Dendrimer-Stabilized Ru Nanoparticles Immobilized in Organo-Silica Materials for Hydrogenation of Phenols
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
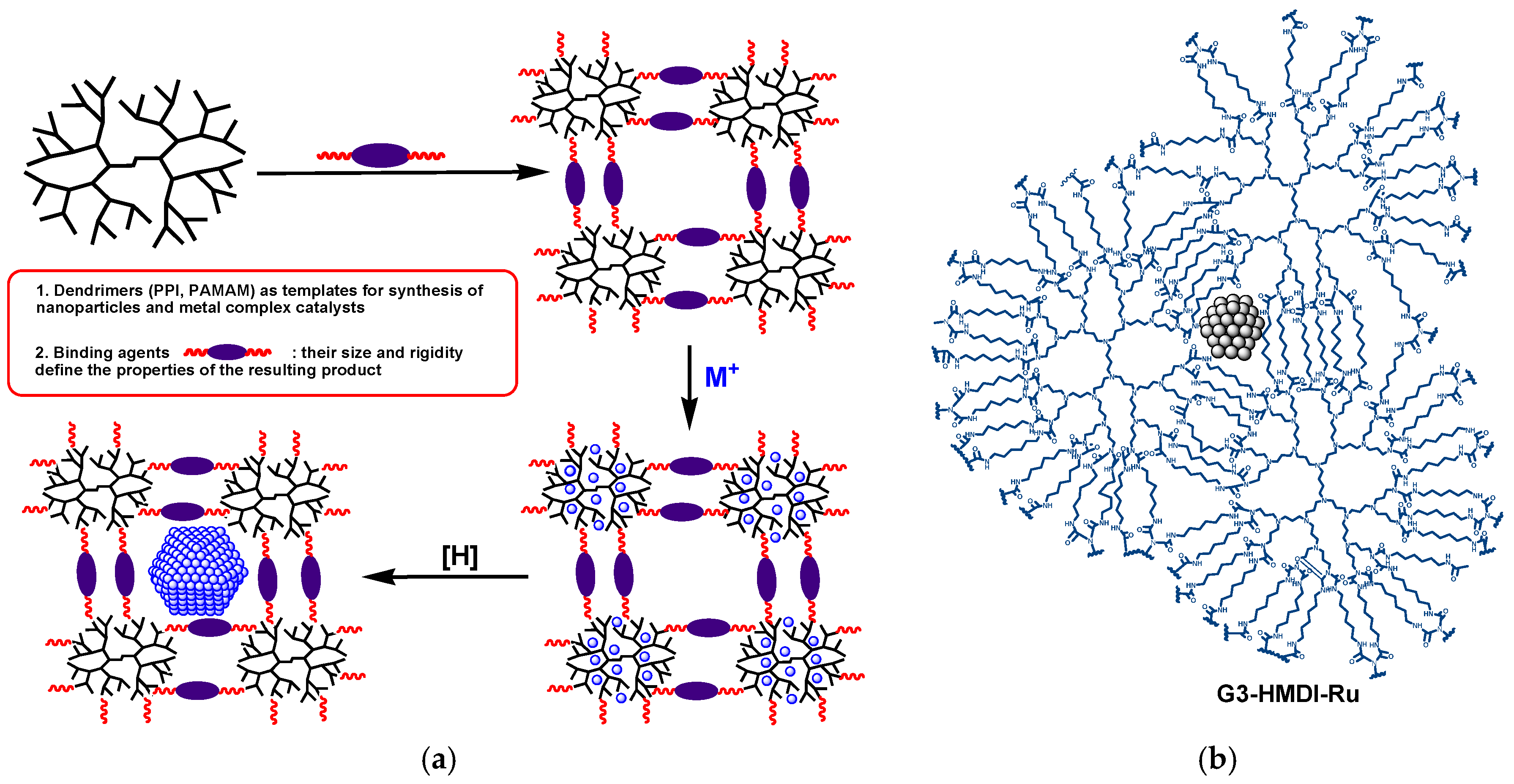
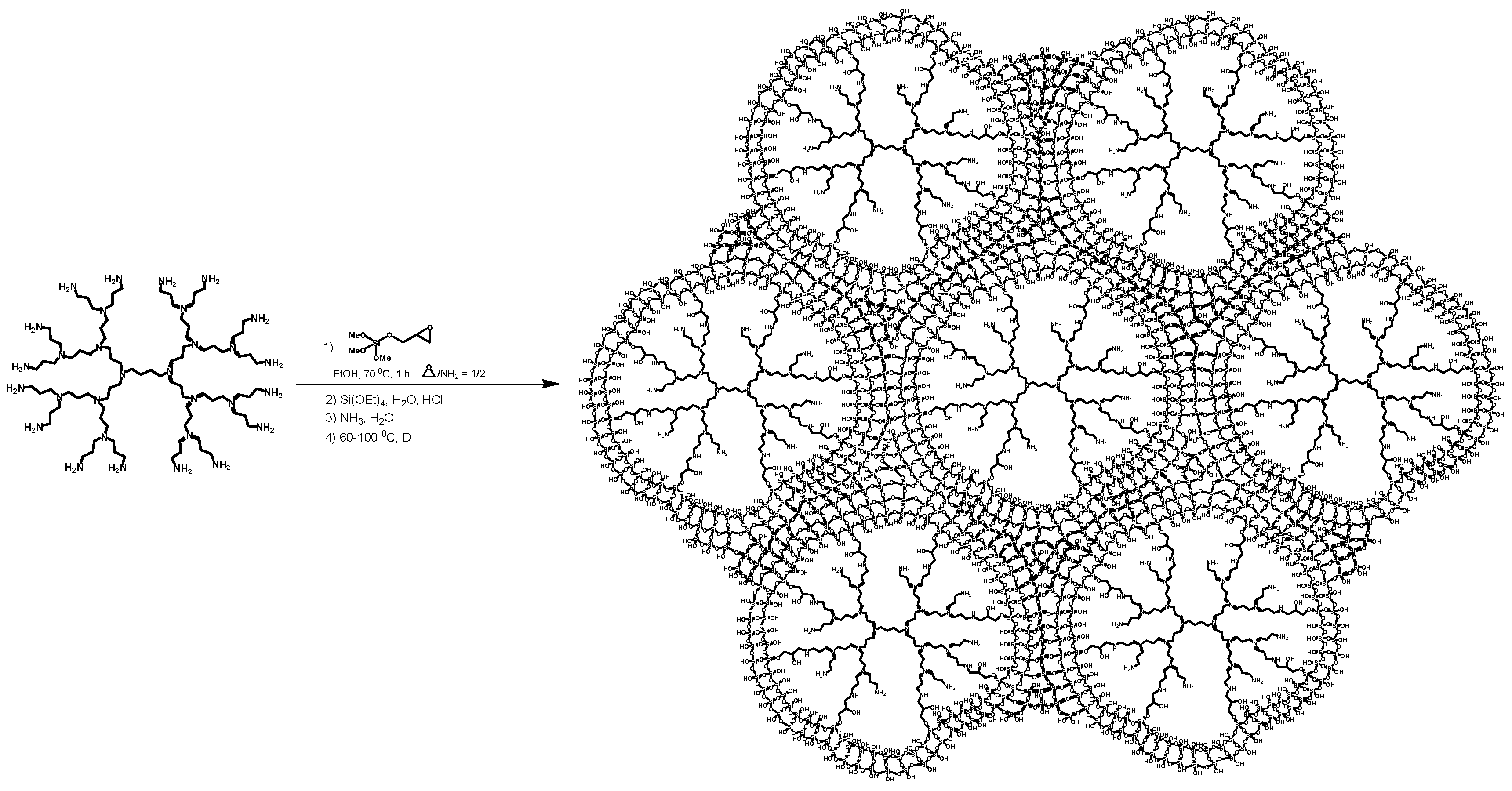
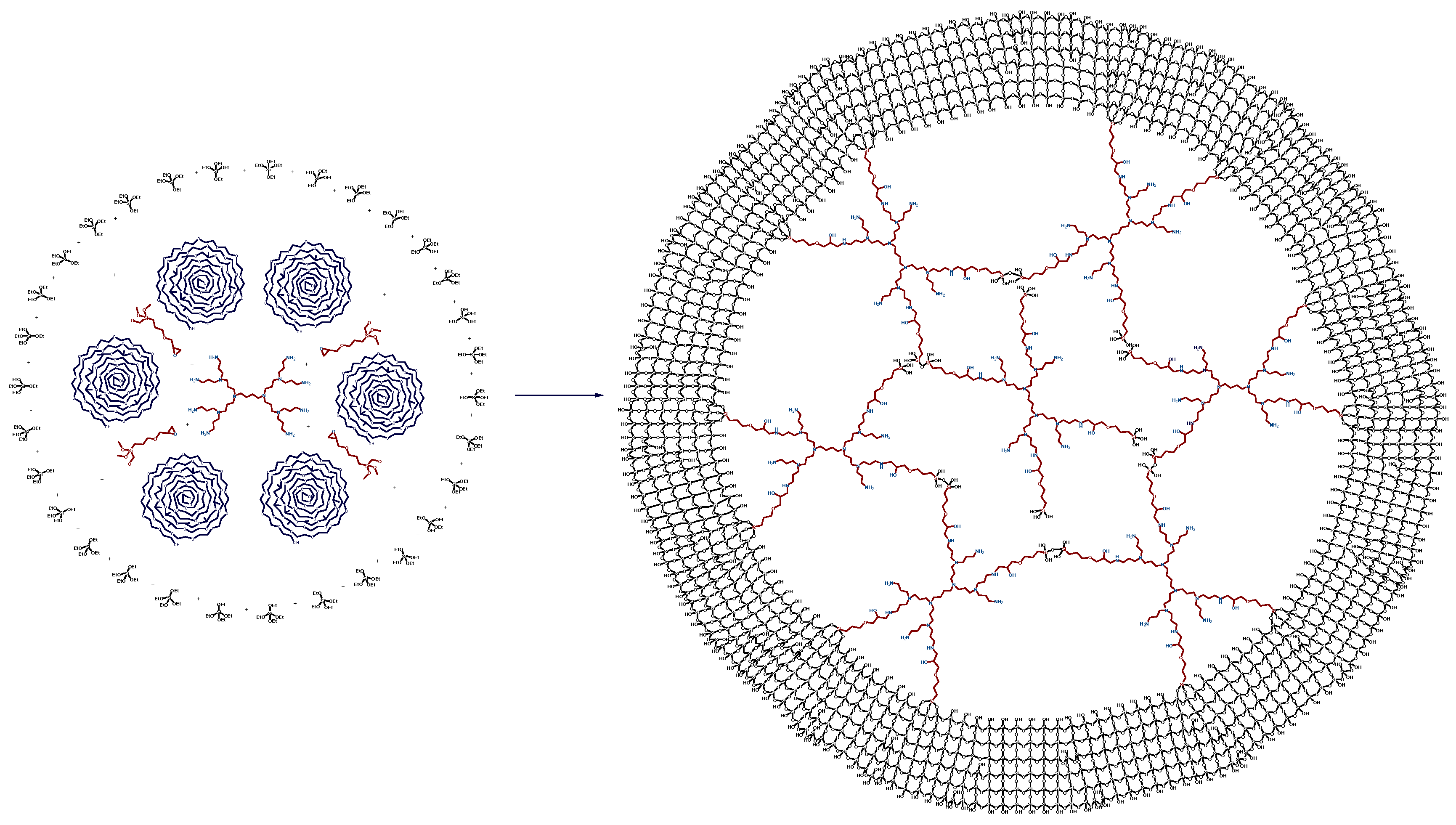
2.1. The Synthesis of Heterogeneous Dendrimer-Based Catalysts
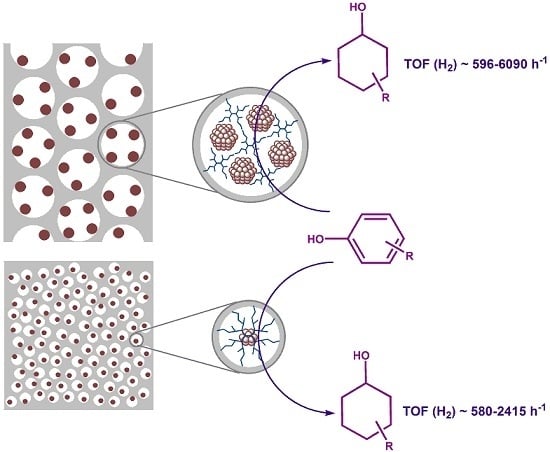
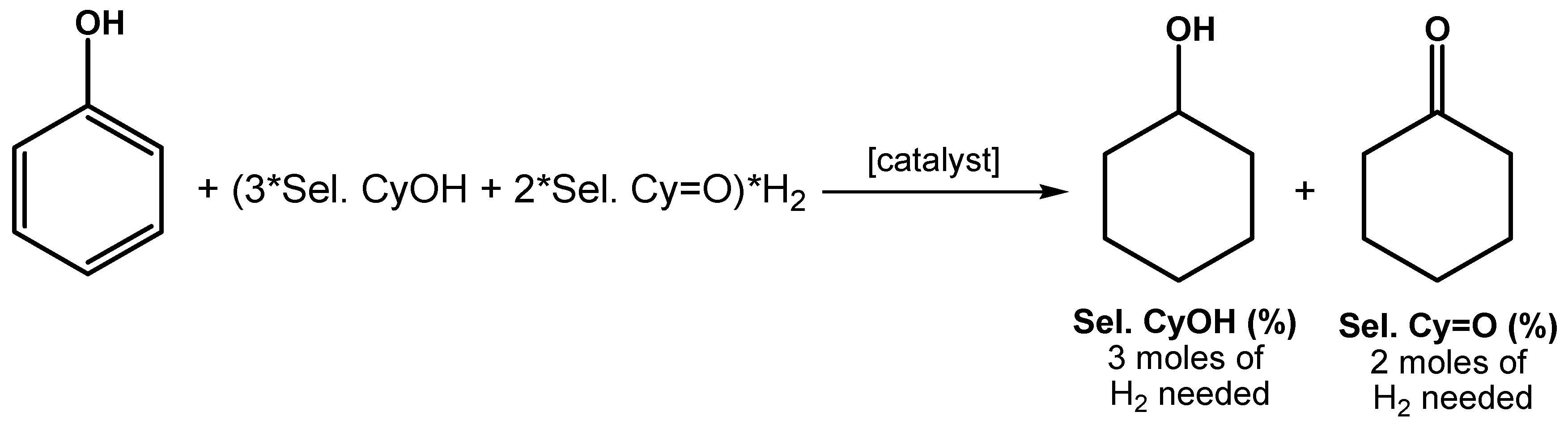
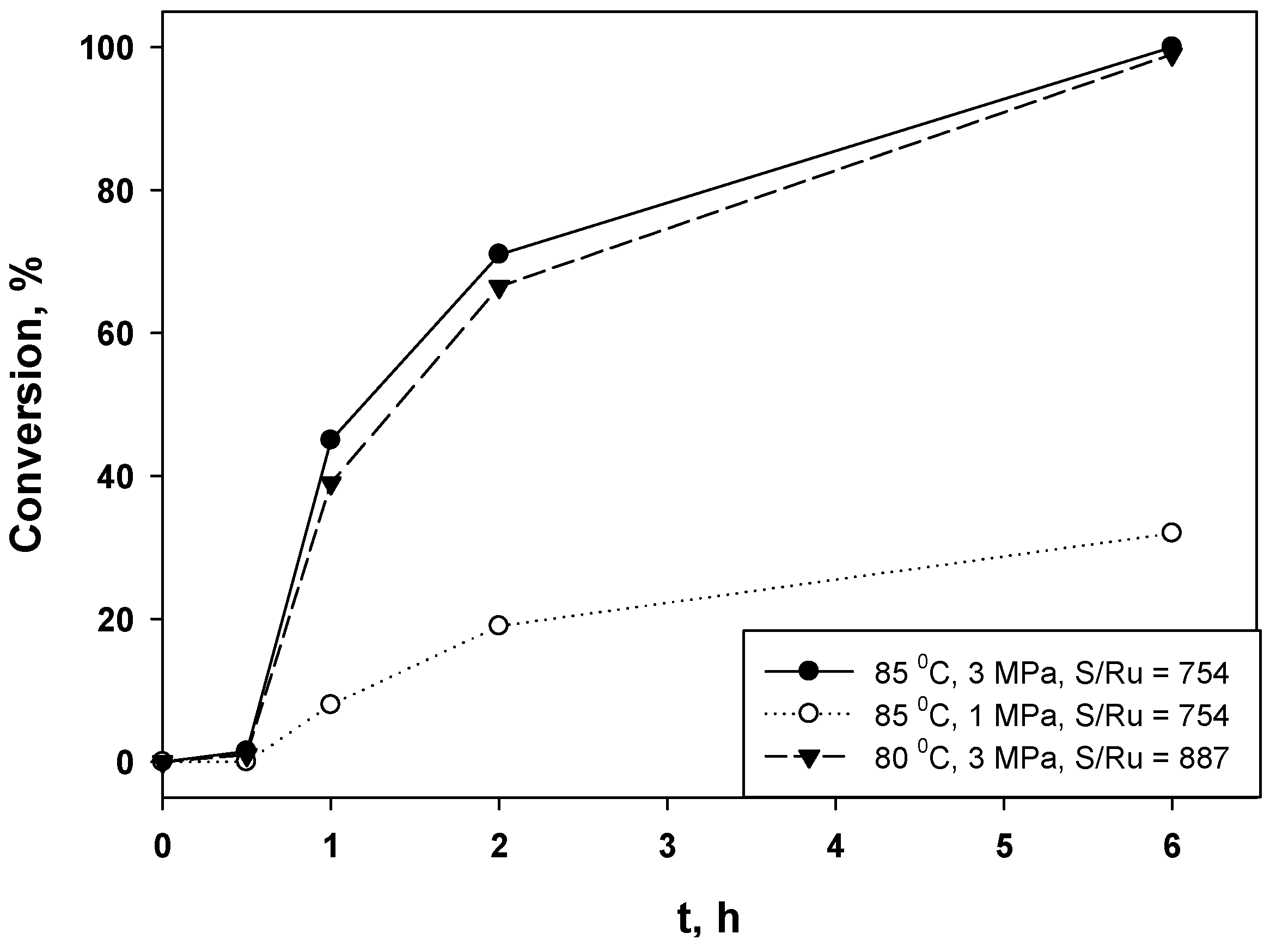
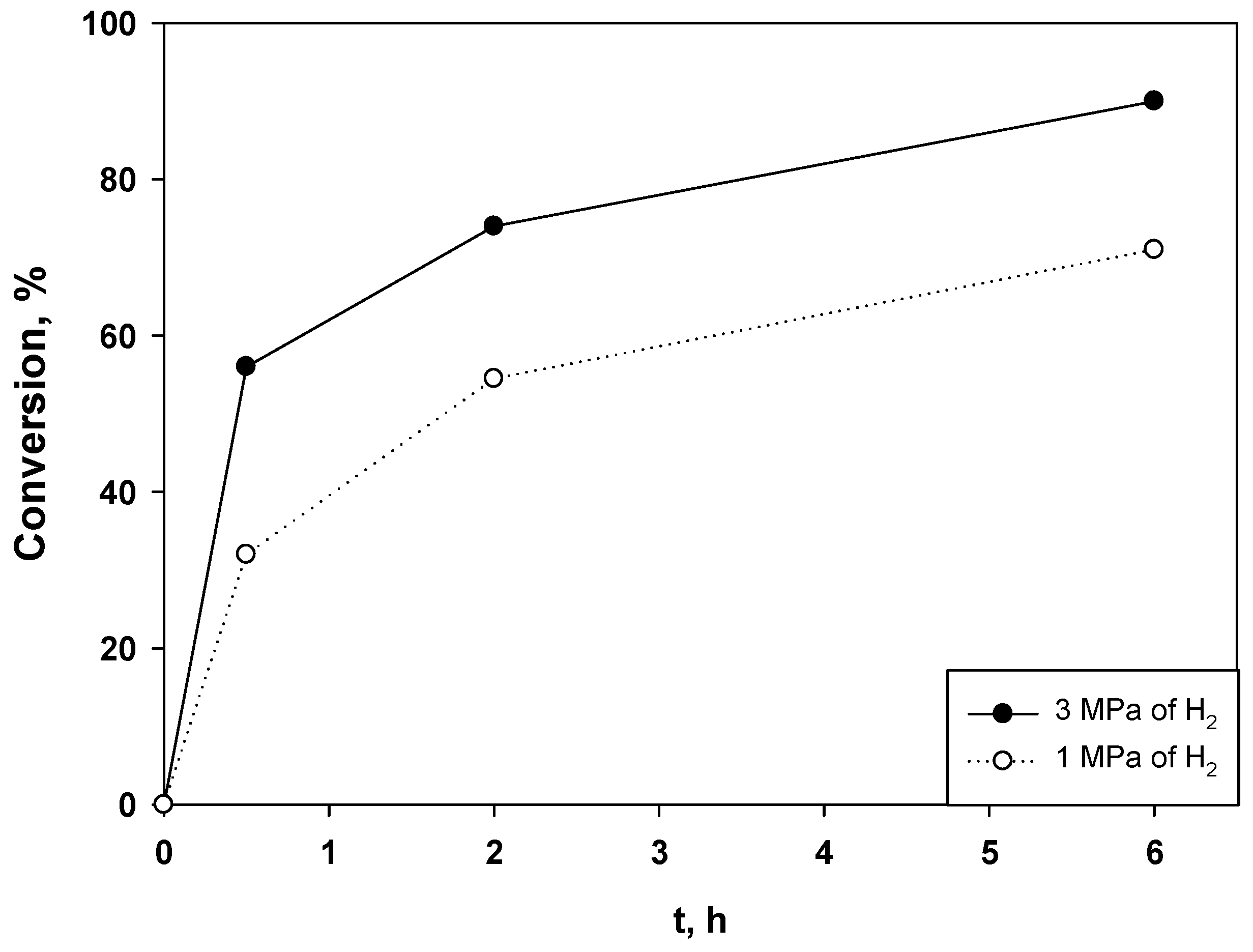
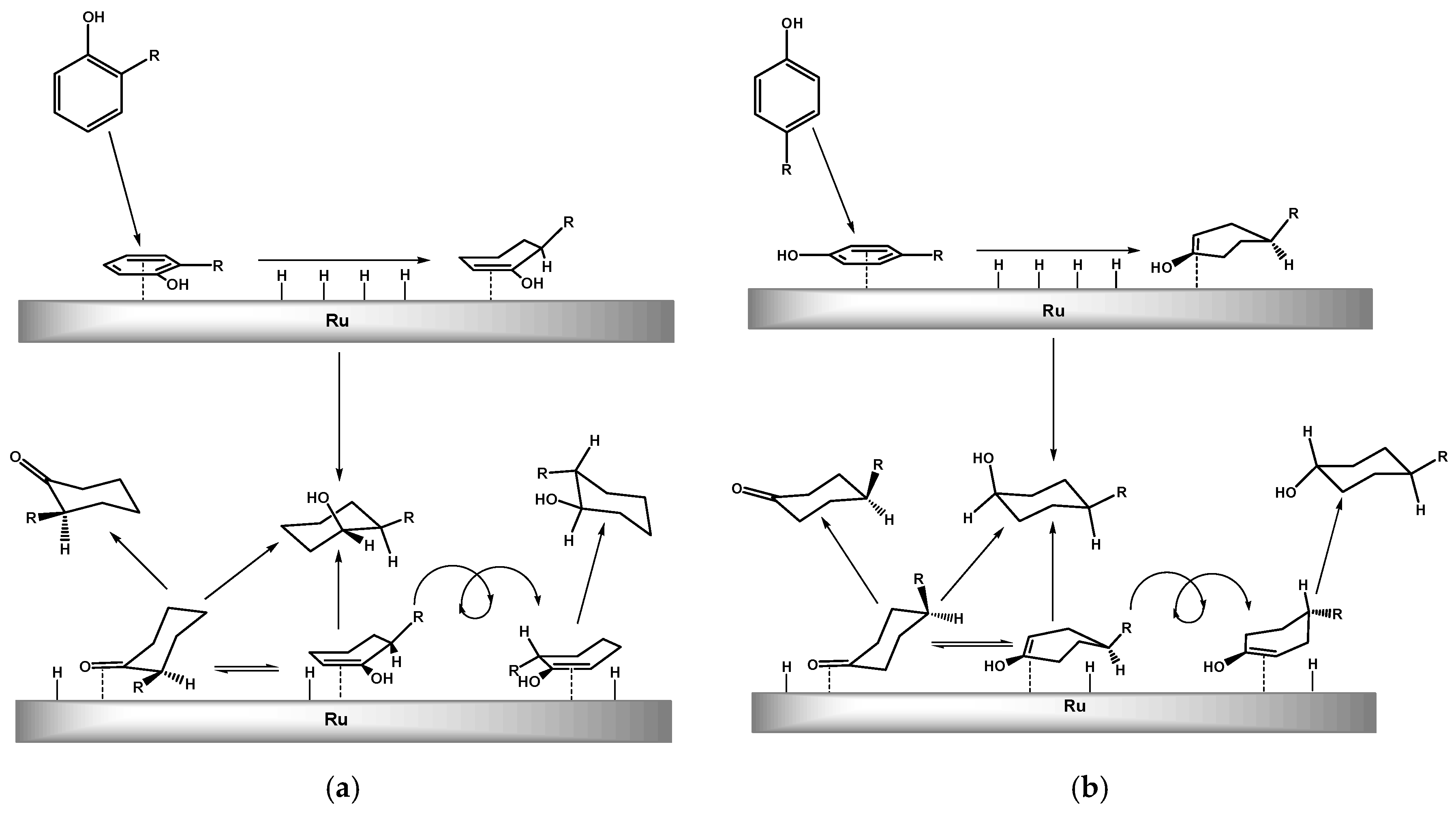
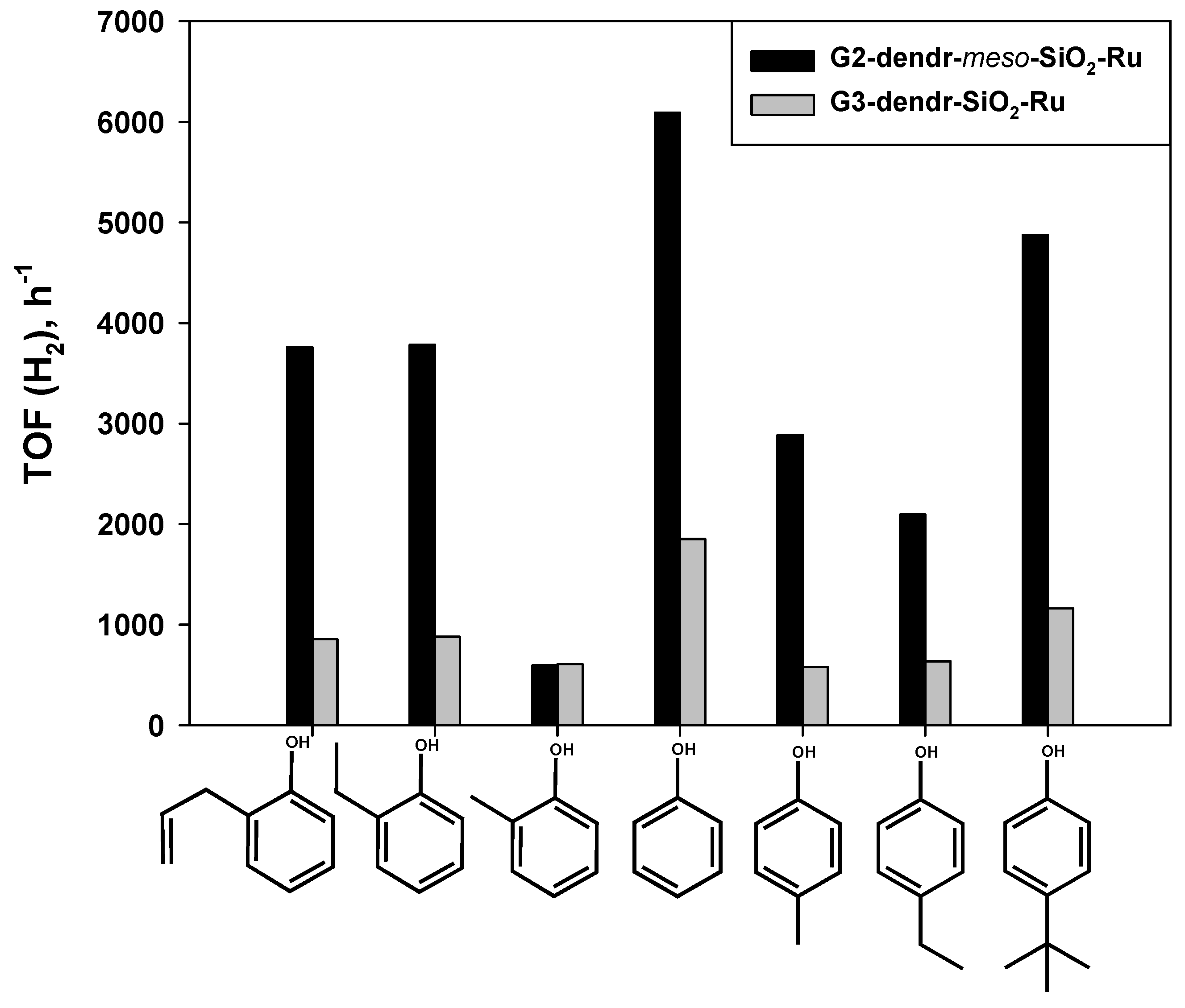
2.2. Hydrogenation of Phenols in the Presence of Heterogeneous Dendrimer-Based Catalysts
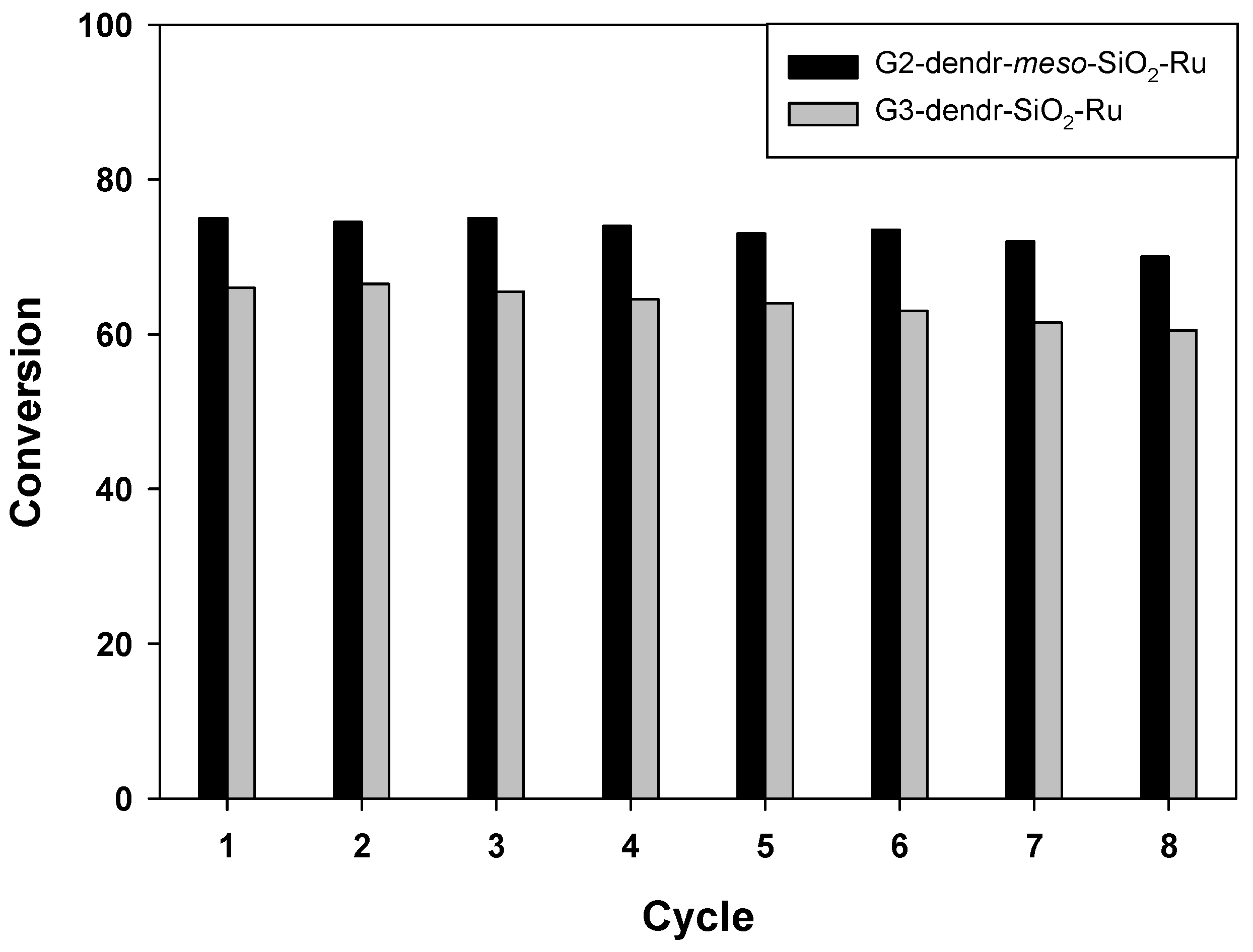
2.3. Catalyst Recycling
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Analyses and Instrumentations
3.3. Synthetic Procedures for the Dendrimer-Based Catalysts
3.3.1. The Synthesis of Microporous G3-Dendr-SiO2 Hybrid Support
3.3.2. The Synthesis of Mesoporous G2-Dendr-meso-SiO2 Hybrid Support
3.3.3. The Synthesis of Catalyst G2-Dendr-meso-SiO2-Ru
3.3.4. The Synthesis of Catalyst G3-Dendr-SiO2-Ru
3.4. Protocol for the Catalytic Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weissermel, K.; Arpe, H.-J. Industrial Organic Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 1993; p. 457. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Ma, L.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Aqueous system for the improved hydrogenation of phenol and its derivatives. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulman, E.M.; Ivanov, A.A.; Chernyavsky, V.S.; Sulman, M.G.; Bykov, A.I.; Sidirov, A.I.; Doluda, V.Y.; Matveeva, V.G.; Bronstein, L.M.; Stein, B.D.; et al. Kinetics of phenol hydrogenation over Pd-containing hypercrosslinked polystyrene. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 176–177, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; He, J.; Lemonidou, A.A.; Li, X.; Lercher, J.A. Aqueous-phase hydrodeoxygenation of bio-derived phenols to cycloalkanes. J. Catal. 2011, 280, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Güvenatam, B.; Kurşun, O.; Heeres, E.H.J.; Pidko, E.A.; Hensen, E.J.M. Hydrodeoxygenation of mono- and dimeric lignin model compounds on noble metal catalysts. Catal. Today 2014, 233, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, Sh. Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation for Organic Synthesis; JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 427–441. [Google Scholar]
- Karakhanov, E.A.; Dedov, A.G.; Tskhai, L.E.; Shatalov, V.V. Hydrogenation of oxygen-containing functionalized derivates of aromatic hydrocarbons. Petrol. Chem. 1993, 33, 202–227. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, F.; Fujita, S.; Arai, M. Hydrogenation of phenol in scCO2 over carbon nanofiber supported Rh catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, N.; Xu, W.-C. Selective hydrogenation of phenol to cyclohexanone using palladium-based membranes as catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 1993, 107, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipatiev, V.N. Catalytic reactions under high pressures and temperatures. J. Russ. Phys. Chem. Soc. 1906, 38, 75–92. [Google Scholar]
- Sabatier, P. Catalysis in Organic Chemistry; Goschimtechizdat: Leningrad, Soviet Union, 1932; p. 418, (translated in Russian from: Sabatier, P. Die Katalyse in der organischen Chemie, 2. A. Finkelstein, B.; Häuber, H., Eds.; Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft: Leipzig, Germany, 1927; S. 466). [Google Scholar]
