Immobilization of Thermostable Lipase QLM on Core-Shell Structured Polydopamine-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
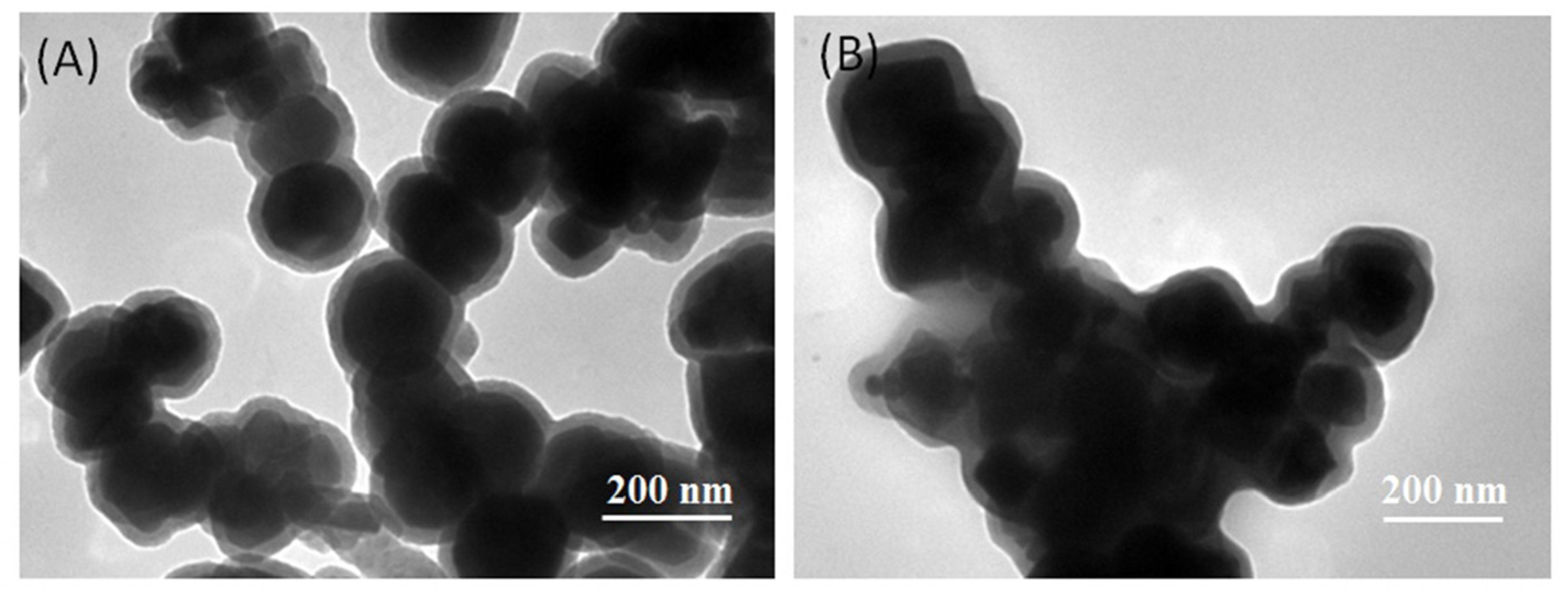
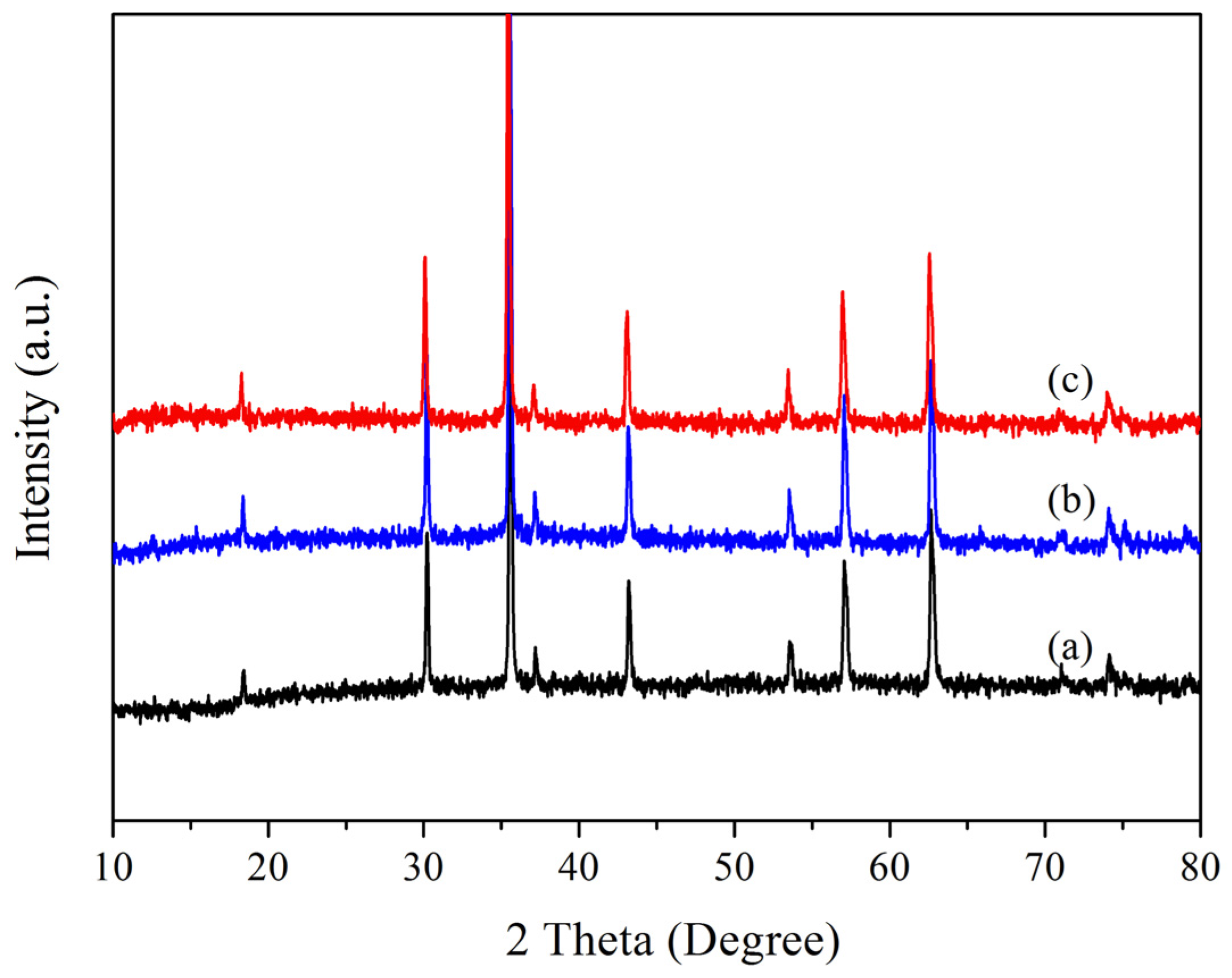
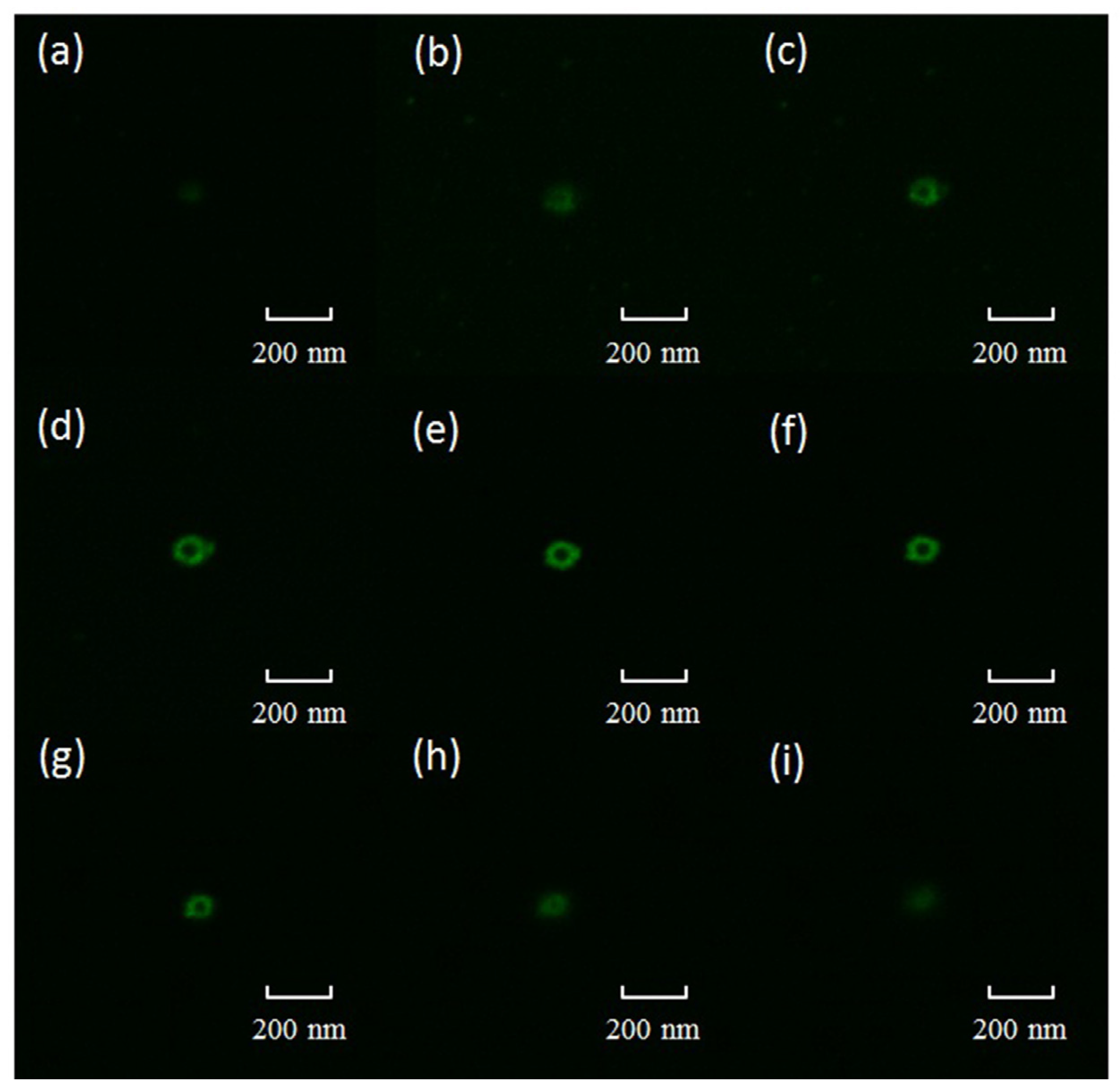
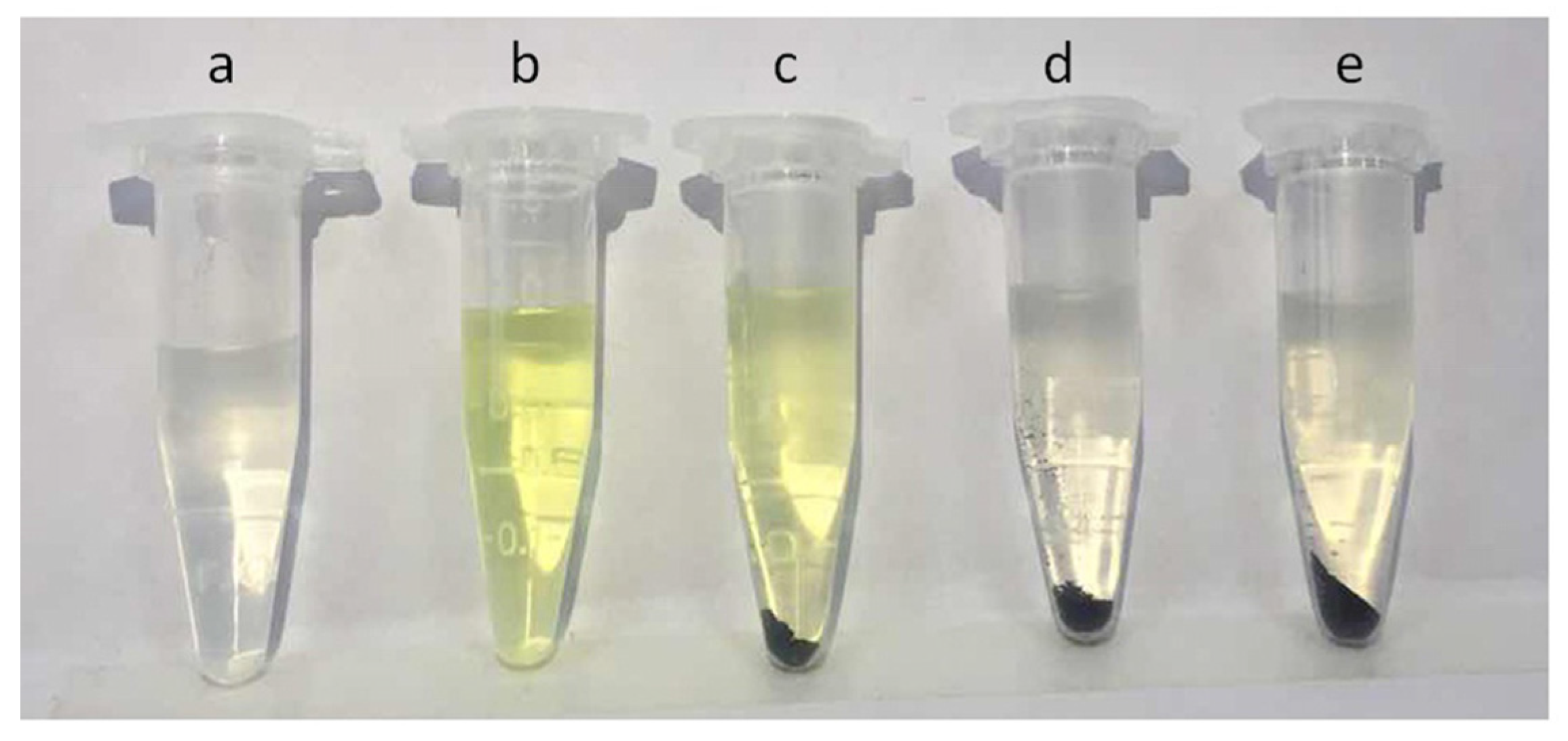
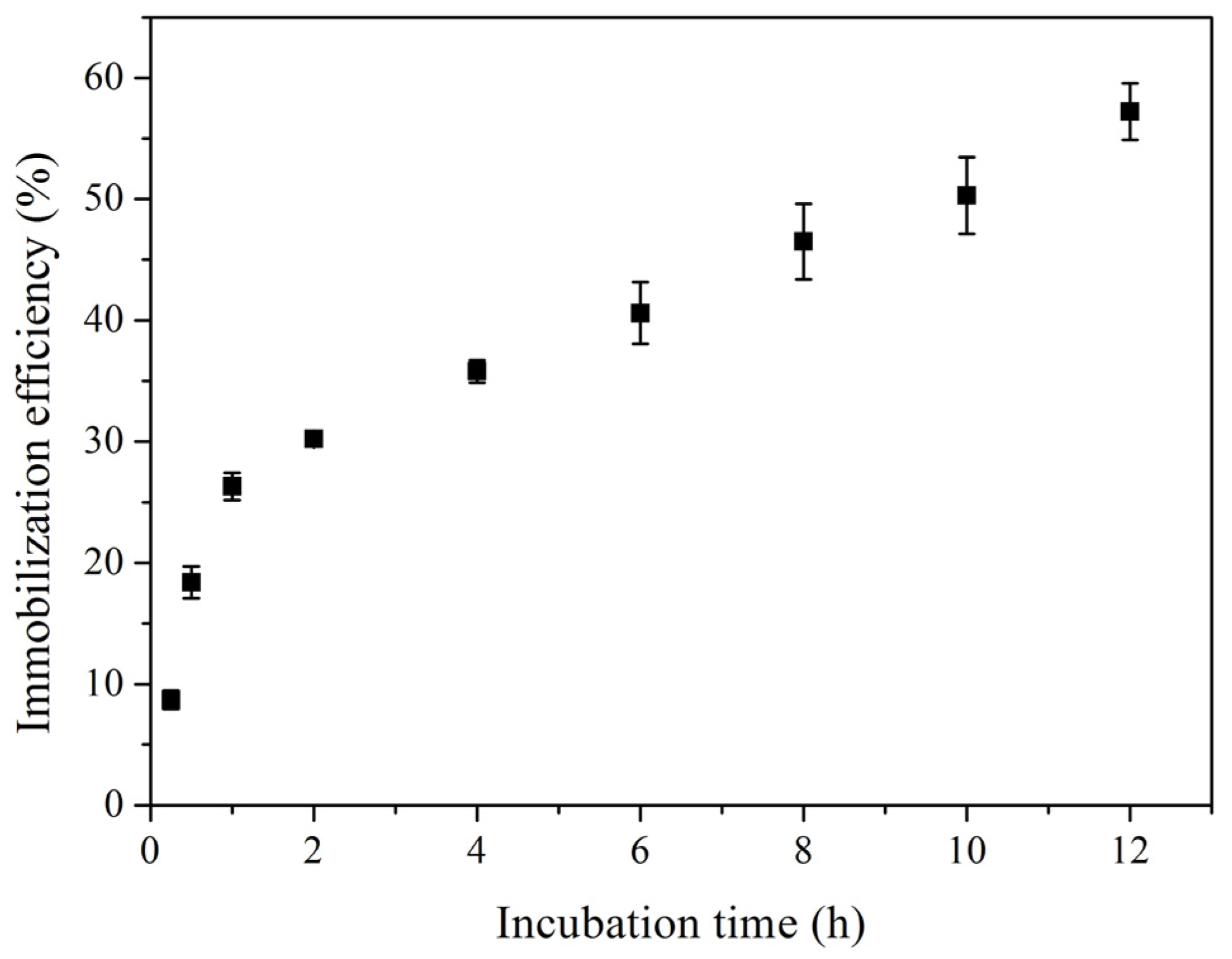
2.1. Characterization of Immobilized Lipase QLM on Polydopamine-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
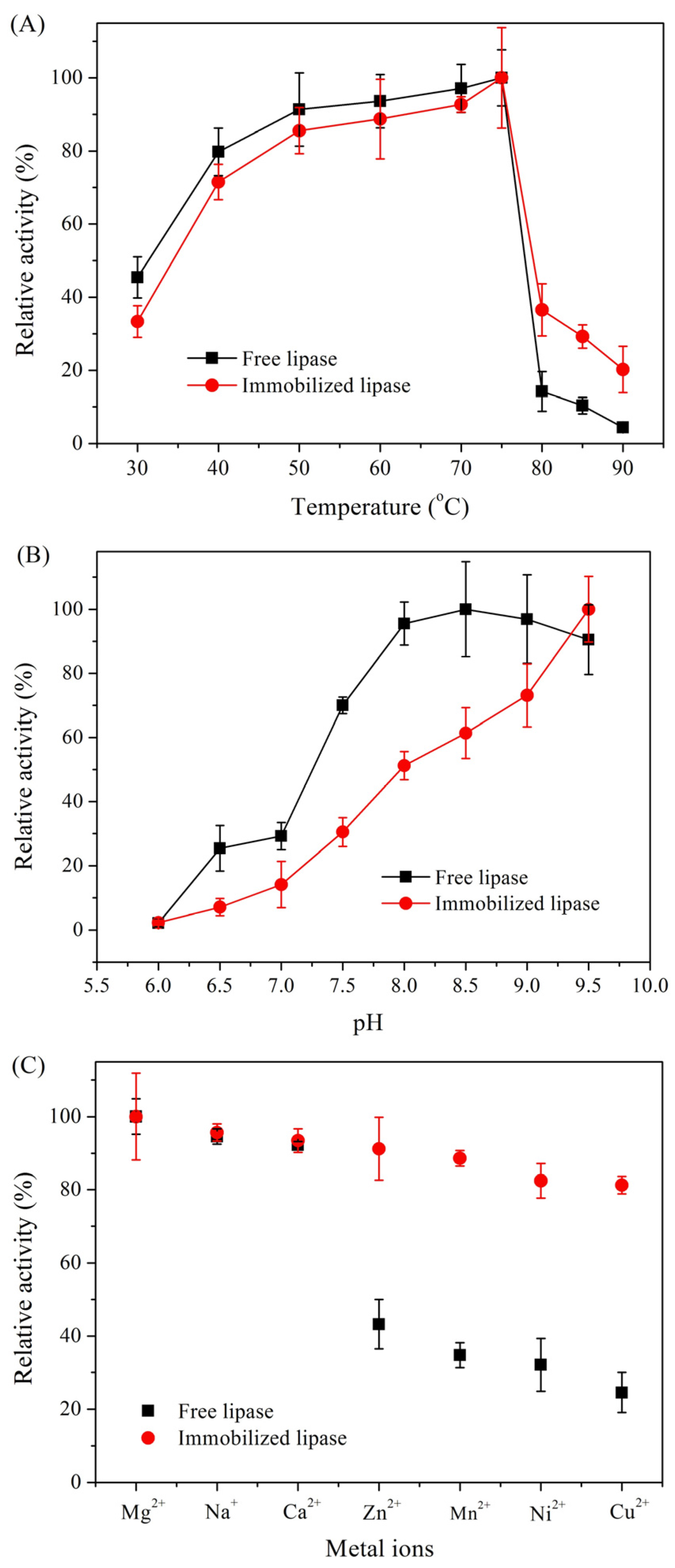
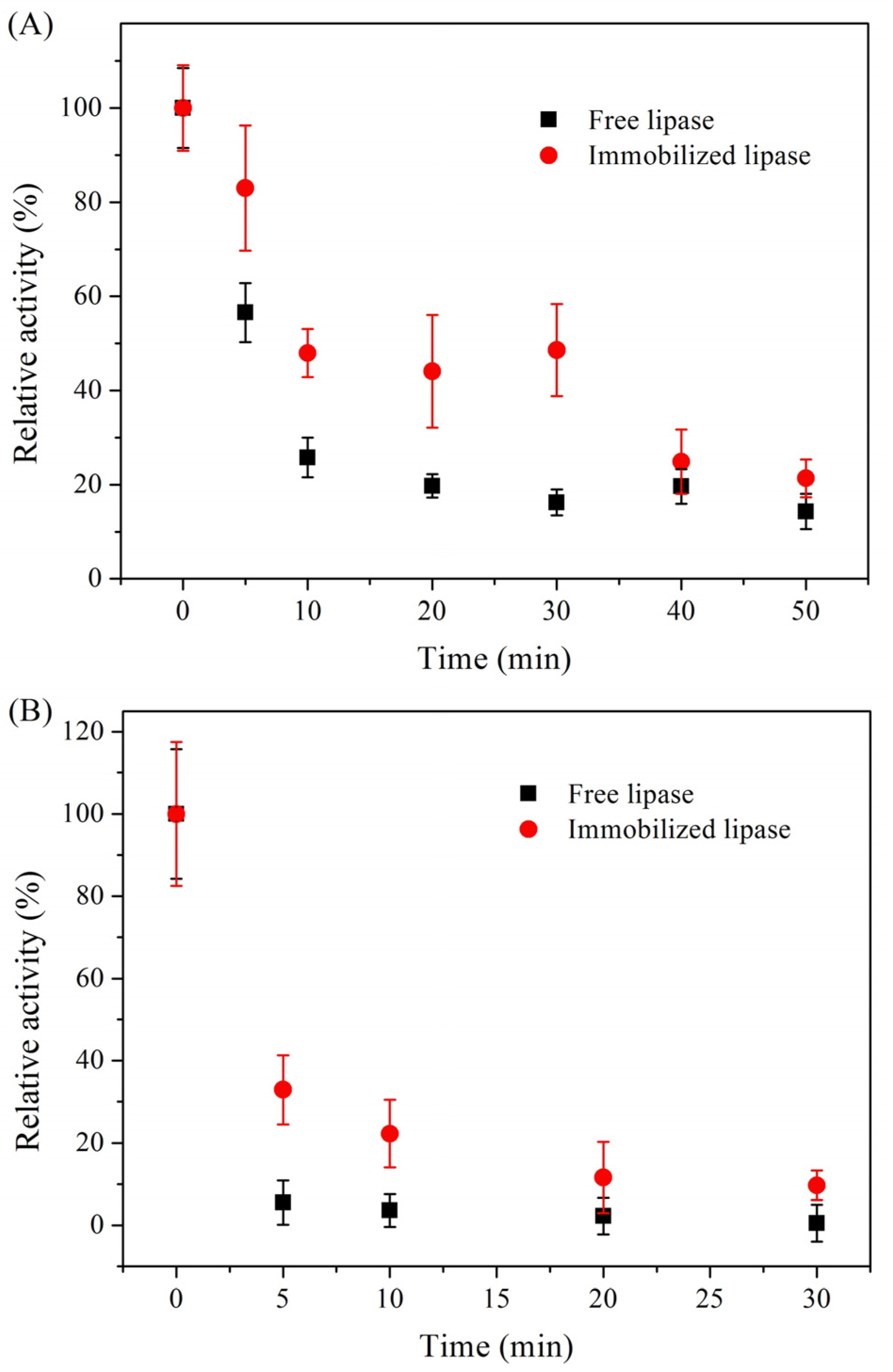
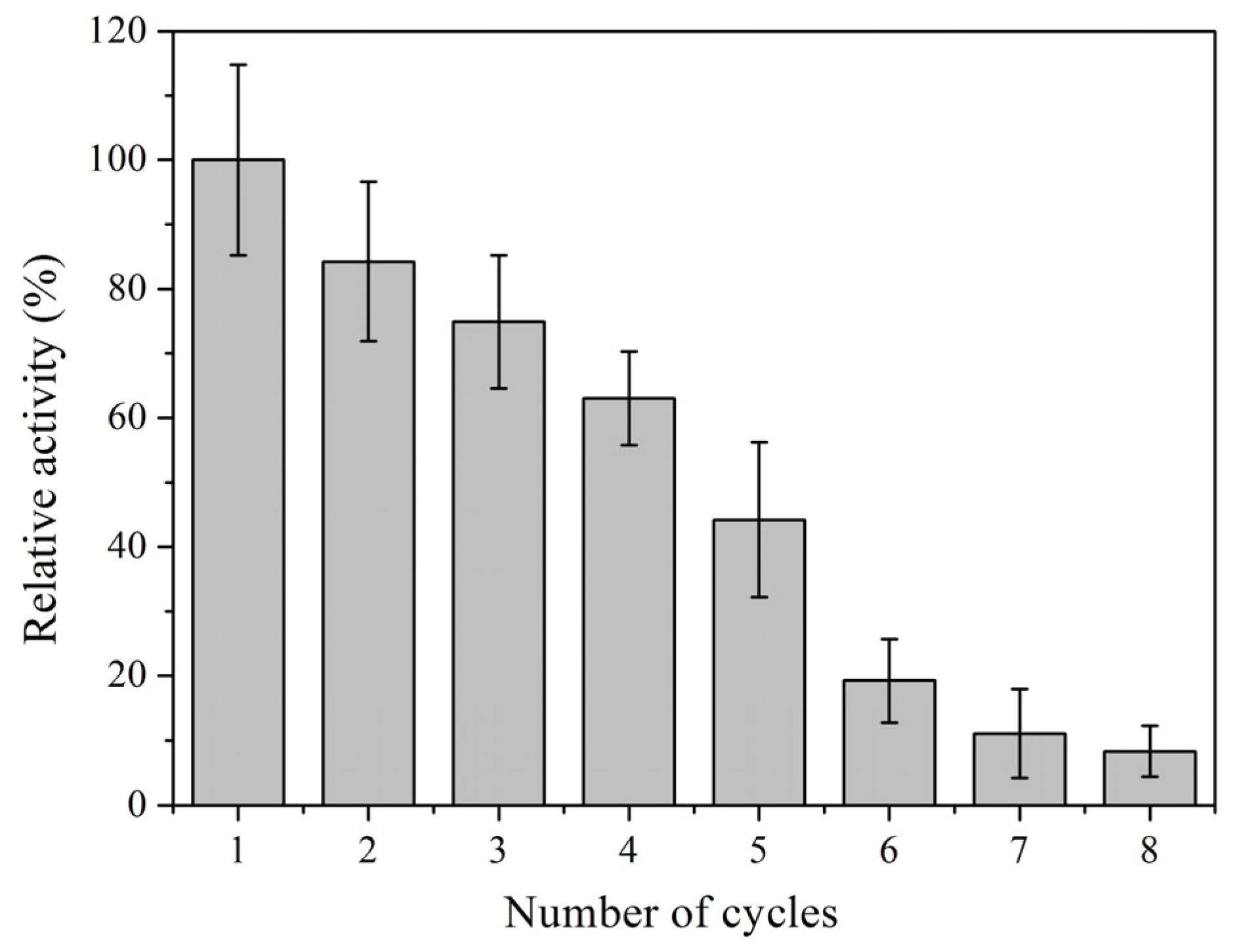
2.2. Ester Hydrolysis Catalyzed by the Immobilized Enzyme
2.3. Kinetic Resolution Catalyzed by the Immobilized Enzyme
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Immobilization of Lipase QLM on Polydopamine-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticle
3.3. Characterization of Immbozilized Enzyme
3.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic Analysis
3.5. Ester Hydrolysis Catalyzed by an Immobilized Enzyme
3.6. Kinetic Resolution Catalyzed by the Immobilized Enzyme
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Miranda, A.S.; Miranda, L.S.; de Souza, R.O. Lipases: Valuable catalysts for dynamic kinetic resolutions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 