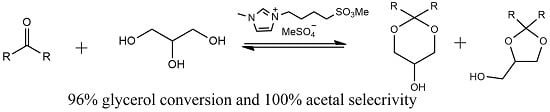
Catalytic Acetalization: An Efficient Strategy for High-Value Utilization of Biodiesel-Derived Glycerol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
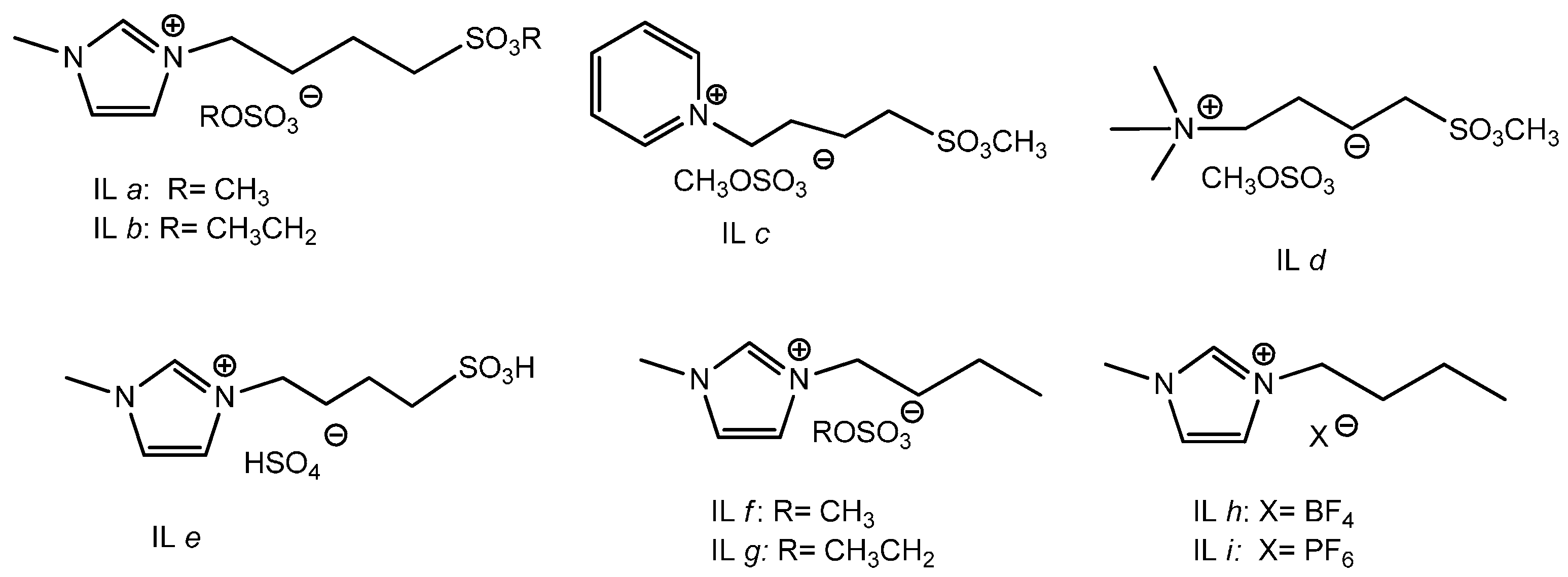
2.1. Catalytic Activities of Ester Sulfate-Functionalized ILs
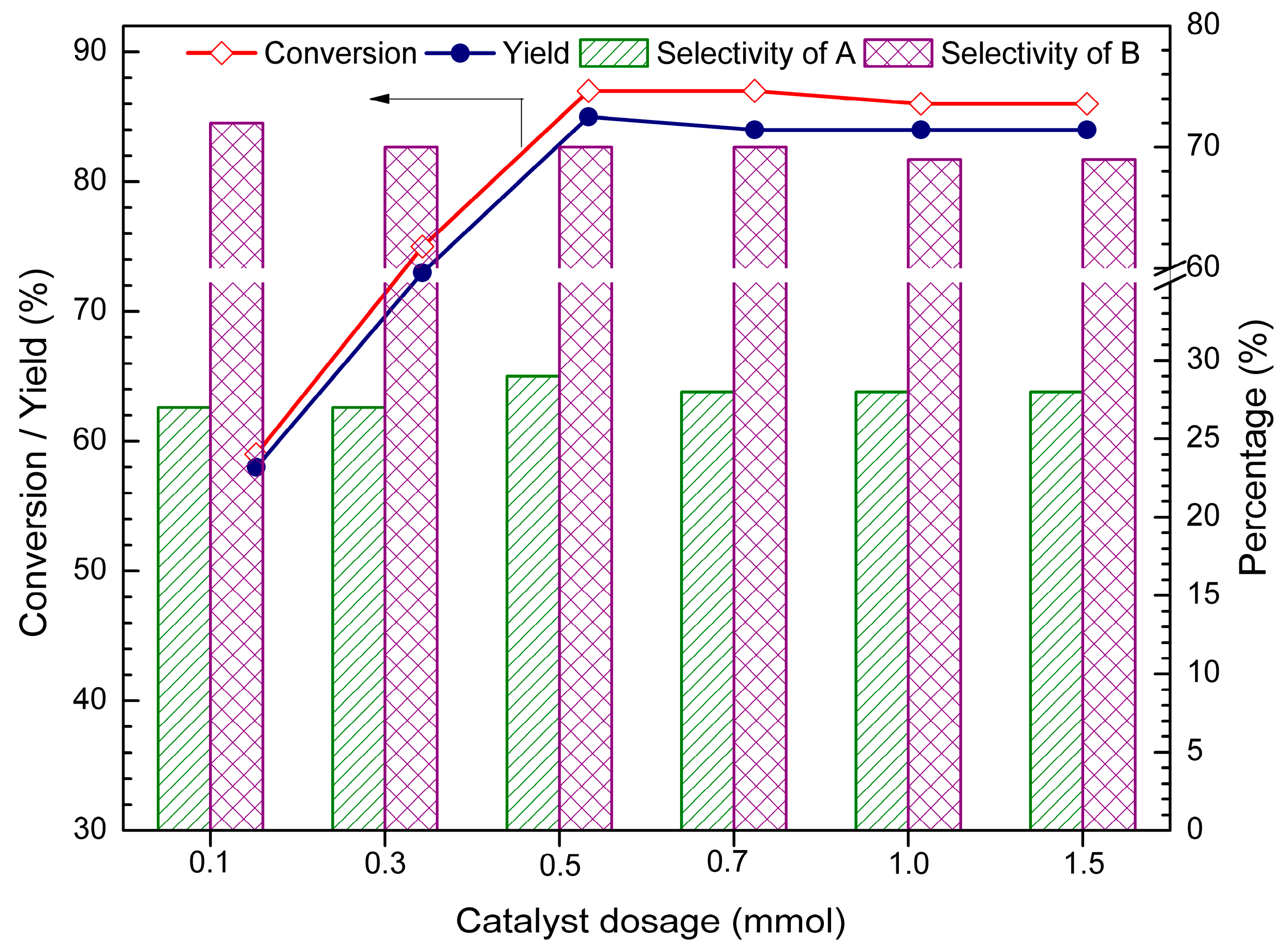
2.2. Effect of Catalyst Dosage
2.3. Influence of Solvent and Reaction Temperature
2.4. Effect of Reaction Time and Molar Ratio of Feedstock
2.5. Feedstock Adaptability of the IL Catalytic System
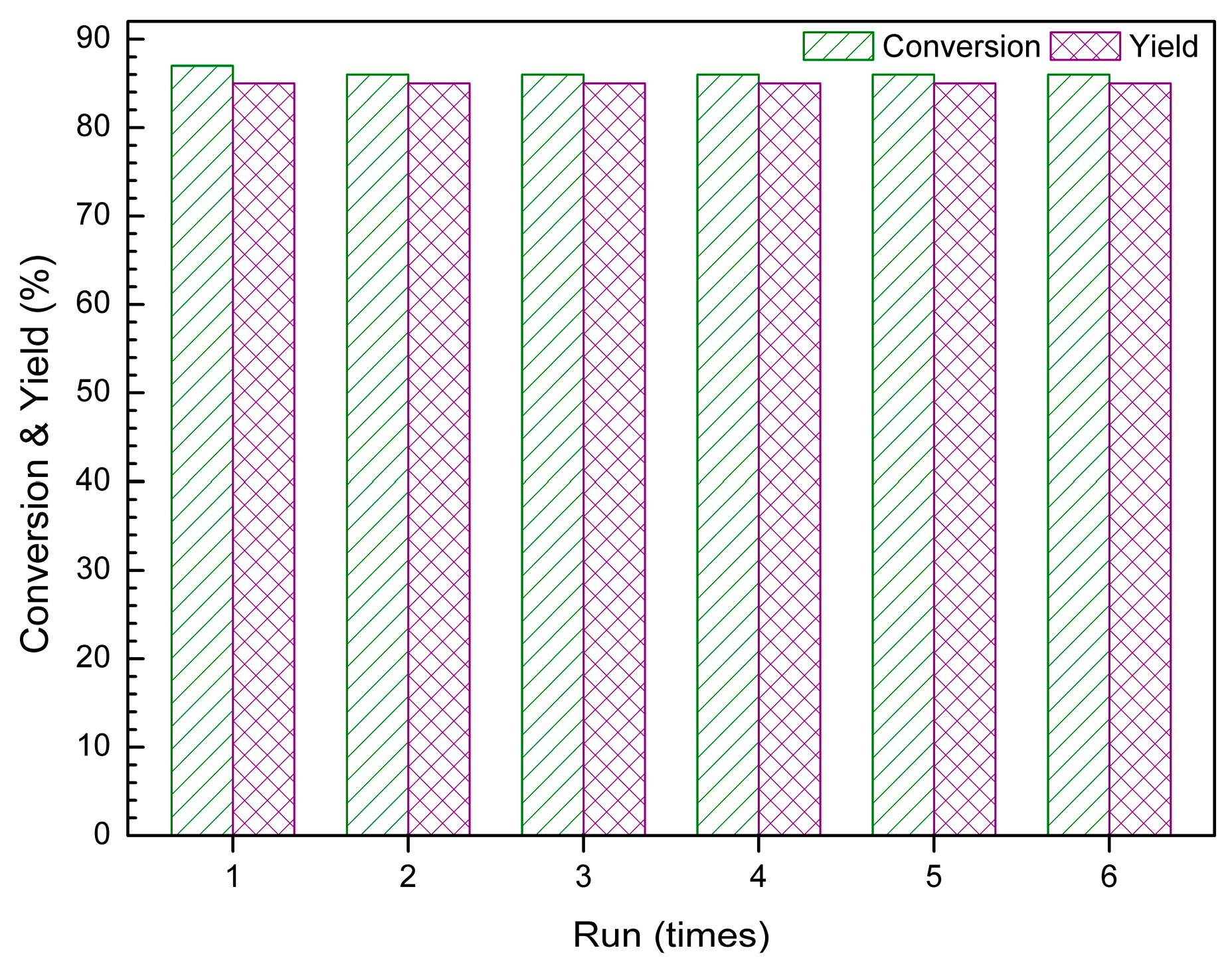
2.6. The Recyclability of IL Catalyst
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. IL Synthesis and Characterization
3.3. Typical Process for Glycerol Acetalization
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuck, C.O.; Perez, E.; Horvath, I.T.; Sheldon, R.A.; Poliakoff, M. Valorization of biomass: Deriving more value from waste. Science 2012, 337, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, L.; Amiri, M.T.; Questell-Santiago, Y.M.; Heroguel, F.; Li, Y.; Kim, H.; Meilan, R.; Chapple, C.; Ralph, J.; Luterbacher, J.S. Formaldehyde stabilization facilitates lignin monomer production during biomass depolymerization. Science 2016, 354, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, H.; Kondo, A.; Noda, H. Biodiesel fuel production by transesterification of oils. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 92, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.R.; Hanna, M.A. Biodiesel production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 70, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.; Mandelli, D.; Goncalves, N.S.; Pescarmona, P.P.; Carvalho, W.A. Acetalization of acetone with glycerol catalyzed by niobium-aluminum mixed oxides synthesized by a sol-gel process. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 422, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, M.; Sato, S.; Takahashi, R.; Inui, K.; Yokota, M. Dehydration-hydrogenation of glycerol into 1,2-propanediol at ambient hydrogen pressure. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 371, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandarias, I.; Luis, A.P.; Fernandez, S.G.; Requies, J.; El Doukkali, M.; Belen Gueemez, M. Hydrogenolysis through catalytic transfer hydrogenation: Glycerol conversion to 1,2-propanediol. Catal. Today 2012, 195, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrettin, S.; McMorn, P.; Johnston, P.; Griffin, K.; Hutchings, G.J. Selective oxidation of glycerol to glyceric acid using a gold catalyst in aqueous sodium hydroxide. Chem. Commun. 2002, 696–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katryniok, B.; Kimura, H.; Skrzynska, E.; Girardon, J.S.; Fongarland, P.; Capron, M.; Ducoulombier, R.; Mimura, N.; Paul, S.; Dumeignil, F. Selective catalytic oxidation of glycerol: Perspectives for high value chemicals. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1960–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Thaw, C.; Campisi, S.; Wang, D.; Prati, L.; Villa, A. Selective oxidation of raw glycerol using supported AuPd nanoparticles. Catalysts 2015, 5, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkhede, N.; Patel, A. Sustainable valorisation of glycerol via acetalization as well as carboxylation reactions over silicotungstates anchored to zeolite H beta. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 515, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Beltramini, J.N.; Fan, Y.X.; Lu, G.Q. Chemoselective catalytic conversion of glycerol as a biorenewable source to valuable commodity chemicals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 527–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh, L.T.; Okitsu, K.; Boi, L.V.; Maeda, Y. Catalytic technologies for biodiesel fuel production and utilization of glycerol: A review. Catalysts 2012, 2, 191–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakruthi, H.R.; Chandrashekara, B.M.; Prakash, B.S.J.; Bhat, Y.S. Microwave rehydrated Mg-Al-LDH as base catalyst for the acetalization of glycerol. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 3667–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Nohair, B.; Kaliaguine, S. Glycerol acetalization with formaldehyde using water-tolerant solid acids. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 509, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.J.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Julio, A.A. SnF2-catalyzed glycerol ketalization: A friendly environmentally process to synthesize solketal at room temperature over on solid and reusable Lewis acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, L.; Song, C.; Wang, F. Comparative investigation on hydrothermal and alkali catalytic liquefaction of bagasse: Process efficiency and product properties. Fuel 2016, 186, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Lou, W.; Wang, L.; Yin, B.; Li, X. [C4H8SO3Hmim]HSO4 as an efficient catalyst for direct liquefaction of bagasse lignin: Decomposition properties of the inner structural units. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 122, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasekara, A.S. Acidic ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 6133–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, S.; Zhou, Z.; Yamasaki, K.; Norinaga, K.; Hayashi, J. Sulfonate ionic liquid as a stable and active catalyst for levoglucosenone production from saccharides via catalytic pyrolysis. Catalysts 2013, 3, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.M.; Shi, F.; Peng, J.J.; Guo, S.; Deng, Y.Q. Application of functional ionic liquids possessing two adjacent acid sites for acetalization of aldehydes. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 3582–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, J. The study of the catalytic activity of functional ionic liquids for acetalization. J. Mol. Catal. (China) 2008, 22, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Shen, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, F.; Sun, R. Conversion of platform chemical glycerol to cyclic acetals promoted by acidic ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 18917–18923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Long, J. Organosolv liquefaction of sugarcane bagasse catalyzed by acidic ionic liquids. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Yuan, Z.; Ma, H.; Shu, R.; Li, X. Catalytic synthesis of trimethylolpropane in the presence of basic ionic liquid. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2015, 31, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.M.; March, J. March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, R.T.; Boyd, R.N. Organic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Allyn and Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, A.C.; Jensen, J.L.; Ntai, I.; Tran, K.L.T.; Weaver, K.J.; Forbes, D.C.; Davis, J.H. Novel Brønsted acidic ionic liquids and their use as dual solvent—Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 5962–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalyst | IL Catalyst Structure | Conversion (%) | Yield (%) | Selectivity (%) | |
| A | B | |||||
| 1 | None | / | Trace | Trace | - | - |
| 2 | [MeSO3bmim][MeSO4] (IL a) |  | 86 | 84 | 28 | 69 |
| 3 | [MeSO3Py][MeSO4] (IL c) |  | 83 | 80 | 26 | 70 |
| 4 | [MeSO3bm3N][MeSO4] (IL d) |  | 86 | 83 | 26 | 71 |
| 5 | [EtSO3bmim][EtSO4] (IL b) |  | 81 | 78 | 27 | 70 |
| 6 | [HSO3bmim][HSO4] (IL e) |  | 84 | 81 | 24 | 73 |
| 7 | [bmim][MeSO4] (IL f) |  | 80 | 78 | 17 | 80 |
| 8 | [bmim][EtSO4] (IL g) |  | 73 | 71 | 16 | 82 |
| 9 | [bmim][BF4] (IL h) |  | Trace | Trace | - | - |
| 10 | [bmim][PF6] (IL i) |  | Trace | Trace | - | - |
| 11 | H2SO4 | / | 79 | 75 | 16 | 80 |