- Sandescu, N.; Grigoras, D.; Bozga, P. Catalytic Manufacture of Cyclohexanone. Rom. Patent 91,636, 30 May 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Ortiz, J.I.; Gonzalez-Velasco, J.R.; Salvador, A.R.; Gonzalez-Marcos, J.A. Etapas de transporte en la hidrogenación catalitica del fenol. II. Gradientes intraparticulares. Afinidad 1986, 43, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Baltz, H.; Blume, H.; Lunau, J.; Meye, H.; Oberender, H.; Schäfer, H.; Timm, D. Cyclohexanone by Catalytic Hydrogenation of Phenol. GDR Patent 2,059,938, 8 July 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Velasco, J.R.; Gutierrez-Ortiz, J.I.; Gonzalez-Marcos, J.A.; Romero, A. Kinetics of the selective hydrogenation of phenol to cyclohexanone over a Pd-alumina catalyst. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 1986, 32, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shono, S.; Itabashi, K.; Yamada, M.; Kikuchi, M. Catalytic hydrogenation of organic compounds by Mo trisulfide. Kogyo Kagaku Zasshi 1961, 64, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, C.V.; Joshi, U.D.; Sato, O.; Shirai, M. Catalytic ring hydrogenation of phenol under supercritical carbon dioxide. Chem. Commun. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagovsky, Y.S.; Strelets, M.M.; Borisov, V.V. Kinetics of Phenol Hydrogenation on Palladium and Nickel; Siberian Department of USSR Academy of Sciences: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1973; pp. 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Liquid-phase selective hydrogenation of phenol to cyclohexanone over the Ce-doped Pd–B amorphous alloy catalyst. Mat. Lett. 2008, 62, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maegawa, T.; Akashi, A.; Yaguchi, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Shigetsura, M.; Monguchi, Y.; Sajiki, H. Efficient and practical arene hydrogenation by heterogeneous catalysts under mild conditions. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 6953–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahata, N.; Raghavan, K.V.; Vishwanathan, V.; Park, C.; Keane, M.A. Phenol hydrogenation over palladium supported on magnesia: Relationship between catalyst structure and performance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 2712–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, J.; Corma, A. Selective phenol hydrogenation in aqueous phase on Pd-based catalysts supported on hybrid TiO2-carbon materials. Appl. Catal. A 2011, 404, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, Y.; Fajardo, M.; Corma, A. Highly selective palladium supported catalyst for hydrogenation of phenol in aqueous phase. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasshoff, E.; Hoerinklee, W.; Kojda, P. Cyclohexanone and Cyclohexanol. GDR Patent 218,092 A2, 30 January 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Grasshoff, E.; Meye, H.; Naumann, H. Selective Hydrogenation of Phenol to Cyclohexanone. GDR Patent 150,999, 30 September 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Murtha, T.P. Selective Hydrogenation of Organic Materials. U.S. Patent 4,409,401, 11 October 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Van Peppen, J.F.; Fisher, W.B. Cyclohexanone. Can. Patent 1,127,139 A2, 6 July 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Van Peppen, J.F.; Fisher, W.B. Process for Producing Cyclohexanone. U.S. Patent 4,200,553, 29 April 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, L.M.; Machado, G. Ruthenium nanoparticles prepared from ruthenium dioxide precursor: Highly active catalyst for hydrogenation of arenes under mild conditions. J. Mol. Catal. A 2009, 298, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarev, A.A.; Chegolya, A.S.; Smirnova, N.S. Liquid-phase hydrogenation of some monocyclic aromatic compounds in the presence of Ru catalysts. Russ. Chem. Bull. Chem. 1965, 163, 379–382. [Google Scholar]
- Karakhanov, E.A.; Dedov, A.G.; Loktev, A.S.; Pshezhetsky, V.S. A Method of Cyclohexanol Obtaining. USSR Patent 1,051,056 A1, 30 October 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Pomogailo, A.D. Catalysis by Polymer-Immobilized Metal Complexes; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1991; p. 448, CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 1999; p. 424. [Google Scholar]
