Correlation of Microstructure, Rheological and Morphological Characteristics of Synthesized Polypropylene (PP) Reactor Blends Using Homogeneous Binary Metallocene Catalyst
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Methods
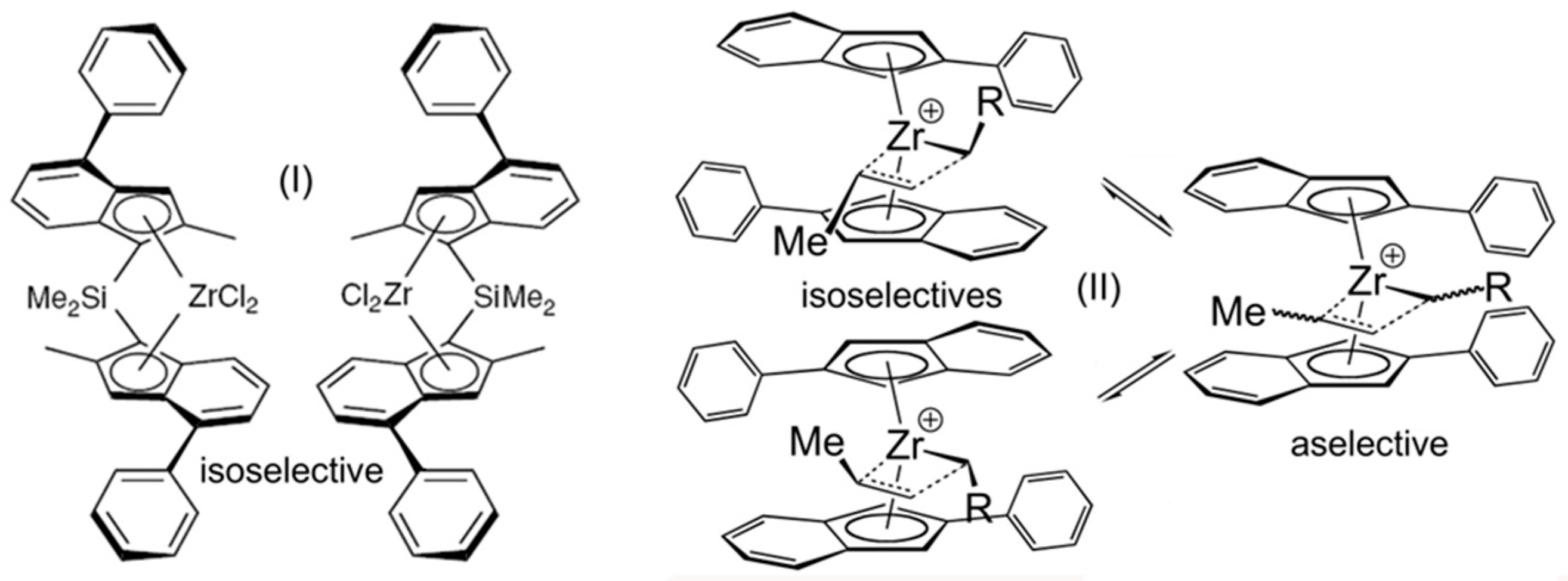
2.2. Catalyst Preparation
2.3. Polymerization
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
2.4.2. Xylene Solubility
2.4.3. Rheological Properties
2.4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.5. FTIR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polymerization
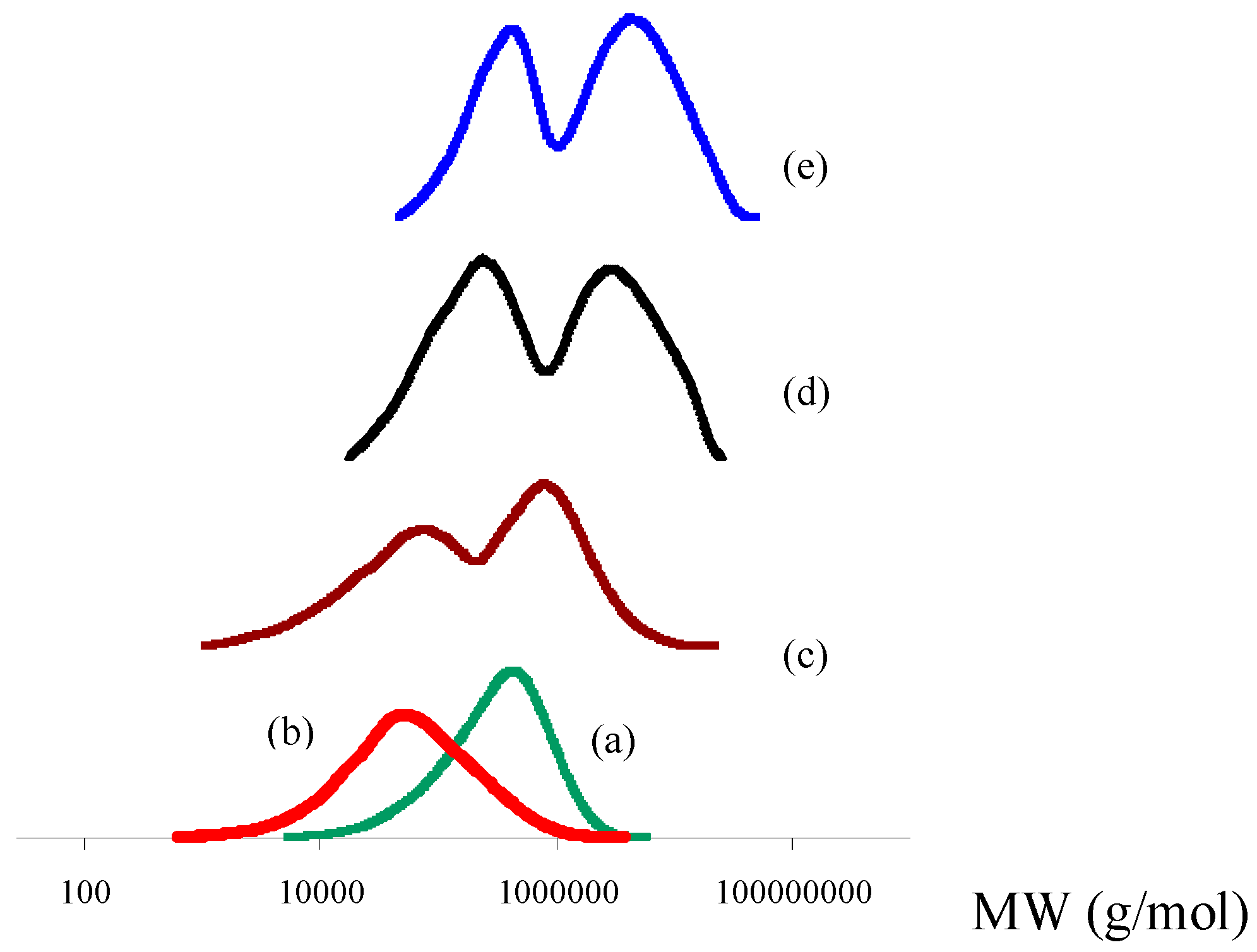
