Overexpression of MiR482c in Tomato Induces Enhanced Susceptibility to Late Blight
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Strains, Phytophthora Infestans Infections
2.2. Construction of the MiR482c-Overexpression Plasmids
2.3. Transient Overexpression of MiR482c in Tomato
2.4. Generation of Transgenic Tomato Overexpressing MiR482c
2.5. Disease Resistance of Transgenic Plants Overexpressing MiR482c
2.6. DAB/NBT Staining and Measurements of Hydrogen Peroxide/MDA Content
2.7. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression Patterns of MiR482c and Its Target Genes upon Infection
3.2. Transient Overexpression of MiR482c Compromised Tomato Resistance
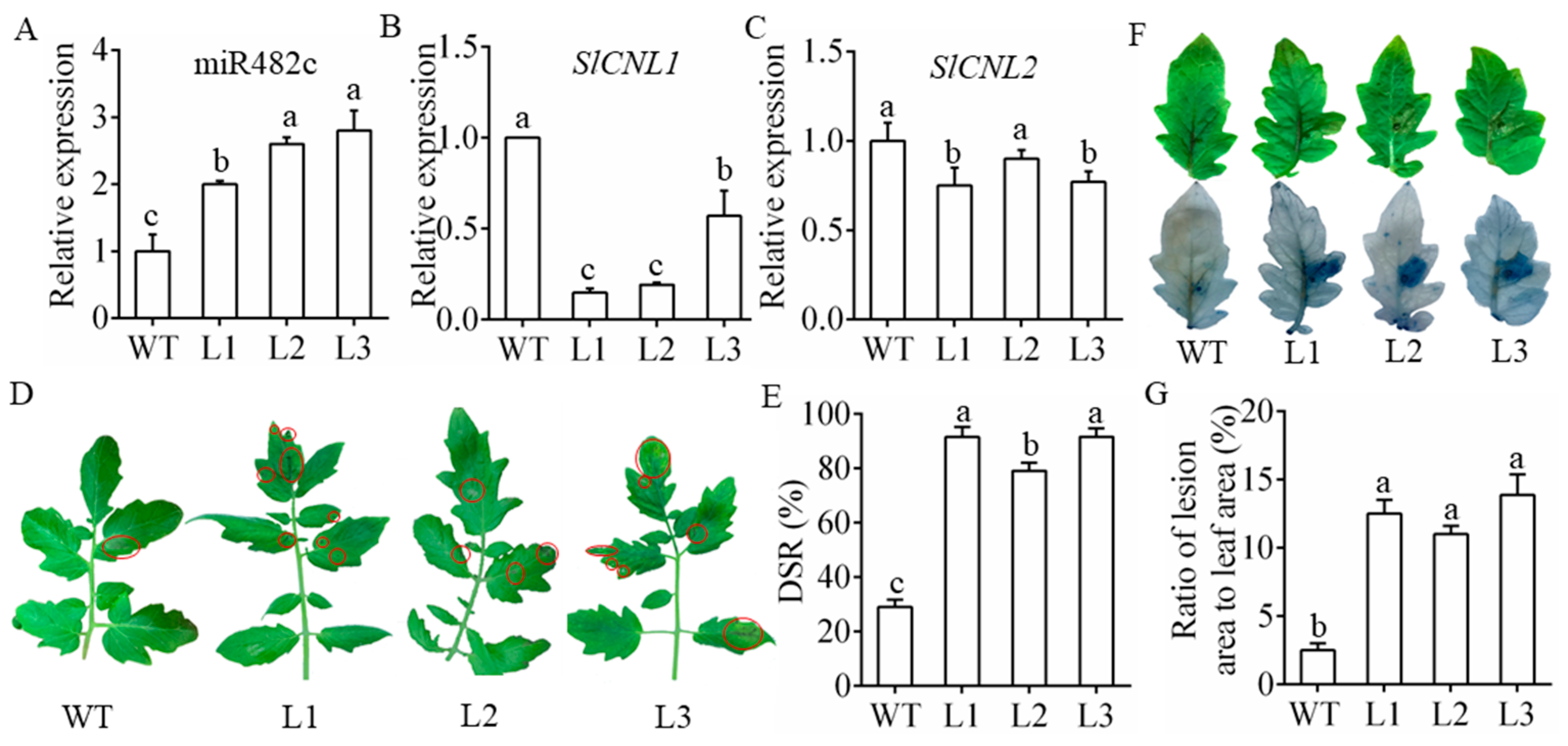
3.3. MiR482c Had a Negative Effect on Tomato Resistance
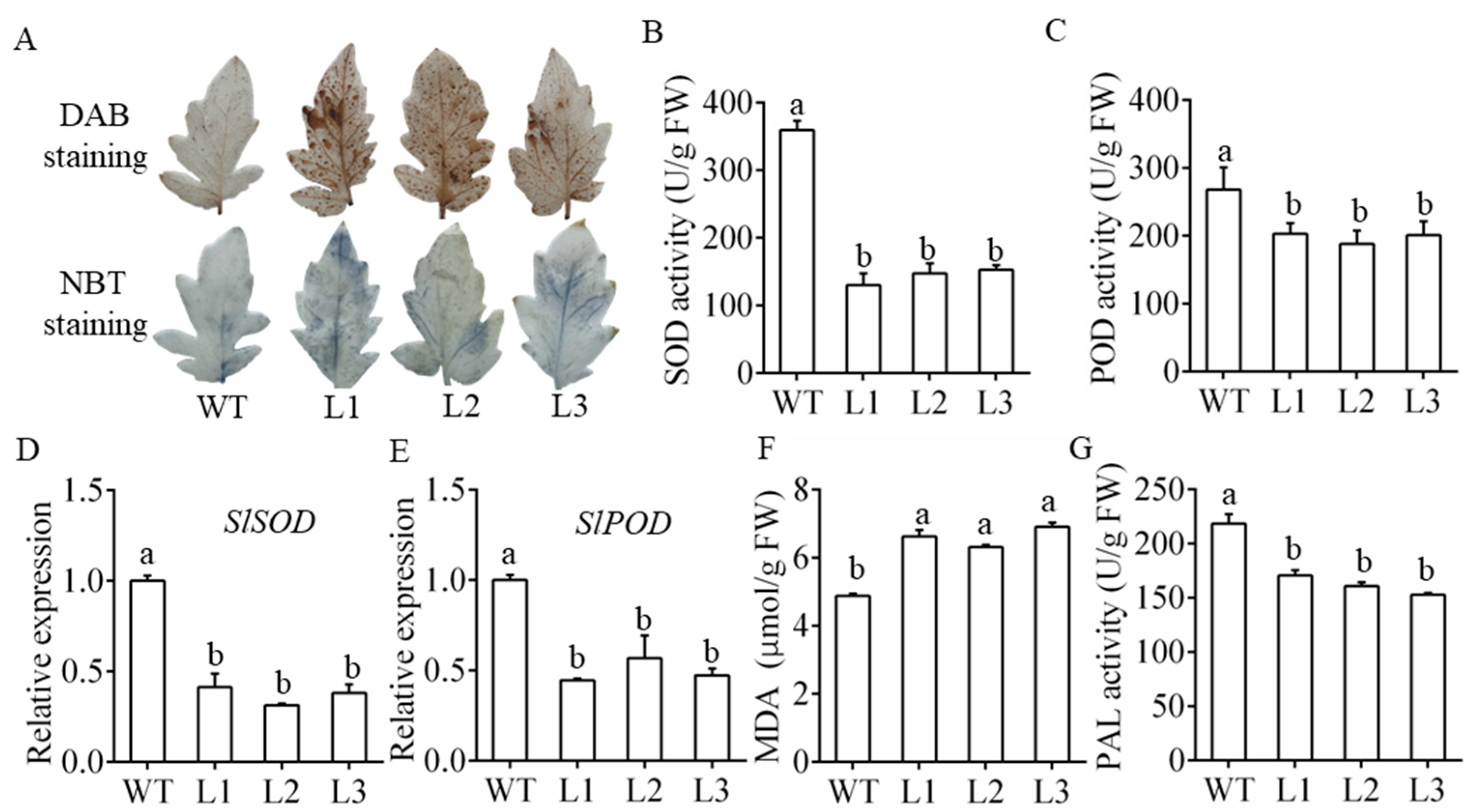
3.4. Overexpression of MiR482c Contributed to Changes in Physiological Indicators
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations Used
| H2O2 | hydrogen peroxide |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| NBT | malondialdehyde |
| O2− | superoxide |
| PAL | phenylalanine ammonia-lyase |
| POD | peroxidase |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative real-time PCR |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| WT | wild type |
References
- Tieman, D.; Zhu, G.; Bies, D.; Beltran, K.S.O.; Fisher, J.; Zemach, I.; Monforte, A.J.; Zamir, D.; Rambla, J.L.; Huang, S.; et al. A chemical genetic roadmap to improved tomato flavor. Science 2017, 355, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Z.J.; Joung, J.G.; Tang, X.M.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, M.Y.; Lee, J.M.; McQuinn, R.; Tieman, D.M.; Alba, R.; Klee, H.J.; et al. Tomato Functional Genomics Database: A comprehensive resource and analysis package for tomato functional genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Data. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Fry, W.E.; Birch, P.R.; Judelson, H.S.; Grunwald, N.J.; Danies, G.; Everts, K.L.; Gevens, A.J.; Gugino, B.K.; Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, S.B.; et al. Five reasons to consider phytophthora infestans a reemerging pathogen. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 966–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicki, M.; Foolad, M.R.; Nowakowska, M.; Kozik, E.U.; Kozik, E.U. Potato and Tomato Late Blight Caused byPhytophthora infestans: An Overview of Pathology and Resistance Breeding. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, B.S.; Lee, S.-J.; Damasceno, C.M.B.; Chakravarthy, S.; Kim, B.-D.; Martin, G.B.; Rose, J.K.C. A secreted effector protein (SNE1) from Phytophthora infestans is a broadly acting suppressor of programmed cell death. Plant J. 2010, 62, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cells 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Gupta, V.K.; Jiang, Y.M.; Yang, B.; Gong, L.; Zhu, H. Cross-Kingdom Small RNAs among Animals, Plants and Microbes. Cell 2019, 8, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ario, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Kim, M. Small RNAs: Big Impact on Plant Development. Trends Plant Science 2017, 22, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, M.