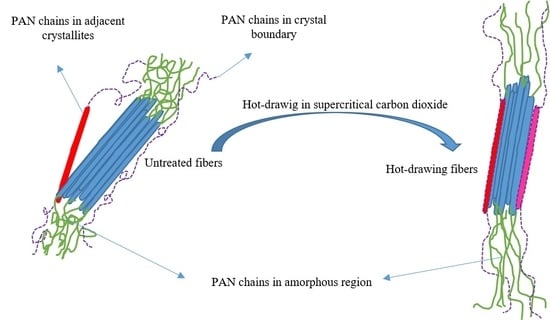
Effect of Different Pressures of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide on the Microstructure of PAN Fibers during the Hot-Drawing Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
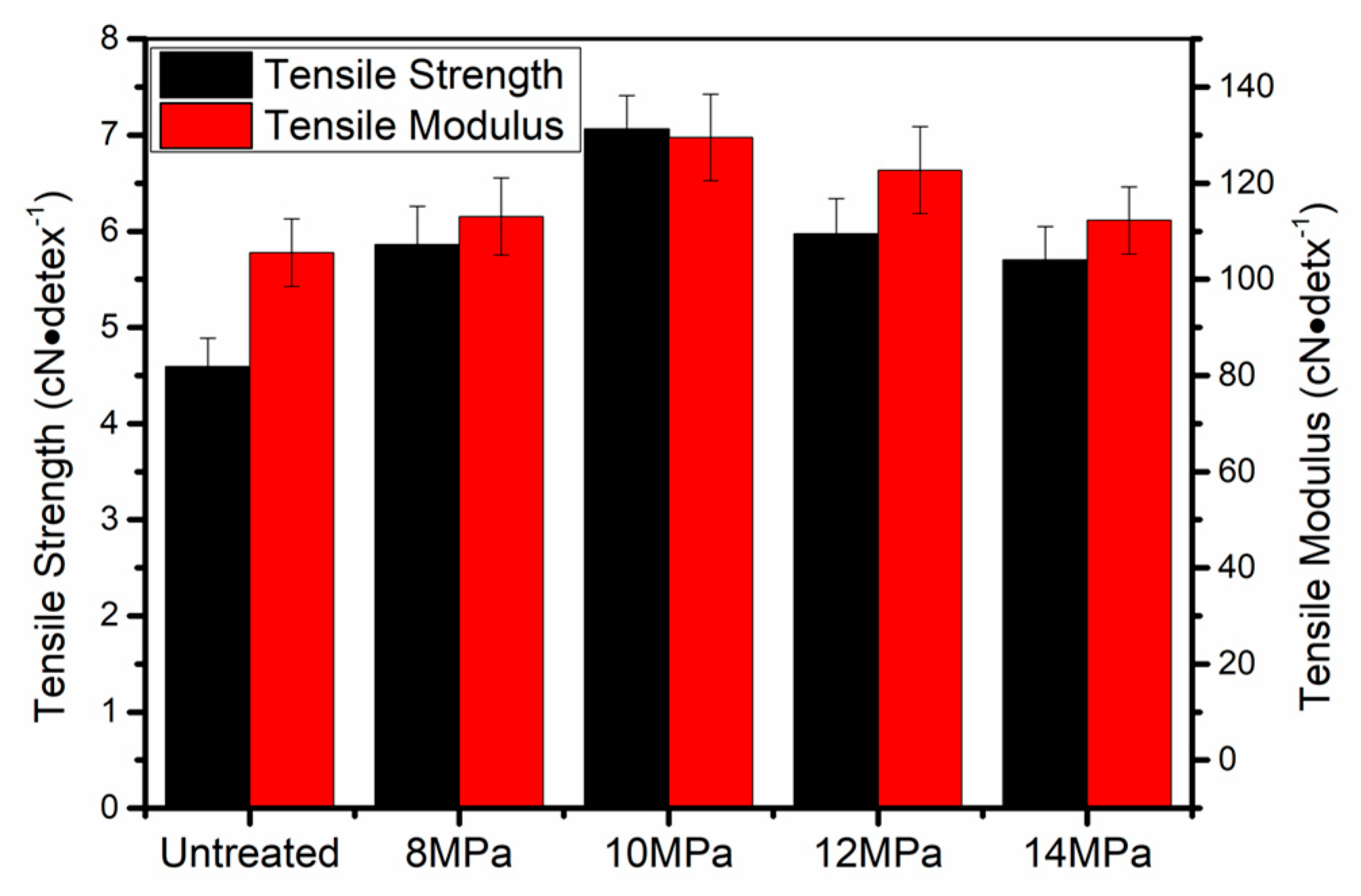
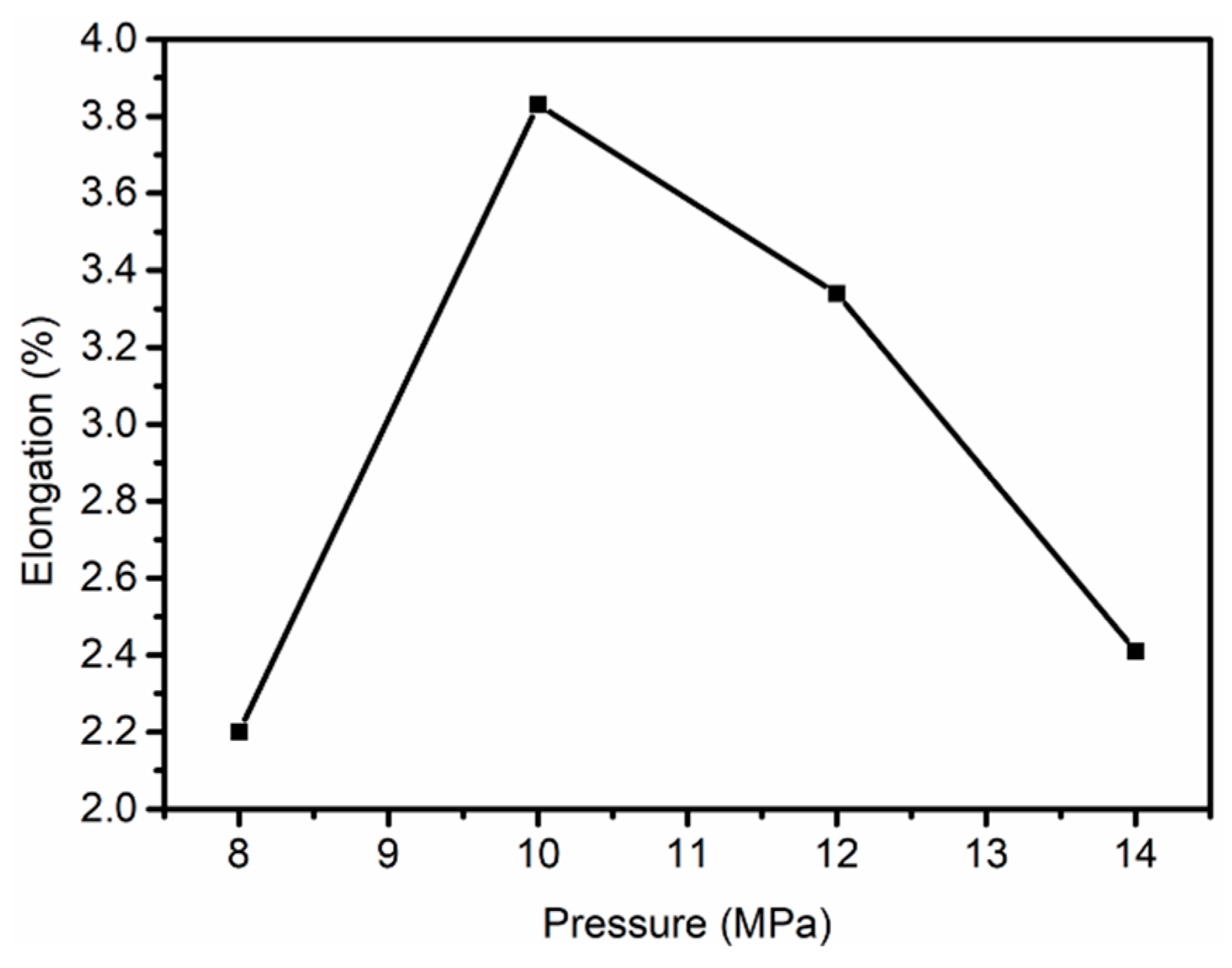
3.1. Mechanical Properties of PAN Fibers Treated at Different Pressures
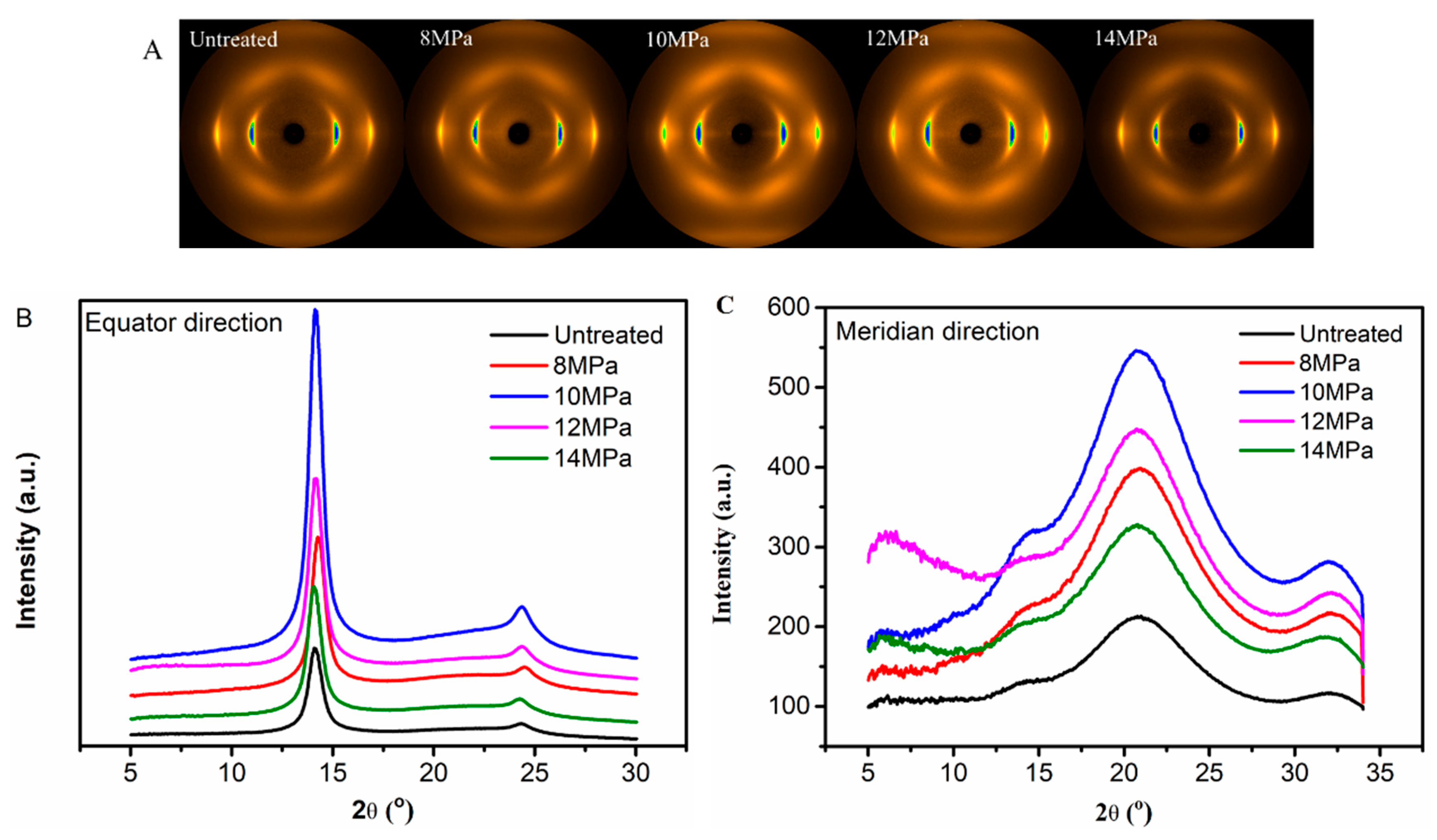
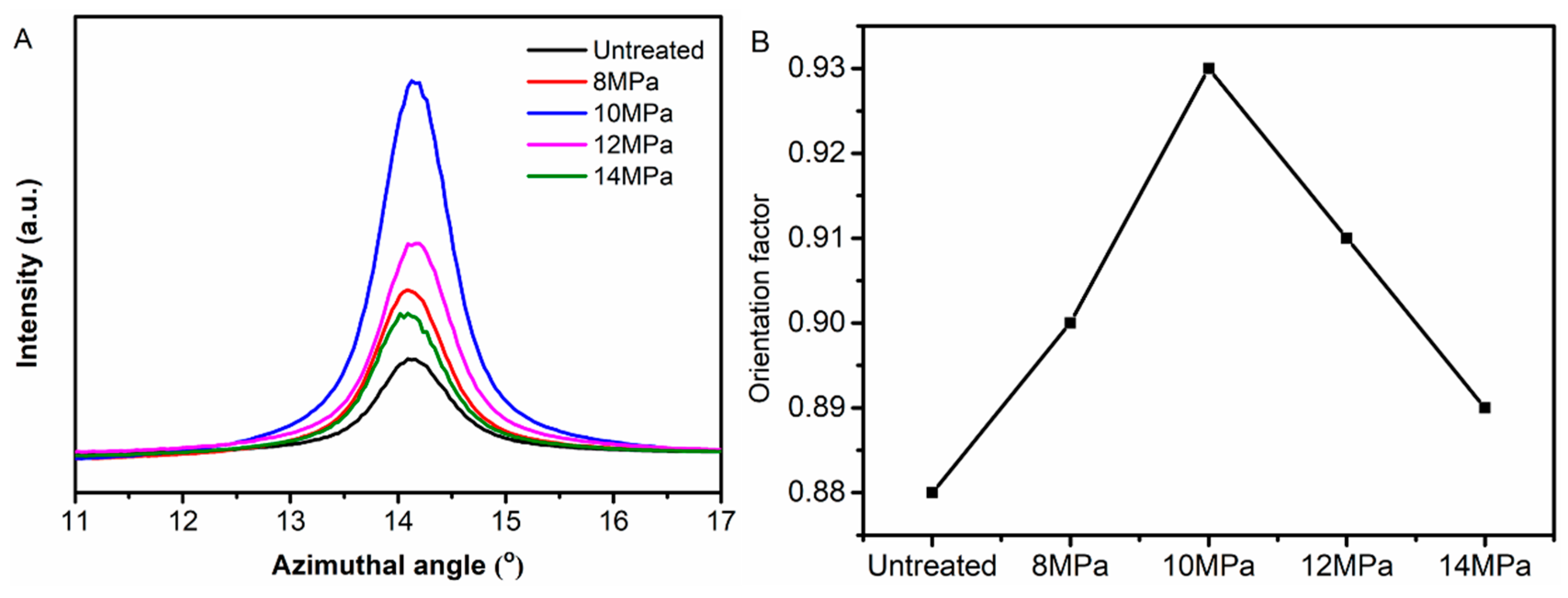
3.2. Wide Angle X-Ray Diffraction (WAXD) Analysis of PAN Fibers Treated at Different Pressures
3.3. Small Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS) Analysis of PAN Fibers Treated at Different Pressures
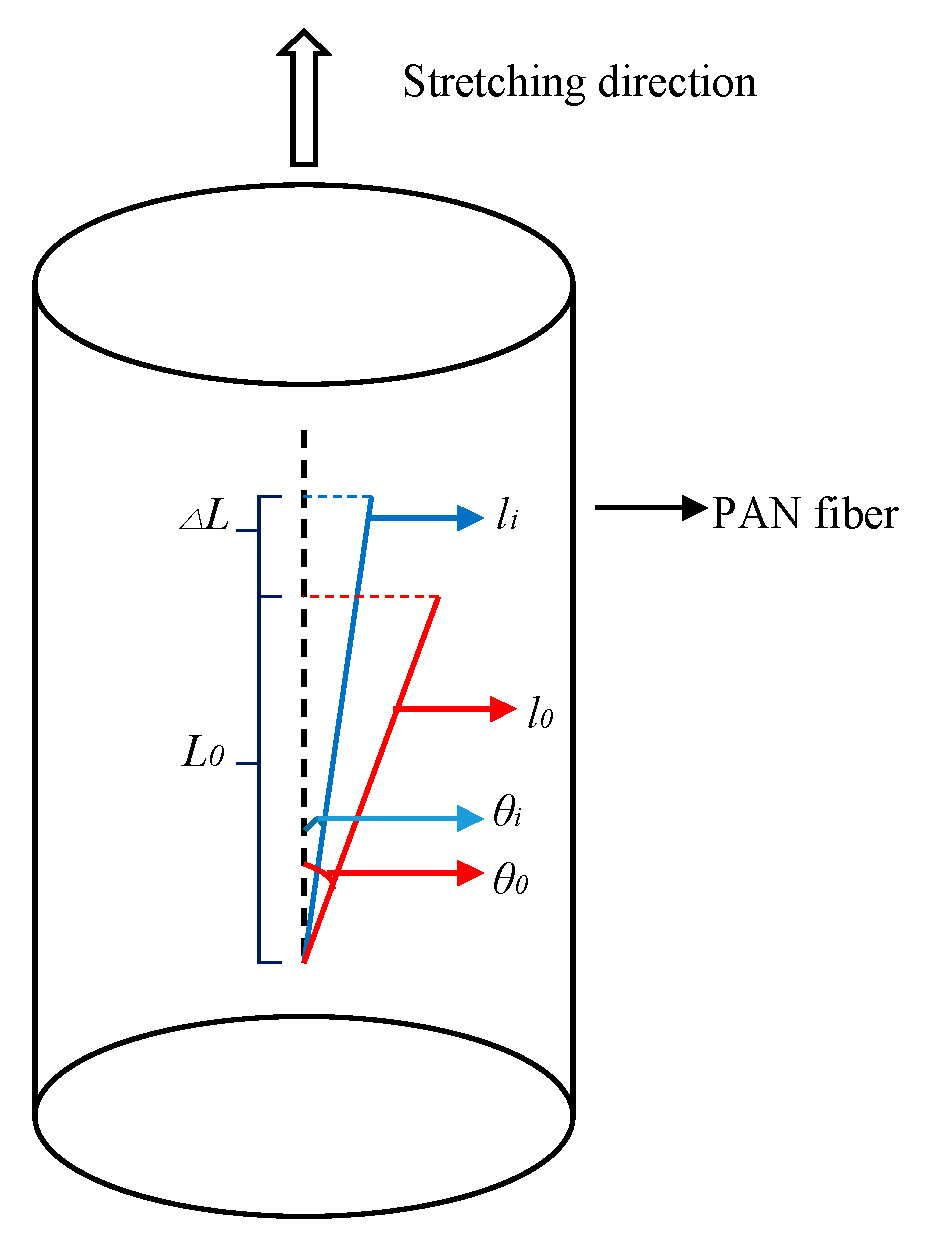
3.4. Stretching Behavior Analysis of the PAN Fibers Heated at Different Pressures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, S.-J. History and Structure of Carbon Fibers; Springer Nature: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-J. Novel Carbon Fibers and Their Composites; Springer Nature: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 295–342. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi-Ping, G.U. Development and application of carbon fiber brush for DC motor. Carbon 2017, 2, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Barile, C.; Casavola, C. Mechanical characterization of carbon fiber reinforced plastics specimens for aerospace applications. Polym. Compos. 2018, 40, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kuk, Y.