Anhydrides-Cured Bimodal Rubber-Like Epoxy Asphalt Composites: From Thermosetting to Quasi-Thermosetting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
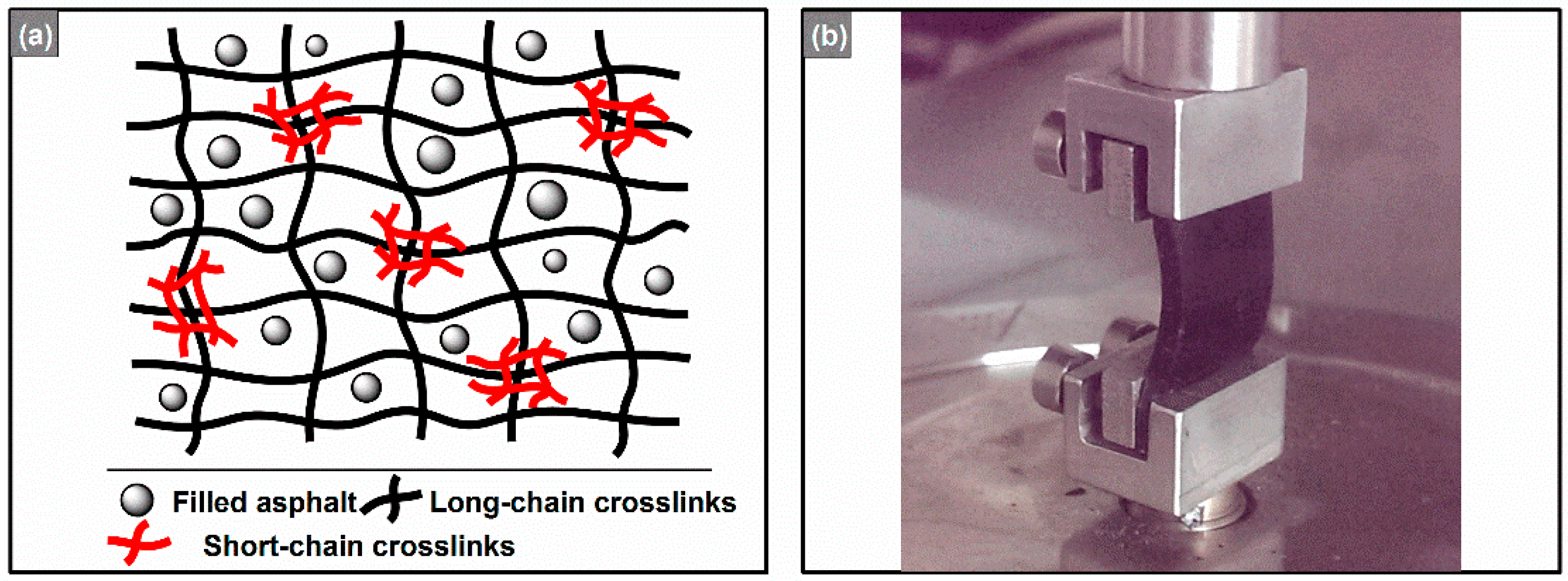
2.2.1. Preparation of the Bimodal Anhydrides-Cured REACs
2.2.2. Characterization Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Direct Tensile Tests
3.2. Linear Viscoelastic Regions
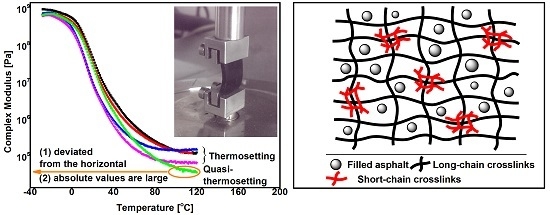
3.3. Temperature Sweeps
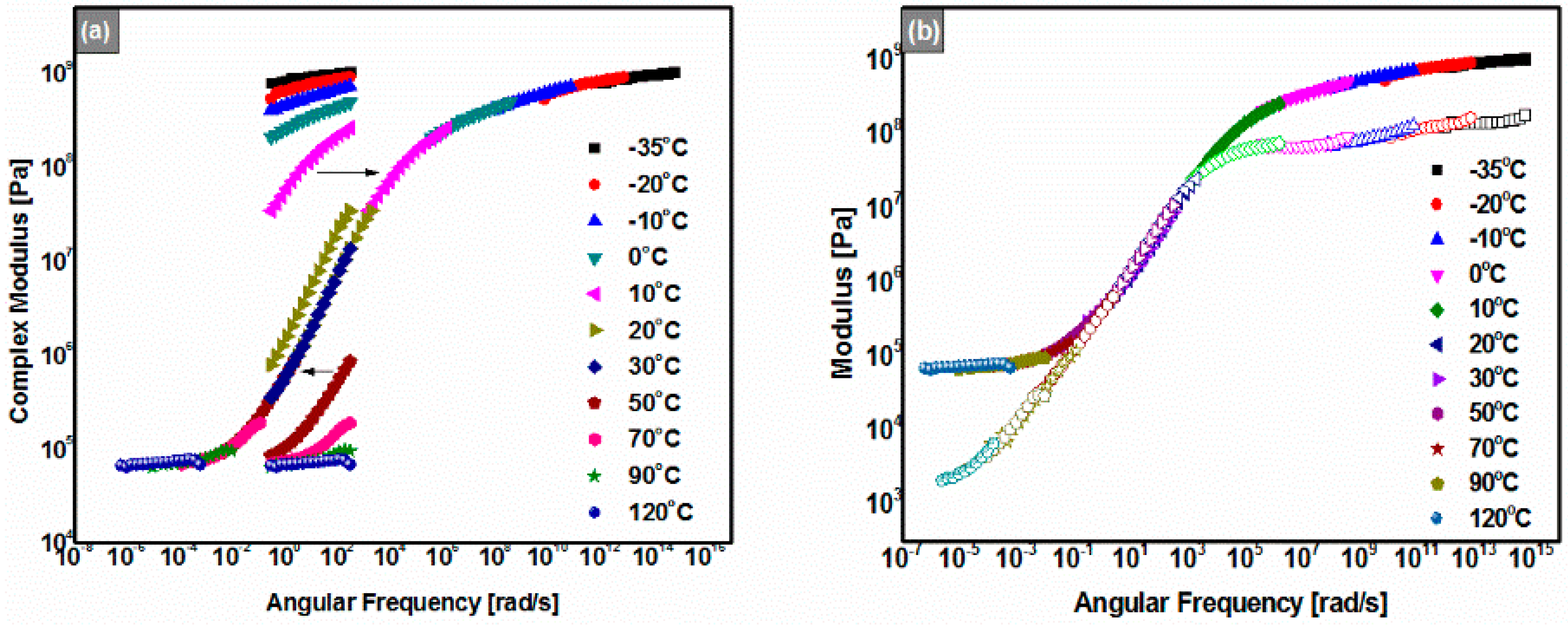
3.4. Frequency Sweeps
3.5. Cole–Cole Plot and Black Diagram
3.6. Master Curves
3.7. Generalized Logistic Sigmoidal Model
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lesueur, D. The colloidal structure of bitumen: Consequences on the rheology and on the mechanisms of bitumen modification. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 42–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacco, G.; Stastna, J.; Biondi, D.; Zanzotto, L. Relation between polymer architecture and nonlinear viscoelastic behavior of modified asphalts. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munera, J.C.; Ossa, E.A. Polymer modified bitumen: Optimization and selection. Mater. Design 2014, 62, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Liang, P.; Fan, W.; Qian, C.; Xin, X.; Shi, J.; Nan, G. Thermo-rheological behavior and compatibility of modified asphalt with various styrene-butadiene structures in SBS copolymers. Mater. Design 2015, 88, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yidirim, Y. Polymer modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar, Z.N.; Karim, M.R.; Mahrez, A. A review of using waste and virgin polymer in pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 33, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, C.F.; Richardson, J.; Stevenson, A.; James, D. Long life surfaces for busy roads. In Proceedings of the 12th ISAP International Conference on Asphalt Pavements, Raleigh, NC, USA, 1–5 June 2014; CRC Press-Taylor&Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Herrington, P.; Alabaster, D. Epoxy modified open-graded porous asphalt. Road Mater. Pavement Design 2008, 9, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, The International Transport Forum. Long-Life Surfaces for Busy Roads. 2008. Available online: http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/content/book/9789282101209-en (accessed on 7 November 2015).
