Use of a µ-Scale Synthetic Gas Bench for Direct Comparison of Urea-SCR and NH3-SCR Reactions over an Oxide Based Powdered Catalyst
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
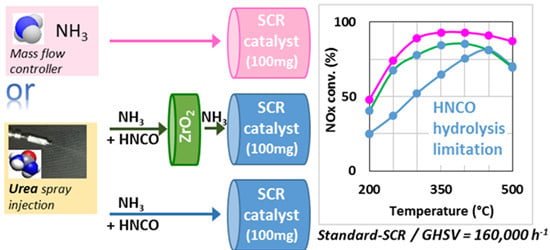
2.1. Comparison of Urea-SCR and NH3-SCR Behaviour—Effect of the Urea Residence Time

| Temperature | Reductant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3 | Urea, tR = 5.2 s/6.2 s | Urea, tR = 4.0 s | Urea, tR = 4.0 s + ZrO2 (150 mg) | |
| 200 °C | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.03 |
| 250 °C | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 1.01 |
| 300 °C | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 1.01 |
| 350 °C | 1.02 | 1.01 | 1.16 | 1.01 |
| 400 °C | 1.04 | 1.05 | 1.20 | 1.07 |
| 450 °C | 1.08 | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.15 |
| 500 °C | 1.14 | 1.16 | 1.36 | 1.36 |

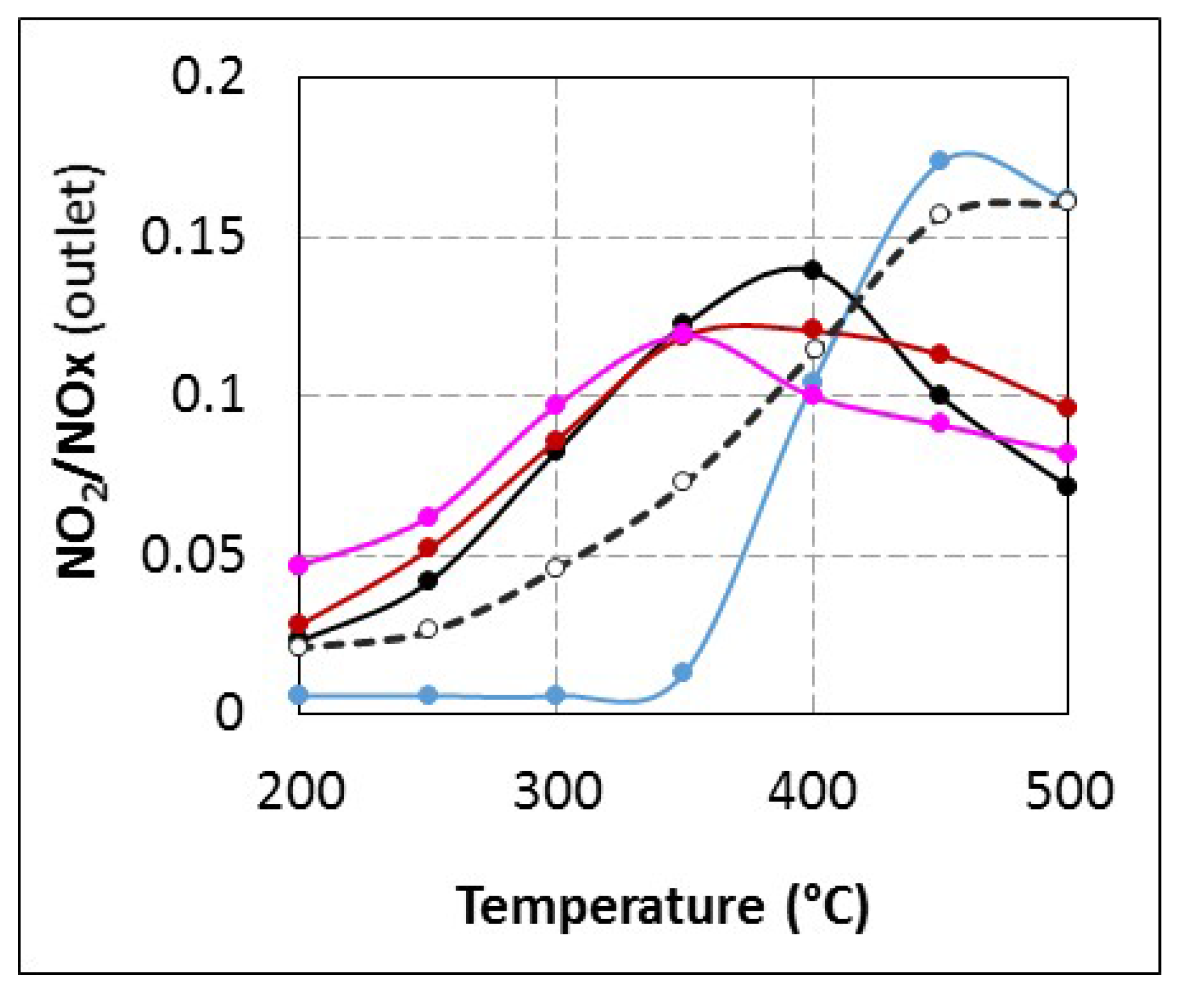
2.2. Impact of Short Urea Residence Time in Urea-SCR
2.2.1. Study of the Possible Poisoning of the Active SCR Sites


| Catalytic Bed | SCR Catalyst Alone | Double Catalytic Bed | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 (100 mg) + SCR Sample | TiO2 (100 mg) + SCR Sample | ZrO2 (100 mg) + SCR Sample | ZrO2 (150 mg) + SCR Sample | |||||
| Reductant | NH3 | Urea tR = 5.2 s | Urea tR = 4.0 s | Urea tR = 4.0s + NH3 | Urea tR = 4.0s | |||
| 200 °C | 4.7 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 4.8 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 3.4 |
| 250 °C | 6.2 | 4.1 | 0.6 | 6.4 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 5.7 |
| 300 °C | 9.7 | 8.2 | 0.6 | 9.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 8.5 |
| 350 °C | 11.9 | 12.2 | 1.3 | 11.0 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 12.5 |
| 400 °C | 10.0 | 13 | 10.3 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 9.7 | 10.2 | 10.8 |
| 450 °C | 9.1 | 10.0 | 17.2 | 9.3 | 15.4 | 10.7 | 15.0 | 9.3 |
| 500 °C | 8.2 | 7.1 | 16.1 | 8.0 | 15.0 | 7.3 | 14.3 | 9.8 |
2.2.2. Reactivity of Urea or By-Products with Oxygen
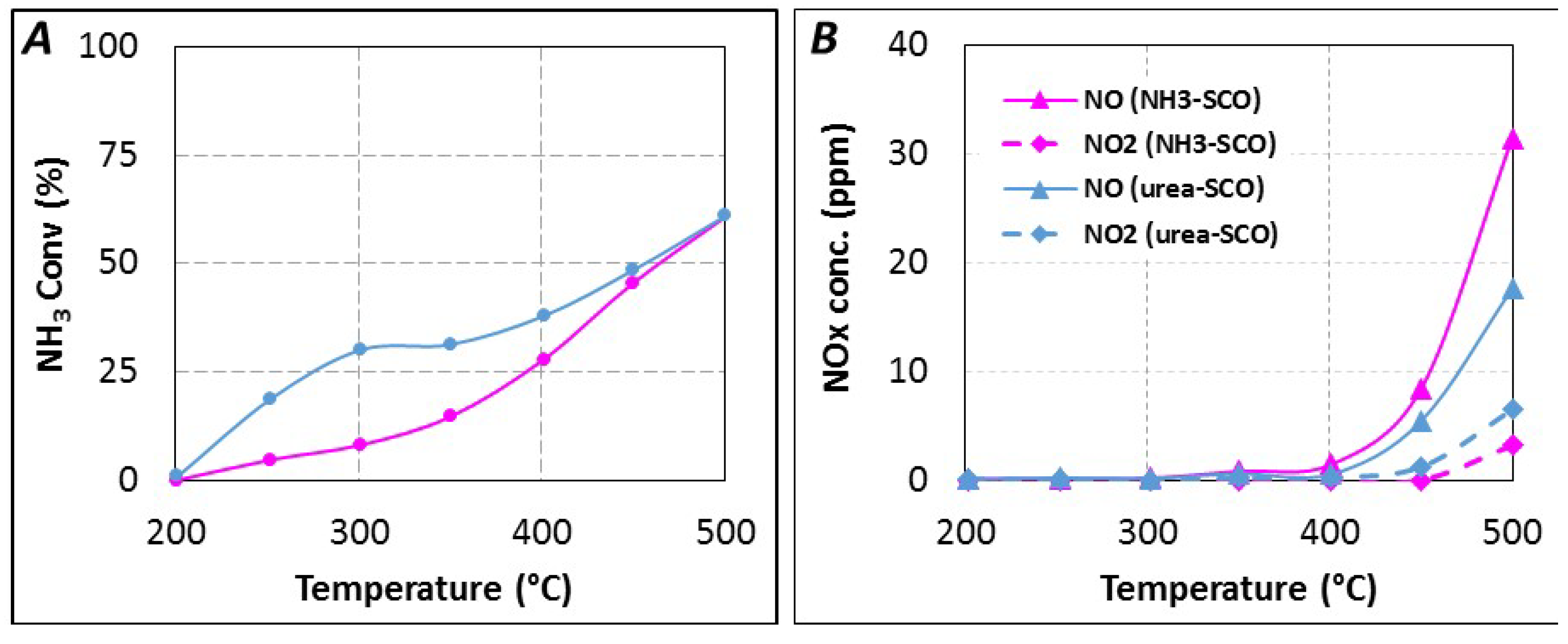
2.2.3. SCR Reaction Stoichiometry
2.2.4. Understanding of the Loss of Activity Observed for tR = 4.0 s


3. Material and Methods
3.1. Catalysts
3.2. Physical and Surface Properties
3.3. Catalytic Tests

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kobayashi, T.; Yamada, T.; Kayano, K. Study of NOx Trap Reaction by Thermodynamic Calculation; SAE Technical Papers 970745; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, February 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, F.; Courtois, X.; Royer, S.; Blanchard, G.; Rousseau, S.; Duprez, D. An overview of the production and use of ammonia in NSR + SCR coupled system for NOx reduction from lean exhaust gas. Catal. Today 2012, 197, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, E.; Courtois, X.; Marécot, P.; Duprez, D. NO reduction by hydrocarbons and oxygenated compounds in O2 excess over a Pt/Al2O3 catalyst: A comparative study of the efficiency of different reducers (hydrocarbons and oxygenated compounds). Appl. Catal. B 2006, 64, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Yentekakis, I.V. The Reduction of NO by Propene over Ba-Promoted Pt/γ-Al2O3 Catalysts. J. Catal. 2001, 198, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, J.; Shimizu, K.I.; Satsuma, A.; Hattori, T. Influence of hydrocarbon structure on selective catalytic reduction of NO by hydrocarbons over Cu–Al2O3. Appl. Catal. B 2002, 37, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulou, E.F.; Evdou, A.P.; Lemonidou, A.A.; Vasalos, I.A. Ag/alumina catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx using various reductants. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 274, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, P.; Giroir-Fendler, A.; Praliaud, H.; Primet, M. Role of the Nature of the Support (Alumina or Silica), of the Support Porosity, and of the Pt Dispersion in the Selective Reduction of NO by C3H6 under Lean-Burn Conditions. J. Catal. 2000, 189, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunula, T.; Ahola, J.; Hamada, H. Reaction mechanism and kinetics of NOx reduction by propene on CoOx/alumina catalysts in lean conditions. Appl. Catal. B 2000, 26, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M.; Elsener, M.; Kröcher, O.; Schär, C.; Röthlisberger, R.; Jaussi, F.; Mangold, M. NOx Reduction in the Exhaust of Mobile Heavy-Duty Diesel Engines by Urea-SCR. Top. Catal. 2004, 30–31, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; McCabe, R.W.; Hammerle, R.H. NOx self-inhibition in selective catalytic reduction with urea (ammonia) over a Cu-zeolite catalyst in diesel exhaust. Appl. Catal. B 2002, 39, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.A.; Doherty, J.A. NH3 and urea in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx over oxide-supported copper catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2005, 55, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, F.; Berland, S.; Royer, S.; Courtois, X.; Duprez, D. Composition-Dependent Performance of CexZr1−xO2 Mixed-Oxide-Supported WO3 Catalysts for the NOx Storage Reduction—Selective Catalytic Reduction Coupled Process. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M.; Elsener, M.; Kleemann, M. Urea-SCR: A promising technique to reduce NOx emissions from automotive diesel engines. Catal. Today 2000, 59, 335–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flura, A.; Can, F.; Courtois, X.; Royer, S.; Duprez, D. High-surface-area zinc aluminate supported silver catalysts for low-temperature SCR of NO with ethanol. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 126, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, F.; Flura, A.; Courtois, X.; Royer, S.; Blanchard, G.; Marecot, P.; Duprez, D. Role of the alumina surface properties on the ammonia production during the NOx SCR with ethanol over Ag/Al2O3 catalysts. Catal. Today 2011, 164, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietti, L.; Nova, I.; Forzatti, P. Role of ammonia in the reduction by hydrogen of NOx stored over Pt–Ba/Al2O3 lean NOx trap catalysts. J. Catal. 2008, 257, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M.; Madia, G.; Elsener, M. Selective catalytic reduction of NO and NO2 at low temperatures. Catal. Today 2002, 73, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nova, I.; Ciardelli, C.; Tronconi, E.; Chatterjee, D.; Bandl-Konrad, B. NH3–NO/NO2 chemistry over V-based catalysts and its role in the mechanism of the Fast SCR reaction. Catal. Today 2006, 114, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzatti, P.; Lietti, L.; Tronconi, E. Nitrogen Oxides Removal—Industrial. Encyclopaedia of Catalysis, 1st ed.; Horvath, I.T., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, A.; Matsuda, S.; Kamo, T.; Nakajima, F.; Kuroda, H.; Narita, T. Reaction between nitrogen oxide (NOx) and ammonia on iron oxide-titanium oxide catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. 1981, 85, 4099–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.L.; DaCosta, H.F.M. Urea thermolysis and NOx reduction with and without SCR catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2003, 46, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M.; Strutz, E.O. Thermal and Hydrolytic Decomposition of Urea for Automotive Selective Catalytic Reduction Systems: Thermochemical and Practical Aspects. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhard, A.M.; Peitz, D.; Elsener, M.; Schildhauer, T.; Kröcher, O. Catalytic urea hydrolysis in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx: Catalyst screening and kinetics on anatase TiO2 and ZrO2. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, P.M.; Colson, J.; Higgins, S.; Thielen, D.; Anspach, B.; Brauer, B. Thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) of urea in an open reaction vessel. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 424, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M.; Elsener, M. Determination of urea and its thermal decomposition products by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 689, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoelo, E.F. A lumped model for thermal decomposition of urea. Uncertainties analysis and selective non-catalytic reduction of NO. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebelius, S.; Le, T.T.; Pettersson, L.J.; Lind, H. Identification of urea decomposition from an SCR perspective; A combination of experimental work and molecular modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grout, S.; Blaisot, J.B.; Pajot, K.; Osbat, G. Experimental investigation on the injection of an urea-water solution in hot air stream for the SCR application: Evaporation and spray/wall interaction. Fuel 2013, 106, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkhold, F.; Meingast, U.; Wassermann, P.; Deutschmann, O. Modeling and simulation of the injection of urea-water-solution for automotive SCR DeNOx-systems. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 70, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitz, D.; Bernhard, A.; Elsener, M.; Kröcher, O. Laboratory test reactor for the investigation of liquid reducing agents in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitto, C.; Delahay, G. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 on Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts: Influence of silicium content on the activity of calcined and hydrotreated samples. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdier, S.; Rohart, E.; Bradshaw, H.; Harris, D. Acidic Zirconia Materials for Durable NH3-SCR deNOx Catalysts; SAE Technical Paper 2008-01-1022; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, April 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Nanba, T.; Sasaki, M.; Haneda, M.; Suzuki, K.; Hamada, H. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over different copper exchanged zeolites in the presence of decane. Catal. Today 2011, 164, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seneque, M.; Can, F.; Duprez, D.; Courtois, X. Use of a µ-Scale Synthetic Gas Bench for Direct Comparison of Urea-SCR and NH3-SCR Reactions over an Oxide Based Powdered Catalyst. Catalysts 2015, 5, 1535-1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5031535
Seneque M, Can F, Duprez D, Courtois X. Use of a µ-Scale Synthetic Gas Bench for Direct Comparison of Urea-SCR and NH3-SCR Reactions over an Oxide Based Powdered Catalyst. Catalysts. 2015; 5(3):1535-1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5031535
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeneque, Mickael, Fabien Can, Daniel Duprez, and Xavier Courtois. 2015. "Use of a µ-Scale Synthetic Gas Bench for Direct Comparison of Urea-SCR and NH3-SCR Reactions over an Oxide Based Powdered Catalyst" Catalysts 5, no. 3: 1535-1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5031535
APA StyleSeneque, M., Can, F., Duprez, D., & Courtois, X. (2015). Use of a µ-Scale Synthetic Gas Bench for Direct Comparison of Urea-SCR and NH3-SCR Reactions over an Oxide Based Powdered Catalyst. Catalysts, 5(3), 1535-1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5031535