3.2. Molecular Weight and Molecular Weight Distribution
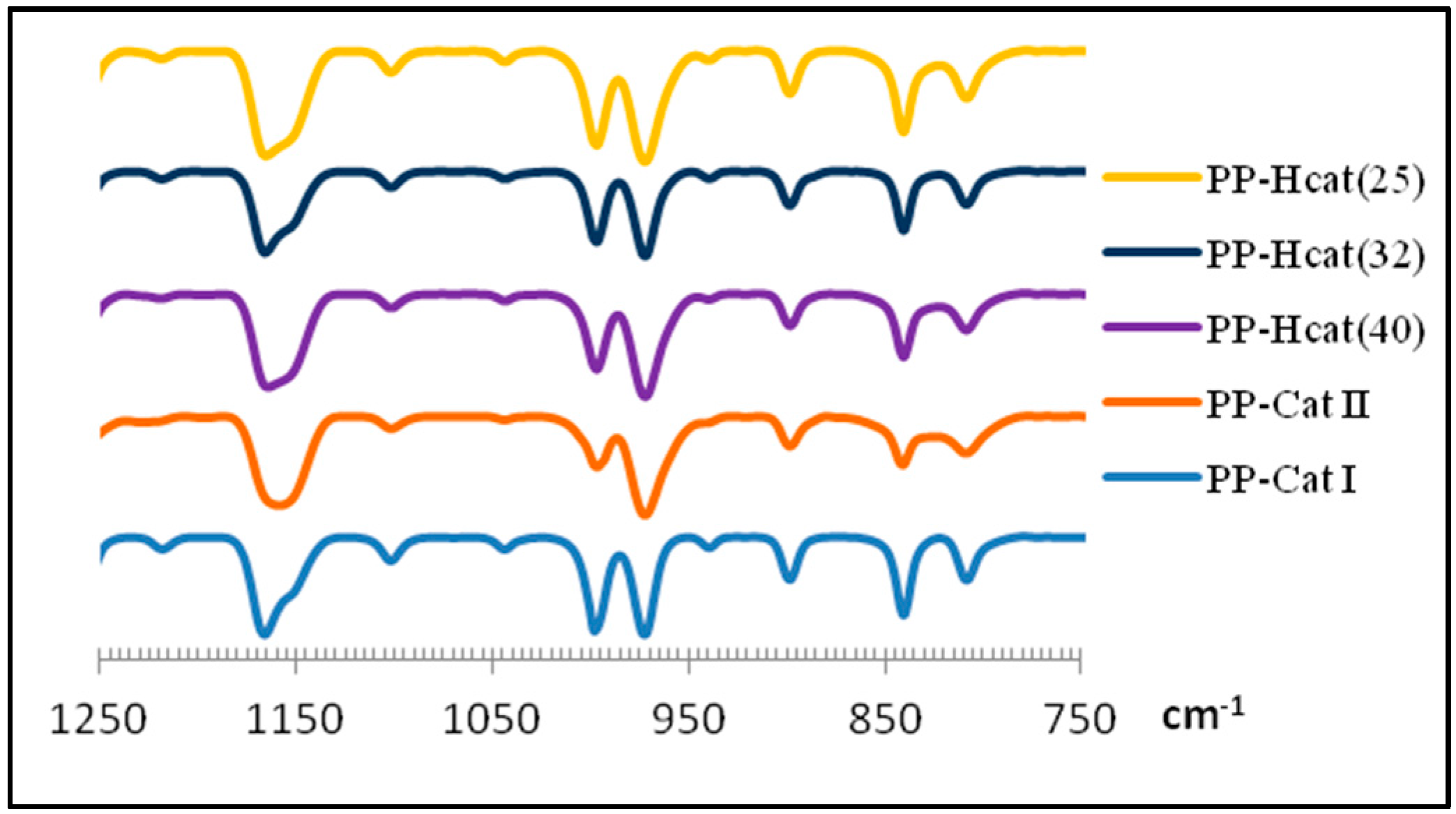
3.3. FTIR Results
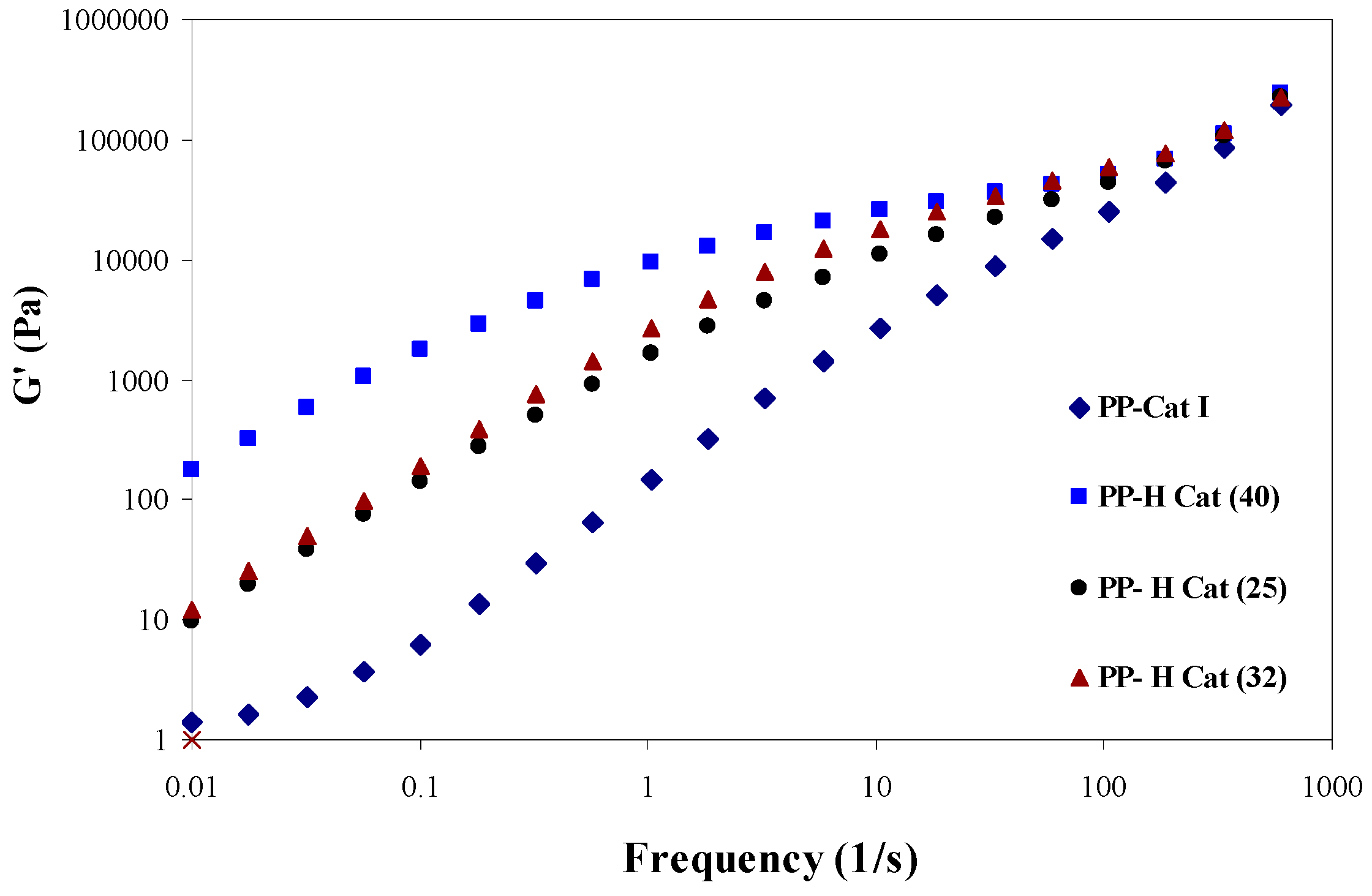
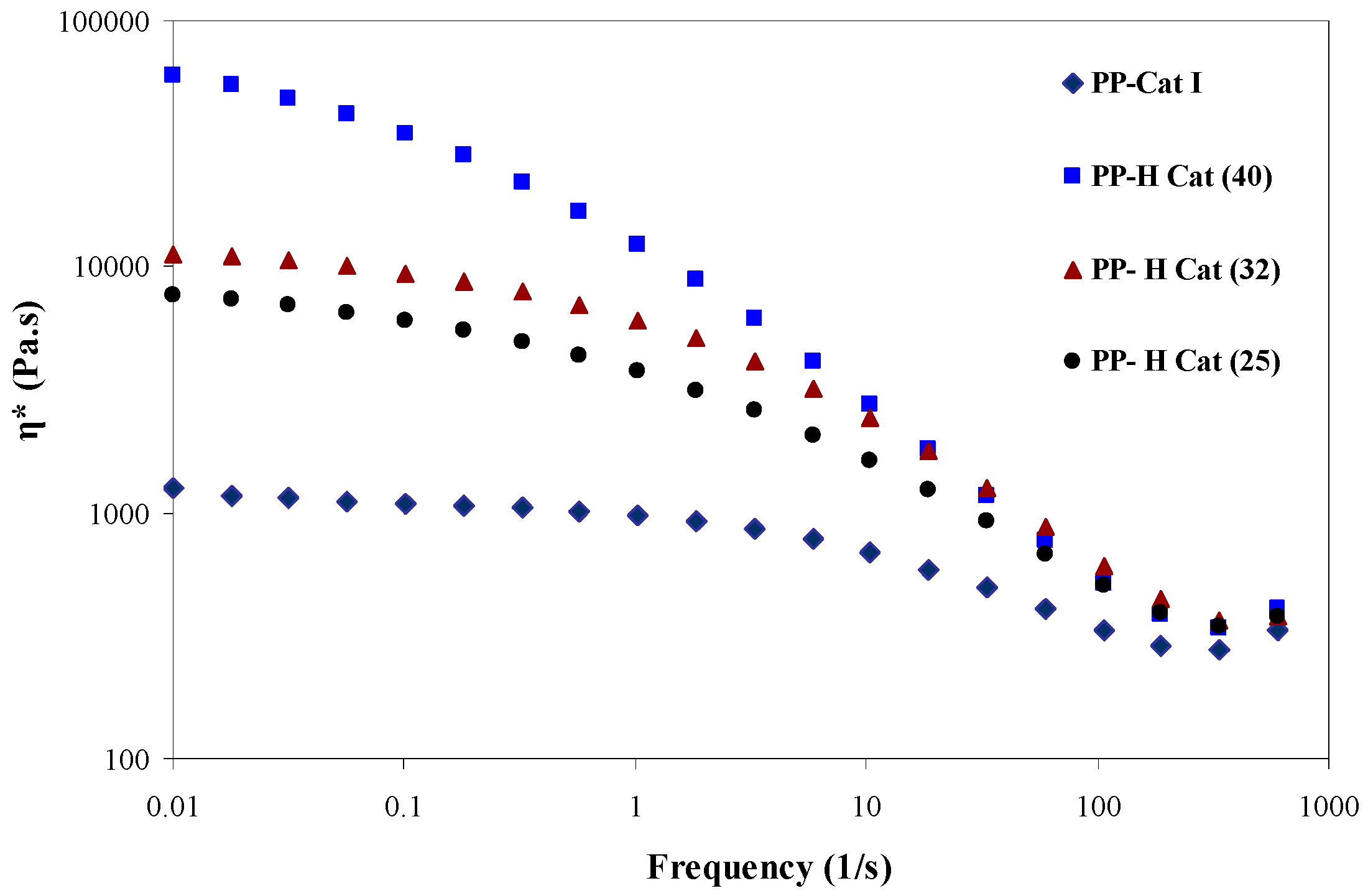
3.4. Linear Rheological Behavior
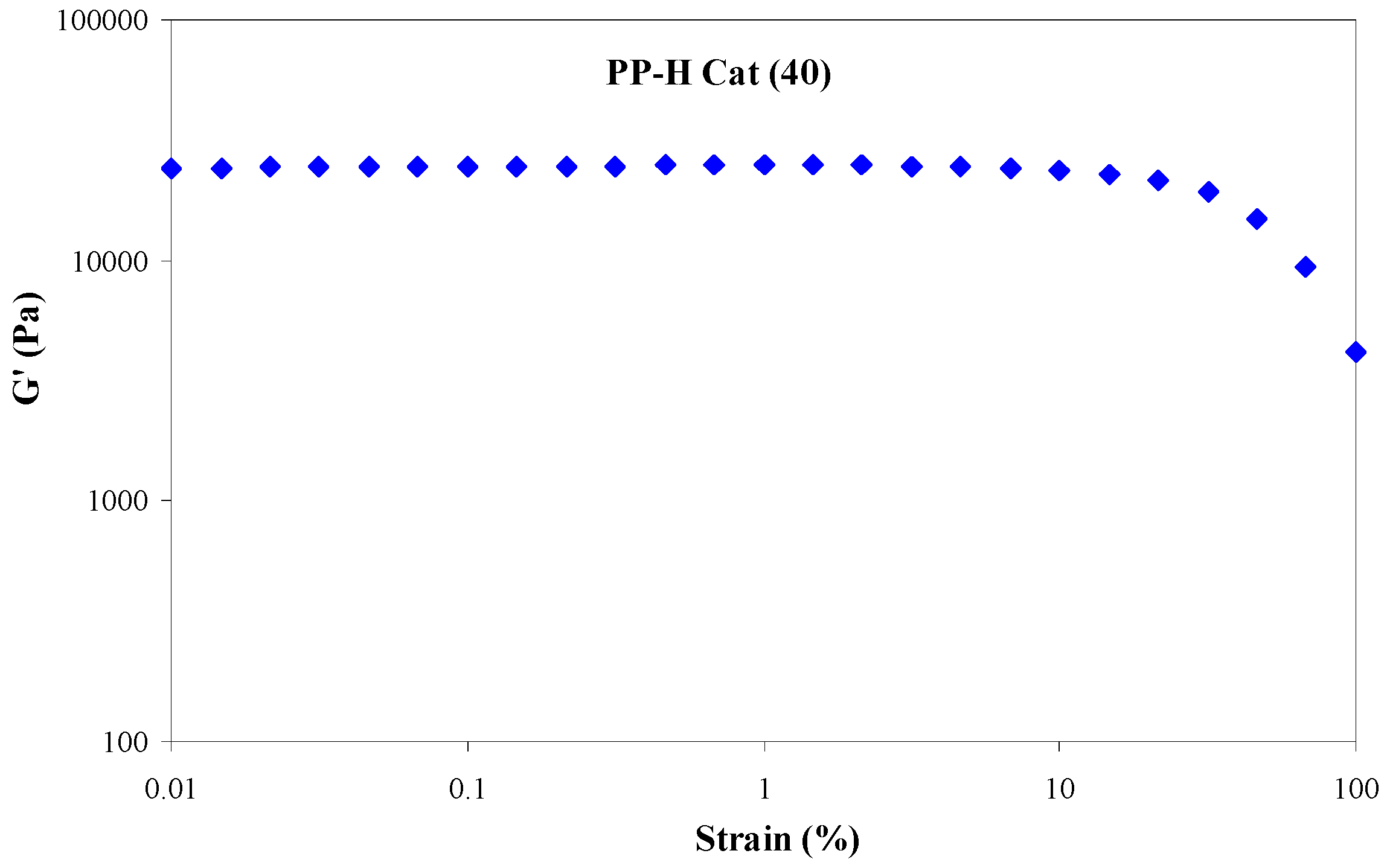
3.4.1. Strain Sweep
3.4.2. Frequency Sweep
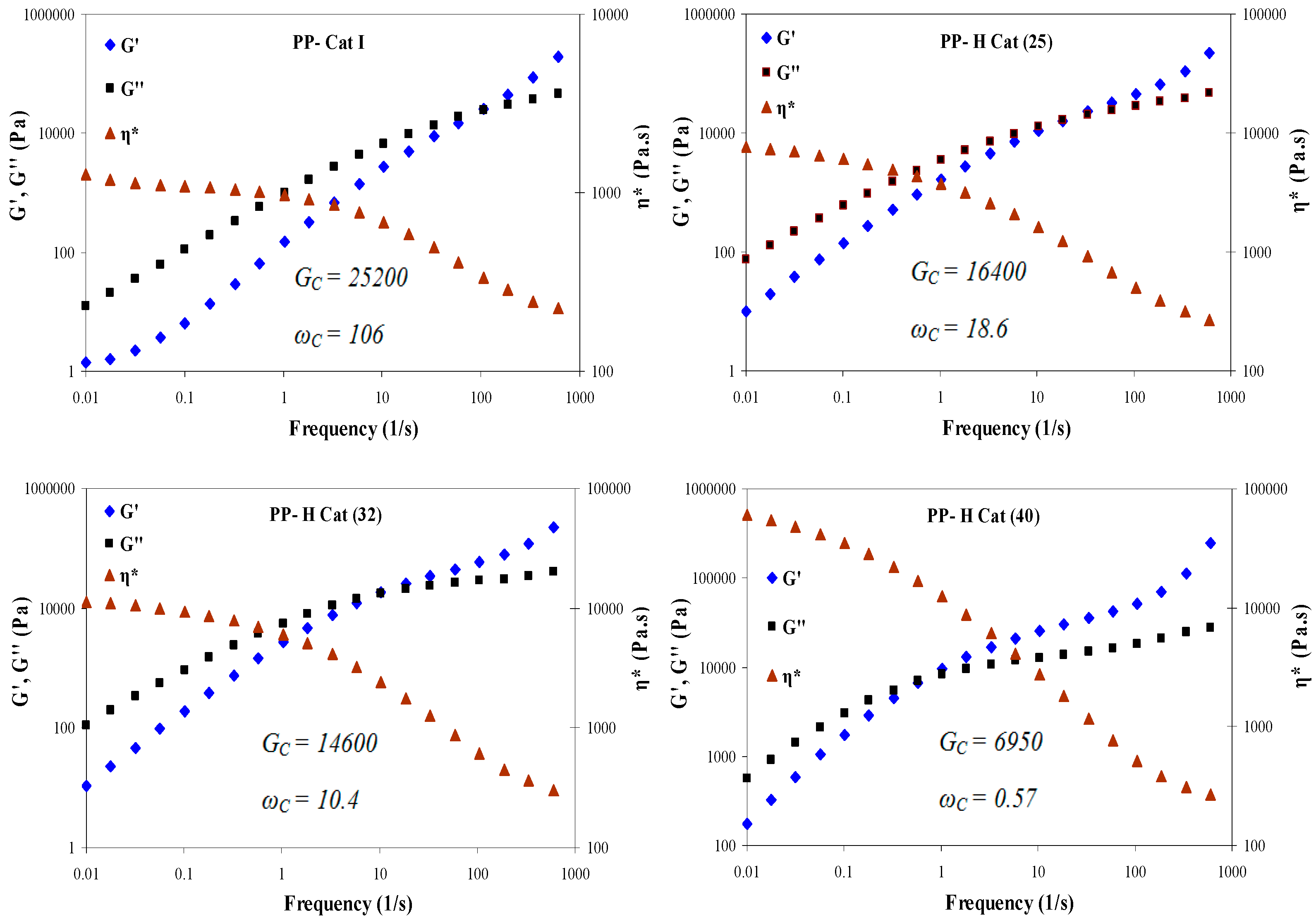
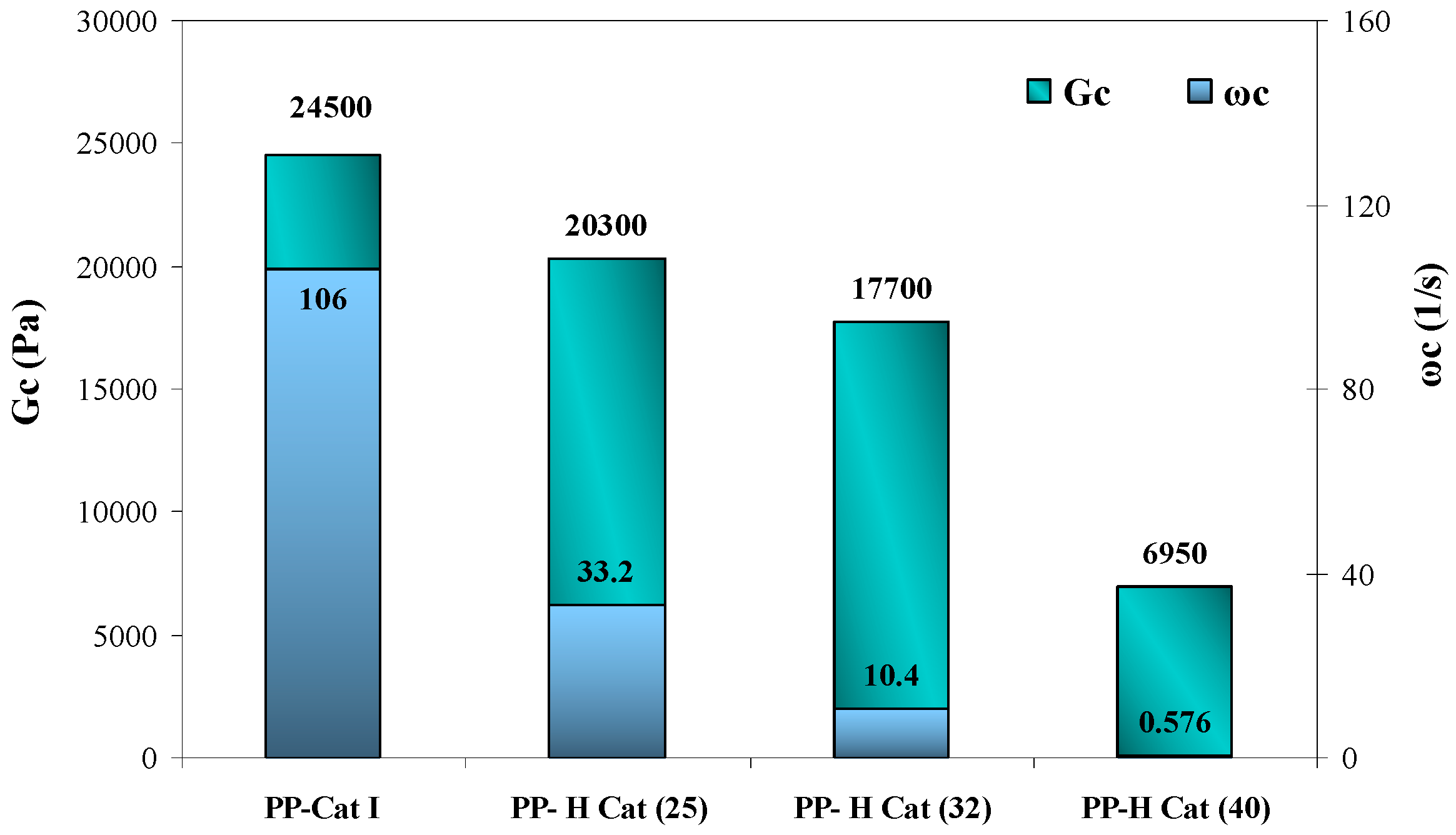
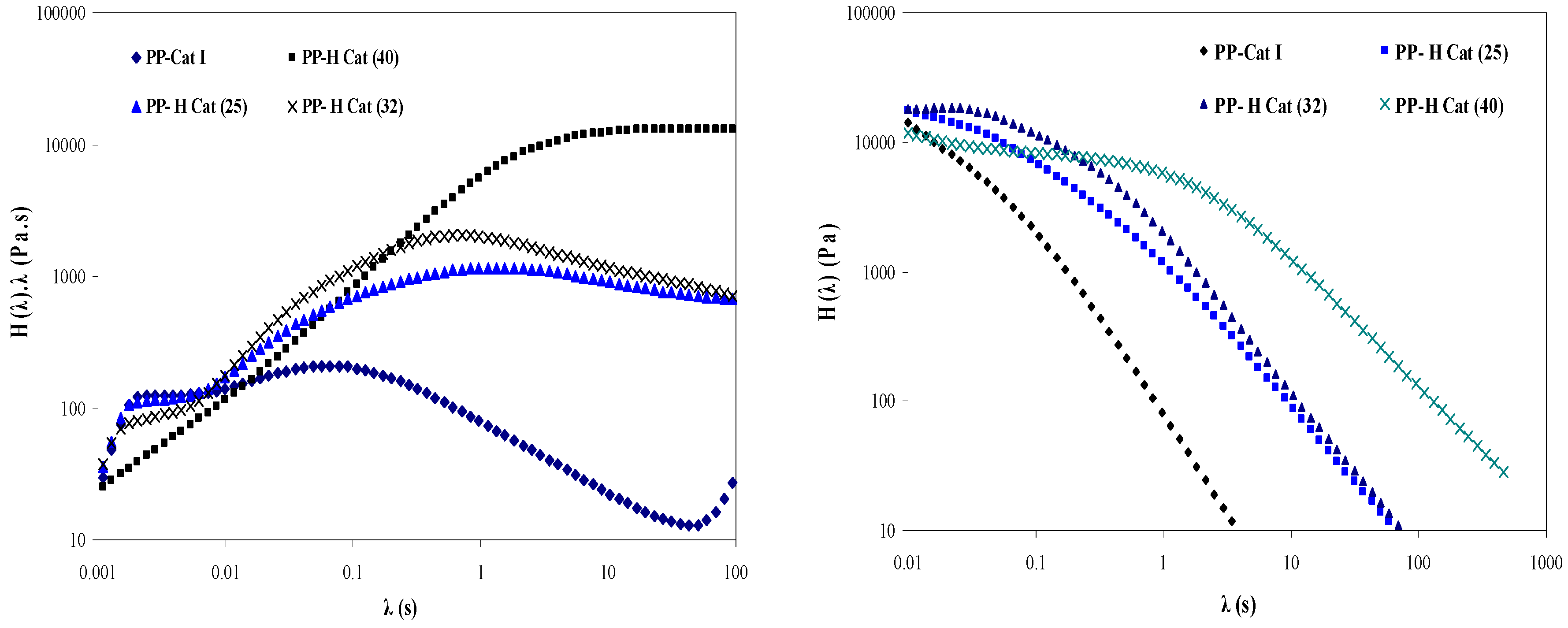
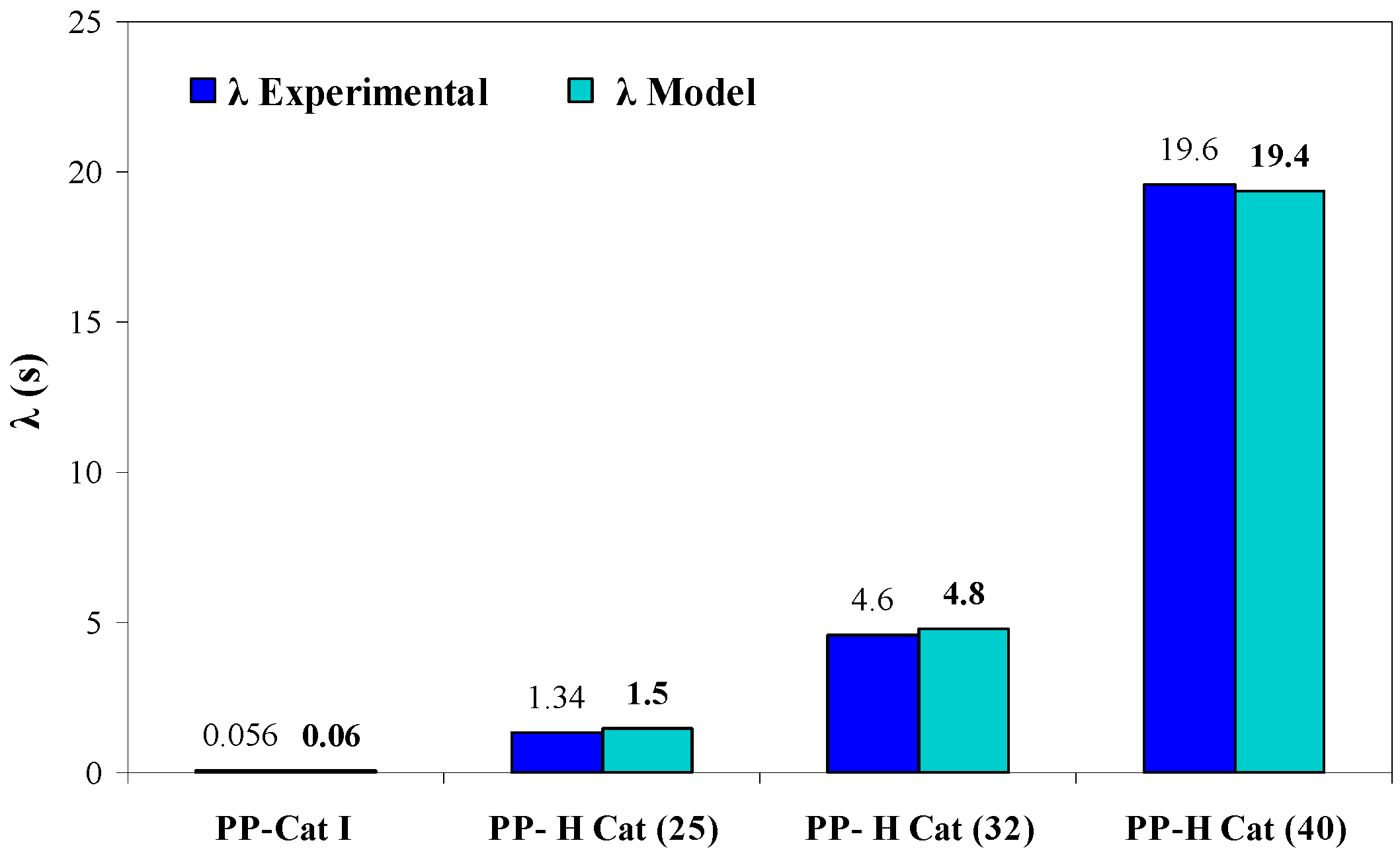
3.4.3. Effect of Increasing Molar Ratio of Cat (II)/Cat (I) on the Relaxation Time
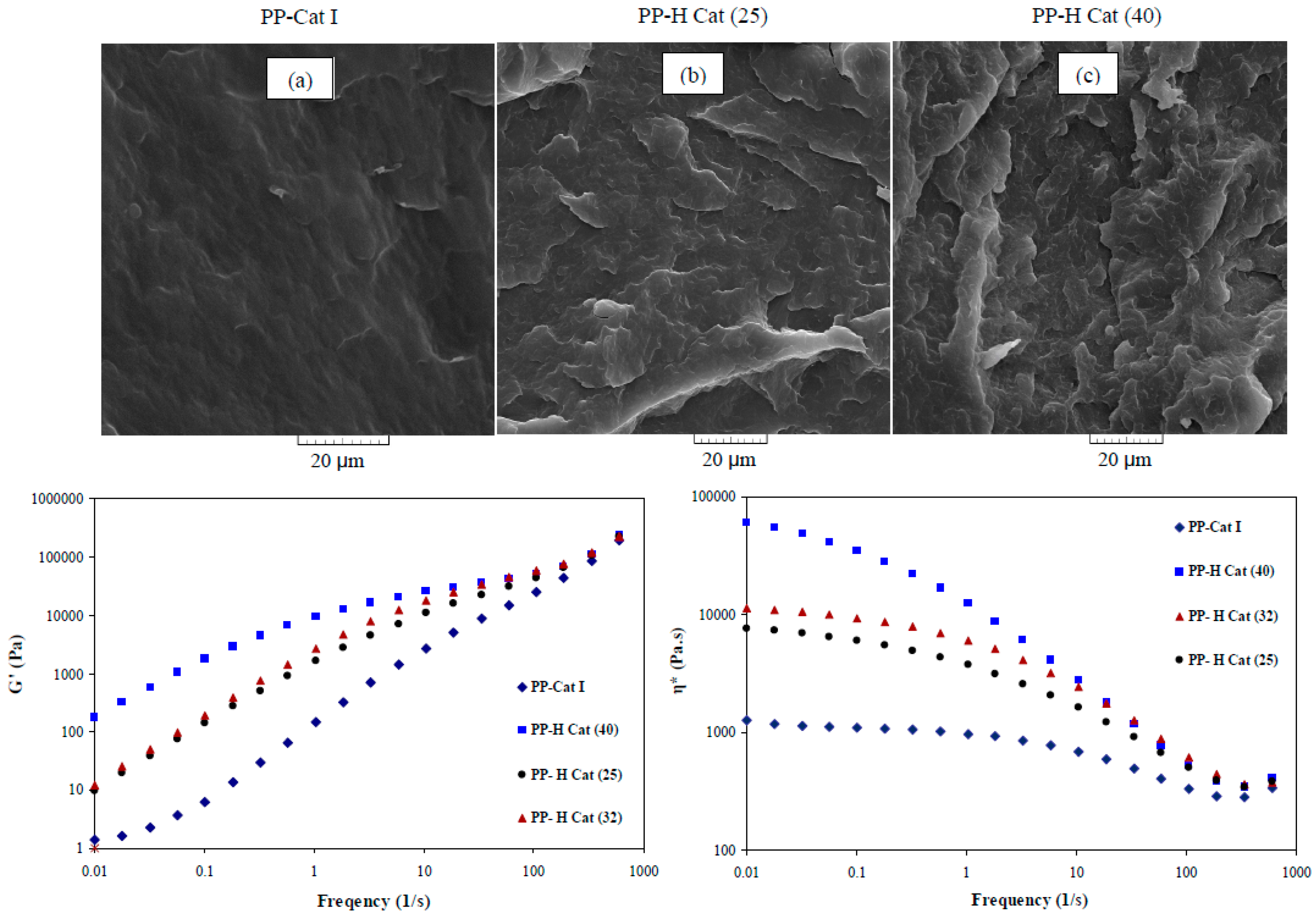
3.5. Correlation of Morphological and Rheological Properties