- Kang, Y.; Chen, Z.M.; Jiao, Z.; Huang, W. Rubber-Like thermosetting epoxy asphalt composites exhibiting atypical yielding behaviors. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Jin, R.; Yu, P.F.; Cheng, J.X. Rubber-like Quasi-thermosetting polyetheramine-cured epoxy asphalt composites capable of being opened to traffic immediately. Sci. Rep. 2015, 6, 18882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Qian, Z.; Chen, G.; Yang, J. Epoxy asphalt concrete paving on the deck of long-span steel bridges. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 2391–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.T.; MacKnight, W.J. Introduction to Polymer Viscoelasticity, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, S.; Medina-Torres, L.; Zitzumbo, R.; Avalos, F. Rheology of asphalt and styrene—butadiene blends. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 2591–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.N. The Viscoelastic Mechanics Theory and Application of Asphalt and Asphalt Mixture; China Communication Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Song, M.Y.; Pu, L.; Liu, T.F. Rheological behaviors of epoxy asphalt binder in comparison of base asphalt binder and SBS modified asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, J.E.; Schaefer, D.W.; Lin, G. The Polysiloxanes; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.T. Theory of Thermo-Viscoelasticity; Tianjin University Press: Tianjin, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Oeser, M.; Pellinien, T. Computational framework for common visco-elastic models in engineering based on the theory of rheology. Comput. Geotech. 2012, 42, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailleux, E.; Ramond, G.; Such, C.; Roche, C.D.L. A mathematical-based master-curve construction method applied to complex modulus of bituminous materials. Road Mater. Pavement 2006, 7, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Q.; Guo, M. Study on the phase behavior of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Long chain branching and polydispersity effects on the rheological properties of polyethylenes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2000, 40, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olard, F.; Benedetto, H.D. General “2S2P1D” Model and relation between the linear viscoelastic behavioursof bituminous binders and mixes. Road Mater. Pavement 2003, 4, 185–224. [Google Scholar]
- Olard, F.; Benedetto, H.D.; Eckmann, B.; Triquigneaux, J.P. Linear viscoelastic properties of bituminous binders and mixtures at low and intermediate temperatures. Road Mater. Pavement 2003, 4, 77–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellinen, T.K.; Witczak, M.W.; Bonaquist, R.F. Asphalt mix master curve construction using sigmoidal fitting function with non-linear least squares optimization. Geotech. Special Publ. 2003, 123, 83–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yusoff, N.I.M.; Shaw, M.T.; Airey, G.D. Modelling the linear viscoelastic rheological properties of bituminous binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2171–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, G.; Baumgardner, G.; Sharrock, M. Functional forms for master curve analysis of bituminous materials. In Proceedings of the 7th International RILEM Symposium ATCBM09 on Advanced Testing and Characterisation of Bituminous Materials, Rhodes, Greece, 27–29 May 2009; Loizos, A., Partl, M.N., Scarpas, T., Al-Qadi, I.L., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Ltd: London, UK, 2009; pp. 81–91. [Google Scholar]






| Properties of asphalt | Method | |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Source | Saudi Arabia | |
| Density@ 15 °C/g·cm−3 | 1.013 | JTJ 052 T0603-2011 |
| Penetration@ 25 °C/0.1 mm | 88.0 | JTJ 052 T0604-2011 |
| Soft Point (°C) | 46.5 | JTJ 052 T0606-2011 |
| Viscosity@60 °C/Pa·s | 225.0 | JTJ 052 T0625-2011 |
| Ductility@ 15 °C/cm | >100 | JTJ 052 T0624-2011 |
| Flash point (°C) | 308 | JTJ 052 T0611-2011 |
| Fraass breaking point (°C) | −17.8 | JTJ 052 T0613-1993 |
| SARA | JTJ 052 T0618-1993 | |
| Saturate (%) | 23.8 | |
| Aromatic (%) | 37.2 | |
| Resin (%) | 22.1 | |
| Asphaltene (%) | 16.9 | |
| No. | δ | α | β | γ | λ | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120# | 5.096 | 4.054 | 0.846 | 0.543 | 2.097 | 0.9997 |
| 150# | 4.714 | 4.436 | 0.394 | 0.394 | 1.480 | 0.9993 |
| 180# | 4.981 | 4.169 | 0.854 | 0.671 | 2.610 | 0.9995 |
| 210# | 4.753 | 4.397 | 1.455 | 0.776 | 3.301 | 0.9991 |
| 240# | 4.678 | 4.472 | 0.829 | 0.618 | 2.454 | 0.9988 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, Y.; Jin, R.; Wu, Q.; Pu, L.; Song, M.; Cheng, J.; Yu, P. Anhydrides-Cured Bimodal Rubber-Like Epoxy Asphalt Composites: From Thermosetting to Quasi-Thermosetting. Polymers 2016, 8, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040104
Kang Y, Jin R, Wu Q, Pu L, Song M, Cheng J, Yu P. Anhydrides-Cured Bimodal Rubber-Like Epoxy Asphalt Composites: From Thermosetting to Quasi-Thermosetting. Polymers. 2016; 8(4):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040104
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Yang, Rui Jin, Qiang Wu, Liang Pu, Mingyu Song, Jixiang Cheng, and Pengfei Yu. 2016. "Anhydrides-Cured Bimodal Rubber-Like Epoxy Asphalt Composites: From Thermosetting to Quasi-Thermosetting" Polymers 8, no. 4: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040104
APA StyleKang, Y., Jin, R., Wu, Q., Pu, L., Song, M., Cheng, J., & Yu, P. (2016). Anhydrides-Cured Bimodal Rubber-Like Epoxy Asphalt Composites: From Thermosetting to Quasi-Thermosetting. Polymers, 8(4), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040104