The Triple Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosome Technology as a Potential Tool for Treating Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Extracellular Vesicles, Exosomes and Clinical Applications of ASC Exosomes
2.1. Extracellular Vesicles: Composition and Subtypes
2.2. Exosomes: Composition, Biological Properties and ASC Exosomes
3. Breast Cancer as Triple Entity: Classification System and General Therapeutical Options
3.1. Breast Cancer Classification Systems: Tumor Size, Local Receptors and Immunohistochemistry
3.2. Basic Knowledge and Novel Therapeutical Options for Breast Cancer Therapy
4. TNBC and Tumor Exosomes: Mutual Friends or Potential Enemies?
4.1. TNBC and Tumor Exosomes: Mutual Friends…
4.2. TNBC and Tumor Exosomes: … or Potential Enemies
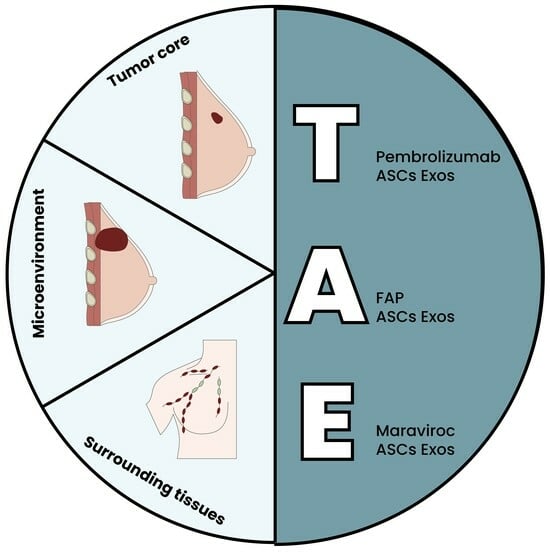
5. The Triple ASC Exosome [T.A.E.] Technology as an In Vitro Preconditioning Tool for TNBC Cells
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borràs, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: A Compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community Annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kang, B.; Kim, O.Y.; Choi, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.R.; Go, G.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.C.; et al. EVpedia: An integrated database of high-throughput data for systemic analyses of extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.J.; Kalra, H.; Mathivanan, S. ExoCarta as a resource for exosomal research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2012, 1, 18374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimian, M.; Hashemi, M.; Etemad, L.; Salmasi, Z. Thymoquinone-loaded mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome as an efficient nano-system against breast cancer cells. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 14116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, S.; Moradi-Chaleshtori, M.; Paryan, M.; Koochaki, A.; Sharifi, K.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes enriched with miR-218 reduce the epithelial–mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brett, E.; Duscher, D.; Pagani, A.; Daigeler, A.; Kolbenschlag, J.; Hahn, M. Naming the Barriers between Anti-CCR5 Therapy, Breast Cancer and Its Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escrevente, C.; Keller, S.; Altevogt, P.; Costa, J. Interaction and uptake of exosomes by ovarian cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, P.A.; Pisitkun, T.; Hoffert, J.D.; Tchapyjnikov, D.; Star, R.A.; Kleta, R.; Wang, N.S.; Knepper, M.A. Large-scale proteomics and phosphoproteomics of urinary exosomes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Nawrocki, A.; Jensen, S.G.; Thorsen, K.; Whitehead, B.; Howard, K.A.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Ørntoft, T.F.; Larsen, M.R.; Ostenfeld, M.S. Quantitative proteomics of fractionated membrane and lumen exosome proteins from isogenic metastatic and nonmetastatic bladder cancer cells reveal differential expression of EMT factors. Proteomics 2014, 14, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aatonen, M.T.; Öhman, T.; Nyman, T.A.; Laitinen, S.; Grönholm, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M. Isolation and characterization of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Moita, C.; van Niel, G.; Kowal, J.; Vigneron, J.; Benaroch, P.; Manel, N.; Moita, L.F.; Théry, C.; Raposo, G. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126 Pt 24, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.C.; Ramamurthi, K.S. Macromolecules that prefer their membranes curvy. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Meer, G.; Vaz, W.L. Membrane curvature sorts lipids: Stabilized lipid rafts in membrane transport. Embo Rep. 2005, 6, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Théry, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bebelman, M.P.; Smit, M.J.; Pegtel, D.M.; Baglio, S.R. Biogenesis and function of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 188, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, C.; Lv, N.; Liang, Z.; Ma, T.; Cheng, H.; Xia, Y.; Shi, L. AdMSC-derived exosomes alleviate acute lung injury via transferring mitochondrial component to improve homeostasis of alveolar macrophages. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2928–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Tan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Potential role of exosomes in the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of hypoxic diseases. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 1184–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, M.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, W.; Zhao, C.; Lv, W.; Yi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, M. Exosomes From Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: The Emerging Roles and Applications in Tissue Regeneration of Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 574223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghadban, S.; Bunnell, B.A. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Immunomodulatory Effects and Therapeutic Potential. Physiology 2020, 35, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, A.; Pham, A.; Cress, M.J.; Pincelli, T.; TerKonda, S.P.; Bruce, A.J.; Zubair, A.C.; Wolfram, J.; Shapiro, S.A. Adipose-derived cellular and cell-derived regenerative therapies in dermatology and aesthetic rejuvenation. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 54, 100933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajek, A.; Gurtowska, N.; Olkowska, J.; Kazmierski, L.; Maj, M.; Drewa, T. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as a Tool in Cell-Based Therapies. Arch. Immunol. et Ther. Exp. 2016, 64, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zocchi, M.L.; Vindigni, V.; Pagani, A.; Pirro, O.; Conti, G.; Sbarbati, A.; Bassetto, F. Regulatory, ethical, and technical considerations on regenerative technologies and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2019, 42, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocchi, M.L.; Facchin, F.; Pagani, A.; Bonino, C.; Sbarbati, A.; Conti, G.; Vindigni, V.; Bassetto, F. New perspectives in regenerative medicine and surgery: The bioactive composite therapies (BACTs). Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2022, 45, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-X.; Sun, J.-M.; Ho, C.-K.; Gao, Y.; Wen, D.-S.; Liu, Y.-D.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.-F. Advancements in adipose-derived stem cell therapy for skin fibrosis. World J. Stem Cells 2023, 15, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Won, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Choi, M.; Lee, E.; Ryoou, B.; Lee, S.-G.; Cho, B.S. Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, W.; Pu, G.; Wu, J.; Qin, F. Exosomes derived from miR-338-3p-modified adipose stem cells inhibited inflammation injury of chondrocytes via targeting RUNX2 in osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Liang, W. ASCs -derived exosomes loaded with vitamin A and quercetin inhibit rapid senescence-like response after acute liver injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 572, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Huang, L.; Xu, Y.; Lu, W.; Wen, W.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y. Hypoxic ASCs-derived Exosomes Attenuate Colitis by Regulating Macrophage Polarization via miR-216a-5p/HMGB1 Axis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 29, 602–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Liu, T.; Im, W.; Kim, M. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate phenotype of Huntington’s disease in vitro model. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2016, 44, 2114–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantug, G.R.; Hess, C. The immunometabolic ecosystem in cancer. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, E.J. Overview of breast cancer. J. Am. Acad. Physician Assist. 2019, 32, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steward, L.; Conant, L.; Gao, F.; Margenthaler, J.A. Predictive Factors and Patterns of Recurrence in Patients with Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 2165–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.Y.; Wyse, C.; Ho, M.; O’Beirne, E.; Howard, J.; Lindsay, S.; Kelly, P.; Higgins, M.; McCann, A. Exosomes in triple negative breast cancer: Garbage disposals or Trojan horses? Cancer Lett. 2020, 473, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, A.S.; Taylor, E.M. Recent Advances in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 145, 421e–432e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Harris, S.L.; Levine, A.J. The regulation of exosome secretion: A novel function of the p53 protein. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4795–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevic, I.; Müller, V.; Weber, K.; Fasching, P.A.; Karn, T.; Marmé, F.; Schem, C.; Stickeler, E.; Denkert, C.; van Mackelenbergh, M.; et al. Specific microRNA signatures in exosomes of triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy within the GeparSixto trial. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Hernandez, O.; Villegas-Comonfort, S.; Candanedo, F.; González-Vázquez, M.-C.; Chavez-Ocaña, S.; Jimenez-Villanueva, X.; Sierra-Martinez, M.; Salazar, E.P. Elevated concentration of microvesicles isolated from peripheral blood in breast cancer patients. Arch. Med. Res. 2013, 44, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, E.L.; Lindsay, S.; Halasz, M.; Gubbins, L.C.; Weiner-Gorzel, K.; Guang, M.H.Z.; McGoldrick, A.; Collins, E.; Henry, M.; Blanco-Fernández, A.; et al. Protein and chemotherapy profiling of extracellular vesicles harvested from therapeutic induced senescent triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’brien, K.; Rani, S.; Corcoran, C.; Wallace, R.; Hughes, L.; Friel, A.M.; McDonnell, S.; Crown, J.; Radomski, M.W.; O’driscoll, L. Exosomes from triple-negative breast cancer cells can transfer phenotypic traits representing their cells of origin to secondary cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 1845–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Liu, C.; Su, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Cong, Y.; Kimberly, R.; Grizzle, W.E.; et al. Tumor Exosomes Inhibit Differentiation of Bone Marrow Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6867–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, A.; Mitchell, J.P.; Court, J.; Linnane, S.; Mason, M.D.; Tabi, Z. Human Tumor-Derived Exosomes Down-Modulate NKG2D Expression. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7249–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skog, J.; Würdinger, T.; Van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Curry, W.T., Jr.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.S.; Cho, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Choi, E.-J.; Rho, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.-S.; Kim, Y.-K.; Hwang, D.; et al. Colorectal cancer cell-derived microvesicles are enriched in cell cycle-related mRNAs that promote proliferation of endothelial cells. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.J.; Christianson, H.C.; Wittrup, A.; Bourseau-Guilmain, E.; Lindqvist, E.; Svensson, L.M.; Mörgelin, M.; Belting, M. Exosome Uptake Depends on ERK1/2-Heat Shock Protein 27 Signaling and Lipid Raft-mediated Endocytosis Negatively Regulated by Caveolin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17713–17724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keulers, T.G.; Schaaf, M.B.E.; Rouschop, K.M.A. Autophagy-Dependent Secretion: Contribution to Tumor Progression. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Rezaie, J. Tumor cells derived-exosomes as angiogenenic agents: Possible therapeutic implications. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaravadi, R.; Kimmelman, A.C.; White, E. Recent insights into the function of autophagy in cancer. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1913–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; He, P.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.-F.; Lu, J.; Li, M.; Kurihara, H.; Luo, Z.; Meng, T.; Onishi, M.; et al. Selective autophagy of intracellular organelles: Recent research advances. Theranostics 2021, 11, 222–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.Q.; Kumar, A.V.; Mills, J.; Lapierre, L.R. Autophagy in aging and longevity. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colletti, M.; Ceglie, D.; Di Giannatale, A.; Nazio, F. Autophagy and Exosomes Relationship in Cancer: Friends or Foes? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 614178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.S.; Vats, S.; Chia, A.Y.-Q.; Tan, T.Z.; Deng, S.; Ong, M.S.; Arfuso, F.; Yap, C.T.; Goh, B.C.; Sethi, G.; et al. Dual role of autophagy in hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1142–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrie, A.; Krumeich, S.; Reyal, F.; Recchi, C.; Moita, L.F.; Seabra, M.C.; Ostrowski, M.; Théry, C.; Bobrie, A.; Krumeich, S.; et al. Rab27a Supports Exosome-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms That Modify the Tumor Microenvironment and Can Promote Tumor Progression. Cancer Res 2012, 72, 4920–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Chen, J.; Su, F.; Yu, B.; Su, F.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.-D.; Song, E. Microvesicles secreted by macrophages shuttle invasion-potentiating microRNAs into breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boelens, M.C.; Wu, T.J.; Nabet, B.Y.; Xu, B.; Qiu, Y.; Yoon, T.; Azzam, D.J.; Victor, C.T.-S.; Wiemann, B.Z.; Ishwaran, H.; et al. Exosome transfer from stromal to breast cancer cells regulates therapy resistance pathways. Cell 2014, 159, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diluvio, G.; Del Gaudio, F.; Giuli, M.V.; Franciosa, G.; Giuliani, E.; Palermo, R.; Besharat, Z.M.; Pignataro, M.G.; Vacca, A.; D’amati, G.; et al. NOTCH3 inactivation increases triple negative breast cancer sensitivity to gefitinib by promoting EGFR tyrosine dephosphorylation and its intracellular arrest. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Camargo, L.C.B.; Guaddachi, F.; Bergerat, D.; Ourari, N.; Coillard, L.; Parietti, V.; Le Bras, M.; Lehmann-Che, J.; Jauliac, S. Extracellular vesicles produced by NFAT3-expressing cells hinder tumor growth and metastatic dissemination. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Sang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Q. MiR-770 suppresses the chemo-resistance and metastasis of triple negative breast cancer via direct targeting of STMN1. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomari, H.; Moghadam, M.F.; Soleimani, M.; Ghavami, M.; Khodashenas, S. Targeted delivery of doxorubicin to HER2 positive tumor models. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5679–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Ma, J.; Su, C.; Chen, Y.; Shu, Y.