Wood-Biochar-Supported Magnetite Nanoparticles for Remediation of PAH-Contaminated Estuary Sediment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
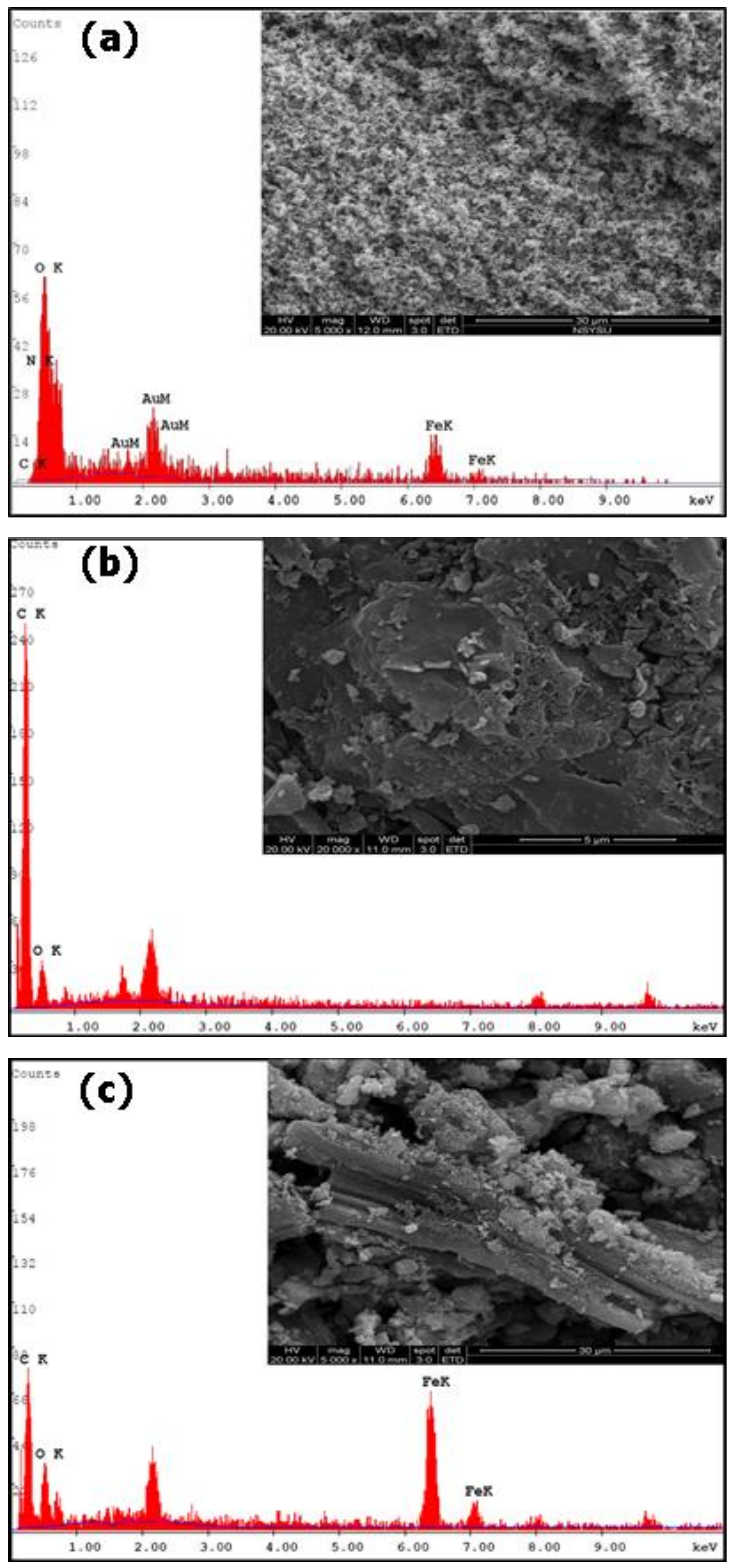
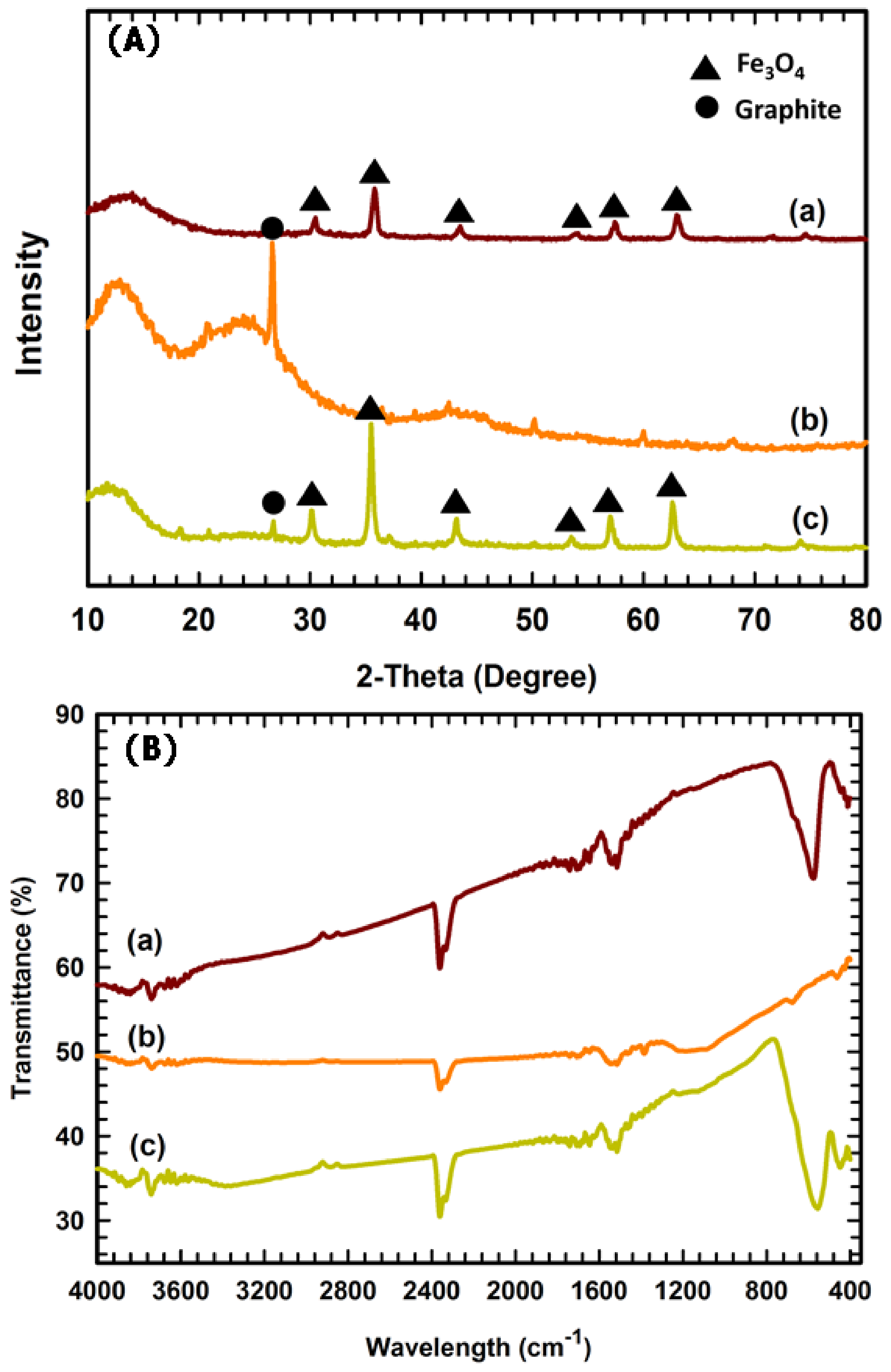
2.1. Characterization of Fe3O4, WB, and Fe3O4–WB Samples
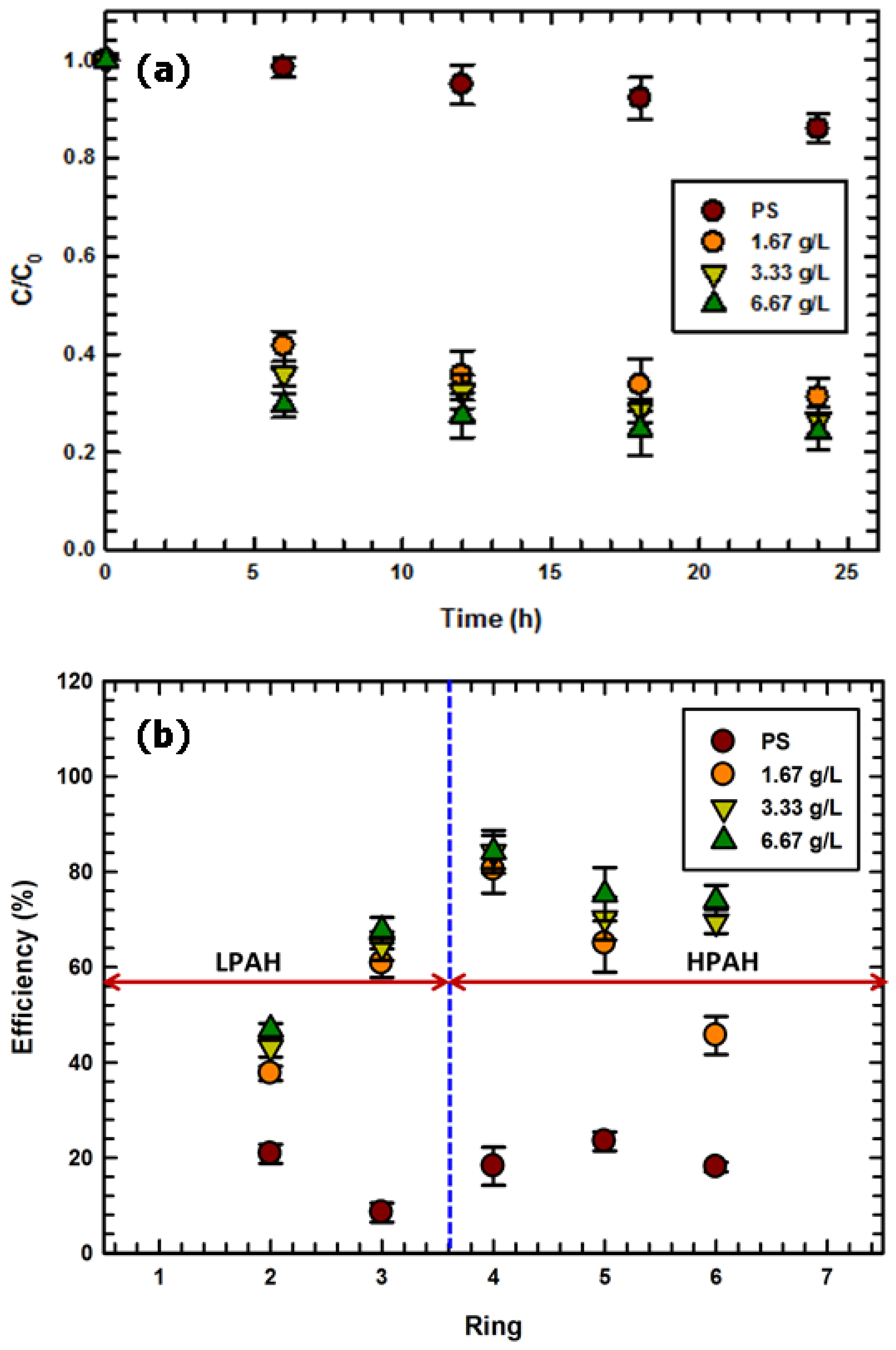
2.2. Catalytic Activity of Fe3O4–WB with Respect to PAH Reduction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.1.1. Sediment Samples
3.1.2. Chemicals Used
3.2. Experimental Methods
3.3. Instrumental Analyses
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardoso, F.D.; Dauner, A.L.L.; Martins, C.C. A critical and comparative appraisal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments and suspended particulate material from a large South American subtropical estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintado-Herrera, M.G.; Wang, C.; Lu, J.; Chang, Y.P.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Lara-Martín, P.A. Distribution, mass inventories, and ecological risk assessment of legacy and emerging contaminants in sediments from the Pearl River Estuary in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Thavamani, P.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Lee, Y.B.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Remediation approaches for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contaminated soils: Technological constraints, emerging trends and future directions. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 944–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Shen, G.; Huang, H.; He, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, B. Removal and transformation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during electrocoagulation treatment of an industrial wastewater. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacławek, S.; Lutze, H.V.; Grübel, K.; Padil, V.V.T.; Černík, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.M.; Chen, C.W.; Liu, Y.Y.; Dong, C.D. Decolorization of methylene blue by persulfate activated with FeO magnetic particles. Water Environ. Res. 2016, 88, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Liao, X.; Yan, X.; Huling, S.G.; Chai, T.; Tao, H. Effect and mechanism of persulfate activated by different methods for PAHs removal in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254–255, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleszczuk, P.; Kołtowski, M. Effect of co-application of nano-zero valent iron and biochar on the total and freely dissolved polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal and toxicity of contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.W.; Choi, B.H.; Jeong, T.U.; Ahn, K.H. Facile synthesis of magnetic biochar/Fe3O4 nanocomposites using electro-magnetization technique and its application on the removal of acid orange 7 from aqueous media. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.M.; Chen, C.W.; Jhuang, Y.J.; Dong, C.D. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles: Characterization and performance exemplified by the degradation of methylene blue in the presence of persulfate. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2016, 19, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C. Environmental implications and applications of engineered nanoscale magnetite and its hybrid nanocomposites: A review of recent literature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 48–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.Y.; Son, J.G.; Chiu, P.C. Biochar-mediated reductive transformation on nitro herbicides and explosives. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Luo, Z.; Tu, S.; Yin, Y. Properties of biochar obtained from pyrolysis of bamboo shoot shell. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 114, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saquing, J.M.; Yu, Y.H.; Chiu, P.C. Wood-derived black carbon (biochar) as a microbial electron donor and acceptor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 3, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.A.; Shimabuku, K.K.; Kearns, J.P.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Summers, R.S.; Cook, S.M. Environmental comparison of biochar and activated carbon for tertiary wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11253–11262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pukalchik, M.; Mercl, F.; Panova, M.; Břendová, K.; Terekhova, V.A.; Tlustoš, P. The improvement of multi-contaminated sandy loam soil chemical and biological properties by the biochar, wood ash, and humic substances amendments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 229, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, D.; Kumar, H.; Sarswat, A.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Pittman, C.U. Cadmium and lead remediation using magnetic oak wood and oak bark fast pyrolysis bio-chars. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayakaduwa, S.S.; Kumarathilaka, P.; Herath, I.; Ahmad, M.; Al-Wabel, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Usman, A.; Abduljabbar, A.; Vithanage, M. Equilibrium and kinetic mechanisms of woody biochar on aqueous glyphosate removal. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2516–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klüpfel, L.; Keiluweit, M.; Kleber, M.; Sander, M. Redox properties of plant biomass-derived black carbon (Biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5601–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska, A.; Oleszczuk, P. Bioavailability and bioaccessibility of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in historically contaminated soils after lab incubation with sewage sludge-derived biochars. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołtowski, M.; Hilber, I.; Bucheli, T.D.; Charmas, B.; Skubiszewska-Zięba, J.; Oleszczuk, P. Activated biochars reduce the exposure of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in industrially contaminated soils. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; Yan, J.; Qian, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, L.; Su, A.; Zhang, W.; Ni, H.; Chen, M. Degradation of 1,4-dioxane by biochar supported nano magnetite particles activating persulfate. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, G.; Liu, C.; Gao, J.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Zhou, D. Manipulation of persistent free radicals in biochar to activate persulfate for contaminant degradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5645–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Han, L.; Gao, W.; Xue, S.; Chen, M. Biochar supported nanoscale zerovalent iron composite used as persulfate activator for removing trichloroethylene. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.D.; Chen, C.W.; Hung, C.M. Synthesis of magnetic biochar from bamboo biomass to activate persulfate for the removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine sediments. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Feng, Q.; Yang, H.; Alam, E.; Gao, B.; Gu, D. Modified biochar supported Ag/Fe nanoparticles used for removal of cephalexin in solution: Characterization, kinetics and mechanisms. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 517, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Lou, L.; Luo, L.; Cao, R.; Duan, D.; Chen, Y. Effect of bamboo biochar on pentachlorophenol leachability and bioavailability in agricultural soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyakoshi, A.; Ueno, A.; Ichikawa, M. XPS and TPD characterization of manganese-substituted iron–potassium oxide catalysts which are selective for dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene into styrene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 219, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wan, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y. Synthesis of novel core-chell Fe0@Fe3O4 as heterogeneous activator of persulfate for oxidation of dibutyl phthalate under neutral conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 301, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Kang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, J.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Xu, D.; Wu, F.; Xing, B. Impact of deashing treatment on biochar structural properties and potential sorption mechanisms of phenanthrene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11473–11481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gregorio, M.R.; García-Falcón, M.S.; Martínez-Cerballo, E.; Simal-Gándara, J. Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from organic solvents by ashes wastes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xi, B.; Yang, T.; Peng, X.; Lian, X.; Yan, K.; Liu, H. Enhanced degradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene in groundwater by persulfate activated using iron–carbon micro-electrolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanayake, A.G.; Dewage, N.B.; Todd, O.A.; Essandoh, M.; Anderson, R.; Mlsna, T.; Mlsna, D. Salicylic acid and 4-nitroaniline removal from water using magnetic biochar: An environmental and analytical experiment for the undergraduate laboratory. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 1935–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, C.-D.; Chen, C.-W.; Kao, C.-M.; Chien, C.-C.; Hung, C.-M. Wood-Biochar-Supported Magnetite Nanoparticles for Remediation of PAH-Contaminated Estuary Sediment. Catalysts 2018, 8, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8020073
Dong C-D, Chen C-W, Kao C-M, Chien C-C, Hung C-M. Wood-Biochar-Supported Magnetite Nanoparticles for Remediation of PAH-Contaminated Estuary Sediment. Catalysts. 2018; 8(2):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8020073
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Cheng-Di, Chiu-Wen Chen, Chih-Ming Kao, Chuan-Chi Chien, and Chang-Mao Hung. 2018. "Wood-Biochar-Supported Magnetite Nanoparticles for Remediation of PAH-Contaminated Estuary Sediment" Catalysts 8, no. 2: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8020073
APA StyleDong, C.-D., Chen, C.-W., Kao, C.-M., Chien, C.-C., & Hung, C.-M. (2018). Wood-Biochar-Supported Magnetite Nanoparticles for Remediation of PAH-Contaminated Estuary Sediment. Catalysts, 8(2), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8020073