372–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornscheuer, U.T. Immobilizing enzymes: How to create more suitable biocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3336–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Ke, C.; Huang, Y.; Yan, Y. Immobilized Aspergillus niger lipase with SiO2 nanoparticles in sol-gel materials. Catalysts 2016, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.E.; Eggert, T. Lipases for biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, F.; Shah, A.A.; Hameed, A. Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levisson, M.; van der Oost, J.; Kengen, S.W.M. Carboxylic ester hydrolases from hyperthermophiles. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, L.; Palomo, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Illanes, A.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.F. Effect of lipase-lipase interactions in the activity, stability and specificity of a lipase from Alcaligenes sp. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Feng, Y. Solvent effects on the enantioselectivity of the thermophilic lipase QLM in the resolution of (R, S)-2-octanol and (R, S)-2-pentanol. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2009, 56, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Han, H.; Shi, H.; Tian, Y.; Sun, F.; Song, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhu, G. Construction of thermophilic lipase-embedded metal-organic frameworks via biomimetic mineralization: A biocatalyst for ester hydrolysis and kinetic resolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24517–24524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L. Immobilised enzymes: science or art? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 9, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanefeld, U.; Gardossi, L.; Magner, E. Understanding enzyme immobilisation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, R.A.; van Pelt, S. Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: Why, what and how. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6223–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiu, H.H.P.; Keane, M.A. Enzyme-magnetic nanoparticle hybrids: New effective catalysts for the production of high value chemicals. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilnejad-Ahranjani, P.; Kazemeini, M.; Singh, G.; Arpanaei, A. Amine-functionalized magnetic nanocomposite particles for efficient immobilization of lipase: Effects of functional molecule size on properties of the immobilized lipase. