Co-Al Mixed Oxides Prepared via LDH Route Using Microwaves or Ultrasound: Application for Catalytic Toluene Total Oxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
| Solids | Specific surface area (m2·g−1) | Chemical composition M2+/Al3+ | T50 (°C) | Crystallite size of oxide * (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical | Experimental | ||||
| Mg6Al2HTCT500 | 216 | 3 | 2.79 | 477 | 11.6 |
| Mg6Al2HTUS500 | 272 | 3 | 2.84 | 421 | 4.5 |
| Mg6Al2HTMW500 | 342 | 3 | 2.95 | 395 | 3.7 |
| Co6Al2HTCT500 | 123 | 3 | 2.85 | 287 | 9.4 |
| Co6Al2HTUS500 | 157 | 3 | 3.15 | 278 | 7.0 |
| Co6Al2HTMW500 | 167 | 3 | 3.00 | 271 | 7.6 |




| Catalyst | Temperature (°C) H2 consumption (μmol·g−1) | Consumption ratio peak 2/1 | Consumption ratio peak 4/3 | H2 consumption (μmol·g−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 3 | Peak 4 | ||||
| Co6Al2HTCT500 | 288 °C 644 | 345 °C 2012 | 597 °C 1458 | 690 °C 7410 | 3.12 | 5.08 | 11715 |
| Co6Al2HTUS500 | 259 °C 651 | 337 °C 2192 | 572 °C 1557 | 680 °C 7444 | 3.36 | 4.78 | 11845 |
| Co6Al2HTMW500 | 232 °C 777 | 322 °C 2242 | 523 °C 1229 | 669 °C 7711 | 2.88 | 4.69 | 11961 |
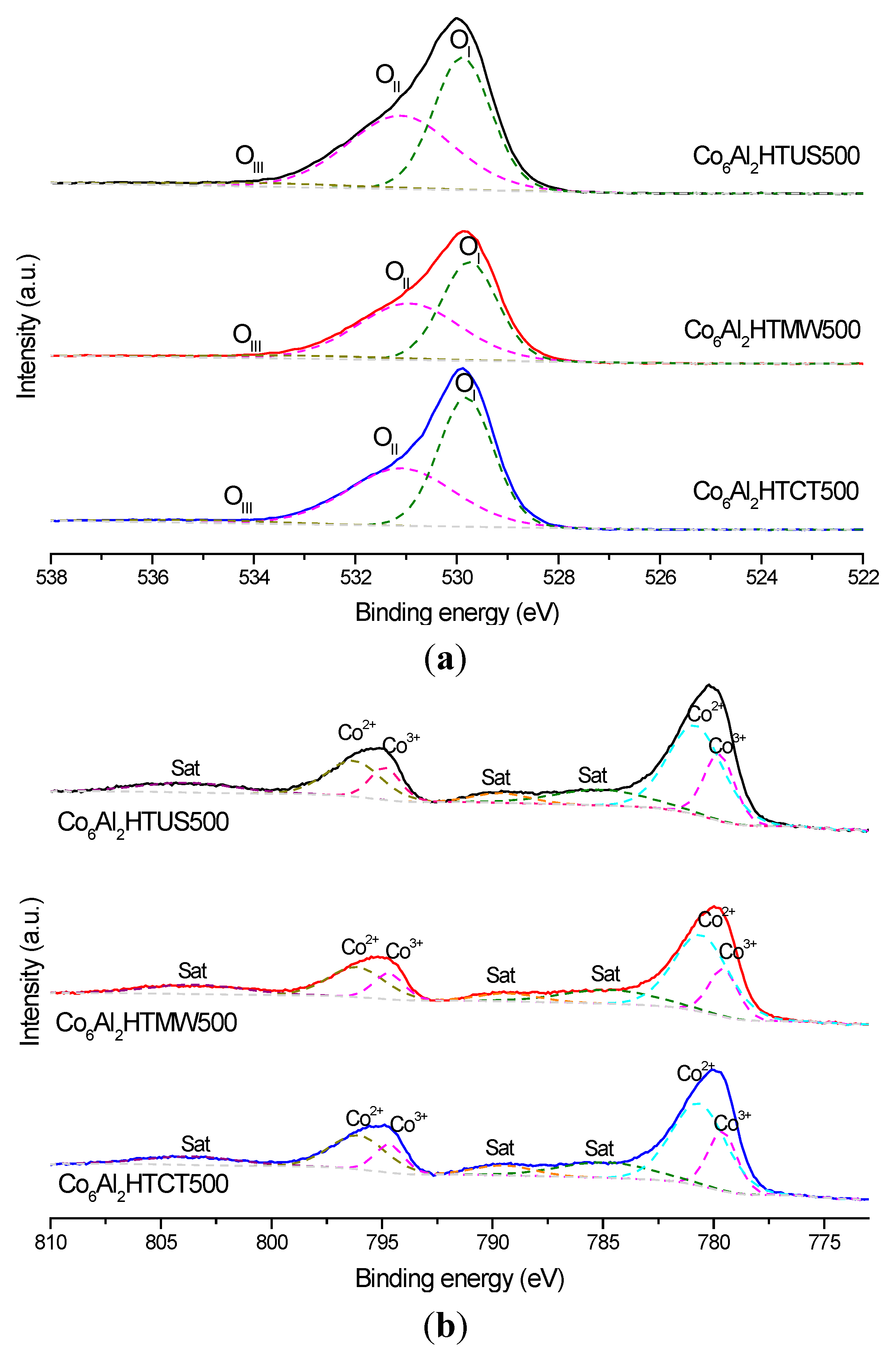
