A Heterozygous ZMPSTE24 Mutation Associated with Severe Metabolic Syndrome, Ectopic Fat Accumulation, and Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Molecular Studies
2.3. Immunofluorescence
2.4. Population Doubling Level
2.5. SiRNA
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Senescence-Associated Beta-Galactosidase Assay
2.8. Cellular BrdU Labelling
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
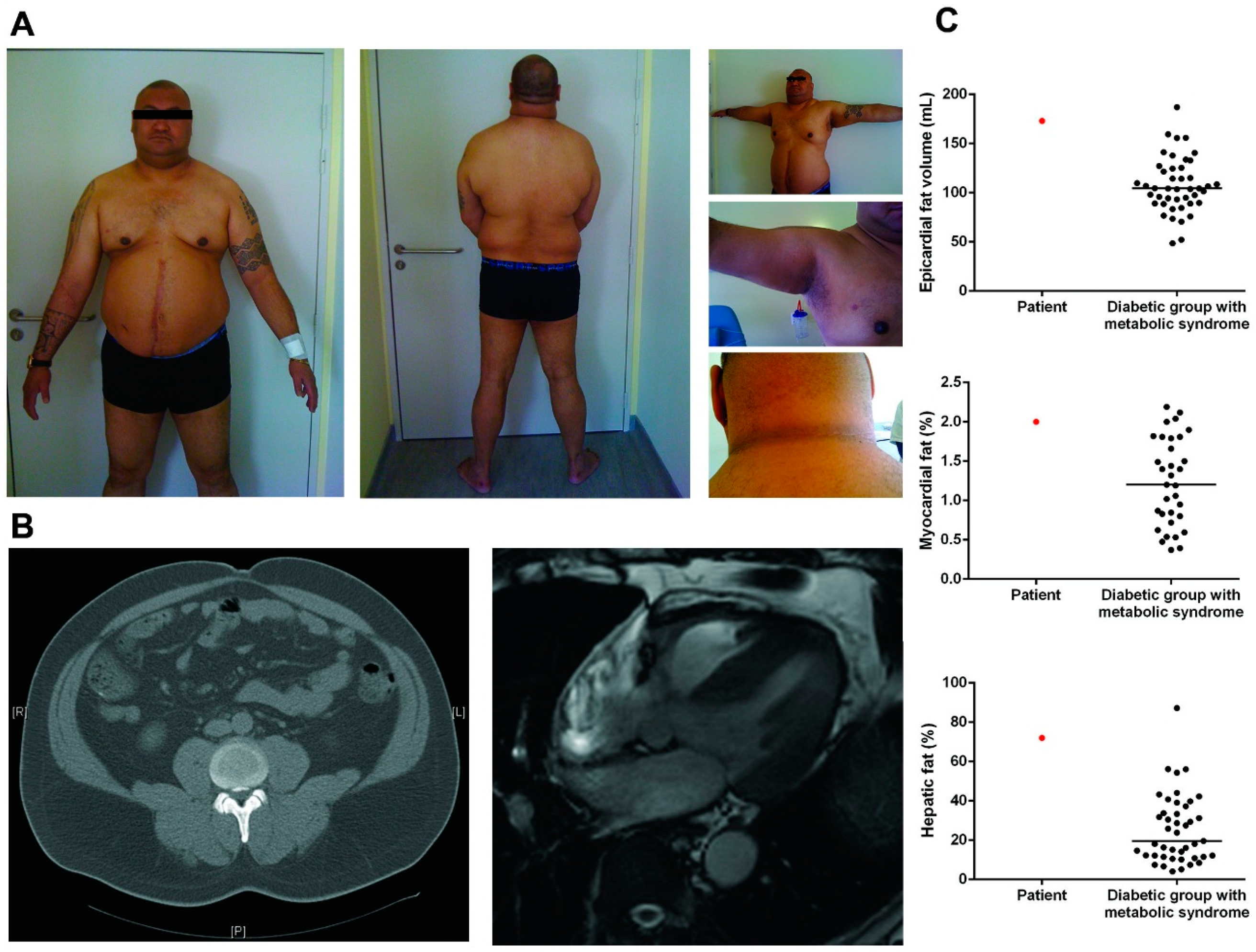
3.1. Patient Description
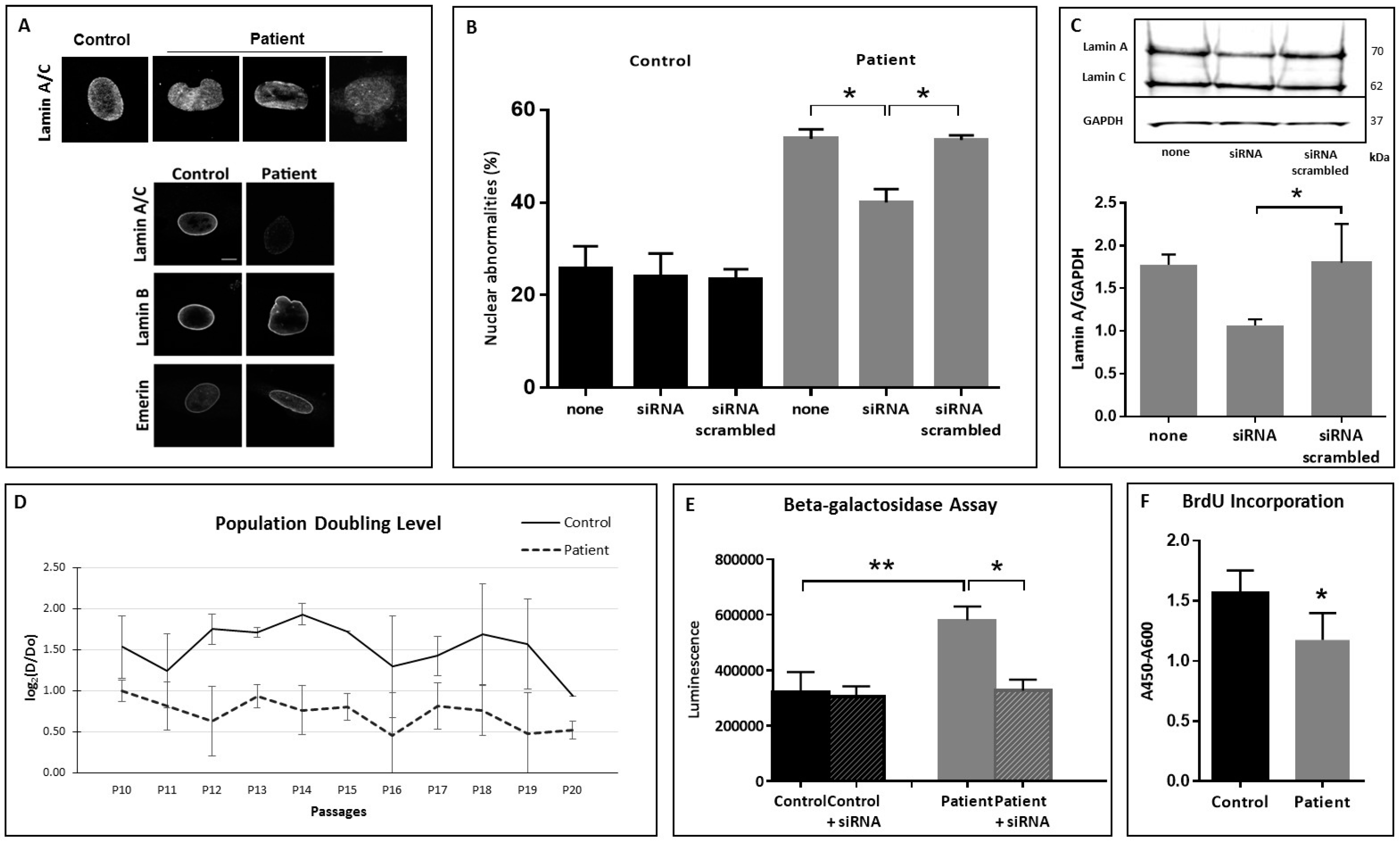
3.2. Nuclear Shape Anomalies and Senescence Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrowman, J.; Michaelis, S. ZMPSTE24, an integral membrane zinc metalloprotease with a connection to progeroid disorders. Biol. Chem. 2009, 390, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sandre-Giovannoli, A.; Bernard, R.; Cau, P.; Navarro, C.; Amiel, J.; Boccaccio, I.; Lyonnet, S.; Stewart, C.L.; Munnich, A.; Le Merrer, M.; et al. Lamin a truncation in hutchinson-gilford progeria. Science 2003, 300, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, M.; Brown, W.T.; Gordon, L.B.; Glynn, M.W.; Singer, J.; Scott, L.; Erdos, M.R.; Robbins, C.M.; Moses, T.Y.; Berglund, P.; et al. Recurrent de novo point mutations in lamin a cause hutchinson-gilford progeria syndrome. Nature 2003, 423, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cau, P.; Navarro, C.; Harhouri, K.; Roll, P.; Sigaudy, S.; Kaspi, E.; Perrin, S.; de Sandre-Giovannoli, A.; Levy, N. Nuclear matrix, nuclear envelope and premature aging syndromes in a translational research perspective. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, C.L.; Cadinanos, J.; de Sandre-Giovannoli, A.; Bernard, R.; Courrier, S.; Boccaccio, I.; Boyer, A.; Kleijer, W.J.; Wagner, A.; Giuliano, F.; et al. Loss of ZMPSTE24 (face-1) causes autosomal recessive restrictive dermopathy and accumulation of lamin a precursors. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, C.L.; Esteves-Vieira, V.; Courrier, S.; Boyer, A.; Duong Nguyen, T.; Huong le, T.T.; Meinke, P.; Schroder, W.; Cormier-Daire, V.; Sznajer, Y.; et al. New ZMPSTE24 (face1) mutations in patients affected with restrictive dermopathy or related progeroid syndromes and mutation update. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. EJHG 2014, 22, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, C.L.; Cau, P.; Levy, N. Molecular bases of progeroid syndromes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, R151–R161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Fryns, J.P.; Auchus, R.J.; Garg, A. Zinc metalloproteinase, ZMPSTE24, is mutated in mandibuloacral