4. Conclusions
- The MWD curves of synthesized products by the individual use of catalysts (I) and (II) and their binary systems show that MWD was broadened and became bimodal for products obtained from the catalysts’ mixtures. In addition, the average MWs were shifted to higher values in PP reactor blends. Actually, the appearance of two peaks in the MWD curves is indicative of the fact that two catalysts are active during the polymerization in the case of binary systems. In these blends, the peak at higher MW leads to a product with remarkable enhancement in mechanical properties, while the peak at lower MW leads to a product with improved processability. In other words, the improved tensile strength of the products is accompanied by their improved processability.
- The complex viscosity of the synthesized blends shows a remarkable 47-fold enhancement as the molar ratio of II/I is increased. It can be concluded that upon the changes in the molar ratio of catalyst (II), the structure of the growing chains is changed such that the amorphous blocks along the polymer chains are formed due to the presence of catalyst (II) and its activeness in the course of polymerization. The formation of those amorphous blocks along the polymer chains increases the chains’ entanglements and thus enhances the complex viscosity of the synthesized PP reactor blends.
- As the molar ratio of II/I changes, the cross-over modulus and frequency are reduced due to the increased elasticity of the polymer melt as a result of the existence of amorphous blocks along the polymer chains.
- With increasing the molar ratio of II/I, all the peaks exhibited an individual relaxation peak which tends towards longer times as the molar ratio of catalyst (II) is increased. As a result, PP-H Cat (40) exhibits the longest relaxation time among the samples.
- The changes in morphological features of obtained products induced by the increased molar ratio of II/I in the synthesized blends was precisely demonstrated via SEM images and also dynamic rheological data. Therefore, it can be concluded that there exists a robust relationship between the obtained results of linear rheology and morphological characteristics such that with increasing the molar ratio of the catalyst (II) within the binary system, the chains’ elasticity was significantly increased. It was also found that the amount of the mentioned enhancement within the low-frequency region is dependent on the formation of amorphous blocks along the PP chains.
