Influence of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Properties on Bacterial Adhesion Capacity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Polyelectrolytes
2.1.2. Substrates
2.1.3. Bacteria
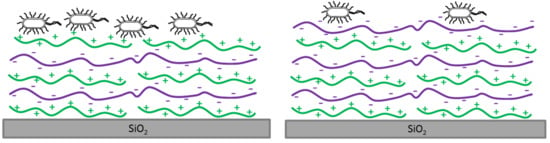
2.2. Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Preparation
2.2.1. Multilayers on Silica Particles
2.2.2. Multilayers on Silica Plates
2.3. Surface Characterization
2.3.1. Electrokinetic Measurements
2.3.2. Surface Roughness Measurements
2.3.3. Surface Hydrophobicity Measurements
2.4. Monitoring of the Bacterial Adhesion on Surfaces
3. Results
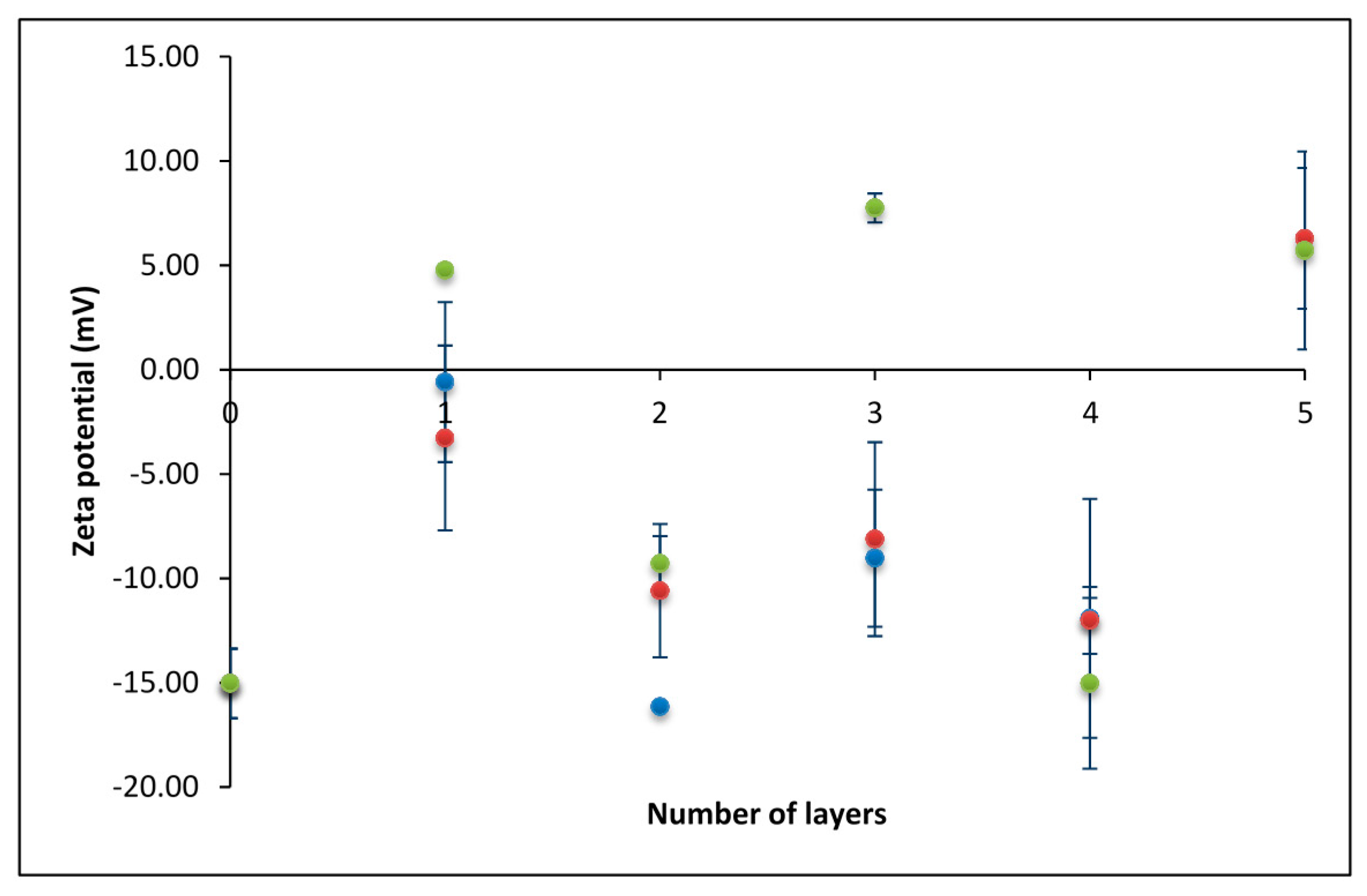
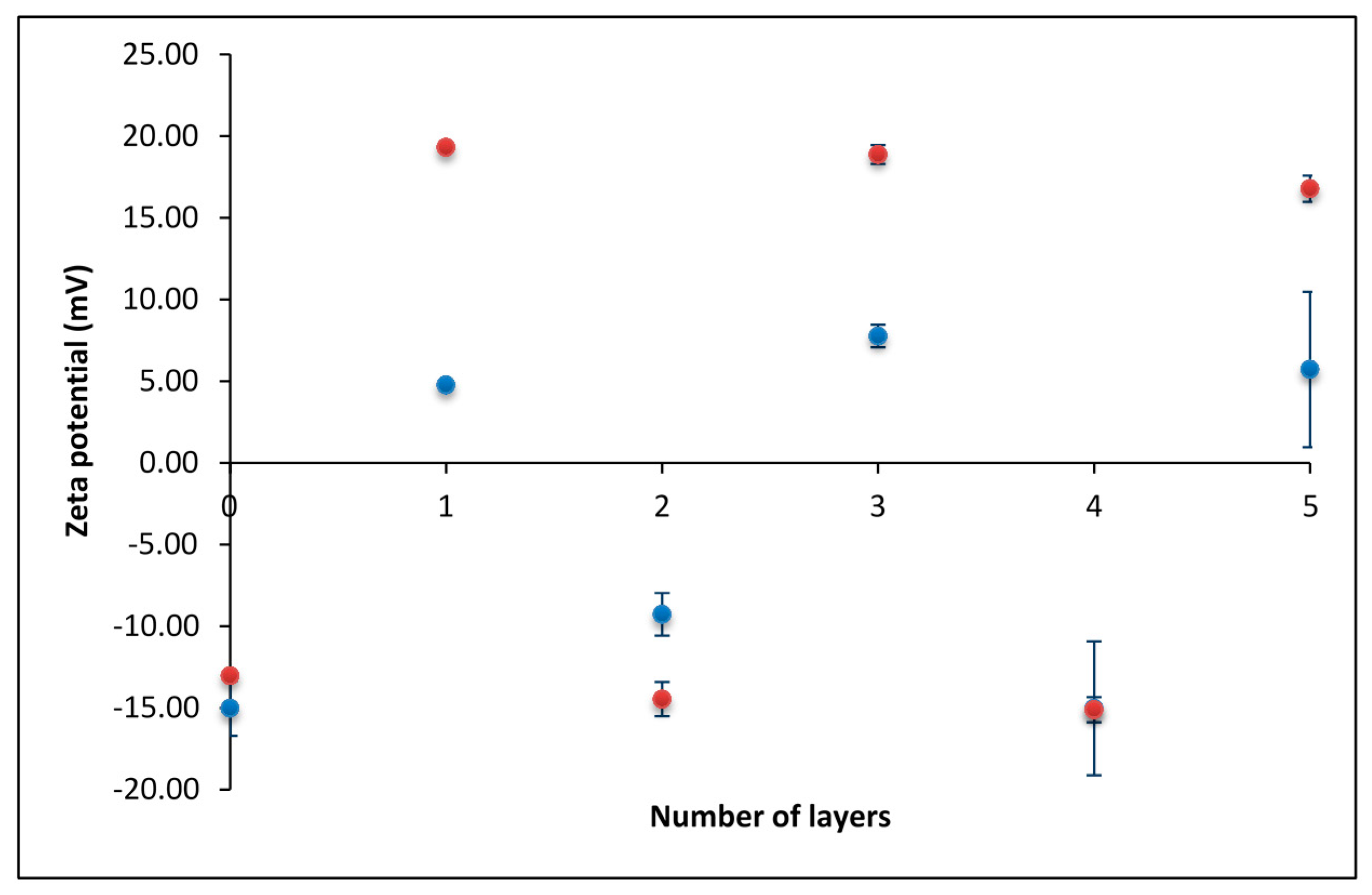
3.1. Zeta Potential of the SiO2 Particles Covered with PEMs
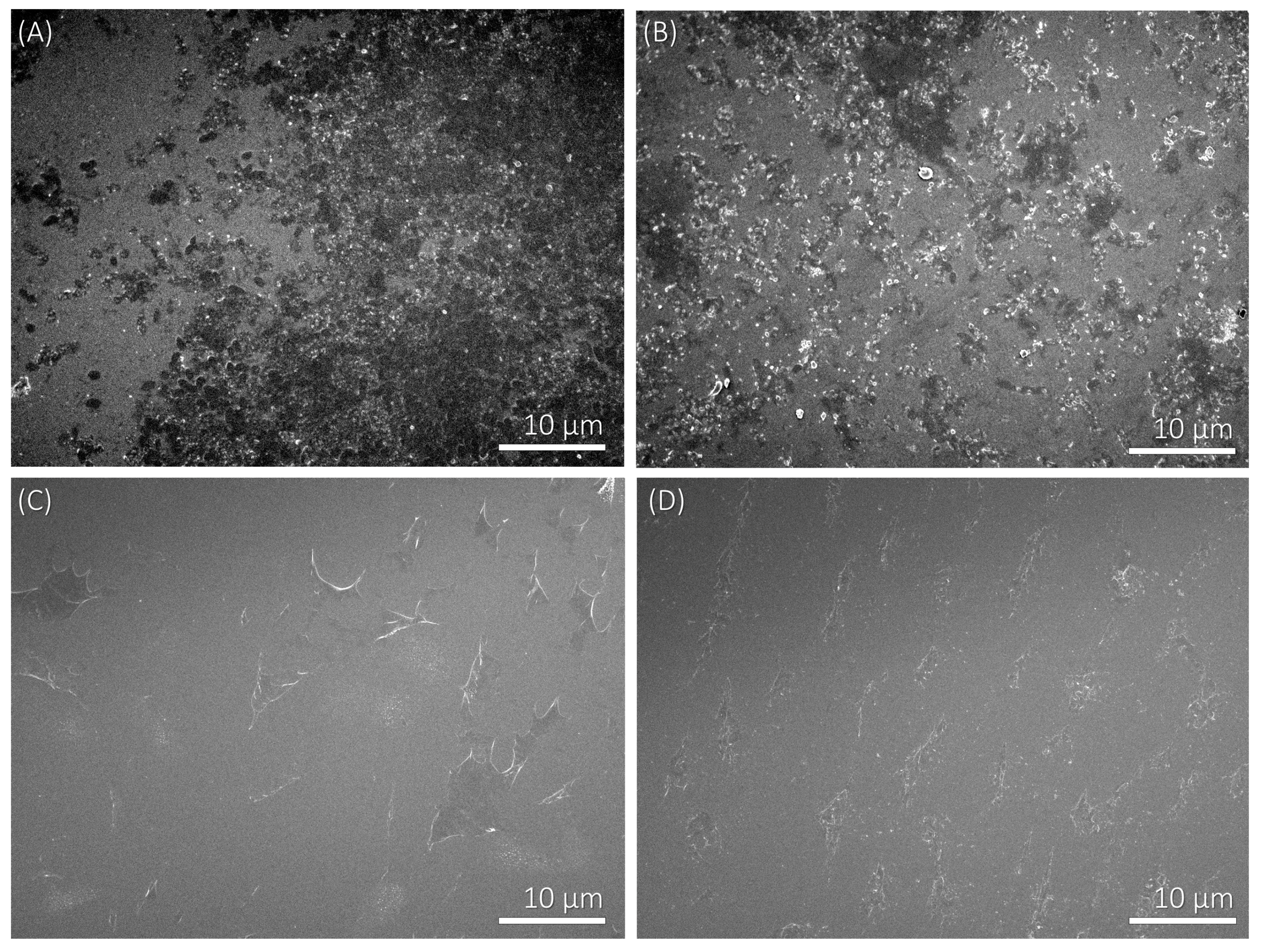
3.2. Adhesion of Bacteria on Polyelectrolyte Multilayers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Decher, G. Fuzzy nanoassemblies: Toward layered polymeric multicomposites. Science 1997, 227, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, K.; Yamauchi, Y.; Rydzek, G.; Ji, Q.; Yonamine, Y.; Wu, K.C.-W.; Hill, J.P. Layer-by-layer nanoarchitectonics: Invention, innovation, and evolution. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 36–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.; Mano, J.F. Molecular interactions driving the layer-by-layer assembly of multilayers. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8883–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.J.; Björnmalm, M.; Caruso, F. Multilayer assembly. Technology-driven layer-by-layer assembly of nanofilms. Science 2015, 348, aaa2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovačević, D.; van der Burgh, S.; de Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M.A. Kinetics of formation and dissolution of weak polyelectrolyte multilayers: Role of salt and free polyions. Langmuir 2002, 18, 5607–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Požar, J.; Kovačević, D. Complexation of polyallylammonium cation with polystyrenesulfonate anion: The effect of ionic strength and electrolyte type. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 6530–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechler, S.L.; Lynn, D.M. Characterization of degradable polyelectrolyte multilayers fabricated using DNA and a fluorescently-labeled poly(β-amino ester): Shedding light on the role of the cationic polymer in promoting surface-mediated gene delivery. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.R.; Mano, J.F. Polyelectrolyte multilayered assemblies in biomedical technologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3453–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saurer, E.M.; Jewell, C.M.; Roenneburg, D.A.; Bechler, S.L.; Torrealba, J.R.; Hacker, T.A.; Lynn, D.M. Polyelectrolyte multilayers promote stent-mediated delivery of DNA to vascular tissue. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1696–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossfeld, S.; Nolte, A.; Hartmann, H.; Recke, M.; Schaller, M.; Walker, T.; Kjems, J.; Schlosshauer, B.; Stoll, D.; Wendel, H.