dysplasia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutour, A.; Roll, P.; Gaborit, B.; Courrier, S.; Alessi, M.C.; Tregouet, D.A.; Angelis, F.; Robaglia-Schlupp, A.; Lesavre, N.; Cau, P.; et al. High prevalence of laminopathies among patients with metabolic syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 3779–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrowman, J.; Wiley, P.A.; Hudon-Miller, S.E.; Hrycyna, C.A.; Michaelis, S. Human ZMPSTE24 disease mutations: Residual proteolytic activity correlates with disease severity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 4084–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. Bedtools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. Annovar: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, U.M.; Chavez, E.A.; Poon, S.S.; Schmoor, C.; Lansdorp, P.M. Accumulation of short telomeres in human fibroblasts prior to replicative senescence. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 256, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Metabolic syndrome: A closer look at the growing epidemic and its associated pathologies. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2015, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rother, K.I.; Brown, R.J. Novel forms of lipodystrophy: Why should we care? Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2142–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaudain, A.; Vantyghem, M.C.; Guerci, B.; Hecart, A.C.; Auclair, M.; Reznik, Y.; Narbonne, H.; Ducluzeau, P.H.; Donadille, B.; Lebbe, C.; et al. New metabolic phenotypes in laminopathies: Lmna mutations in patients with severe metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 4835–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, M.E.; Kropman, E.; Kranendonk, M.E.; Koppen, A.; Hamers, N.; Stroes, E.S.; Kalkhoven, E.; Monajemi, H. Characterisation of non-obese diabetic patients with marked insulin resistance identifies a novel familial partial lipodystrophy-associated ppargamma mutation (y151c). Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, V.A.; Fernandez-Galilea, M. Lipodystrophies: Adipose tissue disorders with severe metabolic implications. J. Phys. Biochem. 2015, 71, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatier, C.; Bidault, G.; Briand, N.; Guenantin, A.C.; Teyssieres, L.; Lascols, O.; Capeau, J.; Vigouroux, C. What the genetics of lipodystrophy can teach us about insulin resistance and diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2013, 13, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigouroux, C.; Caron-Debarle, M.; Le Dour, C.; Magre, J.; Capeau, J. Molecular mechanisms of human lipodystrophies: From adipocyte lipid droplet to oxidative stress and lipotoxicity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizino, M.B.; Sala, M.L.; de Heer, P.; van der Tol, P.; Smit, J.W.; Webb, A.G.; de Roos, A.; Lamb, H.J. MR of multi-organ involvement in the metabolic syndrome. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2015, 23, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy-Matos, A.F.; Valerio, C.M.; Braganca, J.B.; Oliveira Rde, A.; Zagury, R.L.; Lustosa Rde, P.; Camargo, G.C.; Nascimento, C.A.; Moreira, R.O. Evaluation of epicardial adipose tissue in familial partial lipodystrophy. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2015, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaborit, B.; Kober, F.; Jacquier, A.; Moro, P.J.; Cuisset, T.; Boullu, S.; Dadoun, F.; Alessi, M.C.; Morange, P.; Clement, K.; et al. Assessment of epicardial fat volume and myocardial triglyceride content in severely obese subjects: Relationship to metabolic profile, cardiac function and visceral fat. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.D.; Victor, R.G.; Szczepaniak, E.W.; Simha, V.; Garg, A.; Szczepaniak, L.S. Cardiac steatosis and left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with generalized lipodystrophy as determined by magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 112, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenantin, A.C.; Briand, N.; Bidault, G.; Afonso, P.; Bereziat, V.; Vatier, C.; Lascols, O.; Caron-Debarle, M.; Capeau, J.; Vigouroux, C. Nuclear envelope-related lipodystrophies. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 29, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadille, B.; D’Anella, P.; Auclair, M.; Uhrhammer, N.; Sorel, M.; Grigorescu, R.; Ouzounian, S.; Cambonie, G.; Boulot, P.; Laforet, P.; et al. Partial lipodystrophy with severe insulin resistance and adult progeria werner syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, M.; Auclair, M.; Donadille, B.; Bereziat, V.; Guerci, B.; Laville, M.; Narbonne, H.; Bodemer, C.; Lascols, O.; Capeau, J.; et al. Human lipodystrophies linked to mutations in a-type lamins and to hiv protease inhibitor therapy are both associated with prelamin a accumulation, oxidative stress and premature cellular senescence. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidault, G.; Garcia, M.; Vantyghem, M.C.; Ducluzeau, P.H.; Morichon, R.; Thiyagarajah, K.; Moritz, S.; Capeau, J.; Vigouroux, C.; Bereziat, V. Lipodystrophy-linked lmna p.R482w mutation induces clinical early atherosclerosis and in vitro endothelial dysfunction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2162–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, P.; Schneebeli, S.; Vigouroux, C.; Lascols, O.; Schaaf, M.; Chevalier, P. Metabolic and cardiac phenotype