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, B.; Shi, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Engineered exosome-like nanovesicles suppress tumor growth by reprogramming tumor microenvironment and promoting tumor ferroptosis. Acta Biomater. 2021, 135, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Shao, L.; Chen, Y.; Tang, L.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Zhu, H. Synergistic strategy with hyperthermia therapy based immunotherapy and engineered exosomes−liposomes targeted chemotherapy prevents tumor recurrence and metastasis in advanced breast cancer. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.O.; Jo, H.; Yu, J.H.; Gambhir, S.S.; Pratx, G. Development and MPI tracking of novel hypoxia-targeted theranostic exosomes. Biomaterials 2018, 177, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Rugo, H.S.; Cescon, D.W.; Im, S.-A.; Yusof, M.M.; Gallardo, C.; Lipatov, O.; Barrios, C.H.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Iwata, H.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervaiz, A.; Zepp, M.; Georges, R.; Bergmann, F.; Mahmood, S.; Faiza, S.; Berger, M.R.; Adwan, H. Antineoplastic effects of targeting CCR5 and its therapeutic potential for colorectal cancer liver metastasis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Velasco-Velázquez, M.A.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Rui, H.; Peck, A.R.; Korkola, J.E.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; DuHadaway, J.B.; et al. CCR5 Governs DNA Damage Repair and Breast Cancer Stem Cell Expansion. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1657–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinton, L.T.; Sloane, H.S.; Kester, M.; Kelly, K.A. Formation and role of exosomes in cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| TNBC & ASCs EXOSOMES | |
|---|---|
| Mutual Friends…. …or Enemies | |
| Yu et al. [39] TSAP–6 upregulation enhances exos concentrations in blood plasma of breast cancer women | Camargo et al. [60] NFAT–3 expressing cells derived EVs impede tumor growth and metastasis in a TNBC mice model |
| Galindo-Hernandez et al. [41] Elevated concentrations of microvesicles from peripheral blood in breast cancer patients | Gomari et al. [62] pLEX–LAMP DARPin–loaded Exos can enable DARPin expression on their surface and effectively address Her–2+ tumor cells |
| Kavanagh et al. [42] TIS Cal 51 chemoresistant cells produce more exosomes after Paclitaxel treatment | Gomari et al. [62] Doxorubicin–loaded Exos target Her–2+ cells with reduction of tumor growth and reduced adverse effects in a murine breast cancer model |
| O’ Brien et al. [43] Malignant Hs5787T(i)8–derived Exos increase proliferation, migration, invasiveness, endothelial tubules formation and angiogenesis of recipient cells (TME) | O’ Brien et al. [43] Exosomes–mediated transfection of miR–134 into Hs578Ts(i)8 cells is associated with reduced tumor cells proliferation |
| Li W et al. [52] Exosomes–mediated autophagy upregulated cancer development impacting proliferation, invasion and immune evasion | Li Y et al. [61] Engineered miR–770 Exos are more sensitive to Doxorubicin in therapeutic–induced apoptosis |
| Colletti et al. [54] An oncological environment activates exosomes release and authophagy which support tumor growth | Colletti et al. [54] An oncological environment activates exosomes release and authophagy which support tumor suppression |
| Bobrie et al. [56]–Yang et al. [57] Exosomal Rab27a and miR–223 supports exosomes secretion and TNBC progression and invasiveness | Bobrie et al. [56] Silencing the Exosomal Rab27a reduces local growth and tumor metastasis |
| Boelens et al. [58]–Diluvio et al. [59] Stromal cells–derived Exos mediate drug resistance in TNBC cells by modulating the NOTCH–3 pathway | Huang et al. [64] HELA–Exos is able to boost antitumor immunity in breast cancer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pagani, A.; Duscher, D.; Geis, S.; Klein, S.; Knoedler, L.; Panayi, A.C.; Oliinyk, D.; Felthaus, O.; Prantl, L. The Triple Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosome Technology as a Potential Tool for Treating Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cells 2024, 13, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13070614
Pagani A, Duscher D, Geis S, Klein S, Knoedler L, Panayi AC, Oliinyk D, Felthaus O, Prantl L. The Triple Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosome Technology as a Potential Tool for Treating Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cells. 2024; 13(7):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13070614
Chicago/Turabian StylePagani, Andrea, Dominik Duscher, Sebastian Geis, Silvan Klein, Leonard Knoedler, Adriana C. Panayi, Dmytro Oliinyk, Oliver Felthaus, and Lukas Prantl. 2024. "The Triple Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosome Technology as a Potential Tool for Treating Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" Cells 13, no. 7: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13070614