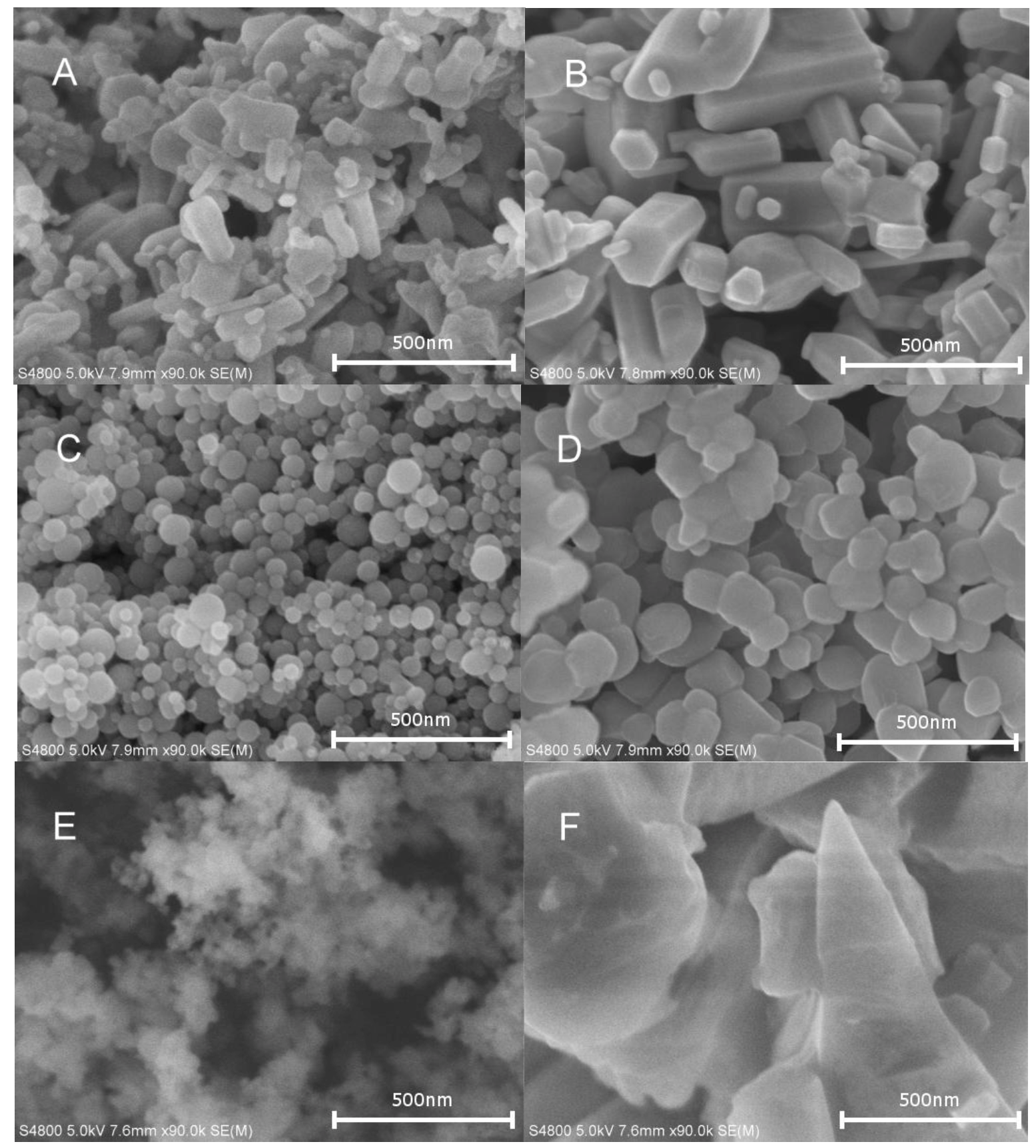
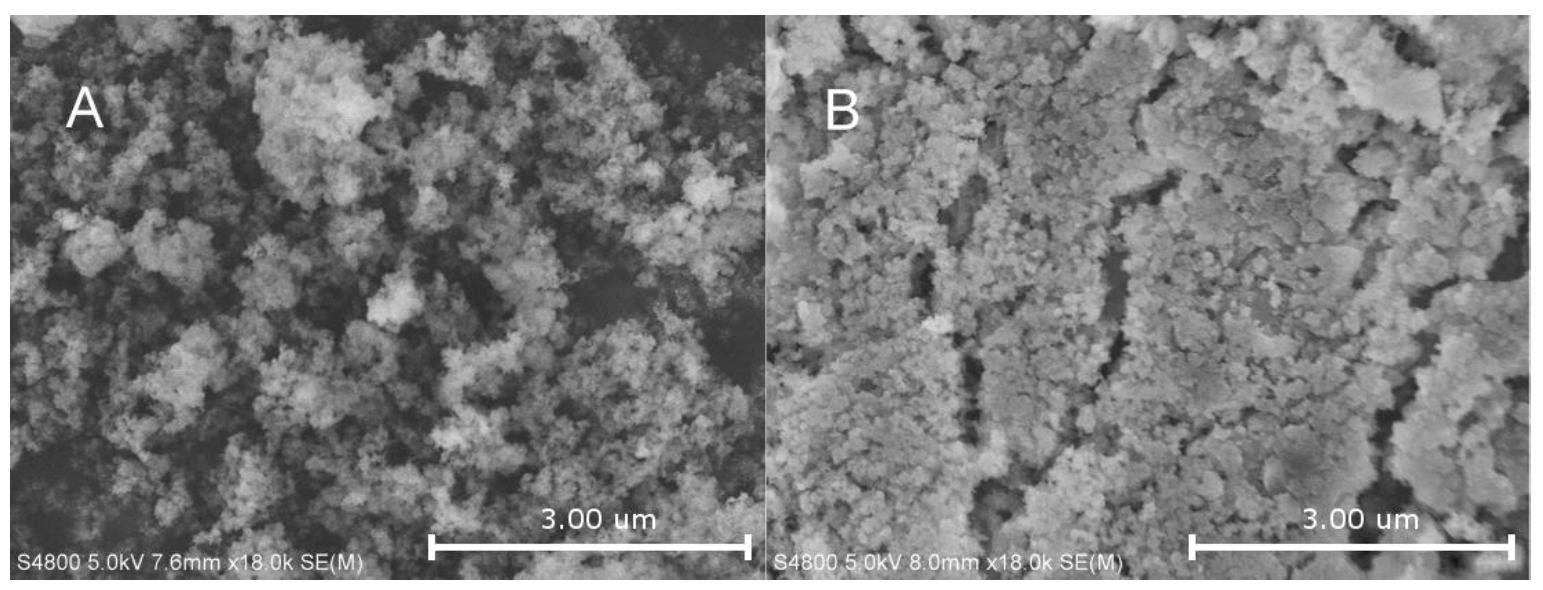
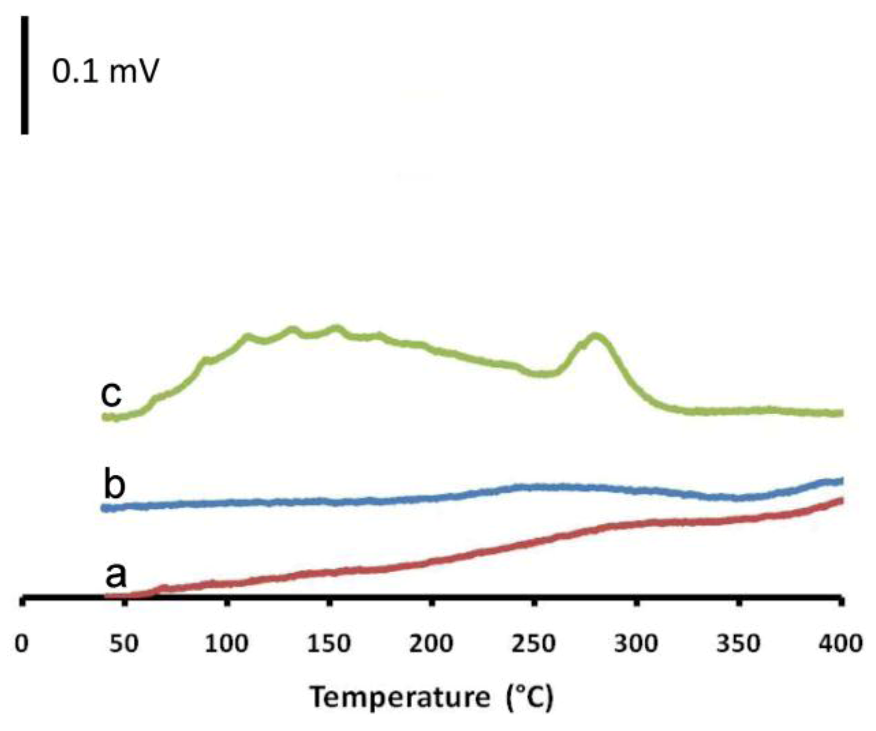
2.2. Characterization of Supported Catalyst Systems
| Entry | Catalyst | Acidic areas (%) a | NH3 consumption (ml/gCat.) | NH3 consumption per BET surface area (mL/m2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak b | Strong c | Weak d | Strong d | Total e | Weak f | Strong f | Totalf | ||
| 1 | Rh/nano-ZnO | 80.3 | 19.7 | 2.09 | 0.51 | 2.61 | 0.174 | 0.043 | 0.217 |
| 2 | Rh/ZnO | 50.3 | 49.7 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 1.31 | 0.082 | 0.081 | 0.164 |
| 3 | Rh/nano-TiO2 | 55.7 | 44.3 | 1.48 | 1.17 | 2.65 | 0.064 | 0.051 | 0.115 |
| 4 | Rh/TiO2 | 47.3 | 52.7 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.66 | 0.021 | 0.023 | 0.044 |
| 5 | Rh/nano-SiO2 | 94.2 | 5.8 | 4.84 | 0.30 | 5.14 | 0.062 | 0.004 | 0.066 |
| 6 | Rh/SiO2 | 0 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0 | 0.164 | 0.164 |


2.3. The Impact of Morphology on the Catalytic Activity
3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Frohning, C.D.; Kohlpaintner, C.W.; Bohnen, H.W. Applied Homogeneous Catalysts with Organometallic Compounds, 2nd; Cornils, B., Herrmann, W.A., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; Volume 1, pp. 31–103. [Google Scholar]
- Likholobov, V.A.; Moroz, B.L. Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis, 2nd; Ertl, G., Knözinger, H., Schüth, F., Weitkamp, J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; Volume 5, pp. 2231–2241. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, V.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Shukla, R.S.; Subrahmanyam, N.; Jasra, R.V. Kinetic Studies on the Hydroformylation of 1-Hexene Using RhCl(AsPh3)3 as a Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 1764–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nagasaka, K.; Qui, X.; Tsubaki, N. Low-pressure hydroformylation of 1-hexene over active carbon-supported noble metal catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 276, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Tsubaki, N.; Sun, S.; Fujimoto, K. Influence of noble metals on the performance of Co/SiO2 catalyst for 1-hexene hydroformylation. Fuel 2002, 81, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadd, A.R.; Marteel, A.; Mason, M.R.; Davies, J.A.; Abraham, M.A. Hydroformylation of 1-Hexene in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Using a Heterogeneous Rhodium Catalyst. 