Adult Neural Stem Cells from Midbrain Periventricular Regions Show Limited Neurogenic Potential after Transplantation into the Hippocampal Neurogenic Niche
Abstract
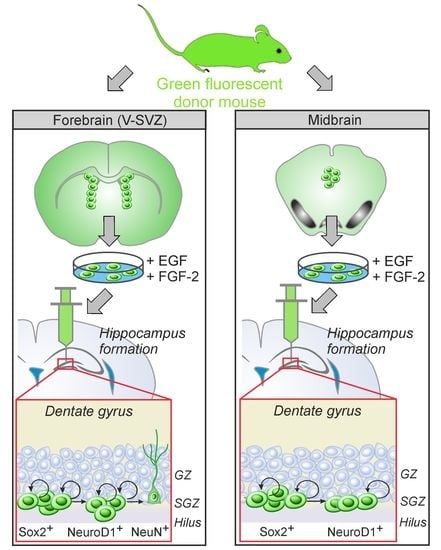
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Neural Stem Cell Culture and Differentiation
2.3. Immunocytochemistry
2.4. Transplantation
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Quantifications and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Comparative Characterization of Transplants Comprising aNSCs from PVRV-SVZ and from PVRMB
3.2. Grafts from PVRMB Compared to PVRV-SVZ Show Decreased Transplant Survival but Similar Proliferative Capacity
3.3. Grafted aNSCs from both PVRV-SVZ and PVRMB Show Similar Neural Stem Cell Properties
3.4. Voluntary Wheel Running of Host Animals Does Not Change PVRV-SVZ Graft Properties
3.5. Grafted aNSCs from PVRMB Are Not Capable of Early Neuronal Differentiation
3.6. Grafted aNSCs from both PVRV-SVZ and PVRMB Show Limited Polydendrocyte Potential
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, D.A.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. The Adult Ventricular-Subventricular Zone (V-SVZ) and Olfactory Bulb (OB) Neurogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigova, T.; Pencea, V.; Wiegand, S.J.; Luskin, M.B. Intraventricular administration of BDNF increases the number of newly generated neurons in the adult olfactory bulb. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1998, 11, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, A.C.; Ferron, S.R.; Vicente, D.; Porlan, E.; Perez-Villalba, A.; Trujillo, C.M.; D’Ocon, P.; Farinas, I. Endothelial NT-3 delivered by vasculature and CSF promotes quiescence of subependymal neural stem cells through nitric oxide induction. Neuron 2014, 83, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, S.; Joyner, A.L. In vivo analysis of quiescent adult neural stem cells responding to Sonic hedgehog. Nature 2005, 437, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.A.; Tramontin, A.D.; Trevejo, J.M.; Herrera, D.G.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Noggin antagonizes BMP signaling to create a niche for adult neurogenesis. Neuron 2000, 28, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimogori, T.; VanSant, J.; Paik, E.; Grove, E.A. Members of the Wnt, Fz, and Frp gene families expressed in postnatal mouse cerebral cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 473, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezun, J.M.; Daszuta, A. Depletion in serotonin decreases neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus and the subventricular zone of adult rats. Neuroscience 1999, 89, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoglinger, G.U.; Rizk, P.; Muriel, M.P.; Duyckaerts, C.; Oertel, W.H.; Caille, I.; Hirsch, E.C. Dopamine depletion impairs precursor cell proliferation in Parkinson disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weselek, G.; Keiner, S.; Fauser, M.; Wagenfuhr, L.; Muller, J.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Brandt, M.D.; Gerlach, M.; Redecker, C.; Hermann, A.; et al. Norepinephrine is a negative regulator of the adult periventricular neural stem cell niche. Stem Cells 2020, 38, 1188–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, F.T.; Mirzadeh, Z.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Mosaic organization of neural stem cells in the adult brain. Science 2007, 317, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuentealba, L.C.; Rompani, S.B.; Parraguez, J.I.; Obernier, K.; Romero, R.; Cepko, C.L.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Embryonic Origin of Postnatal Neural Stem Cells. Cell 2015, 161, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ninkovic, J.; Steiner-Mezzadri, A.; Jawerka, M.; Akinci, U.; Masserdotti, G.; Petricca, S.; Fischer, J.; von Holst, A.; Beckers, J.; Lie, C.D.; et al. The BAF complex interacts with Pax6 in adult neural progenitors to establish a neurogenic cross-regulatory transcriptional network. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 13, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.; Dalgard, C.L.; Wynder, C.; Doughty, M.L. Histone deacetylase inhibitors SAHA and sodium butyrate block G1-to-S cell cycle progression in neurosphere formation by adult subventricular cells. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Coskun, V.; Tao, J.; Xie, W.; Ge, W.; Yoshikawa, K.; Li, E.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.E. Dnmt3a-dependent nonpromoter DNA methylation facilitates transcription of neurogenic genes. Science 2010, 329, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kempermann, G.; Song, H.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the Adult Hippocampus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a018812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filippov, V.; Kronenberg, G.; Pivneva, T.; Reuter, K.; Steiner, B.; Wang, L.P.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kettenmann, H.; Kempermann, G. Subpopulation of nestin-expressing progenitor cells in the adult murine hippocampus shows electrophysiological and morphological characteristics of astrocytes. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seri, B.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; McEwen, B.S.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Astrocytes give rise to new neurons in the adult mammalian hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7153–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukuda, S.; Kato, F.; Tozuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Hisatsune, T. Two distinct subpopulations of nestin-positive cells in adult mouse dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 9357–9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, B.; Klempin, F.; Wang, L.; Kott, M.; Kettenmann, H.; Kempermann, G. Type-2 cells as link between glial and neuronal lineage in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Glia 2006, 54, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, M.D.; Jessberger, S.; Steiner, B.; Kronenberg, G.; Reuter, K.; Bick-Sander, A.; von der Behrens, W.; Kempermann, G. Transient calretinin expression defines early postmitotic step of neuronal differentiation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis of mice. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 24, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G.; Gast, D.; Kronenberg, G.; Yamaguchi, M.; Gage, F.H. Early determination and long-term persistence of adult-generated new neurons in the hippocampus of mice. Development 2003, 130, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmer, J.; Zhao, X.; van Praag, H.; Wodtke, K.; Gage, F.H.; Christie, B.R. Effects of voluntary exercise on synaptic plasticity and gene expression in the dentate gyrus of adult male Sprague-Dawley rats in vivo. Neuroscience 2004, 124, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeper, S.A.; Gomez-Pinilla, F.; Choi, J.; Cotman, C.W. Physical activity increases mRNA for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor in rat brain. Brain Res. 1996, 726, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabel, K.; Fabel, K.; Tam, B.; Kaufer, D.; Baiker, A.; Simmons, N.; Kuo, C.J.; Palmer, T.D. VEGF is necessary for exercise-induced adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carro, E.; Nuñez, A.; Busiguina, S.; Torres-Aleman, I. Circulating insulin-like growth factor I mediates effects of exercise on the brain. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 2926–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhong, C.; Bonaguidi, M.A.; Sun, G.J.; Hsu, D.; Gu, Y.; Meletis, K.; Huang, Z.J.; Ge, S.; Enikolopov, G.; et al. Neuronal circuitry mechanism regulating adult quiescent neural stem-cell fate decision. Nature 2012, 489, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.S.; Piatti, V.C.; Laplagne, D.A.; Morgenstern, N.A.; Ferrari, C.C.; Pitossi, F.J.; Schinder, A.F. Neuronal differentiation in the adult hippocampus recapitulates embryonic development. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10074–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klempin, F.; Beis, D.; Mosienko, V.; Kempermann, G.; Bader, M.; Alenina, N. Serotonin is required for exercise-induced adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 8270–8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munoz, M.D.; Antolin-Vallespin, M.; Tapia-Gonzalez, S.; Sanchez-Capelo, A. Smad3 deficiency inhibits dentate gyrus LTP by enhancing GABAA neurotransmission. J. Neurochem. 2016, 137, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Kang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, W.; Jin, Z.; Li, F.; Gao, N.; Cai, X.; et al. Exploring the potential relationship between Notch pathway genes expression and their promoter methylation in mice hippocampal neurogenesis. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 113, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Praag, H.; Kempermann, G.; Gage, F.H. Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabel, K.; Wolf, S.A.; Ehninger, D.; Babu, H.; Leal-Galicia, P.; Kempermann, G. Additive effects of physical exercise and environmental enrichment on adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Front. Neurosci. 2009, 3, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobilo, T.; Liu, Q.R.; Gandhi, K.; Mughal, M.; Shaham, Y.; van Praag, H. Running is the neurogenic and neurotrophic stimulus in environmental enrichment. Learn. Mem. 2011, 18, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kempermann, G.; Kuhn, H.G.; Gage, F.H. More hippocampal neurons in adult mice living in an enriched environment. Nature 1997, 386, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golmohammadi, M.G.; Blackmore, D.G.; Large, B.; Azari, H.; Esfandiary, E.; Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.; Reynolds, B.A.; Rietze, R.L. Comparative analysis of the frequency and distribution of stem and progenitor cells in the adult mouse brain. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermann, A.; Suess, C.; Fauser, M.; Kanzler, S.; Witt, M.; Fabel, K.; Schwarz, J.; Hoglinger, G.U.; Storch, A. Rostro-caudal gradual loss of cellular diversity within the periventricular regions of the ventricular system. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 928–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazel, C.Y.; Limke, T.L.; Osborne, J.K.; Miura, T.; Cai, J.; Pevny, L.; Rao, M.S. Sox2 expression defines a heterogeneous population of neurosphere-forming cells in the adult murine brain. Aging Cell 2005, 4, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doetsch, F.; Caille, I.; Lim, D.A.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell 1999, 97, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermann, A.; Maisel, M.; Wegner, F.; Liebau, S.; Kim, D.W.; Gerlach, M.; Schwarz, J.; Kim, K.S.; Storch, A. Multipotent neural stem cells from the adult tegmentum with dopaminergic potential develop essential properties of functional neurons. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 949–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaberi, R.; Mirsadeghi, S.; Kiani, S. In vitro characterization of subventricular zone isolated neural stem cells, from adult monkey and rat brain. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachs, F.P.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Engelhardt, M.; Wilhelm, D.; Ploetz, S.; Vroemen, M.; Kaesbauer, J.; Uyanik, G.; Klucken, J.; Karl, C.; et al. High efficacy of clonal growth and expansion of adult neural stem cells. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frielingsdorf, H.; Schwarz, K.; Brundin, P.; Mohapel, P. No evidence for new dopaminergic neurons in the adult mammalian substantia nigra. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10177–10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alonso, G. Neuronal progenitor-like cells expressing polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule are present on the ventricular surface of the adult rat brain and spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 414, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lois, C.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science 1994, 264, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, D.G.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Adult-derived neural precursors transplanted into multiple regions in the adult brain. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidenfaden, R.; Desoeuvre, A.; Bosio, A.; Virard, I.; Cremer, H. Glial conversion of SVZ-derived committed neuronal precursors after ectopic grafting into the adult brain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2006, 32, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigova, T.; Pencea, V.; Betarbet, R.; Wiegand, S.J.; Alexander, C.; Bakay, R.A.; Luskin, M.B. Neuronal progenitor cells of the neonatal subventricular zone differentiate and disperse following transplantation into the adult rat striatum. Cell Transplant. 1998, 7, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.G.; Morris, D.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.J.; Chopp, M. Migration and differentiation of adult rat subventricular zone progenitor cells transplanted into the adult rat striatum. Neuroscience 2003, 116, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K.; Hattiangady, B. Grafted Subventricular Zone Neural Stem Cells Display Robust Engraftment and Similar Differentiation Properties and Form New Neurogenic Niches in the Young and Aged Hippocampus. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhonen, J.O.; Peterson, D.A.; Ray, J.; Gage, F.H. Differentiation of adult hippocampus-derived progenitors into olfactory neurons in vivo. Nature 1996, 383, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, A.L.; Walker, T.L.; Waber Nguyen, A.J.; Berman, R.F.; Kempermann, G.; Waldau, B. Transplanted Dentate Progenitor Cells Show Increased Survival in an Enriched Environment But Do Not Exert a Neurotrophic Effect on Spatial Memory Within 2 Weeks of Engraftment. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 2435–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, M.; Palmer, T.D.; Takahashi, J.; Gage, F.H. Widespread integration and survival of adult-derived neural progenitor cells in the developing optic retina. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1998, 12, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattiangady, B.; Shuai, B.; Cai, J.; Coksaygan, T.; Rao, M.S.; Shetty, A.K. Increased dentate neurogenesis after grafting of glial restricted progenitors or neural stem cells in the aging hippocampus. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 2104–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilli, E.; Reitano, E.; Conti, L.; Conforti, P.; Gulino, R.; Consalez, G.G.; Cesana, E.; Smith, A.; Rossi, F.; Cattaneo, E. Neural stem cells engrafted in the adult brain fuse with endogenous neurons. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lie, D.C.; Dziewczapolski, G.; Willhoite, A.R.; Kaspar, B.K.; Shults, C.W.; Gage, F.H. The adult substantia nigra contains progenitor cells with neurogenic potential. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6639–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shihabuddin, L.S.; Horner, P.J.; Ray, J.; Gage, F.H. Adult spinal cord stem cells generate neurons after transplantation in the adult dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8727–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Praag, H.; Christie, B.R.; Sejnowski, T.J.; Gage, F.H. Running enhances neurogenesis, learning, and long-term potentiation in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13427–13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franklin, K.B.; Paxinos, G. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, M.D.; Krüger-Gerlach, D.; Hermann, A.; Meyer, A.K.; Kim, K.S.; Storch, A. Early Postnatal but Not Late Adult Neurogenesis Is Impaired in the Pitx3-Mutant Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Key, G.; Kubbutat, M.H.; Gerdes, J. Assessment of cell proliferation by means of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on the detection of the Ki-67 protein. J. Immunol. Methods 1994, 177, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdes, J.; Lemke, H.; Baisch, H.; Wacker, H.H.; Schwab, U.; Stein, H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J. Immunol. 1984, 133, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scholzen, T.; Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J. Cell Physiol. 2000, 182, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raedt, R.; Van Dycke, A.; Waeytens, A.; Wyckhuys, T.; Vonck, K.; Wadman, W.; Boon, P. Unconditioned adult-derived neurosphere cells mainly differentiate towards astrocytes upon transplantation in sclerotic rat hippocampus. Epilepsy Res. 2009, 87, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, A.; Brandt, M.D.; Loewenbruck, K.F.; Storch, A. “Silenced” polydendrocytes: A new cell type within the oligodendrocyte progenitor cell population? Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 340, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, J. Autoradiographic investigation of cell proliferation in the brains of rats and cats. Anat. Rec. 1963, 145, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, B.A.; Weiss, S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science 1992, 255, 1707–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magavi, S.S.; Leavitt, B.R.; Macklis, J.D. Induction of neurogenesis in the neocortex of adult mice. Nature 2000, 405, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, L.; Yang, M.; Enikolopov, G.; Iacovitti, L. Circumventricular organs: A novel site of neural stem cells in the adult brain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2009, 41, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lledo, P.M.; Merkle, F.T.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Origin and function of olfactory bulb interneuron diversity. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Tolkovsky, A.M.; Herbert, J. Cell origin and culture history determine successful integration of neural precursor transplants into the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gage, F.H.; Coates, P.W.; Palmer, T.D.; Kuhn, H.G.; Fisher, L.J.; Suhonen, J.O.; Peterson, D.A.; Suhr, S.T.; Ray, J. Survival and differentiation of adult neuronal progenitor cells transplanted to the adult brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11879–11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kreisel, T.; Wolf, B.; Keshet, E.; Licht, T. Unique role for dentate gyrus microglia in neuroblast survival and in VEGF-induced activation. Glia 2019, 67, 594–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreisel, T.; Frank, M.G.; Licht, T.; Reshef, R.; Ben-Menachem-Zidon, O.; Baratta, M.V.; Maier, S.F.; Yirmiya, R. Dynamic microglial alterations underlie stress-induced depressive-like behavior and suppressed neurogenesis. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gemma, C.; Bachstetter, A.D. The role of microglia in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Dolado, M.; Pardal, R.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Fike, J.R.; Lee, H.O.; Pfeffer, K.; Lois, C.; Morrison, S.J.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Fusion of bone-marrow-derived cells with Purkinje neurons, cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. Nature 2003, 425, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, F.; Samper Agrelo, I.; Kury, P. Do Neural Stem Cells Have a Choice? Heterogenic Outcome of Cell Fate Acquisition in Different Injury Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fauser, M.; Loewenbrück, K.F.; Rangnick, J.; Brandt, M.D.; Hermann, A.; Storch, A. Adult Neural Stem Cells from Midbrain Periventricular Regions Show Limited Neurogenic Potential after Transplantation into the Hippocampal Neurogenic Niche. Cells 2021, 10, 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113021
Fauser M, Loewenbrück KF, Rangnick J, Brandt MD, Hermann A, Storch A. Adult Neural Stem Cells from Midbrain Periventricular Regions Show Limited Neurogenic Potential after Transplantation into the Hippocampal Neurogenic Niche. Cells. 2021; 10(11):3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113021
Chicago/Turabian StyleFauser, Mareike, Kai F Loewenbrück, Johannes Rangnick, Moritz D Brandt, Andreas Hermann, and Alexander Storch. 2021. "Adult Neural Stem Cells from Midbrain Periventricular Regions Show Limited Neurogenic Potential after Transplantation into the Hippocampal Neurogenic Niche" Cells 10, no. 11: 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113021