| Catalyst | Eb (O1s) (eV) | Eb (Co2p) (eV) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OI | OII | OIII | Co 2p1/2 | Co 2p3/2 | |||
| Co2+ | Co3+ | Co2+ | Co3+ | ||||
| Co6Al2HTCT500 | 529.8 | 531.1 | 533.9 | 796.1 | 794.7 | 780.7 | 779.6 |
| Co6Al2HTUS500 | 529.9 | 531.1 | 533.8 | 796.1 | 794.7 | 780.8 | 779.7 |
| Co6Al2HTMW500 | 529.8 | 531.0 | 533.5 | 796.2 | 794.8 | 780.7 | 779.6 |
| Catalyst | Surface Content (%) by XPS | T50 (°C) | Catalytic intrinsic activity (mol·m−2·h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OII/OI | Co2+/Co3+ | Co/Al | |||
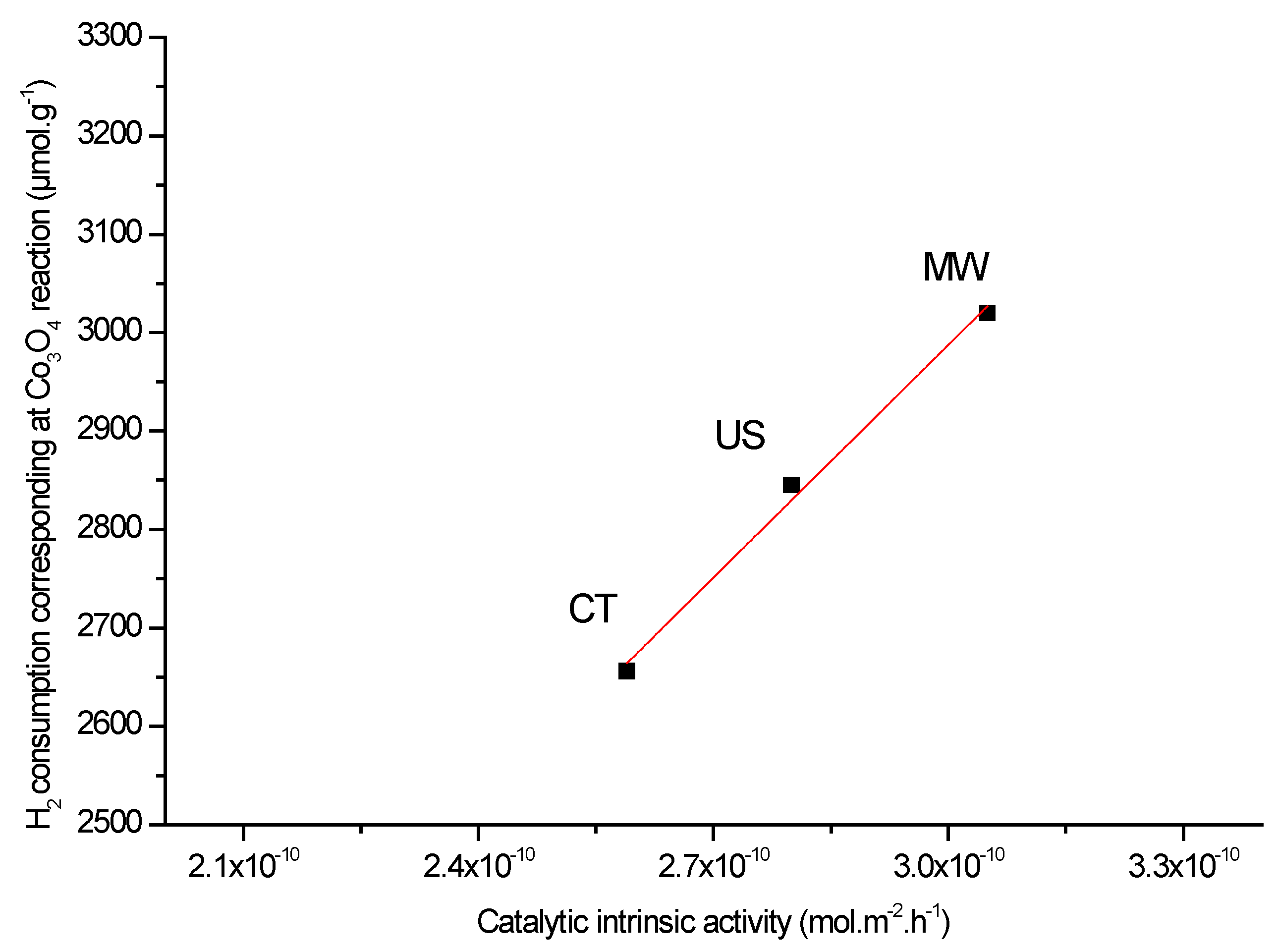
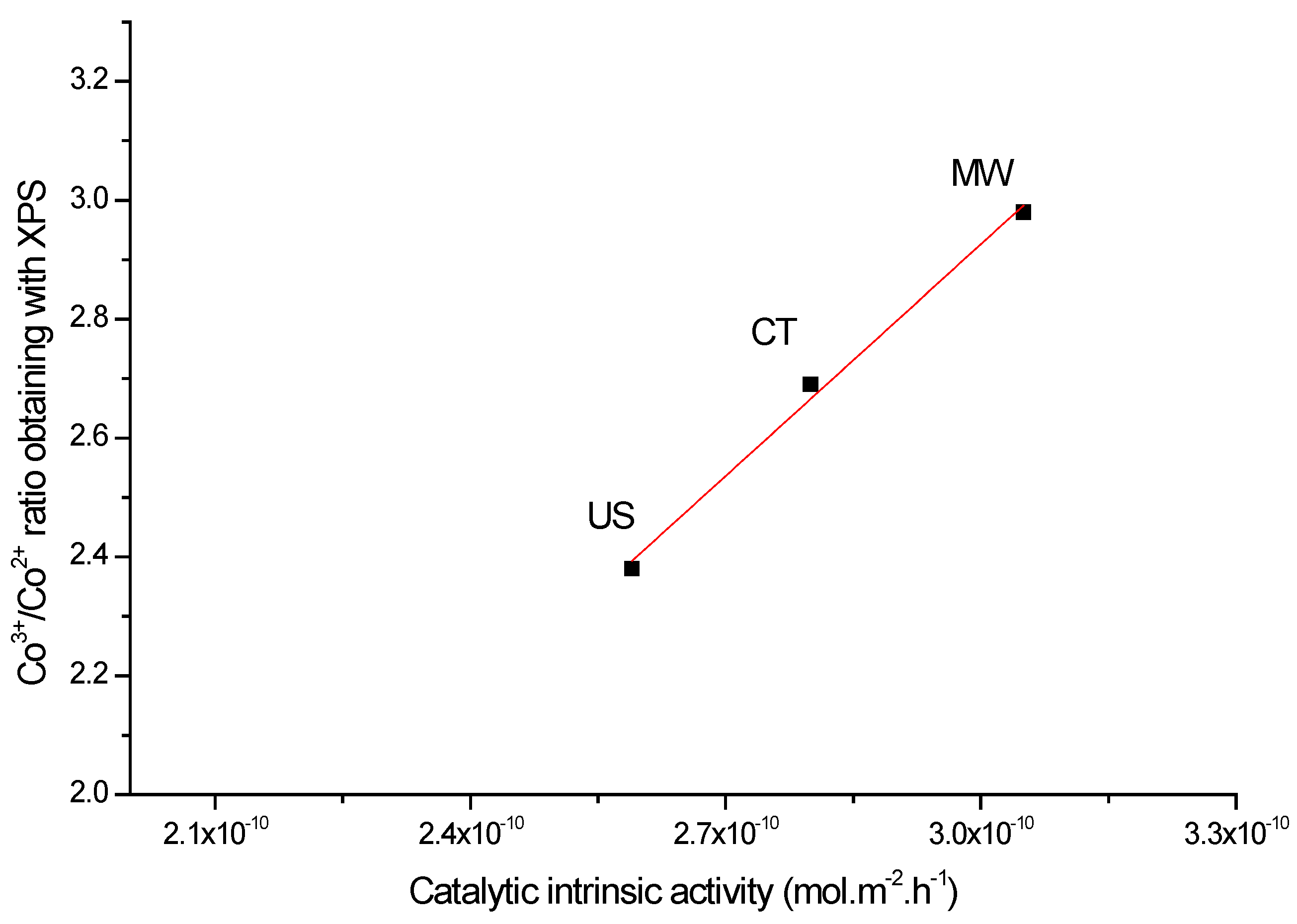
| Co6Al2HTCT500 | 0.86 | 2.38 | 2.9 | 287 | 2.59 × 10−10 |
| Co6Al2HTUS500 | 1.01 | 2.69 | 2.9 | 278 | 2.80 × 10−10 |
| Co6Al2HTMW500 | 1.05 | 2.98 | 3.3 | 271 | 3.05 × 10−10 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of Catalysts
3.2. Characterization Techniques
3.3. Catalytic Tests
- A is the catalytic intrinsic activity (mol·m−2·h−1);
- Q is the volume flow (L·h−1);
- VM is the molar volume (L·mol−1);
- T10 is the catalyst temperature for 10% toluene conversion (K);
- [C7H8]0 is the toluene initial concentration (ppm);
- X is the toluene conversion (%);
- m is the catalyst mass (g);
- SBET is the specific surface area of the catalyst (m2·g−1).