2. Evaluation of Reaction Kinetics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 4514–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Li, C. Heterogeneous asymmetric hydroformylation of olefins on chirally modified Rh/SiO2 catalysts. J. Catal. 2006, 243, 318–325. [Google Scholar]
- Balacos, M.W.; Chuang, S.S.C. Transient Response of Propionaldehyde Formation During CO/H2/C2H4 Reaction on Rh/SiO2. J. Catal. 1995, 151, 253–265. [Google Scholar]
- Bando, K.K.; Asakura, K.; Arakawa, H.; Isobe, K.; Iwasawa, Y. Surface Structures and Catalytic Hydroformylation Activities of Rh Dimers Attached on Various Inorganic Oxide Supports. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 13636–13645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, M.; Mondal, P.; Islam, M.; Bhaumik, A. Highly Efficient Hydroformylation of 1-Hexene over an ortho-Metallated Rhodium(I) Complex Anchored on a 2D-Hexagonal Mesoporous Material. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2, 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa, M. Catalytic hydroformylation of olefins over the rhodium, bimetallic RhCo, and cobalt carbonyl clusters supported with some metal oxides. J. Catal 1979, 59, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainulainen, T.A.; Niemelä, M.K.; Krause, A.O.I. Hydroformylation of 1-hexene on Rh/C and Co/SiO2, catalysts. J.Mol. Cat. A 1997, 122, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, X.; Asami, K.; Fujimoto, K. Low-Pressure Hydroformylation of Middle Olefins over Co and Rh Supported on Active Carbon Catalysts. Energy Fuels 2003, 17, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, K.; Chaudhari, R.V. Heterogenized HRh(CO)(PPh3)3 on zeolite Y using phosphotungstic acid as tethering agent: a novel hydroformylation catalyst. J. Catal. 2003, 213, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Miura, K.; Fukui, H. Reaction of rhodium species with carbon monoxide on freshly prepared Rh-Y zeolite and rhodium trichloride/silica catalysts revealed by the carbon-13 NMR technique. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 2797–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibahara, F.; Nozaki, K.; Matsuo, T.; Hiyama, T. Asymmetric Hydroformylation with Highly Crosslinked Polystyrene-Supported (R,S)-BINAPHOS-Rh(I) Complexes: The Effect of Immobilization Positions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 1825–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, K.; Itoi, Y.; Shibahara, F.; Shirakawa, E.; Ohta, T.; Takaya, H.; Hiyama, T. Asymmetric Hydroformylation of Olefins in a Highly Cross-Linked Polymer Matrix. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4051–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozin, G.A.; Arsenault, A.C. Nanochemistry a Chemical Approach to Nanomaterials; RSC Publishing: London, China, 2005; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Müller, A.; Cheetham, A.K. The Chemistry of Nanomaterials Synthesis, Properties and Applications; Rao, C.N.R., Müller, A., Cheetham, A.K., Eds.; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.H.; Ku, I.; Kim, H.J.; Son, S.U. NHC-Based Submicroplatforms for Anchoring Transition Metals. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1673–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchbreiter, L.; Mecking, S. Hydroformylation with Dendritic-Polymer-Stabilized Rhodium Colloids as Catalyst Precursors. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2007, 208, 1688–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Liu, H. Reaction conducted under rather severe conditions for a colloidal catalyst - hydroformylation of propylene catalyzed by polymer-protected rhodium colloids. Macromol. Symp. 1996, 105, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruss, A.J.; Gelesky, M.A.; Machado, G.; Dupont, J. Rh(0) nanoparticles as catalyst precursors for the solventless hydroformylation of olefins. J. Mol. Catal. A 2006, 252, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, H.; Xiao, C.; Zhong, M.; Ma, D.; Kou, Y. Hydroformylation of 1-hexene over ultrafine cobalt nanoparticle catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A 2010, 330, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Hu, G.; Li, C. Asymmetric hydroformylation of olefins catalyzed by rhodium nanoparticles chirally stabilized with (R)-BINAP ligand. J. Mol. Catal. A 2008, 283, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Jung, O.