A New Sustainable PPT Coating Based on Recycled PET to Improve the Durability of Hydraulic Concrete
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
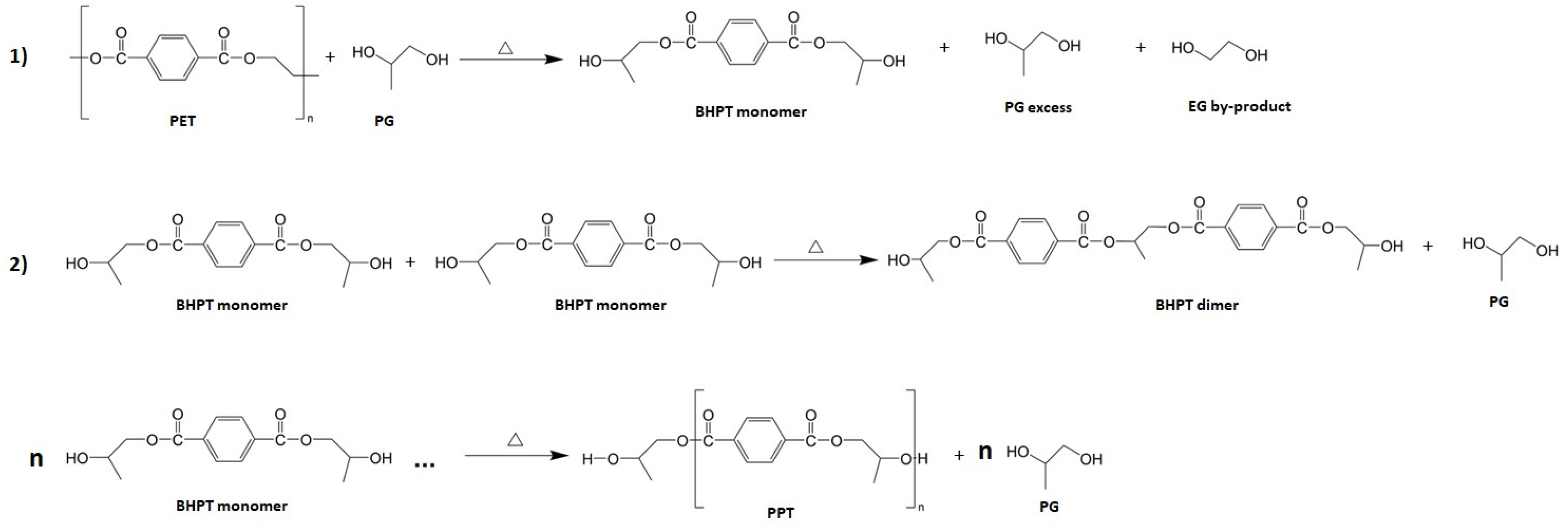
2.2. Synthesis of the Bis(2-hidroxyproyl) Terephthalate (BHPT) Monomers
2.3. Purification Process of BHPT
2.4. Synthesis of Polypropylene Terephthalate (PPT)
2.5. Elaboration of Cementitious Concrete Mixes
2.6. Elaboration of PPT Coatings Hydraulic Concrete Using a Brush
2.7. Characterization
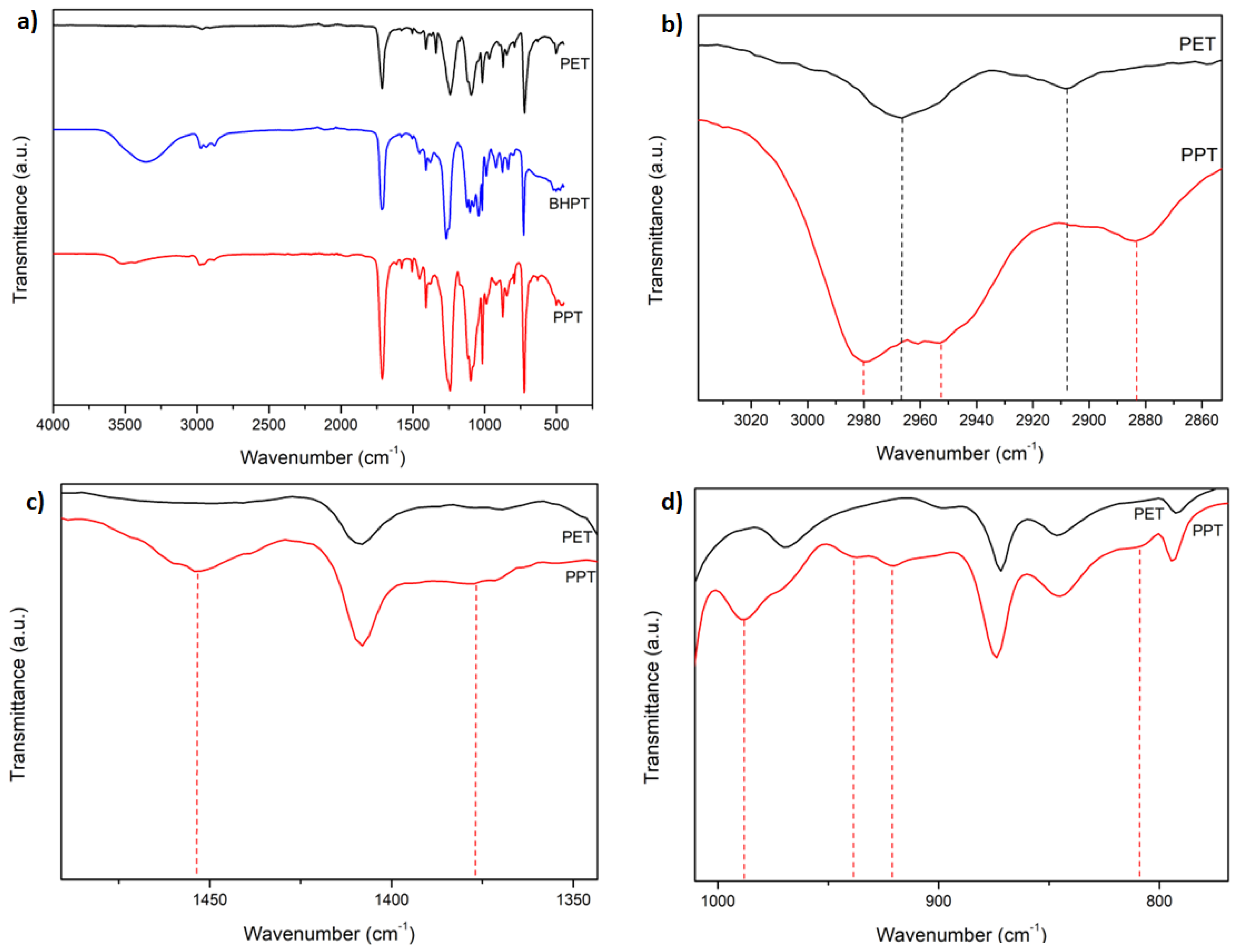
2.7.1. FT-IR
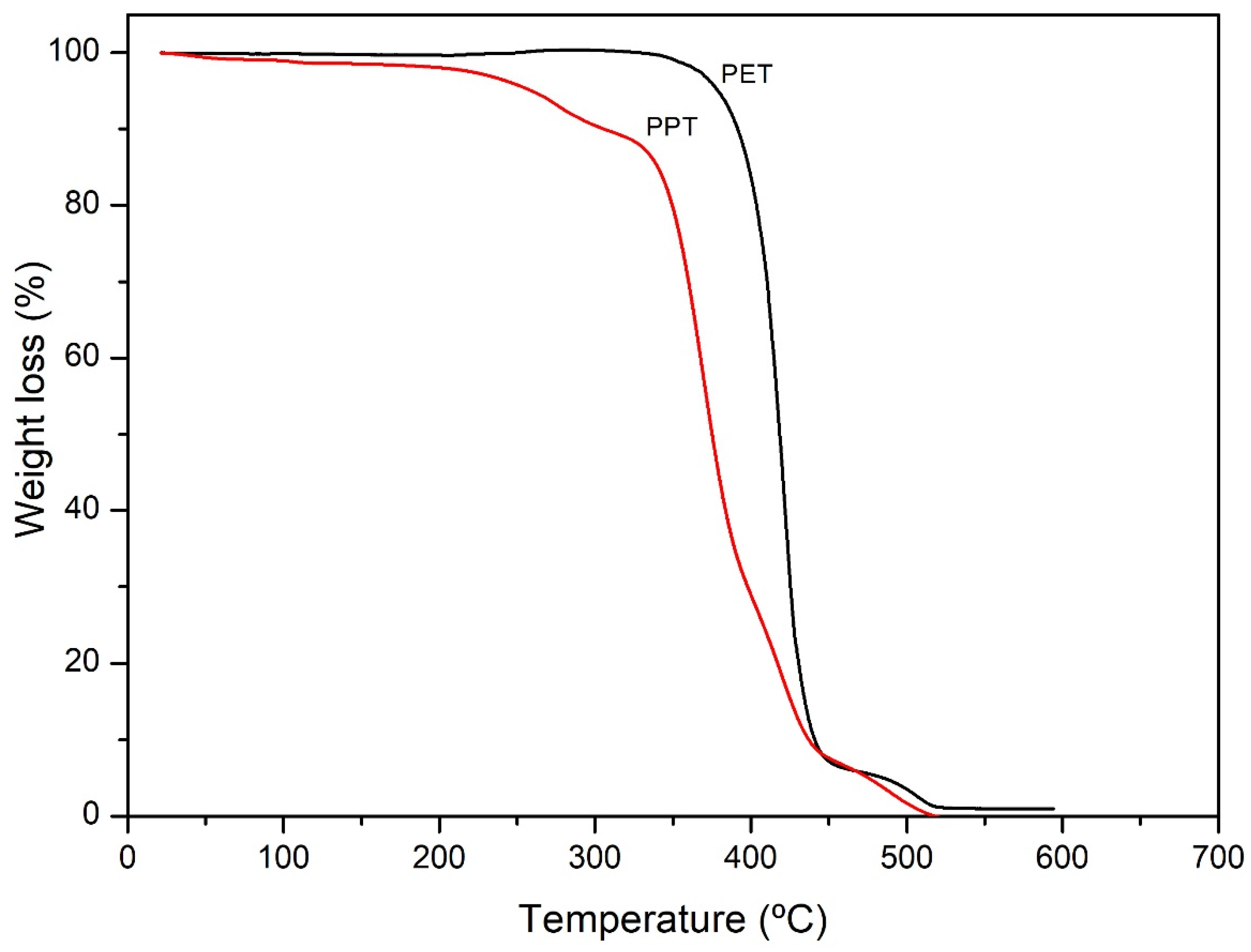
2.7.2. TGA
2.7.3. Physical Properties of Coatings
2.7.4. Durability Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proposed Schematic Drawing of the Synthesis of PPT from PET Recycling
3.2. FT-IR
3.3. TGA
3.4. Physical Properties of PPT and Coatings
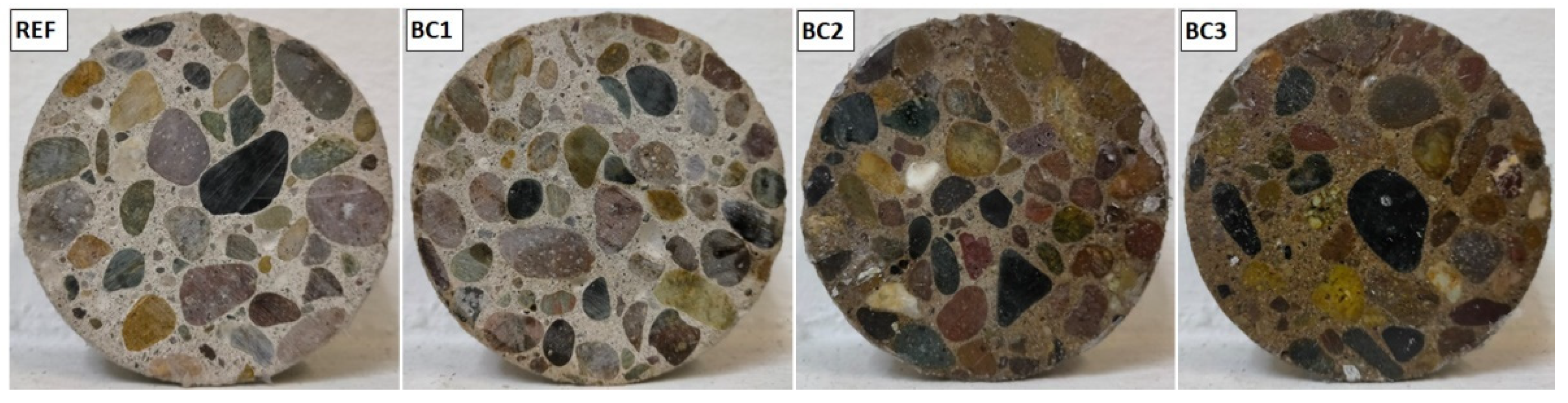
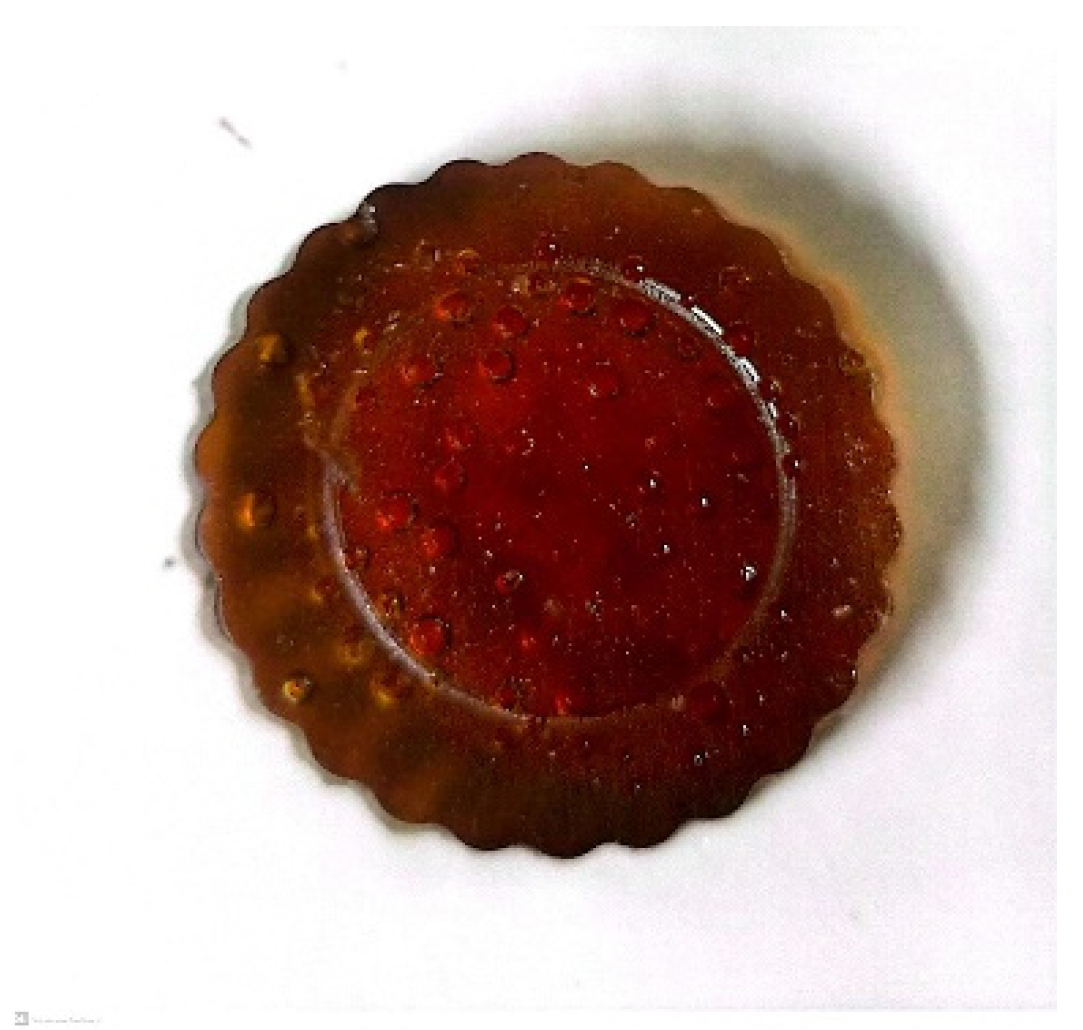
3.4.1. Appearance
3.4.2. Thickness
3.4.3. Adhesion
3.4.4. Wettability Capacity (Water Contact Angle, WCA)
3.5. Durability Properties of Concrete
3.5.1. Rate of Absorption of Water (ASTM C1585-20)
3.5.2. Permeability of Ion Chloride
3.5.3. Electrical Resistivity
3.5.4. Carbonation Depth
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trincardi, F.; Francocci, F.; Pellegrini, C.; Ribera d’Alcalà, M.; Sprovieri, M. 13—The Mediterranean Sea in the Anthropocene. In Oceanography of the Mediterranean Sea; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 501–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyathiar, P.; Kumar, P.; Carpenter, G.; Brace, J.; Mishra, D.K. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Bottle-to-Bottle Recycling for the Beverage Industry: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibria, M.G.; Masuk, N.I.; Safayet, R.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Mourshed, M. Plastic Waste: Challenges and Opportunities to Mitigate Pollution and Effective Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2023, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifian, S.; Asasian-Kolur, N. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) waste to carbon materials: Theory, methods and applications. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 163, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Gao, L.; Qin, L.; Yin, J. Chemical recycling of PET to value-added products. RSC Sustain. 2023, 1, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshanov, K.; Toms, R.; Aliev, G.; Naumova, A.; Melnikov, P.; Gervald, A. Recent Developments and Perspectives of Recycled Poly(ethylene terephthalate)-Based Membranes: A Review. Membranes 2022, 12, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirayil, C.J.; Mishra, R.K.; Thomas, S. 2—Materials Recovery, Direct Reuse and Incineration of PET Bottles. In Plastic Design Library, Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate Bottles, 1st ed.; Thomas, S., Rane, A., Kanny, K., Abithia, V.K., Thomas, M.G., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheel, A.; Pant, D. 4—Chemical Depolymerization of PET Bottles via Glycolysis. In Plastics Design Library, Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate Bottles, 1st ed.; Thomas, S., Rane, A., Kanny, K., Abithia, V.K., Thomas, M.G., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikladious, N.E.; Asaad, J.N.; Emira, H.S.; Mansour, H.S. Alkyd resins based on hyperbranched polyesters and PET waste for coating applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 102, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bórquez-Mendivil, A.; Hurtado-Macías, A.; Leal-Pérez, J.E.; Flores-Valenzuela, J.; Vargas-Ortíz, R.Á.; Cabrera-Covarrubias, F.G.; Almaral-Sánchez, J.L. Hybrid Coatings of SiO2–Recycled PET Unsaturated Polyester Resin by Sol-Gel Process. Polymers 2022, 14, 3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, K.; Ünlü, K.C.; Acar, I.; Güçlü, G. Epoxy-based paints from glycolysis products of postconsumer PET bottles: Synthesis, wet paint properties and film properties. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.; Fedel, M.; Deflorian, F.; Cotting, F.; Lins, V. Properties of Post-Consumer Polyethylene Terephthalate Coating Mechanically Deposited on Mild Steels. Coatings 2019, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xia, X.; Ruan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; LeBlanc, G.A.; An, L. Ignored microplastic sources from plastic bottle recycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838 Pt 2, 156038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harusato, A.; Seo, W.; Abo, H.; Nakanishi, Y.; Nishikawa, H.; Itoh, Y. Impact of particulate microplastics generated from polyethylene terephthalate on gut pathology and immune microenvironments. iScience 2023, 26, 106474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Yao, J.; Lin, X.; Li, H.; Lam, J.Y.K.; Leung, C.K.Y.; Sham, I.M.L.; Shih, K. Tensile performance of sustainable Strain-Hardening Cementitious Composites with hybrid PVA and recycled PET fibers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 107, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchillas-Chinchillas, M.J.; Gaxiola, A.; Alvarado-Beltrán, C.G.; Orozco-Carmona, V.M.; Pellegrini-Cervantes, M.J.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, M.; Castro-Beltrán, A. A new application of recycled-PET/PAN composite nanofibers to cement–based materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, S.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chow, C.W.K. Preparation and performance analysis of recycled PET fiber reinforced recycled foamed concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, R.; Shafabakhsh, G.; Kheyroddin, A.; Mohammadzadeh Moghaddam, A. Investigating the effects of recycled PET particles, shredded recycled steel fibers and Metakaolin powder on the properties of RCCP. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Romero, P.; Zhang, H.; Huang, M.; Lai, F. Unsaturated polyester resin concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Ren, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, Z. Durability of concrete coupled with life cycle assessment: Review and perspective. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 139, 105041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumman, R.; Bari, M.S.; Manzur, T.; Kamal, M.R.; Noor, M.A. A Durable Concrete Mix Design Approach using Combined Aggregate Gradation Bands and Rice Husk Ash Based Blended Cement. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merah, A.; Khenfer, M.M.; Korichi, Y. The effect of industrial coating type acrylic and epoxy resins on the durability of concrete subjected to accelerated carbonation. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 2446–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Guo, M.; Chen, L.; Hu, F. Carbonation Resistance of Surface Protective Materials Modified with Hybrid NanoSiO2. Coatings 2021, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, P.; Fan, H.; Shang, H.; Guo, S.; Zhao, T. Carbonation of Water Repellent-Treated Concrete. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1343947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashed, Y.L.; Zahran, F.; Youssef, M.A.; Mohamed, M.G.; Mazrouaa, A.M. Performance evaluation of acrylate terpolymer based coating on anti-carbonation. Pigment. Resin. Technol. 2022, 53, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Shi, C.; Zhang, J.; Jia, L.; Chong, L. Effect of inorganic surface treatment on surface hardness and carbonation of cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 90, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, T.Y.; Liao, W.; Wong, C.K.; Tang, W. Evaluation of carbonation resistance of paint coated concrete for buildings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 107, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.Y.; Shin, D.G.; Choi, D.S. Evaluation of the durability of mortar and concrete applied with inorganic coating material and surface treatment system. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Chen, W.G.; Feng, T.; Li, W.Q.; Liu, X.T.; Dong, L.L.; Fu, Y.Q. Enhancing chloride ion penetration resistance into concrete by using graphene oxide reinforced waterborne epoxy coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 138, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, M.R.; Bassuoni, M.T. Effect of Nano-Based Coatings on Concrete under Aggravated Exposures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Lv, Y.; Gao, Z.; Dai, S. Effect of Polymer Coatings on the Permeability and Chloride Ion Penetration Resistances of Nano-Particles and Fibers-Modified Cementitious Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, M.; Helene, P. Efficacy of surface hydrophobic agents in reducing water and chloride ion penetration in concrete. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2008, 41, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Xue, S.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, T. Influence of exposure environments and moisture content on water repellency of surface impregnation of cement-based materials. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12115–12125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, P.; Cai, H.; Xu, Y.; Rasulov, M. Investigation of Silane Impregnation for Protection of Alkali-Activated Slag Mortar. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9970753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husni, H.; Nazari, M.R.; Yee, H.M.; Rohim, R.; Yusuff, A.; Mohd Ariff, M.A.; Ahmad, N.N.R.; Leo, C.P.; Junaidi, M.U.M. Superhydrophobic rice husk ash coating on concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, A.F.B.; Daschevi, P.A.; Langaro, E.A.; Pieralisi, R.; Medeiros, M.H.F. Effectiveness of surface coatings in concrete: Chloride penetration and carbonation. J. Build. Pathol. Rehabil. 2021, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C150/C150M-22; Standard Specification for Portland Cement. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- ACI PRC-211.1-22; Standard Practice for Selecting Proportions for Normal, Heavyweight, and Mass Concrete. American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.concrete.org/store/productdetail.aspx?ItemID=211122&Language=English&Units=US_Units (accessed on 26 March 2024).
- ASTM C31/C31M-22; Standard Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in the Field. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- SSPC-SP-13/NACE 6:2018; Surface Preparation of Concrete. SSPC: The Society for Protective Coatings-NACE International JOINT SURFACE PREPARATION STANDARD. 2018. Available online: https://www.normadoc.com/spanish/sspc-sp-13-nace-6-2018.html (accessed on 26 March 2024).