- Bekturov, E.A.; Kudaibergenov, S.E. Catalysis by Polymers; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; pp. 67–144. [Google Scholar]
- Tskhai, L.E.; Syshchikov, I.G.; Evseev, A.M. About mechanism of phenol hydrogenation on soluble metal-polymer catalysts. Moscow Univ. Chem. Bull. 1992, 33, 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Perchenko, V.N.; Kalashnikova, I.S.; Kamneva, G.L. Hydrogenation of phenol and its derivates on polymeric metal complexes of palladium and rhodium. Petrol. Chem. 1987, 27, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Bayer, E.; Schumann, W. Liquid phase polymer-based catalysis for stereo- and regio-selective hydrogenation. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1986, 12, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Liu, J.; Xu, J. Synthesis of chain-like Ru nanoparticle arrays and its catalytic activity for hydrogenation of phenol in aqueous media. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 108, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimov, A.L.; Kuklin, S.N.; Kardasheva, Y.S.; Karakhanov, E.A. Hydrogenation of phenols in ionic liquids on rhodium nanoparticles. Petrol. Chem. 2013, 53, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklin, S.; Maximov, A.; Zolotukhina, A.; Karakhanov, E. New approach for highly selective hydrogenation of phenol to cyclohexanone: Combination of rhodium nanoparticles and cyclodextrins. Catal. Commun. 2016, 73, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittelkow, M.; Moth-Poulsen, K.; Boas, U.; Christensen, J.B. Poly(amidoamine)-dendrimer-stabilized Pd(0) nanoparticles as a catalyst for the Suzuki reaction. Langmuir 2003, 19, 7682–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakhanov, E.A.; Maksimov, A.L.; Zolotukhina, A.V.; Kardasheva, Y.S. Hydrogenation catalysts based on metal nanoparticles stabilized by organic ligands. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2013, 62, 1465–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertici, P.; Vitulli, G.; Carclini, C.; Clardelli, F. Versatile polystyrene-ruthenium hydrogenation catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. 1981, 11, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximov, A.; Zolotukhina, A.; Kulikov, L.; Kardasheva, Yu.; Karakhanov, E. Ruthenium catalysts based on mesoporous aromatic frameworks for the hydrogenation of arenes. React. Kinet. Mech. Cat. 2016, 117, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspolli Galletti, A.M.; Antonetti, C.; Longo, I.; Capannelli, G.; Venezia, A.M. A novel microwave assisted process for the synthesis of nanostructured ruthenium catalysts active in the hydrogenation of phenol to cyclohexanone. Appl. Catal. A 2008, 350, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, T.; Hu, B.; Jiang, T.; Han, B. Ru nanoparticles stabilized by poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) grafted on to silica: Very active and stable catalysts for hydrogenation of aromatics. J. Mol. Catal. A 2009, 306, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Li, H.; Su, D.; Antonietti, M. Highly selective hydrogenation of phenol and derivatives over a Pd@carbon nitride catalyst in aqueous media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2362–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.; Rosenberg, E.; Karakhanov, E.; Kardashev, S.V.; Maximov, A.; Zolotukhina, A. Catalytic properties of transition metal salts immobilized on nanoporous silica polyamine composites II: Hydrogenation. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2011, 25, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakhanov, E.; Maximov, A.; Kardashev, S.; Kardasheva, Yu.; Zolotukhina, A.; Rosenberg, E.; Allen, J. Nanostructured macromolecular metal containing materials in catalysis. Macromol. Symp. 2011, 304, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Brunelli, N.A.; Didas, S.A.; Ping, E.W.; Jones, C.W. Aminopolymer–silica composite-supported Pd catalysts for selective hydrogenation of alkynes. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaki, M.; Karout, A.; Toufaily, J.; Rataboul, F.; Essayem, N.; Lebeau, B. Synthesis and characterization of acidic ordered mesoporous organosilica SBA-15: Application to the hydrolysis of cellobiose and insight into the stability of the acidic functions. J. Catal. 2013, 305, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishito, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Nakajima, K.; Maegawa, Y.; Inagaki, Sh.; Hara, K.; Fukuoka, A. Ruthenium-immobilized periodic mesoporous organosilica: Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic application for selective oxidation of alkanes. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 15564–15569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Martinez, J.; Linares, N.; Sinibaldi, S.; Coronado, E.; Ribera, A. Incorporation of Pd nanoparticles in mesostructured silica. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2009, 117, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.A.; van Grieken, R.; Iglesias, J.; Morales, V.; Villajos, N. Facile one-pot approach to the synthesis of chiral periodic mesoporous organosilicas SBA-15-type materials. J. Catal. 2010, 274, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newkome, G.R.; Shreiner, C.D. Poly(amidoamine), polypropylenimine, and related dendrimers and dendrons possessing different 1 → 2 branching motifs: An overview of the divergent procedures. Polymer 2008, 49, 1–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Crooks, R.M. Dendrimer-encapsulated metal nanoparticles and their applications to catalysis. C. R. Chimie 2003, 6, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakhanov, E.A.; Maximov, A.L.; Skorkin, V.A.; Zolotukhina, A.V.; Smerdov, A.S.; Tereshchenko, A.Yu. Nanocatalysts based on dendrimers. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximov, A.; Zolotukhina, A.; Murzin, V.; Karakhanov, E.; Rosenberg, E. Ruthenium nanoparticles stabilized in cross-linked dendrimer matrices: Hydrogenation of phenols in aqueous media. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakhanov, E.A.; Maximov, A.L.; Zolotukhina, A.V.; Terenina, M.V.; Vutolkina, A.V. Nanoheterogeneous ruthenium-containing catalysts based on dendrimers in the hydrogenation of aromatic compounds under two-phase conditions. Petrol. Chem. 2016, 56, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharyan, E.M.; Ma, G.; Maksimov, A.L.; Karakhanov, E.A.; Voronina, Z.D. Phenol and dihydroxybenzene hydrogenation catalysts based on polyamide dendrimers and rhodium species. Petrol. Chem. 2014, 54, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buil, M.L.; Esteruelas, M.A.; Niembro, S.; Oliván, M.; Orzechowski, L.; Pelayo, C.; Vallribera, A. Dehalogenation and hydrogenation of aromatic compounds catalyzed by nanoparticles generated from rhodium bis(imino)pyridine complexes. Organometallics 2010, 29, 4375–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakhanov, E.; Maximov, A.; Zolotukhina, A.; Kardasheva, Yu.; Talanova, M. Thermo-responsive ruthenium dendrimer-based catalysts for hydrogenation of the aromatic compounds and phenols. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2016, 26, 1264–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairlie, D.P.; Jackson, W.G. Nitrogen- and oxygen-bonded urethane: hydrolysis and linkage isomerization of [(NH3)5Co(NH2CO2C2H5)]3+ and [(NH3)5CoOC(NH2)OCH2CH3]3+. Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, 3139–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakhanov, E.; Maximov, A.; Kardasheva, Yu.; Semernina, V.; Zolotukhina, A.; Ivanov, A.; Abbott, G.; Rosenberg, E.; Vinokurov, V. Pd Nanoparticles in dendrimers immobilized on silica-polyamine composites as catalysts for selective hydrogenation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 8807–8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweni, P.P.; Alper, H. Silica-supported dendrimer-palladium complex-catalyzed selective hydrogenation of dienes to monoolefins. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2006, 348, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, H.; Sasaki, H.; Tsubokawa, N.; Hoshi, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tsuda, T.; Kuwabata, S. Immobilization of Pd on nanosilica dendrimer as SILC: Highly active and sustainable cluster catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. SynLett. 2010, 13, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Du, Q.; Li, Yi. Synthesis of dendrimers terminated by DABCO ligands and applications of its palladium nanoparticles for catalyzing Suzuki–Miyaura and Mizoroki–Heck couplings. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2013, 27, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gao, Q. Heterogeneous hydrogenation catalyses over recyclable Pd(0) nanoparticle catalysts stabilized by PAMAM-SBA-15 organic-inorganic hybrid composites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 716–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, T.; Cao, R. Monodisperse noble metal nanoparticles stabilized in SBA-15: Synthesis, characterization and application in microwave-assisted Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction. J. Catal. 2010, 270, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, R.; de Jesús, E.; Flores, J.C. Catalysts based on palladium dendrimers. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 1161–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonels, N.C.; Williams, M.B.; Meijboom, R.; Haumann, M. Well-defined dendrimer encapsulated ruthenium SCILL catalysts for partial hydrogenation of toluene in liquid-phase. J. Mol. Catal. A 2016, 421, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, N.N.; Auten, B.J.; Chandler, B.D. Tuning supported catalyst reactivity with dendrimer-templated Pt−Cu nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 8606–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.A.; Ha, H.P. Synthesis and dispersion of dendrimer-encapsulated Pt nanoparticles on γ-Al2O3 for the reduction of NOx by methane. Catal. Lett. 2010, 136, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.X.; Lopez de Jesus, Y.M.; Monnier, J.R.; Williams, C.T. Preparation, characterization, and kinetic evaluation of dendrimer-derived bimetallic Pt–Ru/SiO2 catalysts. J. Catal. 2010, 269, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedov, V.I.; Salyn, Y.V.; Leonhardt, G.; Scheibe, R. A comparison of different spectrometers and charge corrections used in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1977, 10, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, T.; Ramm, M.; Sonntag, H.; Unger, W.; Meijers, H.M.; Adem, E.H. An XPS analysis of different SiO2 modifications employing a C 1s as well as an Au 4f7/2 static charge reference. Surf. Interface Anal. 1992, 18, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamson, G.; Briggs, D. High Resolution XPS of Organic Polymers: The Scienta ESCA300 Database; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1992; p. 295. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, D.; Beamson, G. Primary and secondary oxygen-induced C 1s binding energy shifts in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of polymers. Anal. Chem. 1992, 64, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohmeier, B.R. Evaluation of polymeric standard reference materials for monitoring the performance of X-ray photoelectron spectrometers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1991, 47, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertsin, A.J.; Gorelova, M.M.; Levin, V.Y.; Makarova, L.I. An XPS study of the surface–bulk compositional differences in siloxane-containing block copolymers and polymer blends. J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 1992, 45, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laoharojanaphand, P.; Lin, T.J.; Stoffer, J.O. Glow discharge polymerization of reactive functional silanes on poly(methyl methacrylate). J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 1990, 40, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Huo, Q.; Feng, J.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Nonionic triblock and star diblock copolymer and oligomeric surfactant syntheses of highly ordered, hydrothermally stable, mesoporous silica structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6024–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriu, R.J.P.; Lancelle-Beltran, E.; Mehdi, A.; Reyé, C.; Brandès, S.; Guilard, R. Ordered mesoporous hybrid materials containing cobalt(II) Schiff base complex. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakhanov, E.A.; Maximov, A.L.; Zolotukhina, A.V.; Kardashev, S.V. Design of dendrimer-based nanostructured catalyst systems and their catalytic activity in hydrogenation: Synthesis of ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized in dendrimer networks. Petrol. Chem. 2010, 50, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, P.H.K.; Rao, G.R. Synthesis of CuNi and CuNi/SBA-15 by aqueous method at room temperature and their catalytic activity. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2014, 200, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbasi, R.J.; Zamani, F. Synthesis and characterization of Ni nanoparticles incorporated into hyperbranched polyamidoamine–polyvinylamine/SBA-15 catalyst for simple reduction of nitro aromatic compounds. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 7444–7453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irum, M.; Zaheer, M.; Friedrich, M.; Kempe, R. Mesoporous silica nanosphere supported platinum nanoparticles (Pt@MSN): One-pot synthesis and catalytic hydrogen generation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10438–10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.A.; Nielsen, D.; Rosenberg, E.; Gobetto, R.; Viale, A.; Burton, S.D.; Ferel, J. Structural investigations of silica polyamine composites: Surface coverage, metal ion coordination, and ligand modification. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 6538–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, B.; Colilla, M.; López de Laorden, C.; Vallet-Regí, M. A novel synthetic strategy for covalently bonding dendrimers to ordered mesoporous silica: Potential drug delivery applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 9012–9024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.Y.; Adnot, A.; Kaliaguine, S. An ESCA study of the interaction of oxygen with the surface of ruthenium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1991, 51, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkesson, B. ESCA studies on the charge distribution in some dinitrogen complexes of rhenium, iridium, ruthenium, and osmium. Acta Chem. Scand. 1973, 27, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Winograd, N. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic studies of ruthenium-oxygen surfaces. J. Catal. 1974, 35, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedov, V.I. An influence of the oxidation degree of transition element on its X-ray photoelectron spectra. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 1978, 4, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.I.; Hatfield, W.E. Electrical, magnetic and spectroscopic properties of tetrathiafulvalene charge transfer compounds with iron, ruthenium, rhodium and iridium halides. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1991, 188, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.T.; Srivastava, S. Some new ruthenium(III) schiff base complexes: A photoelectron spectroscopic study. Polyhedron 1988, 7, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, R.E.; Proctor, A.; Henderson, W.W.; Myser, T.K. Assessment of the π-acceptor capability of selected ligands based on the photoelectron spectra of ruthenium ammine complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 2440–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okal, J. The interaction of oxygen with high loaded Ru/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, S.; Kanai, H.; Utani, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Saito, Y.; Imamura, S. State of Ru on CeO2 and its catalytic activity in the wet oxidation of acetic acid. Appl. Catal. B 2003, 45, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, I.; Somorjai, G.A. Heats of chemisorption of O2, H2, CO, CO2, and N2 on polycrystalline and single crystal transition metal surfaces. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 1979, 19, 105–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaston, J.C. Reactions of oxygen with the platinum metals. Platinum Met. Rev. 1965, 9, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Koopman, P.G.J. Ruthenium Hydrogenation Catalysts. Activation Characterization Application. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University, Delft, The Netherlands, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Rylander, P.N.; Rakoncza, N.; Steele, D.; Bolliger, M. Water as co-catalyst in Ru hydrogenation. Engelhard Ind. Tech. Bull. 1963, 4, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gual, A.; Axet, M.R.; Philippot, K.; Chaudret, B.; Denicourt-Nowicky, A.; Roucoux, A.; Castillón, S.; Claver, C. Diphosphite ligands derived from carbohydrates as stabilizers for ruthenium nanoparticles: Promising catalytic systems in arene hydrogenation. Chem. Commun. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Jaenicke, S.; van Bekkum, H.; Chuah, G.-K. Stereoselective cascade hydrogenation of 4-tert-butylphenol and p-cresol over Zr-zeolite beta-supported rhodium. J. Catal. 2007, 246, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiyoshi, N.; Rode, C.V.; Sato, O.; Tetsuka, H.; Shirai, M. Stereoselective hydrogenation of tert-butylphenols over charcoal-supported rhodium catalyst in supercritical carbon dioxide solvent. J. Catal. 2007, 252, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fihri, A.; Bouhrara, M.; Patil, U.; Cha, D.; Saih, Y.; Polshettiwar, V. Fibrous nano-silica supported ruthenium (KCC-1/Ru): A sustainable catalyst for the hydrogenolysis of alkanes with good catalytic activity and lifetime. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornelas, C.; Ruiz Aranzaes, J.; Salmon, L.; Astruc, D. “Click” dendrimers: Synthesis, redox sensing of Pd(OAc)2, and remarkable catalytic hydrogenation activity of precise Pd nanoparticles stabilized by 1,2,3-triazole-containing dendrimers. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooe, M.; Murata, M.; Mizugaki, T.; Ebitani, K.; Kaneda, K. Dendritic nanoreactors encapsulating Pd particles for substrate-specific hydrogenation of olefins. NanoLett. 2002, 2, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brabander-van den Berg, E.M.M.; Meijer, E.W. Poly(propylene imine) dendrimers: Large-scale synthesis by hetereogeneously catalyzed hydrogenations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1993, 32, 1308–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.V.; O’Laughlin, J.W. Spectrophotometric determination of ruthenium with 1,10-phenanthroline. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W. FITC and Ru(phen)32+ co-doped silica particles as visualized ratiometric pH indicator. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.; Deivaraj, T.C.; Too, H.-P.J. A novel synthesis route for ethylenediamine-protected ruthenium nanoparticles. Colliod. Interface Sci. 2003, 268, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