-S.; Chung, Y.K.; Park, K.H. Heterogenized Catalysts Containing Cobalt-Rhodium Heterobimetallic Nanoparticles for Olefin Hydroformulation. Catal. Lett. 2009, 128, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oresmaa, L.; Moreno, M.A.; Jakonen, M.; Suvanto, S.; Haukka, M. Catalytic activity of linear chain ruthenium carbonyl polymer [Ru(CO)4]n in 1-hexene hydroformylation. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 353, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, R.; Serp, P.; Kalck, P.; Kihn, Y.; Schreiber, J.; Marhic, C.; Duvail, J.-L. Preparation of Rhodium Catalysts Supported on Carbon Nanotubes by a Surface Mediated Organometallic Reaction. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 4, 610–617. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.-B.; Lin, G.-D.; Chen, P.; Yuan, Y.-Z.; Tsai, K.R. Preparation, characterization and catalytic hydroformylation properties of carbon nanotubes-supported Rh-phosphine catalyst. Appl. Catal. A 1999, 187, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, H.; Liang, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z. Co/CNF Catalysts Tailored by Controlling the Deposition of Metal Colloids onto CNFs: Preparation and Catalytic Properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 2147–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serp, P.; Cossias, M.; Kalck, P. Carbon nanotubes and nanofibers in catalysis. Appl. Catal. A 2003, 253, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Tan, C.D.; Baker, R.T.K. Ethylene hydroformylation on graphite nanofiber supported rhodium catalysts. Catal. Today 2001, 65, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wryszcz, J.; Zawadzki, M.; Treciak, A.M.; Tylus, W.; Ziolkokowski, J.J. Catalytic activity of rhodium complexes supported on Al.2O3-ZrO2 in isomerization and hydroformylation of 1-hexene. Catal. Lett. 2004, 93, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; He, D. Anchoring RhCl(CO)(PPh3)(2) to -PrPPh2 Modified MCM-41 as Effective Catalyst for 1-Octene Hydroformulation. Catal. Lett. 2009, 127, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Thitsartan, W.; Kawi, S. Highly Active and Selective Nanoalumina-Supported Wilkinson’s Catalysts for Hydroformylation of Styrene. Ing. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 1824–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimowska, M.; Wagner, J.B.; Dziedzic, J.; Camra, J.; Borzęcka-Prokop, B.; Najbar, M. Some aspects of metal-support strong interactions in Rh/Al2O3 catalyst under oxidising and reducing conditions. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 417, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanathan, V.; Narayanan, S. Evidence for strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) in Rh/TiO2 system. Catal. Lett. 1993, 21, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lónyi, F.; Valyon, J. On the interpretation of the NH3-TPD patterns of H-ZSM-5 and H-Mordenite. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2001, 47, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchina, A.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S. Surface acidity and basicity: General concepts. Catal. Today 1998, 41, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G. Spectroscopic characterization of the acid properties of metal oxide catalysts. Catal. Today 1998, 41, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, B.A.; Cody, I.A. Infrared studies of reactions on oxide surfaces. 5. Lewis acid sites on dehydroxylated silica and Infrared studies of reactions on oxide surfaces. 6. Active sites on dehydroxylated silica for the chemisorption of ammonia and water. J. Phys. Chem. 1976, 80, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sonström, P.; Arndt, D.; Stöver, J.; Zielasek, V.; Borchert, H.; Thiel, K.; Al-Shamery, K.; Bäumer, M. Heterogeneous catalysis with supported platinum colloids: A systematic study of the interplay between support and functional ligands. J. Catal. 2011, 278, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ordomsky, V.V.; Sushkevich, V.L.; Ivanova, I.I. Study of acetaldehyde condensation chemistry over magnesia and zirconia supported on silica. J. Mol. Catal. A 2010, 333, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G. The Use of Infrared Spectroscopic Methods in the Field of Heterogeneous Catalysis by Metal Oxides. In Metal Oxide Catalysis; Jackson, S.D., Justin, S.J., Eds.; 2009; Volume 1, pp. 95–175. [Google Scholar]
- Origin 7 SR2 Software, version 7.0383, OriginLab: Northampton, MA, USA, 2002.