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasile, C. (Ed.) Handbook of Polyolefins; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000.
- Moore, E.P. Polypropylene Handbook; Hanser: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Severn, J.R.; Chadwick, J.C. (Eds.) Tailor-Made Polymers: Via Immobilization of Alpha-Olefin Polymerization Catalysts; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008.
- Hoff, R.; Mathers, R.T. (Eds.) Handbook of Transition Metal Polymerization Catalysts; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010.
- Malpass, D.B.; Band, E.I. Introduction to Polymers of Propylene. Catal. Process. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, L.S.; Canich, J.A. (Eds.) Stereoselective Polymerization with Single-Site Catalysts; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007.
- Resconi, L.; Cavallo, L.; Fait, A.; Piemontesi, F. Selectivity in propene polymerization with metallocene catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 1253–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Niu, H.; Dong, J.Y.; Dong, X.; Han, C.C. Self-Similar Growth of Polyolefin Alloy Particles in a Single Granule Multi-Catalyst Reactor. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2914–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Jiang, B.; Yang, Y.; Jie, Z. Ethylene polymerization with hybrid nickel diimine/Cp2TiCl2 catalyst: A new method to prepare blends of linear and branched polyethylene. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Niu, H.; Dong, J.; Du, J.; Han, C.C. Morphology and mechanical properties of polypropylene/poly (propylene-1-octene) in-reactor alloys prepared by Metallocene/Ziegler–Natta hybrid catalyst. Polymer 2012, 53, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.C.; Mihan, S.; Lilge, D.; Delux, L.; Rief, U. Immobilized Me2Si(C5Me4)(N-tBu)TiCl2/(nBuCp)2ZrCl2 hybrid metallocene catalyst system for the production of poly (ethylene-co-hexene) with pseudo-bimodal molecular weight and inverse comonomer distribution. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2007, 47, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, W. Discovery of methylaluminoxane as cocatalyst for olefin polymerization. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 3289–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejabat, G.R.; Nekoomanesh, M.; Arabi, H.; Salehi-Mobarakeh, H.; Zohuri, G.H.; Omidvar, M.; Miller, S.A. Synthesis and microstructural study of stereoblock elastomeric polypropylenes from metallocene catalyst (2-PhInd)2ZrCl2 activated with cocatalyst mixtures. J. Polym. Sci. A 2013, 51, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejabat, G.R.; Nekoomanesh, M.; Arabi, H.; Salehi-Mobarakeh, H.; Zohuri, G.H.; Omidvar, M.; Miller, S.A. Synthesis of Stereoblock Elastomeric Poly(propylene) s Using a (2-PhInd)2ZrCl2 Metallocene Catalyst in the Presence of Co-Catalyst Mixtures: Study of Activity and Molecular Weight. Macromol. React. Eng. 2012, 6, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejabat, G.R.; Nekoomanesh, M.; Arabi, H.; Salehi-Mobarakeh, H.; Zohuri, G.H.; Mortazavi, M.M.; Ahmadjo, S.; Miller, S.A. Study of Ziegler-Natta/(2-PhInd)2ZrCl2 hybrid catalysts performance in slurry propylene polymerization. Polyolefins J. 2015, 2, 73–87. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, B.; van Grieken, R.; Carrero, A.; Lopez-Moya, E. Bimodal polypropylene through binary metallocene catalytic systems: Comparison between hybrid and mixed heterogeneous catalysts. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, P.; Collina, G.; Sgarzi, P.; Baruzzi, G.; Marchetti, E. Combining Ziegler-Natta and mettalocene catalysis: New heterophasic propylene copolymers from the novel multicatalyst reactor granule technology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 66, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S.; Choi, D.J.; Lee, W.Y. Polymerization of ethylene and ethylene/1-hexene over Ziegler-Natta/Metallocene hybrid catalysts supported on SiO2 prepared by a sol-gel method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 2318–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, K.Y.; Li, Y.G.; Bo, S.Q.; Li, Y.S. Thermal and crystallization behaviors of polyethylene blends synthesized by binary late transition metal catalysts combinations. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 4188–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Z. Chain structure and mechanical properties of polyethylene/polypropylene/poly(ethylene-co-propylene)in-reactor alloys synthesized with a spherical Ziegler–Natta catalyst by gas-phase polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, J.C.; Iwamoto, Y.; Rausch, M.D.; Wedler, W.; Winter, H.H. Homogeneous Binary Zirconocenium Catalyst Systems for Propylene Polymerization. 1. Isotactic/Atactic Interfacial Compatibilized Polymers Having Thermoplastic Elastomeric Properties. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 3447–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, J.C.; Iwamoto, Y.; Rausch, M.D. Homogeneous binary zirconocenium catalysts for propylene polymerization. II. Mixtures of isospecific and syndiospecific zirconocene systems. J. Polym. Sci. A 1999, 37, 2439–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, S.; Brintzinger, H.H. Propene polymerization with catalyst mixtures containing different ansa-zirconocenes: Chain transfer to alkylaluminum cocatalysts and formation of stereoblock polymers. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 9192–9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, H.F. Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Premphel, K.; Paecharoechal, W. Polypropylene/metallocene ethylene-octene copolymer blends with a bimodal particle size distribution: Mechanical properties and their controlling factors. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 85, 2412–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, E.L.; Van Grieken, R.; Carrero, A.; Paredes, B. Bimodal Poly(propylene) through Binary Metallocene Catalytic Systems as an Alternative to Melt Blending. Macromol. Symp. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.D.F.V.; Chavez, E.G. Polypropylene fractions produced by binary metallocene catalysts. J. Polym. Sci. A 2003, 41, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fátima, V.M.M.; Pombo, C.C.; Silva, R.A.; Conte, A. Binary metallocene supported catalyst for propylene polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 561–567. [Google Scholar]
- Bastos, Q.C.; Marques, D.F.V. Polypropylene reactor mixture obtained with homogeneous and supported catalysts. J. Polym. Sci. A 2005, 43, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tynys, A.; Eilertsen, J.L.; Seppala, J.V.; Rytter, E. Propylene polymerizations with a binary metallocene system—Chain shuttling caused by trimethylaluminium between active catalyst centers. J. Polym. Sci. A 2007, 45, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tynys, A.; Saarinen, T.; Bartke, M.; Löfgren, B. Propylene polymerisations with novel heterogeneous combination metallocene catalyst systems. Polymer 2007, 48, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.R.; Shamshoum, E.S.; Fina Technology, Inc. Process for a Isotactic/Syndiotactic Polymer Blend in a Single Reactor. U.S. Patent US5,804,524, 8 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, T.O.; Hong, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.H. Control of molecular weight distribution in propylene polymerization with Ziegler–Natta/metallocene catalyst mixtures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 67, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshoum, E.S.; Bauch, C.G. Catalyst Yield from Supported Metallocene Catalysts. U.S. Patent 5,847,059, 8 December 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Auriemma, F.; De Rosa, C.; Corradi, M. Stereoblock Polypropylene as a Prototype Example of Elasticity via a Flip-Flop Reorientation of Crystals in a Compliant Matrix. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macko, T.; Cutillo, F.; Busico, V.; Brüll, R. Separation of poly(propylene) samples according to tacticity using a hypercarb column. Macromol. Symp. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descour, C.; Macko, T.; Cavallo, D.; Parkinson, M.; Hubner, G.; Spoelstra, A.; Villani, M.; Duchateau, R. Synthesis and characterization of iPP-sPP stereoblock produced by a binary metallocene system. J. Polym. Sci. A 2014, 52, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, H.; Mobarakeh, H.S.; Balzadeh, Z.; Nejabat, G.R. Copolymerization of ethylene/5-ethylidene-2-norbornene with bis (2-phenylindenyl) zirconium dichloride catalyst: I. Optimization of the operating conditions by response surface methodology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 3047–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboni, D.; Camurati, I.; Ingurgio, A.C.; Guidotti, S.; Focante, F.; Resconi, L. A counterintuitive, yet efficient synthesis of bis (indenyl) zirconium dihalides. J. Organomet. Chem. 2003, 683, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozzetti, R.A.; de Oliveira Filho, A.P.; Schuchardt, U.; Mandelli, D. Determination of tacticity in polypropylene by FTIR with multivariate calibration. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 85, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burfield, D.R.; Loi, P.S. The use of infrared spectroscopy for determination of polypropylene stereoregularity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1988, 36, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundell, T.; Fagerholm, H.; Crozier, H. Isotacticity determination of polypropylene using FT-Raman spectroscopy. Polymer 1996, 37, 3227–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, J.P. Infrared Study of Polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1960, 3, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarrad, A.; Jahani, Y.; Barikani, M. Investigation on the correlation between rheology and morphology of PA6/ABS blends using ethylene acrylate terpolymer as compatibilizer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 2173–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarrad, A.; Jahani, Y.; Barikani, M. Influence of nanoclay on the rheological properties of polyamide 6/acrylonitrile butadiene styrene nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, E571–E582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seock, C.H.; Suck, C.Y.; Young, L. Control of molecular weight distribution for polyethylene catalyzed over Ziegler–Natta/Metallocene hybrid and mixed catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A 2000, 159, 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zou, H.; Liang, M.; Liu, P. Study on the dynamic rheological behavior of four different bimodal polyethylenes. J. Macromol. Sci. B 2013, 52, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starck, P.; Malmberg, A.; Löfgren, B. Thermal and rheological studies on the molecular composition and structure of metallocene-and Ziegler–Natta-catalyzed ethylene–α-olefin copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 1140–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Escalona, A.; Lafuente, P.; Vega, J.F.; Santamaría, A. Rheology of metallocene-catalyzed monomodal and bimodal polyethylenes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1999, 39, 2292–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood-Adams, P.M.; Dealy, J.M.; Degroot, A.W.; Redwine, O.D. Effect of molecular structure on the linear viscoelastic behavior of polyethylene. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 7489–7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, G.W.; Waymouth, R.M. Oscillating stereocontrol: A strategy for the synthesis of thermoplastic elastomeric polypropylene. Science 1995, 267, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Carlson, E.D.; Fuller, G.G.; Waymouth, R.M. Elastomeric polypropylenes from unbridged 2-phenylindene zirconocene catalysts: Temperature dependence of crystallinity and relaxation properties. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 3334–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzbeck, S.; Oster, F.; Münstedt, H.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Gensler, R. Rheological properties of two polypropylenes with different molecular structure. J. Rheol. 1999, 43, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, I.A.; Hameed, T.; Williams, M.C. Influence of molecular structure on the rheology and thermorheology of metallocene polyethylenes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 1717–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Run | Sample rode | Zr(II)/Zr(I) (Molar ratio) | Zr(t) × 104 (mmol) | Al/Zr(t) | Polymer wt (g) | Productivity (kg PP/mmol Zr(t)·h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PP-Cat I | (I) only | 3.5 | 1100 | 10.0 | 28.8 |
| 2 | PP-Cat II | (II) only | 75 | 1100 | 6.0 | 0.80 |
| 3 | PP-H Cat (25) | 25 | 45.6 | 1100 | 54.3 | 11.9 |
| 4 | PP-H Cat (32) | 32 | 57.8 | 1100 | 66.5 | 11.5 |
| 5 | PP-H Cat (40) | 40 | 71.8 | 1100 | 30.9 | 4.3 |
| Run | Sample code | Zr(II)/Zr(I) | MW (g/mol) | PDI a | Peak max | Xylene solubility (wt %) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low MW (g/mol) | High MW (g/mol) | ||||||
| 1 | PP-Cat I | (I) only | 469,000 | 2.8 | 383,000 b | 2.6 | |
| 2 | PP-Cat II | (II) only | 115,000 | 4.5 | 43,000 b | 84 | |
| 3 | PP-H Cat (25) | 25 | 1,340,000 | b.m c | 66,000 | 704,000 | 23 |
| 4 | PP-H Cat (32) | 32 | 2,850,000 | b.m | 201,000 | 2,410,000 | 28 |
| 5 | PP-H Cat (40) | 40 | 4,420,000 | b.m | 366,000 | 4,120,000 | 35 |
| Sample code | Zr(II)/Zr(I) | A998 (Peak height) | A973 (Peak height) | A998/A973 | Isotacticity 1 | Isotacticity 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP-Cat I | (I) only | 64.7 | 75.2 | 0.86 | 96.8 | 97.4 |
| PP-Cat II | (II) only | 7.8 | 77.9 | 0.10 | 20 | 16 |
| PP-H Cat (25) | 25 | 49.1 | 74.4 | 0.66 | 76.2 | 77 |
| PP-H Cat (32) | 32 | 43.5 | 76.3 | 0.57 | 70.1 | 72 |
| PP-H Cat (40) | 40 | 40.4 | 77.6 | 0.52 | 63.3 | 65 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaezi, J.; Nekoomanesh, M.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Jafari, S.H.; Mojarrad, A. Correlation of Microstructure, Rheological and Morphological Characteristics of Synthesized Polypropylene (PP) Reactor Blends Using Homogeneous Binary Metallocene Catalyst. Polymers 2017, 9, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9030075
Vaezi J, Nekoomanesh M, Khonakdar HA, Jafari SH, Mojarrad A. Correlation of Microstructure, Rheological and Morphological Characteristics of Synthesized Polypropylene (PP) Reactor Blends Using Homogeneous Binary Metallocene Catalyst. Polymers. 2017; 9(3):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9030075
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaezi, Javid, Mehdi Nekoomanesh, Hossein Ali Khonakdar, Seyed Hassan Jafari, and Alireza Mojarrad. 2017. "Correlation of Microstructure, Rheological and Morphological Characteristics of Synthesized Polypropylene (PP) Reactor Blends Using Homogeneous Binary Metallocene Catalyst" Polymers 9, no. 3: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9030075
APA StyleVaezi, J., Nekoomanesh, M., Khonakdar, H. A., Jafari, S. H., & Mojarrad, A. (2017). Correlation of Microstructure, Rheological and Morphological Characteristics of Synthesized Polypropylene (PP) Reactor Blends Using Homogeneous Binary Metallocene Catalyst. Polymers, 9(3), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9030075