| 12 b | [MeSO3bmim][MeSO4] (IL a) |  | 85 | 83 | 29 | 69 |
| 13 c | [MeSO3bmim][MeSO4] (IL a) |  | 87 | 83 | 28 | 69 |
| Entry | Solvent | Temp. (°C) | Conv. (%) | Yield (%) | Selectivity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | |||||
| 1 | cyclohexane | 90 | 73 | 69 | 26 | 68 |
| 2 | cyclohexane | 100 | 78 | 76 | 27 | 69 |
| 3 | toluene | 110 | 87 | 85 | 29 | 70 |
| 4 | toluene | 120 | 87 | 86 | 31 | 61 |
| 5 | none | 110 | 74 | 72 | 29 | 69 |
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Aldehyde/Ketone | Conv. (%) | Yield (%) | Selectivity (%) | |
| A | B | ||||
| 1 |  | 96 | 96 | 15 | 85 |
| 2 |  | 95 | 95 | 15 | 85 |
| 3 |  | 91 | 90 | 18 | 80 |
| 4 |  | 72 | 72 | 22 | 78 |
| 5 |  | 87 | 85 | 29 | 70 |
| 6 |  | 84 | 82 | 25 | 72 |
| 7 |  | 80 | 78 | 28 | 70 |
| 8 |  | 87 | 85 | 27 | 70 |
| 9 |  | 24 | 23 | 31 | 68 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.; He, M.; Dai, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Yao, L. Catalytic Acetalization: An Efficient Strategy for High-Value Utilization of Biodiesel-Derived Glycerol. Catalysts 2017, 7, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7060184
Sun S, He M, Dai Y, Li X, Liu Z, Yao L. Catalytic Acetalization: An Efficient Strategy for High-Value Utilization of Biodiesel-Derived Glycerol. Catalysts. 2017; 7(6):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7060184
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Suqun, Min He, Yuanwei Dai, Xin Li, Zhijun Liu, and Li Yao. 2017. "Catalytic Acetalization: An Efficient Strategy for High-Value Utilization of Biodiesel-Derived Glycerol" Catalysts 7, no. 6: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7060184
APA StyleSun, S., He, M., Dai, Y., Li, X., Liu, Z., & Yao, L. (2017). Catalytic Acetalization: An Efficient Strategy for High-Value Utilization of Biodiesel-Derived Glycerol. Catalysts, 7(6), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7060184