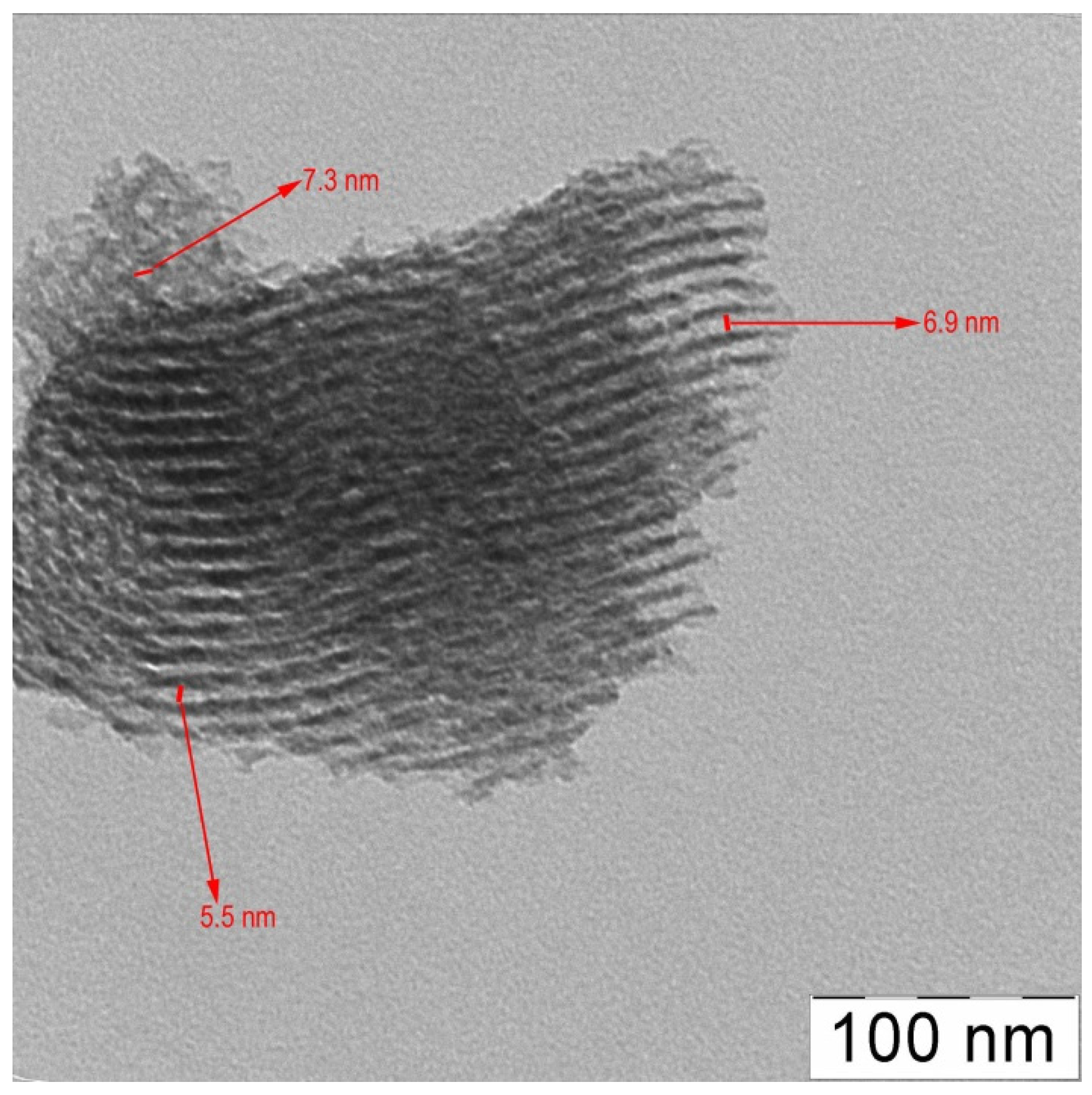
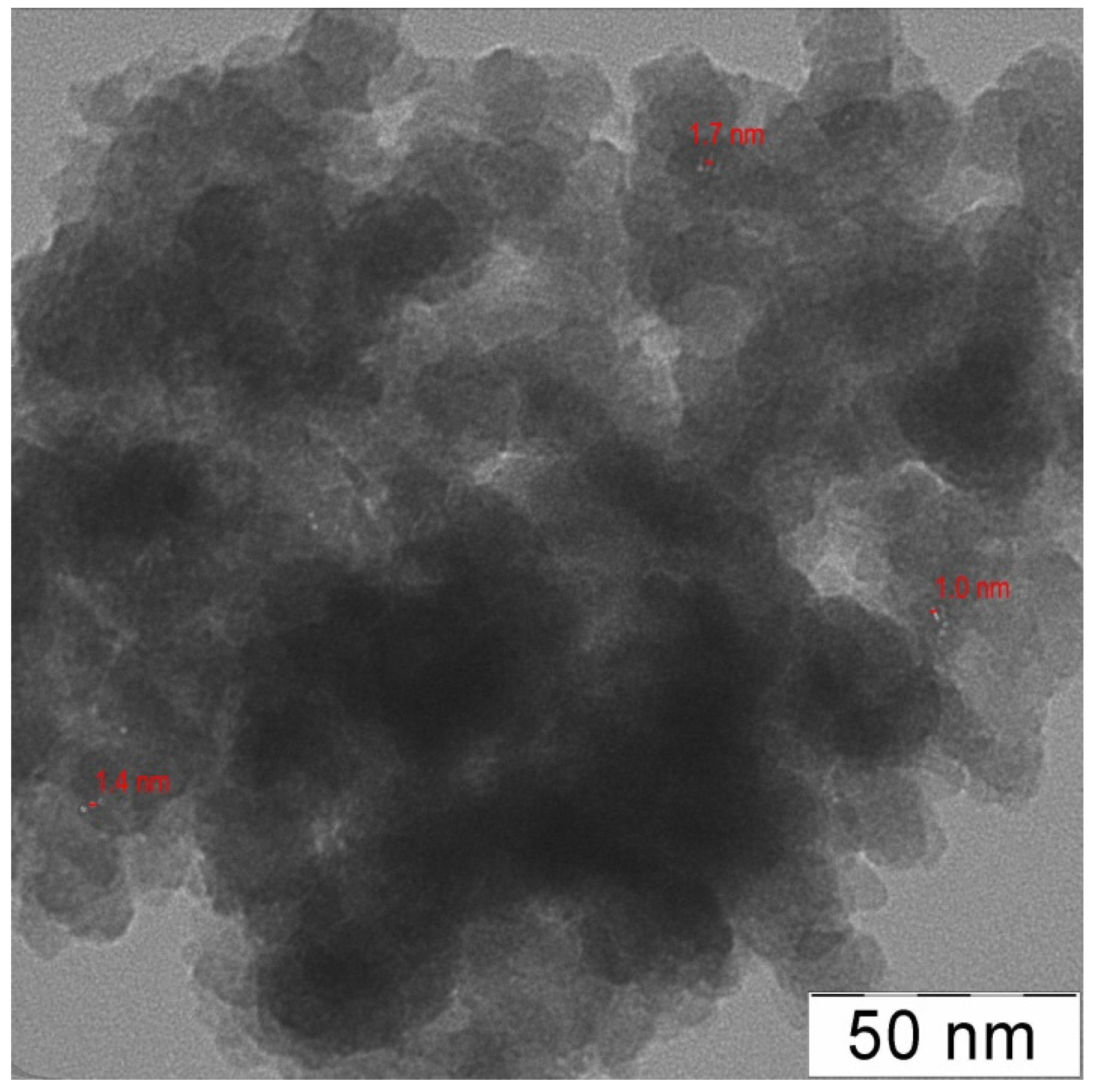
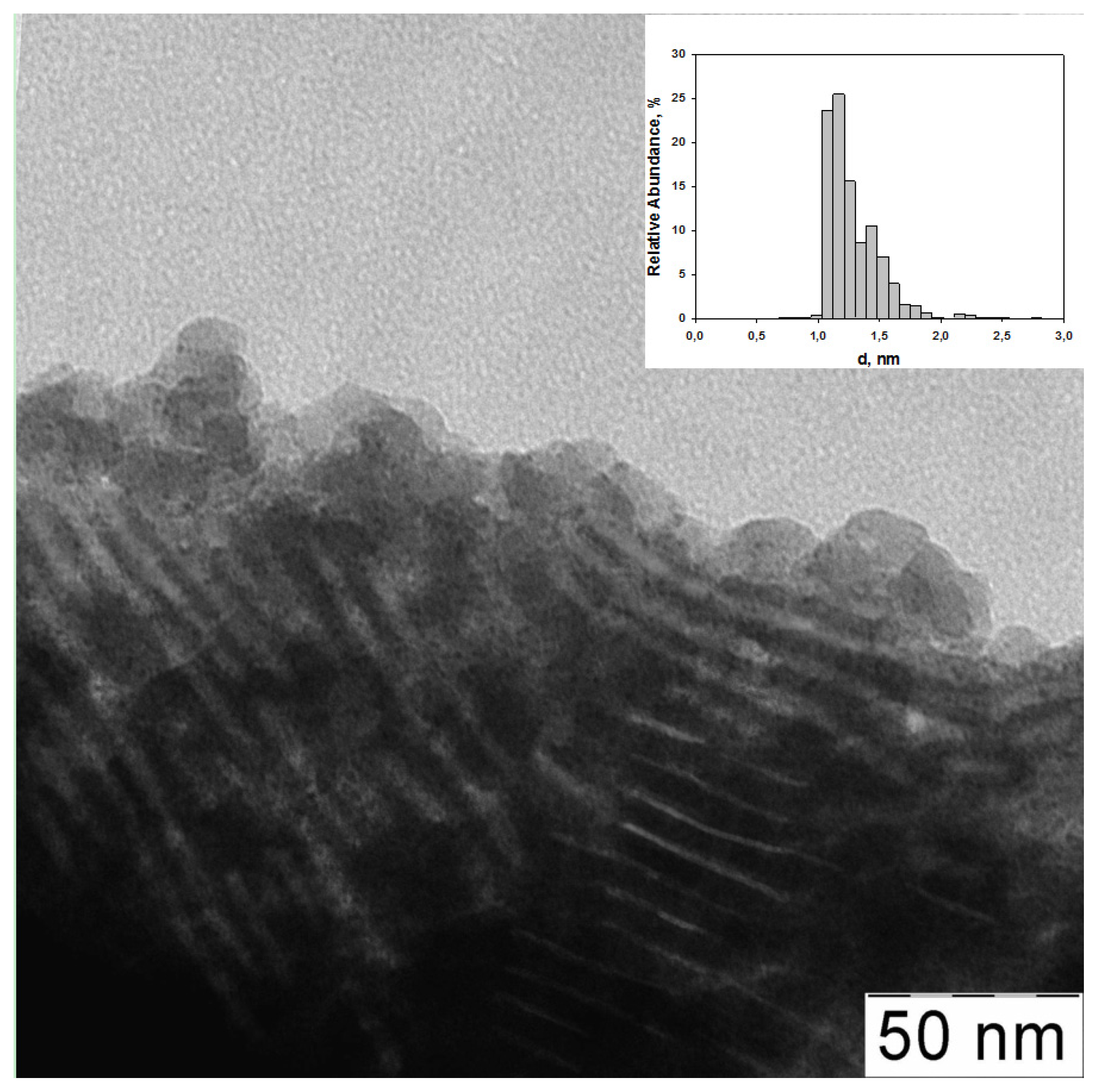
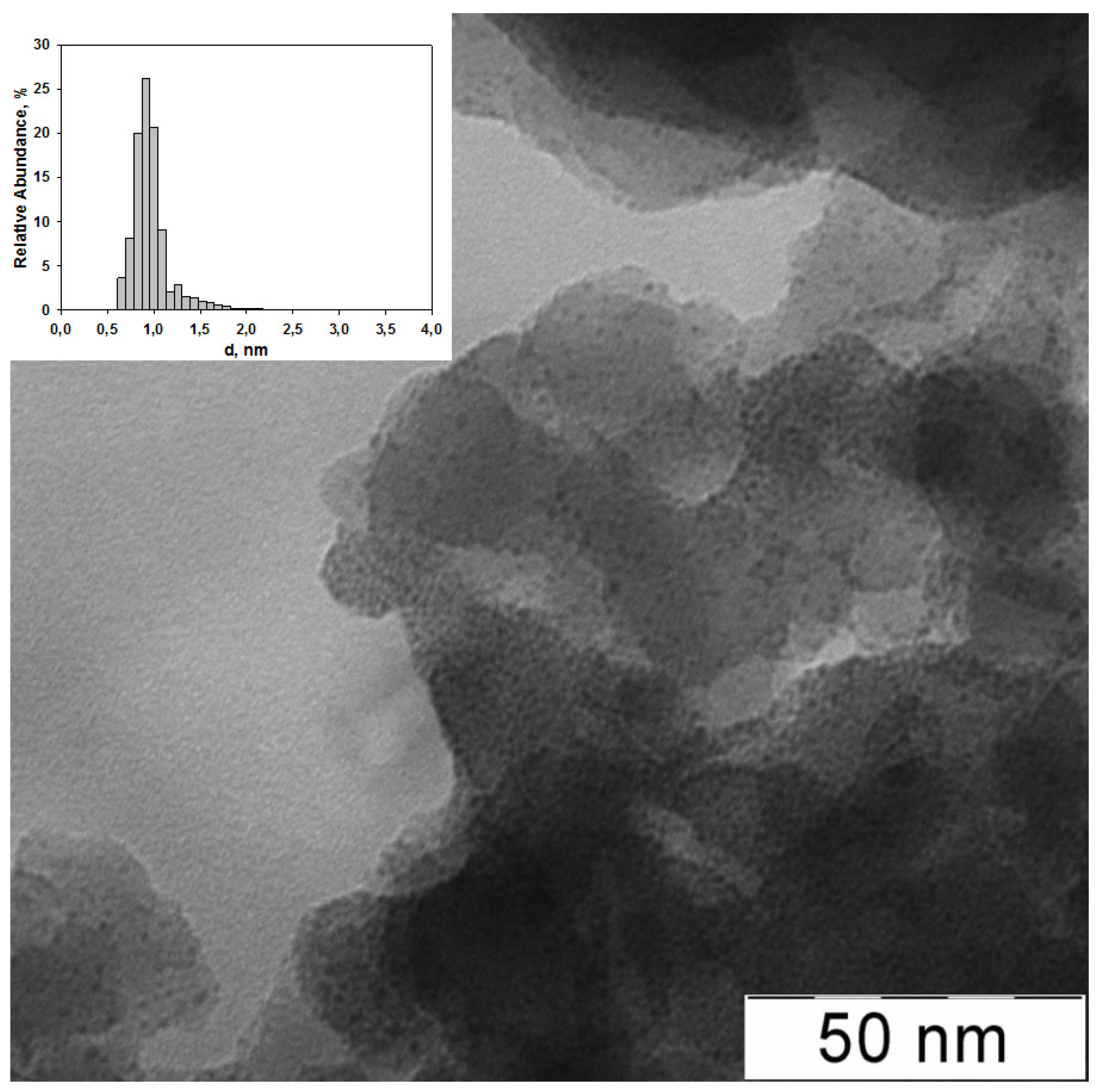

| Entry | Catalyst | Ru (wt %) | d (nm) | Surface concentration by XPS (at. %) | Ru valency states at Ru 3p3/2 line (at. %) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ru | C | N | O | Si | Ru0 (eV) | Ru/RuOx (eV) | RuO2, Ru(II) N-bound (eV) | RuOx/Ru, Ru(III) O,N-bound (eV) | RuCl3·xH2O, RuO3 (eV) | ||||
| 1 | G3-dendr-SiO2-Ru | 5.4 | 0.97 ± 0.09 | 4.2 | 22.1 | 4.5 | 55.9 | 13.3 | 32.7 (461.3) | - | 50.2 (464.0) | - | 17.1 (466.6) |
| 2 | G2-dendr-meso-SiO2-Ru | 3.5 | 1.28 ± 0.09 | 5.7 | 32.7 | - | 35.8 | 25.8 | 2.5 (460.5) | 3.3 (462.2) | 28.3 (463.6) | 40.7 (465.0) | 25.2 (466.4) |
| Entry | Substrate/Ru (mol/mol) | T (°C) | P (MPa) | t (h) | Conv. (%) | TOF (H2) (h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 377 | 85 | 3 | 0.5 | 94 | 1820 |
| 2 | 377 | 85 | 1 | 6 | 71 | 1172 |
| 3 | 377 | 70 | 3 | 6 | 100 | 3100 |
| 4 | 377 | 70 | 1 | 6 | 46 | 225 |
| 5 | 754 | 85 | 3 | 6 | 100 | 1853 |
| 6 | 754 | 85 | 1 | 6 | 32 | 212 |
| 7 | 887 | 80 | 3 | 6 | 99 | 1841 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Phenol/Ru (mol/mol) | T (°C) | Conv. (%) | TOF (H2) (h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | G2-dendr-meso-SiO2-Ru | 1843 | 80 | 56 | 6090 |
| 2 | G1–HMDI–Ru | 910 | 85 | 61 | 2775 |
| 3 | G3-dendr-SiO2-Ru | 887 | 80 | 66.5 | 1841 |
| 4 | G3–HMDI–Ru | 960 | 85 | 57 | 2745 |
| Entry | Substrate | Substrate/Ru (mol/mol) (G1–HMDI/ G2-dendr-meso-SiO2) | t (h) (G1–HMDI/ G2-dendr-meso-SiO2) | G1–HMDI–Ru | G2-dendr-meso-SiO2-Ru | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv. (%) | TOF (H2) (h−1) | Conv. (%) | TOF (H2) (h−1) | ||||
| 1 | phenol | 910/1843 | 0.5/0.5 | 61 | 2775 | 56 | 6090 |
| 2 | o-cresol | 960/1962 | 2/2 | 37 | 532 | 16.5 | 596 |
| 3 | p-cresol | 940/1905 | 2/0.5 | 20 | 282 | 29 | 2886 |
| 4 | o-ethylphenol | 967/1960 | 2/0.5 | 30 | 435 | 32.5 | 3728 |
| 5 | p-ethylphenol | 930/1890 | 0.5/0.5 | 31.5 | 1764 | 24 | 2097 |
| 6 | o-allylphenol | 980/2480 | 2/0.5 | 15 | 221 | 21 | 3759 |
| 7 | p-tert-butylphenol | 950/1922 | 0.5/0.5 | 45 | 2560 | 45 | 4879 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karakhanov, E.; Maximov, A.; Zolotukhina, A.; Mamadli, A.; Vutolkina, A.; Ivanov, A. Dendrimer-Stabilized Ru Nanoparticles Immobilized in Organo-Silica Materials for Hydrogenation of Phenols. Catalysts 2017, 7, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7030086
Karakhanov E, Maximov A, Zolotukhina A, Mamadli A, Vutolkina A, Ivanov A. Dendrimer-Stabilized Ru Nanoparticles Immobilized in Organo-Silica Materials for Hydrogenation of Phenols. Catalysts. 2017; 7(3):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7030086
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarakhanov, Eduard, Anton Maximov, Anna Zolotukhina, Adila Mamadli, Anna Vutolkina, and Andrey Ivanov. 2017. "Dendrimer-Stabilized Ru Nanoparticles Immobilized in Organo-Silica Materials for Hydrogenation of Phenols" Catalysts 7, no. 3: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7030086
APA StyleKarakhanov, E., Maximov, A., Zolotukhina, A., Mamadli, A., Vutolkina, A., & Ivanov, A. (2017). Dendrimer-Stabilized Ru Nanoparticles Immobilized in Organo-Silica Materials for Hydrogenation of Phenols. Catalysts, 7(3), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7030086