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos, V.P.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Tavares, P.B.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Figueiredo, J.L. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental Oxidation of CO, ethanol and toluene over TiO2 supported noble metal catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 99, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.F. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds on supported noble metals. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 100, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, T.; Rooke, J.C.; Genty, E.; Cousin, R.; Siffert, S.; Su, B.-L. Gold catalysts in environmental remediation and water-gas shift technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, S.; Bello, L.; Sastre, H.; Rosal, R.; Fernando, V.D. Kinetics of the deep oxidation of benzene , toluene, n-hexane and their binary mixtures over a platinum on γ-alumina catalyst. Appl. Catal. B 2002, 38, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirè, S.; Liotta, L.F. Supported gold catalysts for the total oxidation of volatile organic compounds. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 125, 222–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q.; He, S.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Wei, M. Catalytic conversion of syngas to mixed alcohols over CuFe-based catalysts derived from layered double hydroxides. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiratova, K.; Cuba, P.; Kovanda, F.; Hilaire, L.; Pitchon, V. Preparation and characterisation of activated Ni(Mn)/Mg/Al hydrotalcites for combustion catalysis. Catal. Today 2002, 76, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovanda, F.; Jiratova, K.; Rymes, J.; Kolousek, D. Characterization of activated CuMgAl hydrotalcites and their catalytic activity in toluene combustion. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 18, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Lu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y. Highly Active and Stable Co3O4/ZSM-5 Catalyst for Propane Oxidation: Effect of the preparation Method. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-W.; Kuo, M.-C.; Lin, C.-J.; Wang, C.-B.; Chien, S.-H. Evaluation of carbon monoxide oxidation over CeO2/Co3O4 catalysts: Effect of ceria loading. Catal. Today 2008, 131, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.F.; Ousmane, M.; di Carlo, G.; Pantaleo, G.; Deganello, G.; Boreave, A.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Catalytic Removal of Toluene over Co3O4–CeO2 Mixed Oxide Catalysts: Comparison with Pt/Al2O3. Catal. Lett. 2008, 127, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.F.; Wu, H.; Pantaleo, G.; Venezia, A.M. Co3O4 nanocrystals and Co3O4–MOx binary oxides for CO, CH4 and VOC oxidation at low temperatures: A review. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 3085–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genty, E.; Cousin, R.; Capelle, S.; Gennequin, C.; Siffert, S. Catalytic Oxidation of Toluene and CO over Nanocatalysts Derived from Hydrotalcite-Like Compounds (X62+Al23+): Effect of the Bivalent Cation. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 2802–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennequin, C.; Siffert, S.; Cousin, R.; Aboukaïs, A. Co–Mg–Al Hydrotalcite Precursors for Catalytic Total Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds. Top. Catal. 2009, 52, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debecker, D.P.; Gaigneaux, E.M.; Busca, G. Exploring, tuning, and exploiting the basicity of hydrotalcites for applications in heterogeneous catalysis. Chemistry 2009, 15, 3920–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.S.; Song, H.; Park, Y.-S.; Woo, J.-W. Analysis of N2O decomposition over fixed bed mixed metal oxide catalysts made from hydrotalcite-type precursors. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 273, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio, L.A.; Velásquez, J.; Echavarría, A.; Faro, A.; Ribeiro, F.R.; Ribeiro, M.F. Total oxidation of toluene over calcined trimetallic hydrotalcites type catalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Tanasoi, S.; Mitran, G.; Tanchoux, N.; Cacciaguerra, T.; Fajula, F.; Săndulescu, I.; Tichit, D.; Marcu, I.-C. Transition metal-containing mixed oxides catalysts derived from LDH precursors for short-chain hydrocarbons oxidation. Appl. Catal. A 2011, 395, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennequin, C.; Barakat, T.; Tidahy, H.L.; Cousin, R.; Lamonier, J.