-P.; et al. Bioactive coronary stent coating based on layer-by-layer technology for siRNA release. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6741–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Gu, W.; Yi, P.; Bitter, J.L.; Hong, J.Y.; Fairbrother, D.H.; Chen, K.L. Bacterial anti-adhesive properties of polysulfone membranes modified with polyelectrolyte multilayers. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichter, J.A.; Rubner, M.F. Polyelectrolyte multilayers with intrinsic antimicrobial functionality: The importance of mobile polycations. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7686–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, T.; Szczepanowicz, K.; Kręgiel, D.; Szyk-Warszyńska, L.; Warszyński, P. Nanostructured multilayer polyelectrolyte films with silver nanoparticles as antibacterial coatings. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 137, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: From the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, R.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Physico-chemistry of initial microbial adhesive interactions—Its mechanisms and methods for study. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 23, 179–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, M.E.; O’Toole, G.A. Microbial biofilms: From ecology to molecular genetics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 847–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molin, S.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Gene transfer occurs with enhanced efficiency in biofilms and induces enhanced stabilisation of the biofilm structure. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurinčič, M.; Jeršek, B.; Klančnik, A.; Smole Možina, S.; Fink, R.; Dražić, G.; Raspor, P.; Bohinc, K. Effects of natural antimicrobials on bacterial cell hydrophobicity, adhesion, and zeta potential. Arh. Hyg. Rada Toxicol. 2016, 67, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, M.; Gutniek, D.; Rosenberg, E. Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: A simple method for measuring cell surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1980, 9, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makin, S.A.; Beveridge, T.J. The influence of A-band and B-band lipopolysacharide on the surface characteristics and adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to surfaces. Microbiology 1996, 142, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohinc, K.; Dražić, G.; Fink, R.; Oder, M.; Jevšnik, M.; Nipič, D.; Godič Torkar, K.; Raspor, P. Metal surface characteristics dictate bacterial adhesion capacity. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 50, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohinc, K.; Dražić, G.; Abram, A.; Jevšnik, M.; Jeršek, B.; Nipič, D.; Kurinčič, M.; Raspor, P. Available surface dictates microbial adhesion capacity. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 68, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrald, P.J.; Zootolla, E.A. Scanning electron microscopic examination of Yersinia enterocolitica attached to stainless steel at elevated temperature and pH values. J. Food Sci. 1988, 51, 