- GRAMS/32, version 4.0, Galactic Industries Corporation: Salem, NH, USA.
- Zumdahl, S.S. Chemical Principles, 3rd ed; Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; p. 572. [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk, A.E.; McKee, D.W. Thermal decomposition of rhodium, iridium, and ruthenium chlorides. J. Catal. 1968, 11, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, M.; Durán, J.A.; Gonález, Á.; Pacheco, I.; Sánchez-Delgado, R.A. Kinetics and mechanisms of homogeneous catalytic reactions. Part 7. Hydroformylation of 1-hexene catalyzed by cationic complexes of rhodium and iridium containing PPh3. J. Mol. Catal. 2007, 270, 250–256. [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt, G.D. Surface chemistry of oxides. Pure Appl. Chem. 1976, 48, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun’ko, V.M. Competitive adsorption. Theor. Experim. Chem. 2007, 43, 139–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noei, H.; Qui, H.; Wang, Y.; Löffler, E.; Wöll, C.; Muhler, M. The identification of hydroxyl groups on ZnO nanoparticles by infrared spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 7092–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun’ko, V.M.; Leboda, R.; Skubiszewska-Zięba, J. Heating effects on morphological and textural characteristics of individual and composite nanooxides. Adsorption 2009, 15, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun’ko, V.M.; Zarko, V.I.; Turov, V.V.; Oranska, O.I.; Goncharuk, E.V.; Nychiporuk, Y.M.; Pakhlov, E.M.; Yurchenko, G.R.; Leboda, R.; Skubiszewska-Zięba, J.; et al. Morphological and structural features of individual and composite nanooxides with alumina, silica, and titania in powders and aqueous suspensions. Powder Technol. 2009, 195, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun’ko, V.M.; Yurchenko, G.R.; Turov, V.V.; Goncharuk, E.V.; Zarko, V.I.; Zabuga, A.G.; Matkovsky, A.K.; Oranska, O.I.; Leboda, R.; Skubiszewska-Zięba, J.; et al. Adsorption of polar and nonpolar compounds onto complex nanooxides with silica, alumina, and titania. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 348, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, A.M.; Conant, T.; Datye, A.K. Controlling ZnO morphology for improved methanol steam reforming reactivity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 5584–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.R.; Hu, T.; Pan, G.L.; Yan, T.Y.; Gao, X.P.; Zhu, H.Y. Morphology−Function Relationship of ZnO: Polar Planes, Oxygen Vacancies, and Activity. J.Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 11859–11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TOPAS V4.2: General Profile Analysis Software for Powder Diffraction Data; Bruker AXS: Karsruhe, Germany, 2008.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kontkanen, M.-L.; Tuikka, M.; Kinnunen, N.M.; Suvanto, S.; Haukka, M. Hydroformylation of 1-Hexene over Rh/Nano-Oxide Catalysts. Catalysts 2013, 3, 324-337. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010324
Kontkanen M-L, Tuikka M, Kinnunen NM, Suvanto S, Haukka M. Hydroformylation of 1-Hexene over Rh/Nano-Oxide Catalysts. Catalysts. 2013; 3(1):324-337. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010324
Chicago/Turabian StyleKontkanen, Maija-Liisa, Matti Tuikka, Niko M. Kinnunen, Sari Suvanto, and Matti Haukka. 2013. "Hydroformylation of 1-Hexene over Rh/Nano-Oxide Catalysts" Catalysts 3, no. 1: 324-337. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010324
APA StyleKontkanen, M.-L., Tuikka, M., Kinnunen, N. M., Suvanto, S., & Haukka, M. (2013). Hydroformylation of 1-Hexene over Rh/Nano-Oxide Catalysts. Catalysts, 3(1), 324-337. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010324





