Biopolymer Electrolyte Based on Derivatives of Cellulose from Kenaf Bast Fiber
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis of Cellulose

2.2. Synthesis of Carboxymethyl Cellulose from Cellulose Fiber
2.3. Preparation of CMC-Based Biopolymer Electrolytes

2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Degree of Substitution (DS) Determination
2.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.4.4. Dynamic Mechanical Analyzer (DMA)
2.4.5. Impedance Spectroscopic Study
2.4.6. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.4.7. Linear Sweep Voltammetry
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Carboxymethyl Cellulose



3.2. Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Polymer Electrolyte

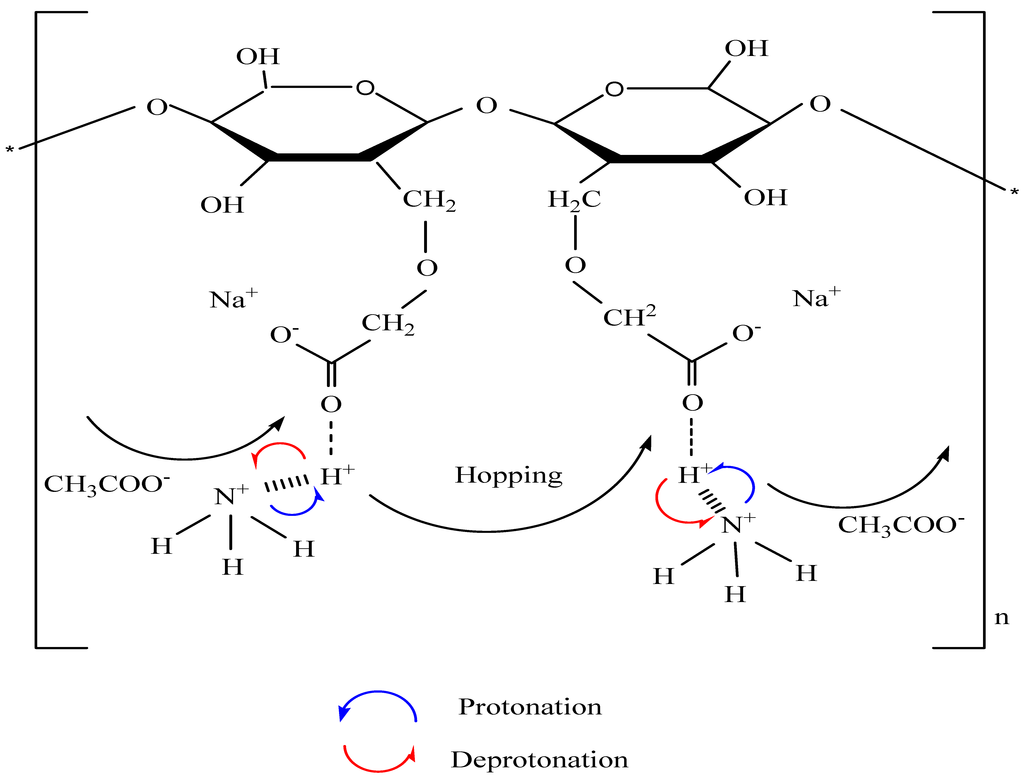
3.3. Impedance Study




3.4. Morphological Studies

3.5. Electrochemical Stability Determination

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandra, S.; Chandra, A. Solid state ionics: Materials aspect. In Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences India Section; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1994; pp. 141–181. [Google Scholar]
- Selvasekarapandian, S.; Baskaran, R.; Hema, M. Complex AC impedance, transference number and vibrational spectroscopy studies of proton conducting PVAc–NH4SCN polymer electrolytes. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2005, 357, 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Fenton, D.E.; Parker, J.M.; Wright, P.V. Complexes of alkali metal ions with poly (ethylene oxide). Polymer 1973, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.V. Electrical conductivity in ionic complexes of poly (ethylene oxide). Br. Polym. J. 1975, 7, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.B.; Chabagno, J.M.; Duclot, M.J. Poly-ethers as solid electrolytes. In Proceedings of the Second International Meeting on Solid Electrolytes, St. Andrews, Scotland, UK, 20–22 September 1978.
- Huang, H.; He, P.; Hu, N.; Zeng, Y. Electrochemical and electrocatalytic properties of myoglobin and haemoglobin incorporated in carboxymethyl cellulose films. Bioelectrochemistry 2003, 61, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adinugraha, M.P.; Marseno, D.W.; Haryadi. Synthesis and characterization of sodium carboxymethylcellulose from cavendish banana pseudo stem (Musa cavendishii LAMBERT). Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 62, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Cuba-Chiem, L.T.; Huynh, L.; Ralston, J.; Beattie, D.A. In situ particle film ATR–FTIR studies of CMC adsorption on talc: The effect of ionic strength and multivalent metal ions. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, D.R.; Singh, R.P. Characterisation of carboxymethyl cellulose and polyacrylamide graft copolymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 57, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K. Controlled functionalization of the polysaccharide chitin. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1921–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyler, R.W.; Klug, E.D.; Diephuis, F. Determination of degree of substitution of sodium carboxymethylcellulose. Anal. Chem. 1947, 19, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoud, O.A.E.; Nawaz, H.; Arêas, E.P.G. Chemistry and applications of polysaccharide solutions in strong electrolytes/dipolar aprotic solvents: An overview. Molecules 2013, 18, 1270–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pushpamalar, V.; Langford, S.J.; Ahmad, M.; Lim, Y.Y. Optimization of reaction conditions for preparing carboxymethyl cellulose from sago waste. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, E.; Leung, A.C.W.; Liu, Y.; Majid, E.; Hrapovic, S.; Male, K.B.; Luong, J.H.T. Green strategy guided by Raman spectroscopy for the synthesis of ammonium carboxylated nanocrystalline cellulose and the recovery of byproducts. J. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargarzadeh, H.; Ahmad, I.; Abdullah, I.; Dufresne, A.; Zainudin, S.Y.; Sheltami, R.M. Effects of hydrolysis conditions on the morphology, crystallinity, and thermal stability of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from kenaf bast fibers. Cellulose 2012, 19, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sain, M.; Panthapulakkal, S. Bioprocess preparation of wheat straw fibres and their characterization. Ind. Crops Prod. 2006, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsudin, A.S.; Lai, H.M.; Isa, M.I.N. Biopolymer materials based carboxymethyl cellulose as a proton conducting biopolymer electrolyte for application in rechargeable proton battery. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 129, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, K.H.; Isa, M.I.N. Structural and DC ionic conductivity studies of carboxy methylcellulose doped with ammonium nitrate as solid polymer electrolytes. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2013, 8, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar]
- Anuar, N.K.; Zainal, N.; Mohamed, N.S.; Subban, R.H.Y. Studies of poly (ethyl methacrylate) complexed with ammonium trifluoromethanesulfonate. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 501, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, C.S.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Savitha, T.; Hirankumar, G.; Angelo, P.C. Vibrational and impedance spectroscopic study on PVP–NH4SCN based polymer electrolytes. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2007, 393, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.N.; Isa, M.I.N. Carboxyl methylcellulose solid polymer electrolytes: Ionic conductivity and dielectric study. J. Curr. Eng. Res. 2011, 3, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Selvasekarapandian, S.; Hirankumar, G.; Kawamura, J.; Kuwata, N.; Hattori, T. H solid state NMR studies on the proton conducting polymer electrolytes. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 2741–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiar, A.S.A.; Puteh, R.; Arof, A.K. Conductivity studies of a chitosan-based polymer electrolyte. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2006, 373, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsudin, A.S.; Isa, M.I.N. Structural and ionic transport study on CMC doped NH4Br: A new types of biopolymer electrolytes. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 12, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Bhattacharya, B. Present scenario of solid state photoelectrochemical solar cell and dye sensitized solar cell using PEO-based polymer electrolytes. In Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells and Solar Cell Performance; Travino, M.R., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011; Chapter 10; pp. 235–266. [Google Scholar]
- Pratap, R.; Singh, B.; Chandra, S. Polymeric rechargeable solid state proton battery. J. Power Sources 2006, 161, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.S.; Mohamad, A.A. Effect of temperature on the performance of proton batteries based on chitosan–NH4NO3–EC membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rani, M.S.A.; Rudhziah, S.; Ahmad, A.; Mohamed, N.S. Biopolymer Electrolyte Based on Derivatives of Cellulose from Kenaf Bast Fiber. Polymers 2014, 6, 2371-2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6092371
Rani MSA, Rudhziah S, Ahmad A, Mohamed NS. Biopolymer Electrolyte Based on Derivatives of Cellulose from Kenaf Bast Fiber. Polymers. 2014; 6(9):2371-2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6092371
Chicago/Turabian StyleRani, Mohd Saiful Asmal, Siti Rudhziah, Azizan Ahmad, and Nor Sabirin Mohamed. 2014. "Biopolymer Electrolyte Based on Derivatives of Cellulose from Kenaf Bast Fiber" Polymers 6, no. 9: 2371-2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6092371
APA StyleRani, M. S. A., Rudhziah, S., Ahmad, A., & Mohamed, N. S. (2014). Biopolymer Electrolyte Based on Derivatives of Cellulose from Kenaf Bast Fiber. Polymers, 6(9), 2371-2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6092371