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- El Abed, S.; Koraichi Ibnsouda, S.; Latrache, H.; Hamadi, F. Scanning Electron Microscopy; Kazmiruk, V., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.H.; Friedman, J. Handbook of Bacterial Adehsion: Principles, Methods, and Applications; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tallósy, S.P.; Janovák, L.; Nagy, E.; Deák, Á.; Juhász, Á.; Csapó, E.; Buzás, N.; Dékány, I. Adhesion and inactivation of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria on photoreactive TiO2/polymer and Ag-TiO2/polymer nanohybrid films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 371, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, G.J.; Noel, R.K.; Sneath, P.H.A.; Staley, J.T.; Williams, T.S. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology; The Williams and Wilkins Company: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Milkova, V.; Radeva, T. Effect of chain length and charge density on the construction of polyelectrolyte multilayers on colloidal particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 308, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Guo, S.; He, T.; Jiang, S.; Jańczewski, D.; Vancso, G.J. Engineered, robust polyelectrolyte multilayers by precise control of surface potential for designer protein, cell, and bacteria adsorption. Langmuir 2016, 32, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Požar, J.; Salopek, J.; Poldrugač, M.; Kovačević, D. The effect of cation type, ionic strength and temperature on the complexation between polyallylammonium cation and polystyrenesulfonate anion. Colloids Surf. A 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Teif, V.; Bohinc, K. Condensed DNA: Condensing the concepts. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2011, 105, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijnaarts, H.M.; Norde, W.; Bouwer, E.J.; Lyklema, J.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Bacterial deposition in porous media: Effects of cell-coating, substratum hydrophobicity, and electrolyte concentration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2877–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zita, A.; Hermansson, M. Effects of bacterial cell surface structures and hydrophobicity on attachment to activated sludge flocs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1168–1170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cowan, M.M.; Mikx, F.H.M.; Busscher, H.J. Electrophoretic mobility and hemagglutination of Treponema denticola ATCC 33520. Colloids Surf. B 1994, 2, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Li, L.; Guo, X. Binding between proteins and cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brushes: Effect of pH, ionic strength, and stoichiometry. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preedy, E.; Perni, S.; Nipič, D.; Bohinc, K.; Prokopovich, P. Surface roughness mediated adhesion forces between borosilicate glass and gram-positive bacteria. Langmuir 2014, 30, 9466–9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
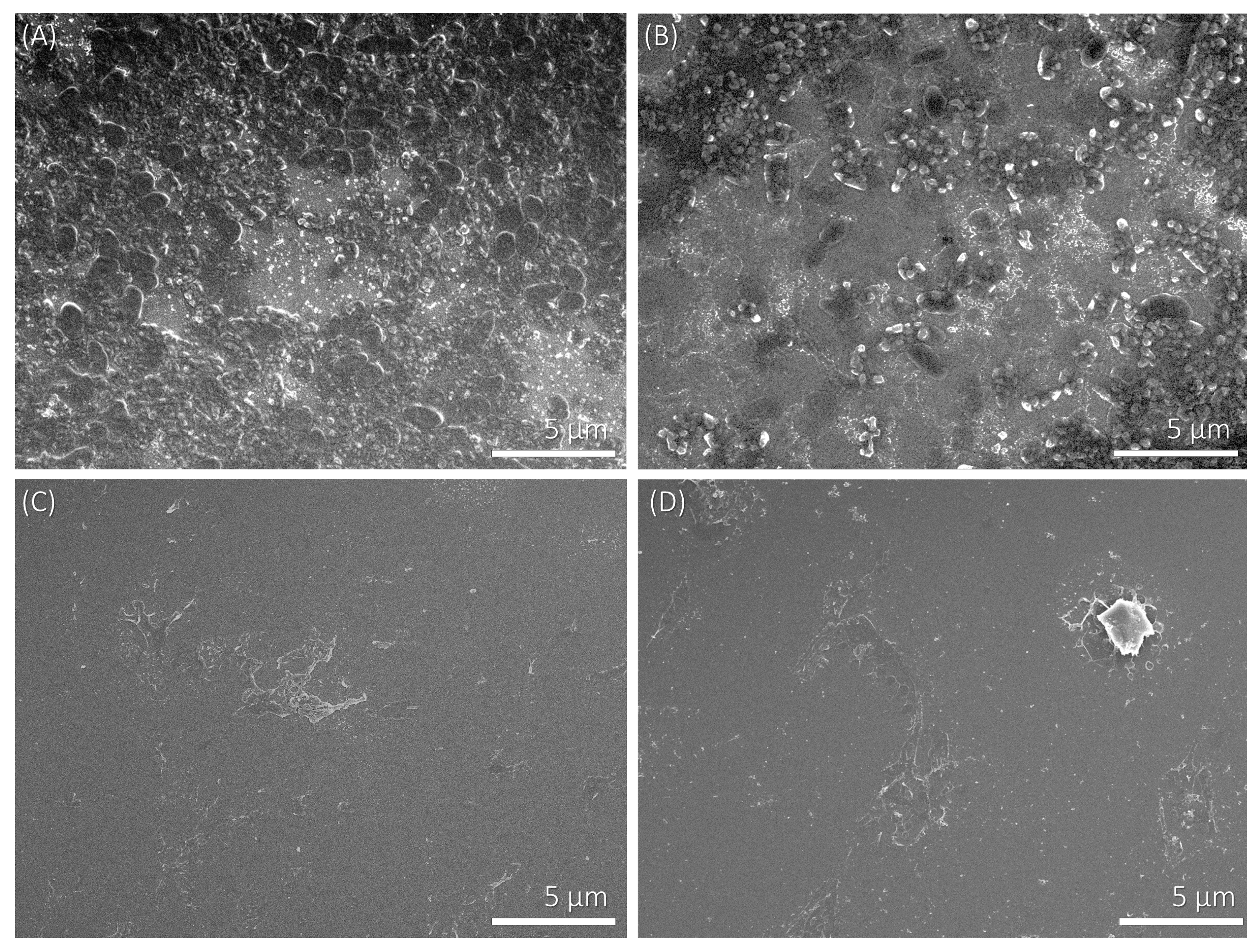
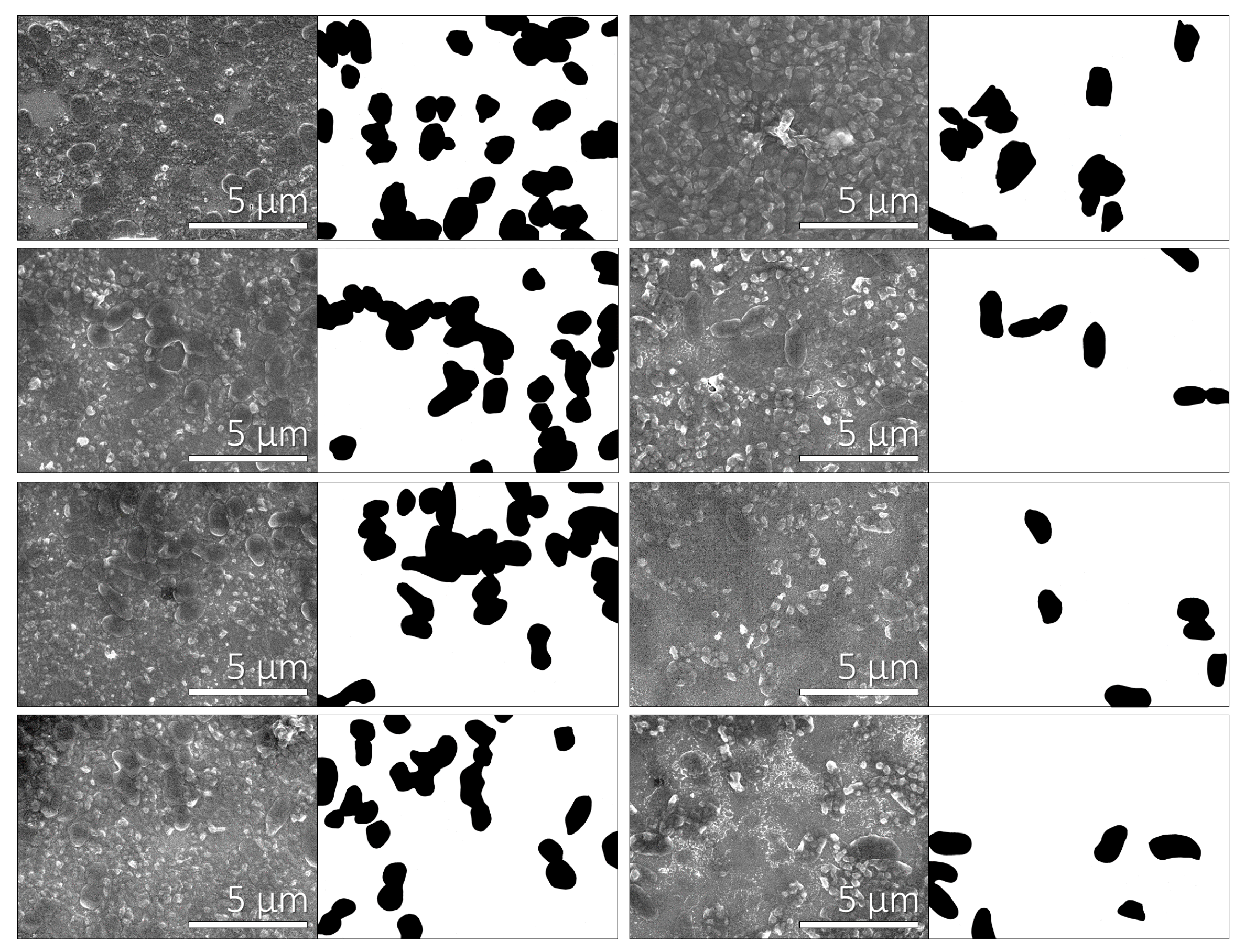