- ASTM D3359-17; Standard Test Methods for Rating Adhesion by Tape Test. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1585-20; Standard Test Method for Measurement of Rate of Absorption of Water by Hydraulic-Cement Concretes. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1202-19; Standard Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concrete’s Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Rilem, T. CPC-18 Measurement of hardened concrete carbonation depth. Mater. Struct. 1988, 21, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravve, A. Principles of Polymer Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, R.K. Fundamentals of Polymer Engineering, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Thanakkasaranee, S.; Shin, H.; Lee, Y.; Tak, G.; Seo, J. Pet/bio-based terpolyester blends with high dimensional thermal stability. Polymers 2021, 13, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingale, N.D.; Palekar, V.S.; Shukla, S.R. Glycolisis of Postconsumer Polyehtylene Terephthalate Waste. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, M.E.; Elsabee, M.Z. Preparation and Characterization of Polyester Based on bis- (2-hydroxypropyl terephthalate). J. Polym. Res. 2002, 9, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, B.H. Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 71–93. [Google Scholar]
- Gall, M.; Freudenthaler, P.J.; Fischer, J.; Lang, R.W. Characterization of Composition and Structure–Property Relationships of Commercial Post-Consumer Polyethylene and Polypropylene Recyclates. Polymers 2021, 13, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miandad, R.; Reahn, M.; Barakat, M.A.; Aburiazaiza, A.S.; Khan, H.; Ismail, I.M.I.; Dhavamani, J.; Gardy, J.; Hassanpour, A.; Nizami, A.-S. Catalytic pyrolysis of plastic waste: Moving toward pyrolysis based biorefineries. Front. Energy Res. 2019, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.; Wang, Q. Study on Thermal Degradation Processes of Polyethylene Terephthalate Microplastics Using the Kinetics and Artificial Neural Networks Models. Processes 2023, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibnu Ali, B.T.; Nareswari, C.; Gunawan, T.; Widiastuti, N.; Kusumawati, Y.; Jaafar, J.; Saputra, H.; Sulistiono, D.O. Utilization of plastic bottle waste of polyethylene terephthalate as a low-cost membrane and its modifications for gas separation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 127, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, Q.; Sun, T.; Zhang, M.; Du, Z.; Wu, M.; Guo, S.; Lei, T.; et al. Synergistic effects and products yield analyses based on co-pyrolysis of poplar tree and rape stalks with polyethylene terephthalate and polypropylene. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 112, 101461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducoli, S.; Federici, S.; Cocca, M.; Gentile, G.; Zendrini, A.; Bergese, P.; Depero, L.E. Characterization of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polyamide (PA) true-to-life nanoplastics and their biological interactions. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Jeong, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.S. Two-stage thermochemical conversion of polyethylene terephthalate using steam to produce a clean and H2- and CO-rich syngas. Energy 2023, 276, 127651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benke, A.; Sonnenberg, J.; Oelschlägel, K.; Schneider, M.; Lux, M.; Potthoff, A. Wettability after Artificial and Natural Weathering of Polyethylene Terephthalate. Environments 2022, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, T.D.; Wei, L.; Luzinov, I. Perfluoropolyether-based oleophobic additives: Influence of molecular weight distribution on wettability of polyethylene terephthalate films. J. Fluor. Chem. 2021, 244, 109747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesel, A.; Zaplotnik, R.; Primc, G.; Mozetič, M. Evolution of the Surface Wettability of PET Polymer upon Treatment with an Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Jet. Polymers 2020, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comité Euro International du Béton. CEB Bull 192: Diagnosis and Assessment of Concrete Structures—State of the Art Report; Comité Euro International du Béton: Lausanne, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, K.; Bugusu, B. Food packaging-Roles, materials, and environmental issues: Scientific status summary. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R39–R55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisticò, R. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in the packaging industry. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



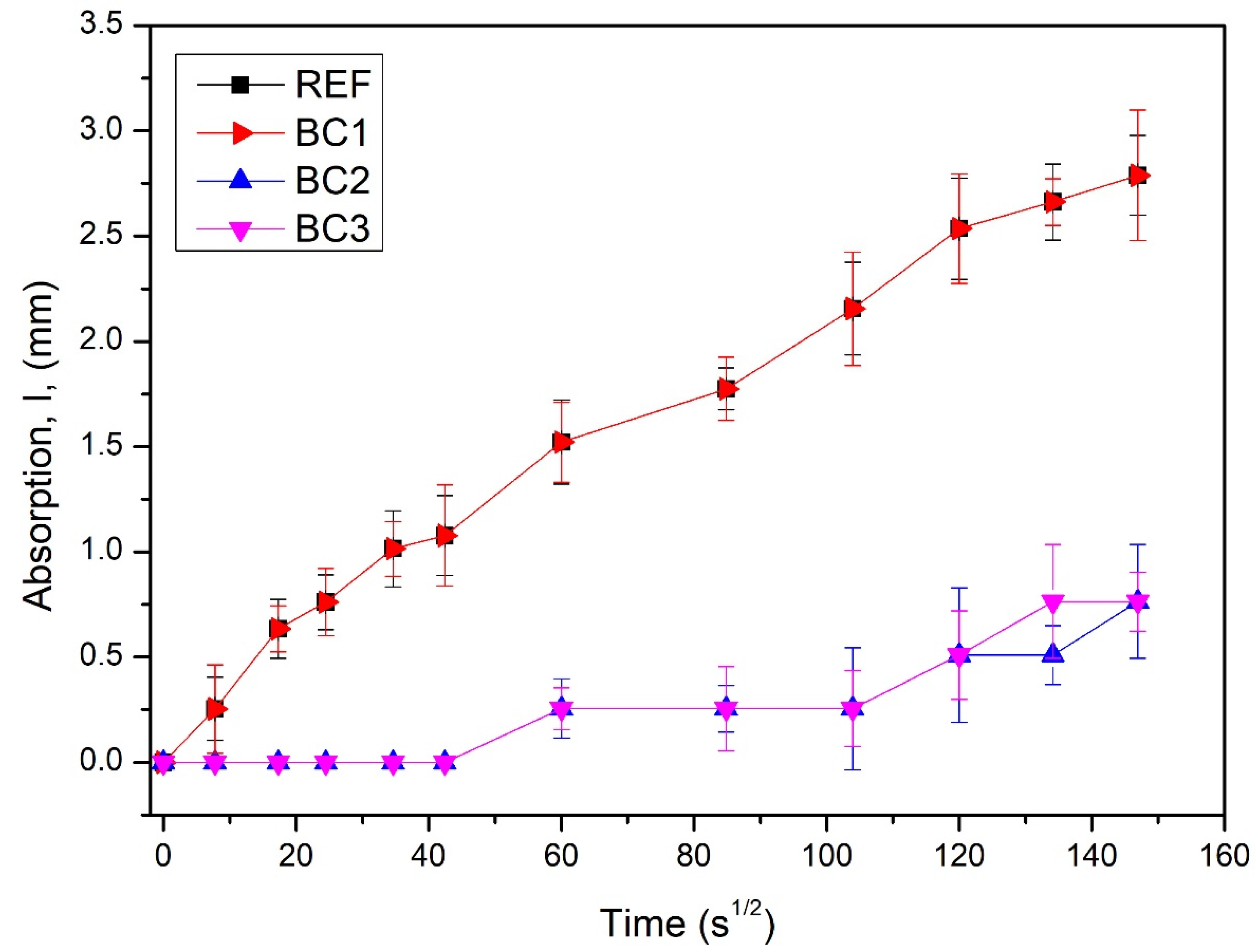
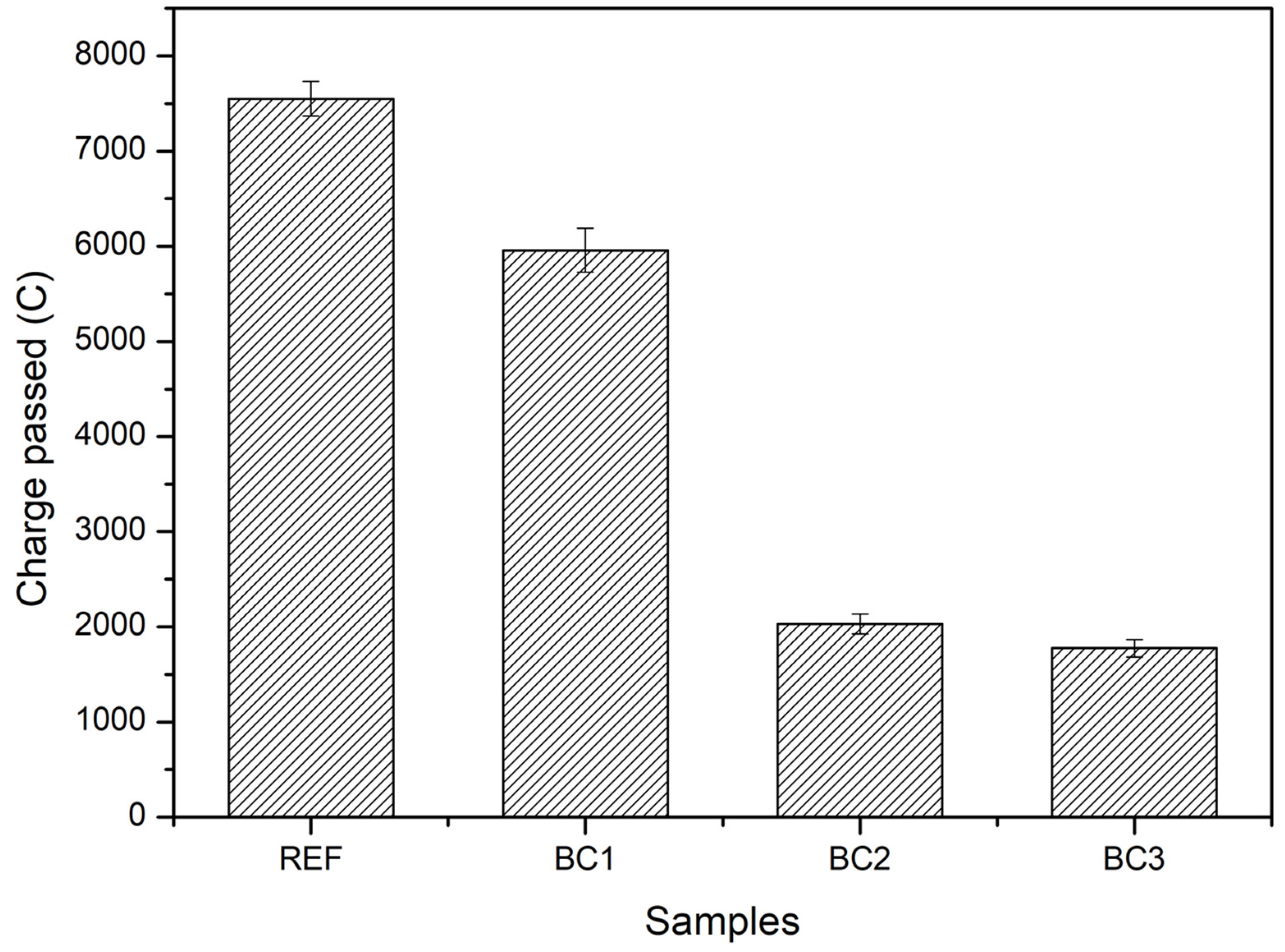

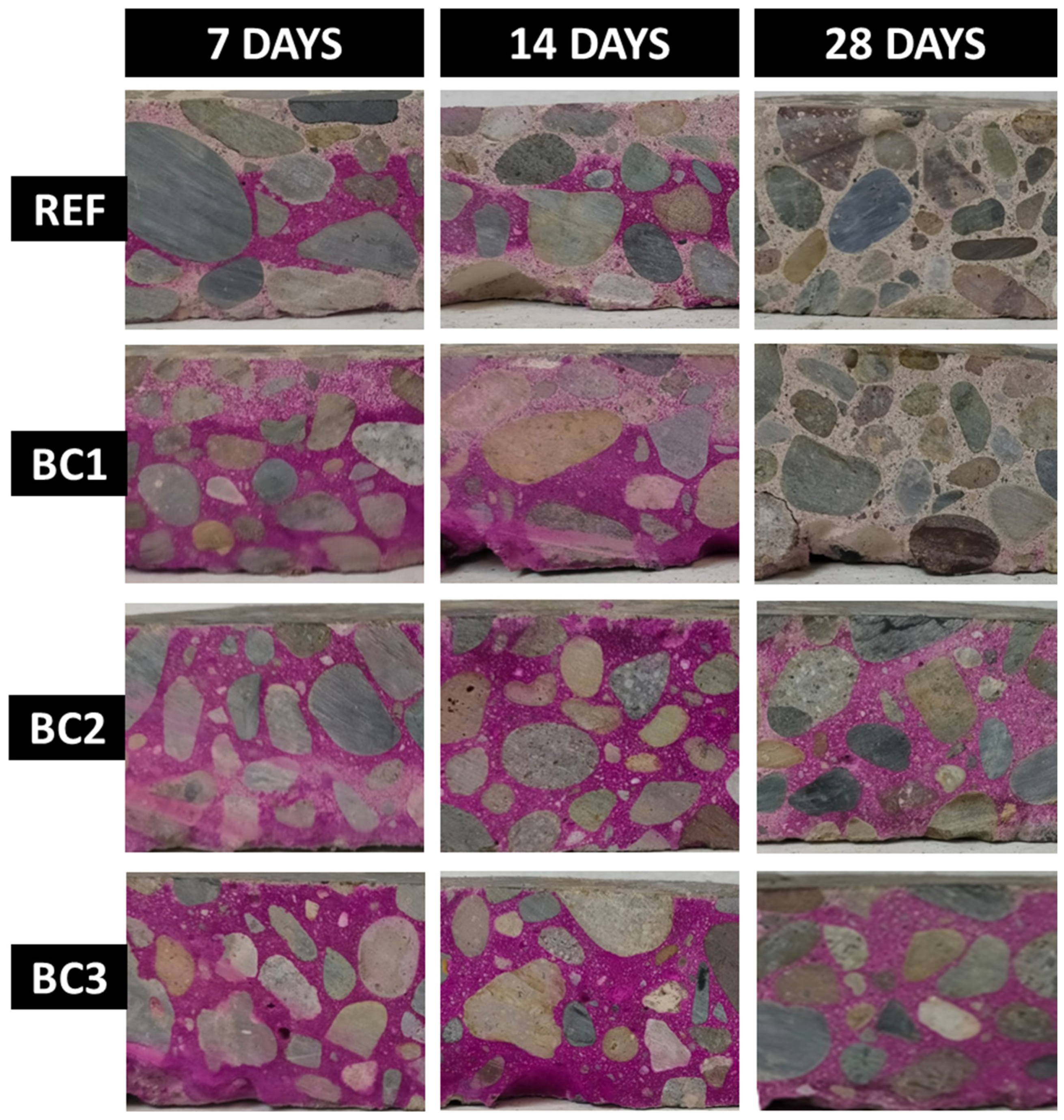
| Material | Dosage (Kg/m3) |
|---|---|
| Cement | 256.25 |
| Water | 205.00 |
| Coarse aggregate | 1024.00 |
| Fine aggregate | 608.40 |
| Carbonation Depth (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure Time/Samples | REF | BC1 | BC2 | BC3 |
| 7 days | 14.97 | 11.27 | 0 | 0 |
| 14 days | 15.65 | 15.65 | 0 | 0 |
| 28 days | 25 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bórquez-Mendivil, A.; Barrios-Durstewitz, C.P.; Núñez-Jáquez, R.E.; Hurtado-Macías, A.; Leal-Pérez, J.E.; Flores-Valenzuela, J.; García-Grajeda, B.A.; Cabrera-Covarrubias, F.G.; Mendivil-Escalante, J.M.; Almaral-Sánchez, J.L. A New Sustainable PPT Coating Based on Recycled PET to Improve the Durability of Hydraulic Concrete. Polymers 2024, 16, 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091297
Bórquez-Mendivil A, Barrios-Durstewitz CP, Núñez-Jáquez RE, Hurtado-Macías A, Leal-Pérez JE, Flores-Valenzuela J, García-Grajeda BA, Cabrera-Covarrubias FG, Mendivil-Escalante JM, Almaral-Sánchez JL. A New Sustainable PPT Coating Based on Recycled PET to Improve the Durability of Hydraulic Concrete. Polymers. 2024; 16(9):1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091297
Chicago/Turabian StyleBórquez-Mendivil, Adrián, Carlos Paulino Barrios-Durstewitz, Rosa Elba Núñez-Jáquez, Abel Hurtado-Macías, Jesús Eduardo Leal-Pérez, Joaquín Flores-Valenzuela, Blanca Alicia García-Grajeda, Francisca Guadalupe Cabrera-Covarrubias, José Miguel Mendivil-Escalante, and Jorge Luis Almaral-Sánchez. 2024. "A New Sustainable PPT Coating Based on Recycled PET to Improve the Durability of Hydraulic Concrete" Polymers 16, no. 9: 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091297