characterization in 37 atypical dunnigan patients with nonfarnesylated mutated prelamin a. Am. Heart J. 2015, 169, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capanni, C.; Mattioli, E.; Columbaro, M.; Lucarelli, E.; Parnaik, V.K.; Novelli, G.; Wehnert, M.; Cenni, V.; Maraldi, N.M.; Squarzoni, S.; et al. Altered pre-lamin a processing is a common mechanism leading to lipodystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 1489–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadrot, N.; Duband-Goulet, I.; Cabet, E.; Attanda, W.; Barateau, A.; Vicart, P.; Gerbal, F.; Briand, N.; Vigouroux, C.; Oldenburg, A.R.; et al. The p.R482w substitution in a-type lamins deregulates srebp1 activity in dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 2096–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, P.; Auclair, M.; Boccara, F.; Vantyghem, M.C.; Katlama, C.; Capeau, J.; Vigouroux, C.; Caron-Debarle, M. Lmna mutations resulting in lipodystrophy and hiv protease inhibitors trigger vascular smooth muscle cell senescence and calcification: Role of ZMPSTE24 downregulation. Atherosclerosis 2015, 245, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galant, D.; Gaborit, B.; Desgrouas, C.; Abdesselam, I.; Bernard, M.; Levy, N.; Merono, F.; Coirault, C.; Roll, P.; Lagarde, A.; et al. A Heterozygous ZMPSTE24 Mutation Associated with Severe Metabolic Syndrome, Ectopic Fat Accumulation, and Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Cells 2016, 5, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5020021
Galant D, Gaborit B, Desgrouas C, Abdesselam I, Bernard M, Levy N, Merono F, Coirault C, Roll P, Lagarde A, et al. A Heterozygous ZMPSTE24 Mutation Associated with Severe Metabolic Syndrome, Ectopic Fat Accumulation, and Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Cells. 2016; 5(2):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalant, Damien, Bénédicte Gaborit, Camille Desgrouas, Ines Abdesselam, Monique Bernard, Nicolas Levy, Françoise Merono, Catherine Coirault, Patrice Roll, Arnaud Lagarde, and et al. 2016. "A Heterozygous ZMPSTE24 Mutation Associated with Severe Metabolic Syndrome, Ectopic Fat Accumulation, and Dilated Cardiomyopathy" Cells 5, no. 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5020021
APA StyleGalant, D., Gaborit, B., Desgrouas, C., Abdesselam, I., Bernard, M., Levy, N., Merono, F., Coirault, C., Roll, P., Lagarde, A., Bonello-Palot, N., Bourgeois, P., Dutour, A., & Badens, C. (2016). A Heterozygous ZMPSTE24 Mutation Associated with Severe Metabolic Syndrome, Ectopic Fat Accumulation, and Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Cells, 5(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5020021