| Quantity | PAH as terminating layer (five layers) | PSS as terminating layer (six layers) |
| Zeta potential | 16.78 mV | −15.11 mV |
| Contact angle | 48.9° ± 2.5° | 46.9° ± 5.0° |
| Roughness | 0.017 ± 0.004 µm | 0.019 ± 0.006 µm |
| Fraction of the multilayer surface covered with P. aeruginosa | 20.4% ± 4.8% | 9.0% ± 3.1% |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovačević, D.; Pratnekar, R.; Godič Torkar, K.; Salopek, J.; Dražić, G.; Abram, A.; Bohinc, K. Influence of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Properties on Bacterial Adhesion Capacity. Polymers 2016, 8, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8100345
Kovačević D, Pratnekar R, Godič Torkar K, Salopek J, Dražić G, Abram A, Bohinc K. Influence of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Properties on Bacterial Adhesion Capacity. Polymers. 2016; 8(10):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8100345
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovačević, Davor, Rok Pratnekar, Karmen Godič Torkar, Jasmina Salopek, Goran Dražić, Anže Abram, and Klemen Bohinc. 2016. "Influence of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Properties on Bacterial Adhesion Capacity" Polymers 8, no. 10: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8100345
APA StyleKovačević, D., Pratnekar, R., Godič Torkar, K., Salopek, J., Dražić, G., Abram, A., & Bohinc, K. (2016). Influence of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Properties on Bacterial Adhesion Capacity. Polymers, 8(10), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8100345