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 33313–33327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, T.; Chen, L.; Yang, R.; Zhou, N. Controllable synthesis of amine-functionalized Fe3O4 polyhedra for lipase immobilization. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 3124–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lou, G.; Dai, Y. In situ preparation of magnetic Fe3O4-chitosan nanoparticles for lipase immobilization by cross-linking and oxidation in aqueous solution. Bioresource Technol. 2009, 100, 3459–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Yi, L.; Yang, Y.; Xia, C. Study on immobilization of lipase onto magnetic microspheres with epoxy groups. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Xu, K.; Song, X.; Hu, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, C. Effective adsorption and separation of lysozyme with PAA-modified Fe3O4@silica core/shell microspheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 336, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Sun, L.; Lin, H.; Guo, Z. Multifunctional composite core-shell nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4474–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, B.; Zhang, F. Synthesis of carbon-coated Fe3O4 composites with pine-tree-leaf structures from catalytic pyrolysis of polyethylene. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 3451–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilnejad-Ahranjani, P.; Kazemeini, M.; Singh, G.; Arpanaei, A. Study of molecular conformation and activity-related properties of lipase immobilized onto core-shell structured polyacrylic acid-coated magnetic silica nanocomposite particles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3242–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Yang, R. Synthesis of Fe3O4/P(St-AA) nanoparticles for enhancement of stability of the immobilized lipases. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 108583–108589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Ponvel, K.M.; Kim, M.; Hwang, S.; Ahn, I.S.; Lee, C.H. Immobilization of lipase on hydrophobic nano-sized magnetite particles. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2009, 57, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, Y.H.; Wu, T.M. Preparation and characterization of thermosensitive polymers grafted onto silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 326, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X. Penicillium expansum lipase-coated magnetic Fe3O4-polymer hybrid hollow nanoparticles: A highly recoverable and magnetically separable catalyst for the synthesis of 1,3-dibutylurea. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 25983–25992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landarani-Isfahani, A.; Taheri-Kafrani, A.; Amini, M.; Mirkhani, V.; Moghadam, M.; Soozanipour, A.; Razmjou, A. Xylanase immobilized on novel multifunctional hyperbranched polyglycerol-grafted magnetic nanoparticles: An efficient and robust biocatalyst. Langmuir 2015, 31, 9219–9227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W. Perspectives on poly(dopamine). Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 3796–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Huang, R.; Qi, W.; Su, R.; He, Z. Interfacial polymerization of dopamine in a pickering emulsion: Synthesis of cross-linkable colloidosomes and enzyme immobilization at oil/water interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14954–14964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Brust, T.F.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.C.; Watts, V.J.; Yeo, Y. Polydopamine-based simple and versatile surface modification of polymeric nano drug carriers. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3347–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Rho, J.; Messersmith, P.B. Facile conjugation of biomolecules onto surfaces via mussel adhesive protein inspired coatings. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, B. Surface modification of PE porous membranes based on the strong adhesion of polydopamine and covalent immobilization of heparin. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, B.; Xu, Y. Immobilization of bovine serum albumin onto porous polyethylene membranes using strongly attached polydopamine as a spacer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 86, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Rivera, J.; He, L.; Kulkarni, H.; Lee, D.K.; Messersmith, P. Facile, high efficiency immobilization of lipase enzyme on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via a biomimetic coating. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.S.; Fujimoto, Y.; Girdaukas, G.; Sih, C.J. Quantitative analysis of biochemical kinetic resolutions of enantiomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 7294–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yu, S.; Han, W.; Wang, H.; Zheng, B.; Feng, Y. A novel thermophilic lipase from Fervidobacterium nodosum Rt17-B1 representing a new subfamily of bacterial lipases. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2010, 66, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Han, H.; Jiang, W.; Ding, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Immobilization of Thermostable Lipase QLM on Core-Shell Structured Polydopamine-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Catalysts 2017, 7, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020049
Wang C, Han H, Jiang W, Ding X, Li Q, Wang Y. Immobilization of Thermostable Lipase QLM on Core-Shell Structured Polydopamine-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Catalysts. 2017; 7(2):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020049
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chenhui, Haobo Han, Wei Jiang, Xiaobo Ding, Quanshun Li, and Yanbo Wang. 2017. "Immobilization of Thermostable Lipase QLM on Core-Shell Structured Polydopamine-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles" Catalysts 7, no. 2: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020049
APA StyleWang, C., Han, H., Jiang, W., Ding, X., Li, Q., & Wang, Y. (2017). Immobilization of Thermostable Lipase QLM on Core-Shell Structured Polydopamine-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Catalysts, 7(2), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020049