-F.; Aboukaïs, A.; Siffert, S. Use and observation of the hydrotalcite “memory effect” for VOC oxidation. Catal. Today 2010, 157, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genty, E.; Cousin, R.; Capelle, S.; Siffert, S. Influence of Gold on Hydrotalcite-like Compound Catalysts for Toluene and CO Total Oxidation. Catalysts 2013, 3, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, J.; Lamonier, J.F.; Siffert, S.; Zhilinskaya, E.A.; Aboukaïs, A. Characterisation of Mg/Al hydrotalcite with interlayer palladium complex for catalytic oxidation of toluene. Appl. Catal. A 2002, 234, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovanda, F.; Rojka, T.; Dobešová, J.; Machovič, V.; Bezdička, P.; Obalová, L.; Jirátová, K.; Grygar, T. Mixed oxides obtained from Co and Mn containing layered double hydroxides: Preparation, characterization, and catalytic properties. J. Solid State Chem. 2006, 179, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovanda, F.; Koloušek, D.; Cílová, Z.; Hulínský, V. Crystallization of synthetic hydrotalcite under hydrothermal conditions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2005, 28, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, R.; Weng, D.; Wu, X.; Fan, J.; Qing, L. Rapid synthesis of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3+λ catalysts by microwave irradiation process. Catal. Today 2007, 126, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Kaddouri, A.; Ifrah, S. Microwave-assisted synthesis of La1−xBxMnO3.15 (B = Sr, Ag; x = 0 or 0.2) via manganese oxides susceptors and their activity in methane combustion. Catal. Commun. 2006, 7, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, Q.; Tao, Y.; Weng, H. Influence of ultrasound impregnation on the performance of Co/Zr/SiO2 catalyst during Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Chin. J. Catal. 2011, 32, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.; Corma, A.; Iborra, S.; Epping, K.; Velty, A. Increasing the basicity and catalytic activity of hydrotalcites by different synthesis procedures. J. Catal. 2004, 225, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, P.; Labajos, F.M.; Rives, V. Microwaves and layered double hydroxides: A smooth understanding. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.; Fetter, G.; Bosch, P. Microwave power effect on hydrotalcite synthesis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 89, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.; Lamonier, J.-F.; Giraudon, J.-M.; Molina, R.; Moreno, S. Catalytic activity of Co–Mg mixed oxides in the VOC oxidation: Effects of ultrasonic assisted in the synthesis. Catal. Today 2011, 176, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, O.R.; Ribeiro, N.F.P.; Perez, C.A.C.; Schmal, M.; Souza, M.M.V.M. Incorporation of cerium ions by sonication in Ni–Mg–Al layered double hydroxides. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M.; Saleh, T.S.; Ahmed, N.S.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; Al-Shareef, R.A. An eco-friendly N-sulfonylation of amines using stable and reusable Zn-Al-hydrotalcite solid base catalyst under ultrasound irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetter, G.; Hernández, F.; Maubert, A. Microwave irradiation effect on hydrotalcite synthesis. J. Porous Mater. 1997, 30, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lars, S.; Andersson, T. Reaction Networks in the Catalytic Vapor-Phase Oxidation of Toluene and Xylenes. J. Catal. 1986, 98, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Swamy, C.S. Catalytic decomposition of nitrous oxide over calcined cobalt aluminum hydrotalcites. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrovska, M.; Edreva-Kardjieva, R.; Tenchev, K.; Tzvetkov, P.; Spojakina, A.; Petrov, L. Effect of Co-content on the structure and activity of Co–Al hydrotalcite-like materials as catalyst precursors for CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 399, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Mul, G.; Kapteijn, F.; Moulijn, J.A. In situ investigation of the thermal decomposition of Co–Al hydrotalcite in different atmospheres. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babay, S.; Bulou, A.; Mercier, A.M.; Toumi, M. The decomposition of the layered double hydroxides of Co and Al: Phase segregation of a new single phase spinel oxide. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2015, 141, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Sub-ambient CO oxidation over mesoporous Co3O4: Effect of morphology on its reduction behavior and catalytic performance. Appl. Catal. A 2012, 431–432, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Haruta, M.; Shen, W. Low-temperature oxidation of CO catalysed by Co3O4 nanorods. Nature 2009, 458, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnoldy, P.; Moulijn, J.A. Temperature-Programmed Reduction of CoO/Al2O3 Catalysts. J. Catal. 1985, 93, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, B.A.; Hughes, A.E.; Turney, T.W. An XPS and TPR Study of the Reduction of Promoted Cobalt-Kieselguhr Fisher-Tropsch Catalysts. J. Catal. 1986, 406, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Finocchio, E.; Ramis, G.; Ricchiardi, G. On the role of acidity in catalytic oxidation. Catal. Today 1996, 32, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.M.; Poudyal, S.; Miller, J.T.; Bartholomew, C.H.; Hecker, W.C. Reducibility of alumina-supported cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts: Effects of noble metal type, distribution, retention, chemical state, bonding, and influence on cobalt crystallite size. Appl. Catal. A 2012, 449, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupin, J.-C.; Gonbeau, D.; Vinatier, P.; Levasseur, A. Systematic XPS studies of metal oxides, hydroxides and peroxides. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delimaris, D.; Ioannides, T. VOC oxidation over MnOx–CeO2 catalysts prepared by a combustion method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, H.; Deng, J.; Xie, S.; Yang, H.; Tan, W.; Han, W.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, G. Mesoporous Co3O4-supported gold nanocatalysts: Highly active for the oxidation of carbon monoxide, benzene, toluene, and O-xylene. J. Catal. 2014, 309, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampanthar, J.T.; Zeng, H.C. Synthesis of CoIICoIII2−xAlxO4-Al2O3 Nanocomposites via Decomposition of CoII0.73CoIII0.27(OH)2.00(NO3)0.23(CO3)0.02·0.5H2O in a Sol-Gel-Derived γ-Al2O3 Matrix. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 4722–4730. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, T.; Agouram, S.; Sánchez-Royo, J.F.; Murillo, R.; Mastral, A.M.; Aranda, A.; Vázquez, I.; Dejoz, A.; Solsona, B. Deep oxidation of volatile organic compounds using ordered cobalt oxides prepared by a nanocasting route. Appl. Catal. A 2010, 386, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Hao, Z. Novel CH4 Combustion Catalysts Derived from Cu-Co/X-Al (X = Fe, Mn, La, Ce) Hydrotalcite-like Compounds. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Solsona, B.; Davies, T.E.; Garcia, T.; Vázquez, I.; Dejoz, A.; Taylor, S.H. Total oxidation of propane using nanocrystalline cobalt oxide and supported cobalt oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2008, 84, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahlawane, N. Kinetics of methane combustion over CVD-made cobalt oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2006, 67, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Genty, E.; Brunet, J.; Poupin, C.; Casale, S.; Capelle, S.; Massiani, P.; Siffert, S.; Cousin, R. Co-Al Mixed Oxides Prepared via LDH Route Using Microwaves or Ultrasound: Application for Catalytic Toluene Total Oxidation. Catalysts 2015, 5, 851-867. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5020851
Genty E, Brunet J, Poupin C, Casale S, Capelle S, Massiani P, Siffert S, Cousin R. Co-Al Mixed Oxides Prepared via LDH Route Using Microwaves or Ultrasound: Application for Catalytic Toluene Total Oxidation. Catalysts. 2015; 5(2):851-867. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5020851
Chicago/Turabian StyleGenty, Eric, Julien Brunet, Christophe Poupin, Sandra Casale, Sylvie Capelle, Pascale Massiani, Stéphane Siffert, and Renaud Cousin. 2015. "Co-Al Mixed Oxides Prepared via LDH Route Using Microwaves or Ultrasound: Application for Catalytic Toluene Total Oxidation" Catalysts 5, no. 2: 851-867. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5020851
APA StyleGenty, E., Brunet, J., Poupin, C., Casale, S., Capelle, S., Massiani, P., Siffert, S., & Cousin, R. (2015). Co-Al Mixed Oxides Prepared via LDH Route Using Microwaves or Ultrasound: Application for Catalytic Toluene Total Oxidation. Catalysts, 5(2), 851-867. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5020851