-Y.; Li, P.-F.; Cao, J.-M. MicroRNAs in Cardiac Autophagy: Small Molecules and Big Role. Cell 2018, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhai, J.; Li, J.; Han, L.; Meng, J. High-throughput sequencing reveals differential expression of miRNAs in tomato inoculated with Phytophthora infestans. Planta 2015, 241, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, L. A Plant miRNA Contributes to Antibacterial Resistance by Repressing Auxin Signaling. Science 2006, 312, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, B.; Song, X.; Ding, S.; Zheng, L.; Feng, R.; Chen, S.; et al. Osa-miR164a targets OsNAC60 and negatively regulates rice immunity against the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant J. 2018, 95, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Meng, J.; He, X.L.; Zhang, M.; Luan, Y.S. Sly-miR1916 targets multiple target genes and negatively regulates the immune response in tomato. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Zou, Z.; Gong, P.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Ziaf, K.; Li, H.X.; Xiao, F.M.; Ye, Z.B. Over-expression of microRNA169 confers enhanced drought tolerance to tomato. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Han, Z.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Song, W.; et al. Ectopic overexpression of bol-miR171b increases chlorophyll content and results in sterility in broccoli (Brassica oleracea L var. italic). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9588–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Ju, Z.; Cao, D.Y.; Zhai, B.Q.; Qin, G.Z.; Zhu, H.L.; Fu, D.Q.; Luo, Y.B.; Zhu, B.Z. MicroRNA profiling analysis throughout tomato fruit development and ripening reveals potential regulatory role of RIN on microRNAs accumulation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, M.; Miura, S.; Nei, M. Origins and Evolution of MicroRNA Genes in Plant Species. Genome Boil. Evol. 2012, 4, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador-Guirao, R.; Hsing, Y.-I.; Segundo, B.S. The Polycistronic miR166k-166h Positively Regulates Rice Immunity via Post-transcriptional Control of EIN2. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Cui, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, N.; Liu, P.; Meng, J. Effective enhancement of resistance to Phytophthora infestans by overexpression of miR172a and b in Solanum lycopersicum. Planta 2018, 247, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto-Pastor, A.; Santos, B.A.M.C.; Valli, A.A.; Summers, W.; Schornack, S.; Baulcombe, D.C. Enhanced resistance to bacterial and oomycete pathogens by short tandem target mimic RNAs in tomato. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2755–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csukasi, F.; Donaire, L.; Casañal, A.; Martínez-Priego, L.; Botella, M.Á.; Medina-Escobar, N.; Llave, C.; Valpuesta, V.; Martínez-Priego, L.; Medina-Escobar, N. Two strawberry miR159 family members display developmental-specific expression patterns in the fruit receptacle and cooperatively regulate Fa-GAMYB. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, K.; Li, F.; Li, K.; Ning, L.; He, J.; Xin, Z.; Yin, D. Small RNA and degradome deep sequencing reveals the roles of microRNAs in seed expansion in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Cheng, H.; Du, X.; Mao, D.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, X. miR164c and miR168a regulate seed vigor in rice. J. Integr. Plant Boil. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Xie, K.; Xiong, L. Conserved miR164-targeted NAC genes negatively regulate drought resistance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2119–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaprasad, P.V.; Chen, H.-M.; Patel, K.; Bond, D.M.; Santos, B.A.; Baulcombe, D.C. A MicroRNA Superfamily Regulates Nucleotide Binding Site–Leucine-Rich Repeats and Other mRNAs[W][OA]. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, S.; Kloesges, T.; Rose, L.E. Evolutionarily Dynamic, but Robust, Targeting of Resistance Genes by the miR482/2118 Gene Family in the Solanaceae. Genome Boil. Evol. 2015, 7, 3307–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Jeong, D.-H.; De Paoli, E.; Park, S.; Rosen, B.D.; Li, Y.; González, A.J.; Yan, Z.; Kitto, S.L.; Grusak, M.A.; et al. MicroRNAs as master regulators of the plant NB-LRR defense gene family via the production of phased, trans-acting siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2540–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, R.; Kuang, H.; Meyers, B.C. The Diversification of Plant NBS-LRR Defense Genes Directs the Evolution of MicroRNAs That Target Them. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2016, 33, 2692–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchik, M.; Sunkar, R.; Damodharan, S.; Stav, R.; Zohar, M.; Isaacson, T.; Arazi, T. Global and local perturbation of the tomato microRNA pathway by a trans-activated DICER-LIKE 1 mutant. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohorianu, I.; Schwach, F.; Jing, R.; Moxon, S.; Szittya, G.; Sorefan, K.; López-Gomollón, S.; Moulton, V.; Dalmay, T. Profiling of short RNAs during fleshy fruit development reveals stage-specific sRNAome expression patterns. Plant J. 2011, 67, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Pignatta, D.; Bendix, C.; Brunkard, J.O.; Cohn, M.M.; Tung, J.; Sun, H.; Kumar, P.; Baker, B. MicroRNA regulation of plant innate immune receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1790–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Meng, J.; Cui, J.; Sun, G.; Luan, Y. Function identification of miR482b, a negative regulator during tomato resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, S.; Kukuk, A.; Von Dahlen, J.K.; Schnake, A.; Kloesges, T.; Rose, L.E. Expression profiling across wild and cultivated tomatoes supports the relevance of early miR482/2118 suppression for Phytophthora resistance. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhou, X.; Hou, X.; Yang, G.; Meng, J.; Luan, Y. Tomato MYB49 enhances resistance to Phytophthora infestans and tolerance to water deficit and salt stress. Planta 2018, 248, 1487–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, N.; Goyary, D.; Singh, N.K.; Shah, P.; Rathore, M.; Anandhan, S.; Sharma, D.; Arif, M.; Ahmed, Z. Transgenic tomato cv. Pusa Uphar expressing a bacterial mannitol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase gene confers abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2010, 103, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, Z.; Luan, Y. SpWRKY6 acts as a positive regulator during tomato resistance to Phytophthora infestans infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 506, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Luan, Y.; Jiang, N.; Meng, J.; Bao, H. Comparative transcriptome analysis between resistant and susceptible tomato allows the identification of lncRNA16397 conferring resistance to Phytophthora infestans by co-expressing glutaredoxin. Plant J. 2017, 89, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, T.; Santovito, E.; Gallitelli, D.; Cillo, F. Evaluation of reference genes for quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction normalization in infected tomato plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 11, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Feng, Q.; Cao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Chandran, V.; Fan, J.; Zhao, J.; Pu, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Osa-miR167d facilitates infection of Magnaporthe oryzae in rice. J. Integr. Plant Boil. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Tan, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Miao, X.; Shi, Z. The OsmiR396-OsGRF8-OsF3H-flavonoid pathway mediates resistance to the brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Xia, J.; Jiang, C.; Qi, B.; Ling, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Jin, H.; Zhao, H. Bacillus cereus AR156 primes induced systemic resistance by suppressing miR825/825* and activating defense-related genes in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Boil. 2016, 58, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, C. MicroRNA268 Overexpression Affects Rice Seedling Growth under Cadmium Stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5860–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.-F.; Li, W.-F.; Xu, H.-Y.; Qi, L.-W.; Han, S.-Y. Role of cin-miR2118 in drought stress responses in Caragana intermedia and Tobacco. Gene 2015, 574, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdogan, G.; Tufekci, E.D.; Uranbey, S.; Unver, T. miRNA-based drought regulation in wheat. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2016, 16, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvar, V.; Mohorianu, I.; Dalmay, T.; Fellner, M. MicroRNA Regulation of Abiotic Stress Response in Male-Sterile Tomato Mutant. Plant Genome 2015, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Mu, X.; Liu, C.; Cai, J.; Shi, K.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Q. Overexpression of potato miR482e enhanced plant sensitivity toVerticillium dahliaeinfection. J. Integr. Plant Boil. 2015, 57, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, K.; Hirt, H. REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES: Metabolism, Oxidative Stress, and Signal Transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Boil. 2004, 55, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, R.; Yang, Z.; Yao, S.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Song, X.; Jin, L.; Zhou, T.; et al. ROS accumulation and antiviral defence control by microRNA528 in rice. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 16203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, R.; Yu, W.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Sheng, J.; Shen, L. Knockout of SlMAPK3 Reduced Disease Resistance to Botrytis cinerea in Tomato Plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8949–8956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-X.; Oono, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, X.-J.; Wu, J.-M.; Iida, K.; Lu, X.-Y.; Cui, X.; Jin, H.; Zhu, J.-K. The Arabidopsis NFYA5 Transcription Factor Is Regulated Transcriptionally and Posttranscriptionally to Promote Drought Resistance[W]. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2238–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Ge, L.; Liang, R.; Li, W.; Ruan, K.; Lin, H.; Jin, Y. Members of miR-169 family are induced by high salinity and transiently inhibit the NF-YA transcription factor. BMC Mol. Boil. 2009, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, Y.-H.; Meng, J.; He, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Luan, Y.-S. Overexpression of MiR482c in Tomato Induces Enhanced Susceptibility to Late Blight. Cells 2019, 8, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080822
Hong Y-H, Meng J, He X-L, Zhang Y-Y, Luan Y-S. Overexpression of MiR482c in Tomato Induces Enhanced Susceptibility to Late Blight. Cells. 2019; 8(8):822. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080822
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Yu-Hui, Jun Meng, Xiao-Li He, Yuan-Yuan Zhang, and Yu-Shi Luan. 2019. "Overexpression of MiR482c in Tomato Induces Enhanced Susceptibility to Late Blight" Cells 8, no. 8: 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080822
APA StyleHong, Y.-H., Meng, J., He, X.-L., Zhang, Y.-Y., & Luan, Y.-S. (2019). Overexpression of MiR482c in Tomato Induces Enhanced Susceptibility to Late Blight. Cells, 8(8), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080822