-S.; Chung, Y.S.; Jin, F.-L.; Park, S.-J. Preparation and characterization of polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber papers. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3440–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Jang, J.; Yoon, S.H.; Mochida, I. A study on the effect of heat treatment on functional groups of pitch based activated carbon fiber using FTIR. Carbon 1997, 35, 1739–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, J.; Ling, L.; Dong, Y.; Liu, A. Mesophase pitch-based carbon fiber spinning through a filter assembly and the microstructure evolution mechanism. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Amp, S. Technical Advances and Development Suggestions for Rayon-based Carbon Fiber and Pitch-based Carbon Fiber. Chem. Fertil. Des. 2017, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, E.; Hermanutz, F. Carbon Fibers: Precursors, Manufacturing, and Properties. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauser, H.R. Encyclopedia/Handbook of Materials, Parts, and Finishes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Hu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, D. Investigating the jet stretch in the wet spinning of PAN fiber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 2267–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohzawa, Y.; Nagano, Y. Studies on dry spinning. II. Numerical solutions for some polymer–solvent systems based on the assumption that drying is controlled by boundary-layer mass transfer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1970, 14, 1879–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-Y.; Chang, H.-C.; Chiu, Y.-T.; Tsai, J.-L. The index of dry-jet wet spinning for polyacrylonitrile precursor fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 132, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.-G.; Wang, C.-G.; Bai, Y.-J.; Cao, W.-W. Effect of DMSO/H2O coagulation bath on the structure and property of polyacrylonitrile fibers during wet-spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Harrison, I. Modification of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) carbon fiber precursor via post-spinning plasticization and stretching in dimethyl formamide (DMF). Carbon 2002, 40, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Qiu, F. Unusual viscosity behavior of polyacrylonitrile in NaSCN aqueous solutions. Polymer 2015, 64, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Jo, S.M.; Chung, I.J. Influence of ZnCl2 on the structure and mechanical properties of polyacrylonitrile fibers. Polym. Int. 1994, 34, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.P.; Pryde, E.H. Supercritical CO2 extraction of lipid-bearing materials and characterization of the products. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1984, 61, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldino, L.; Della Porta, G.; Reverchon, E. Supercritical CO2 processing strategies for pyrethrins selective extraction. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 20, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonthuys, G.J.K.; Schwarz, C.E.; Burger, A.J.; Knoetze, J.H. Separation of alkanes and alcohols with supercritical fluids. Part I: Phase equilibria and viability study. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2011, 57, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonthuys, G.J.K.; Schwarz, C.E.; Burger, A.J.; Knoetze, J.H. Separation of alkanes and alcohols with supercritical fluids. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 2008, 58, 352–359. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, A.A. Reactions in Supercritical Fluids; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1994; pp. 449–479. [Google Scholar]
- Arranz, E.; Jaime, L.; Hazas, M.C.L.D.L.; Reglero, G.; Santoyo, S. Supercritical fluid extraction as an alternative process to obtain essential oils with anti-inflammatory properties from marjoram and sweet basil. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 67, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elgndi, M.A.; Filip, S.; Pavlić, B.; Vladić, J.; Stanojković, T.; Žižak, Ž.; Zeković, Z. Antioxidative and cytotoxic activity of essential oils and extracts of Satureja montana L., Coriandrum sativum L. and Ocimum basilicum L. obtained by supercritical fluid extraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 128, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldino, L.; Reverchon, E. Challenges in the production of pharmaceutical and food related compounds by SC-CO2 processing of vegetable matter. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 134, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, M.; Baldino, L.; Scudieri, C.; Cardea, S.; Ciambelli, P.; Reverchon, E. Supercritical CO2 processing to improve the electrochemical properties of graphene oxide. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 118, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, E.; Porter, R.S. Crystallization of bisphenol a polycarbonate induced by supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1987, 25, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhu, X.; Hu, G.; Liu, T.; Cao, G.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, W. Supercritical carbon dioxide-induced melting temperature depression and crystallization of syndiotactic polypropylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Du, B.; Wei, Q.; Zheng, L. An investigation for the performance of meta-aramid fiber blends treated in supercritical carbon dioxide fluid. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Handa, Y.P. CO2-Assisted Melting of Semicrystalline Polymers†. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 8505–8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, Y.P.; Kruus, P.; O’Neill, M. High-pressure calorimetric study of plasticization of poly(methyl methacrylate) by methane, ethylene, and carbon dioxide. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1996, 34, 2635–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Zhao, N.; Liu, J.; Xu, J. A small-angle X-ray scattering study and molecular dynamics simulation of microvoid evolution during the tensile deformation of carbon fibers. Carbon 2012, 50, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioya, M.; Kawazoe, T.; Okazaki, R.; Suei, T.; Sakurai, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Kikutani, T. Small-Angle X-ray Scattering Study on the Tensile Fracture Process of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Fiber. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 4758–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thünemann, A.F.; Ruland, W. Microvoids in Polyacrylonitrile Fibers: A Small-Angle X-ray Scattering Study. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 1848–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effler, L.J.; Fellers, J.F. Structural orientation functions for anisotropic small-angle scattering. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1992, 25, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioya, M.; Takaku, A. Characterization of microvoids in carbon fibers by absolute small-angle x-ray measurements on a fiber bundle. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 58, 4074–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


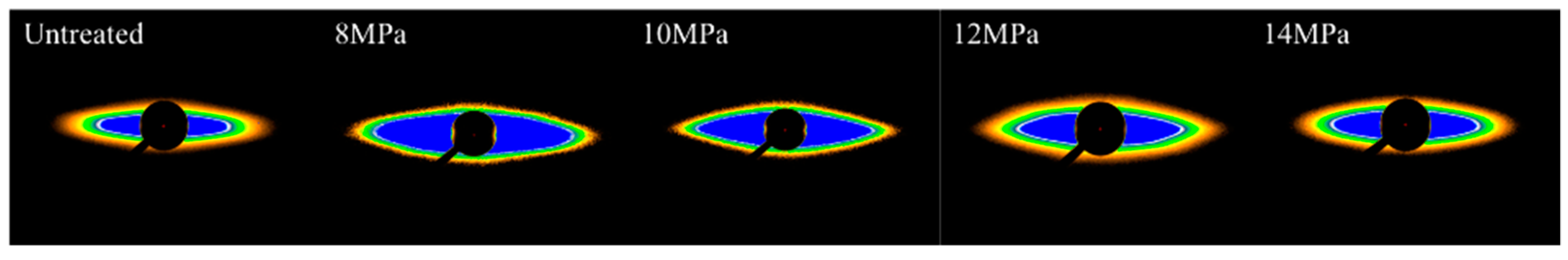

| Sample | Bψ (o) | L (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 28.27777 | 1626.741 |
| 8 MPa | 24.35159 | 340.1361 |
| 10 MPa | 17.95414 | 163.6661 |
| 12 MPa | 18.03325 | 187.2659 |
| 14 MPa | 27.73146 | 373.1343 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, M.; Kong, H.; Ding, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Yu, M. Effect of Different Pressures of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide on the Microstructure of PAN Fibers during the Hot-Drawing Process. Polymers 2019, 11, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030403
Qiao M, Kong H, Ding X, Hu Z, Zhang L, Cao Y, Yu M. Effect of Different Pressures of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide on the Microstructure of PAN Fibers during the Hot-Drawing Process. Polymers. 2019; 11(3):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030403
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Mengmeng, Haijuan Kong, Xiaoma Ding, Zhifeng Hu, Luwei Zhang, Yuanzhi Cao, and Muhuo Yu. 2019. "Effect of Different Pressures of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide on the Microstructure of PAN Fibers during the Hot-Drawing Process" Polymers 11, no. 3: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030403
APA StyleQiao, M., Kong, H., Ding, X., Hu, Z., Zhang, L., Cao, Y., & Yu, M. (2019). Effect of Different Pressures of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide on the Microstructure of PAN Fibers during the Hot-Drawing Process. Polymers, 11(3), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030403