Impact of Cholesterol on Ischemic Stroke in Different Human-Like Hamster Models: A New Animal Model for Ischemic Stroke Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Animals
2.2. Focal Cerebral Ischemic Model
2.3. Analysis of Plasma Lipids in Hamsters on Chow Diet
2.4. Infarct Volume Quantification
2.5. Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Permeability
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Hematologic Parameters
2.9. Statistical Methods
3. Results
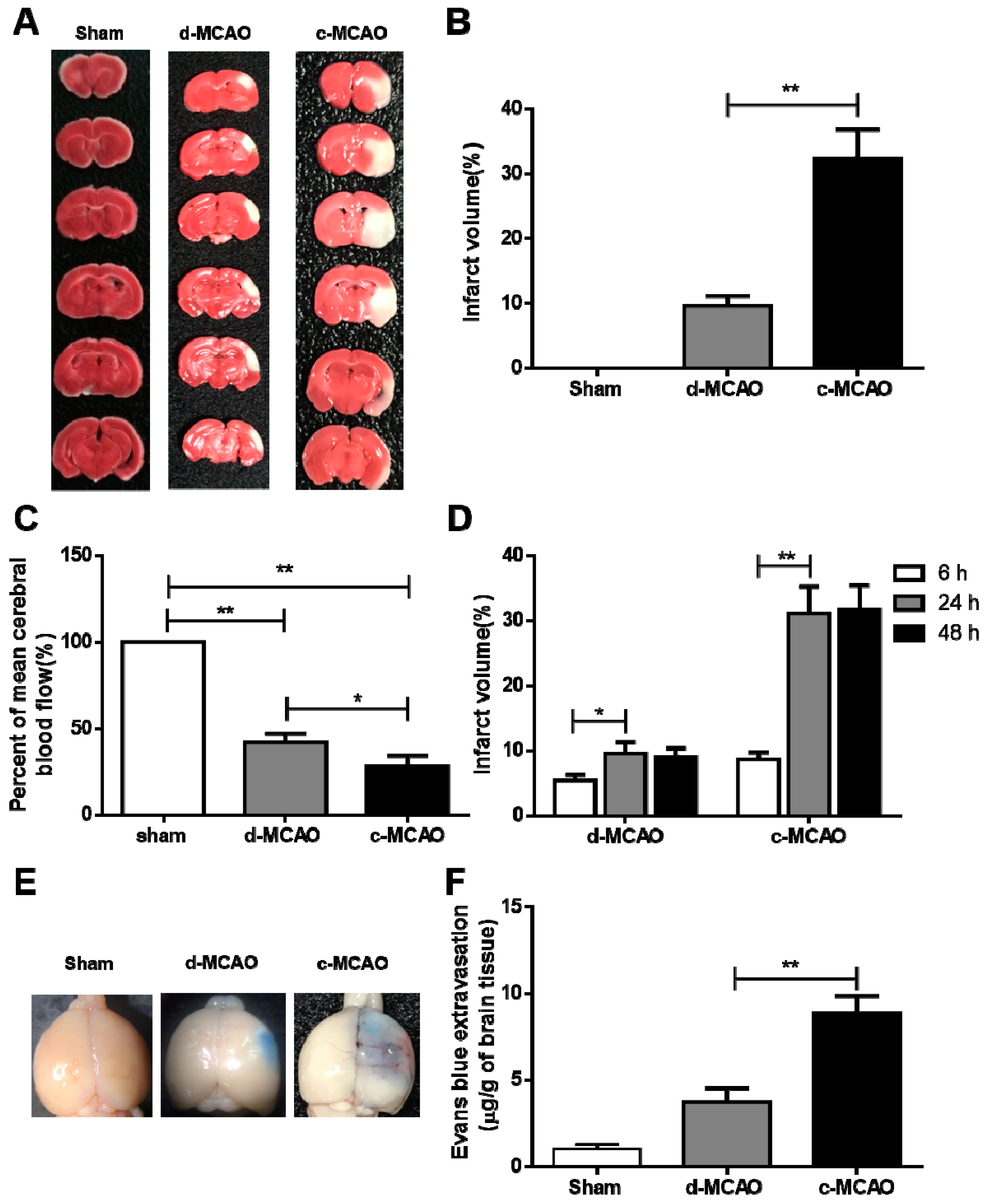
3.1. c-MCAO Significantly Increased the Ischemic Stroke Severity
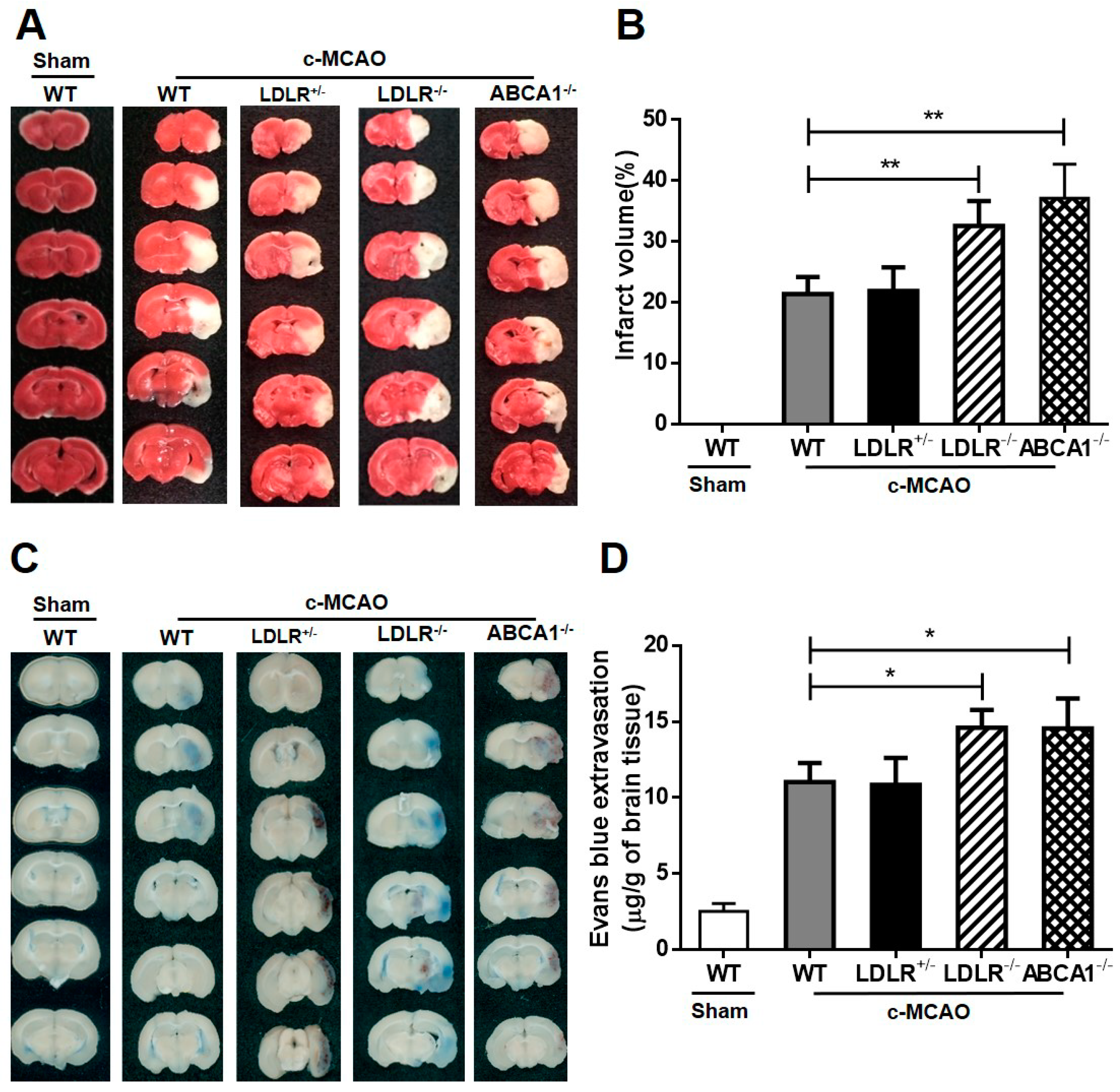
3.2. Effects of LDL-C and HDL-C on Ischemic Stroke in Different Gene-Manipulated Hamster Models.
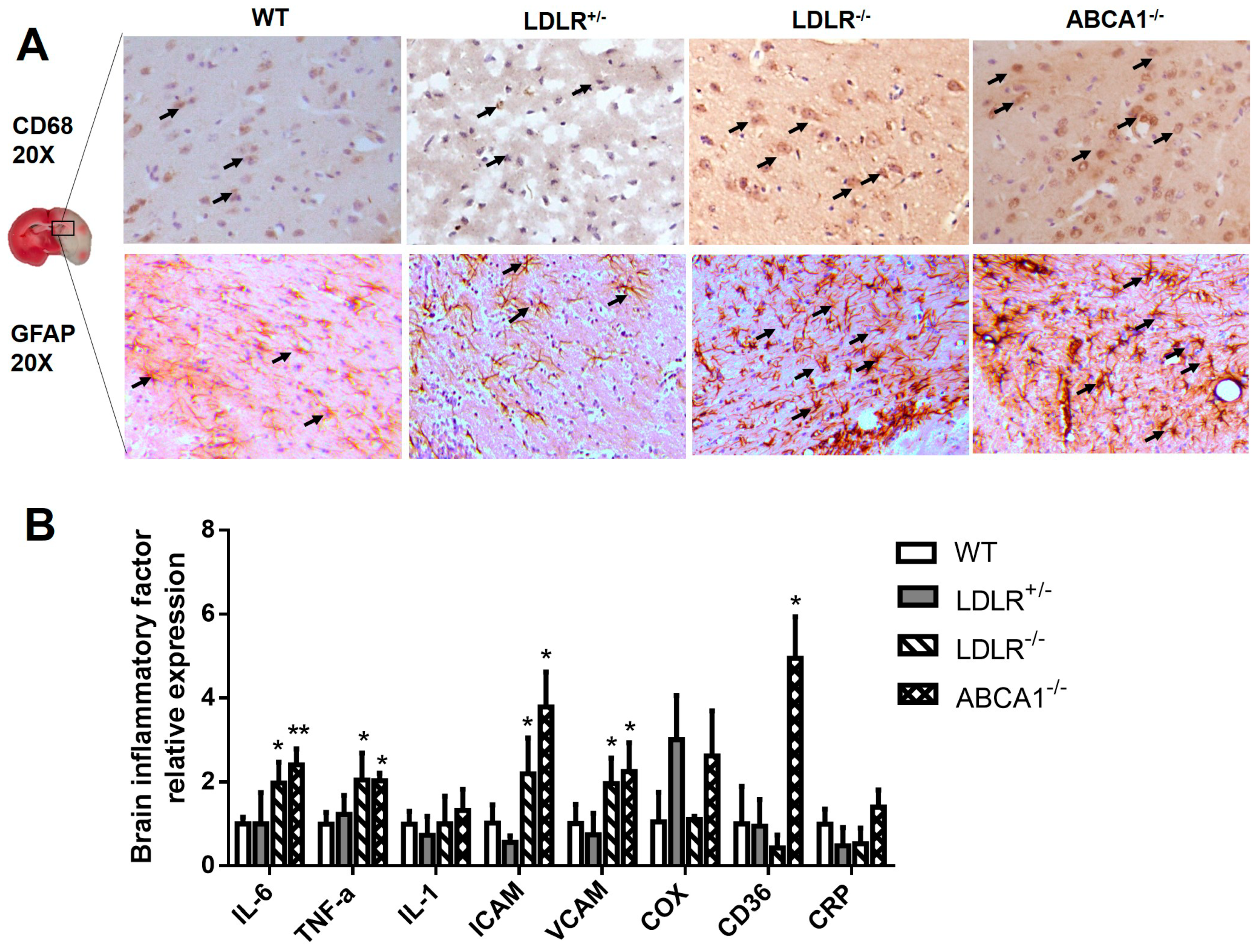
3.3. Enhanced Brain Inflammation in LDLR–/– and ABCA1–/– Hamsters with IS.
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Granitto, M.; Galitz, D. Update on stroke: The latest guidelines. Nurse Pract. 2008, 33, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ye, R.; Yan, T.; Yu, S.P.; Wei, L.; Xu, G.; Fan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Stetler, R.A.; Liu, G.; et al. Cell based therapies for ischemic stroke: From basic science to bedside. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 115, 92–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, V. A review on animal models of stroke: An update. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 122, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, V.; Adeli, K. Postprandial Dyslipidemia: Pathophysiology and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment. EJIFCC 2017, 28, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vallejo-Vaz, A.J.; Robertson, M.; Catapano, A.L.; Watts, G.F.; Kastelein, J.J.; Packard, C.J.; Ford, I.; Ray, K.K. Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Lowering for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Among Men With Primary Elevations of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels of 190 mg/dL or Above: Analyses From the WOSCOPS (West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study) 5-Year Randomized Trial and 20-Year Observational Follow-Up. Circulation 2017, 136, 1878–1891. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Akioyamen, L.E.; Aljenedil, S.; Rivière, J.B.; Ruel, I.; Genest, J. Genetic testing for familial hypercholesterolemia: Impact on diagnosis, treatment and cardiovascular risk. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 2047487319829746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, S.; Madsen, C.M.; Varbo, A.; Benn, M.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Relationship of Familial Hypercholesterolemia and High Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol to Ischemic Stroke. Circulation 2018, 138, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez de Isla, L.; Alonso, R.; Mata, N.; Saltijeral, A.; Muñiz, O.; Rubio-Marin, P.; Diaz-Diaz, J.L.; Fuentes, F.; de Andrés, R.; Zambón, D.; et al. Coronary Heart Disease, Peripheral Arterial Disease, and Stroke in Familial Hypercholesterolaemia: Insights From the SAFEHEART Registry (Spanish Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Cohort Study). Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 2004–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutter, C.M.; Austin, M.A.; Humphries, S.E. Familial hypercholesterolemia, peripheral arterial disease, and stroke: A HuGE minireview. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frikke-Schmidt, R.; Arlien-Søborg, P.; Thorsen, S.; Jensen, H.K.; Vorstrup, S. LDL receptor mutations and ApoB mutations are not risk factors for ischemic cerebrovascular disease of the young, but lipids and lipoproteins are. Eur. J. Neurol. 1999, 6, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rader, D.J.; Hovingh, G.K. HDL and cardiovascular disease. Lancet 2014, 384, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, J.E.; Rong, J.X.; Shamir, R.; Sanson, M.; Vengrenyuk, Y.; Liu, J.; Rayner, K.; Moore, K.; Garabedian, M.; Fisher, E.A. HDL promotes rapid atherosclerosis regression in mice and alters inflammatory properties of plaque monocyte-derived cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7166–7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christiansen-Weber, T.A.; Voland, J.R.; Wu, Y.; Ngo, K.; Roland, B.L.; Nguyen, S.; Peterson, P.A.; Fung-Leung, W.P. Functional loss of ABCA1 in mice causes severe placental malformation, aberrant lipid distribution, and kidney glomerulonephritis as well as high-density lipoprotein cholesterol deficiency. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerterp, M.; Murphy, A.J.; Wang, M.; Pagler, T.A.; Vengrenyuk, Y.; Kappus, M.S.; Gorman, D.J.; Nagareddy, P.R.; Zhu, X.; Abramowicz, S.; et al. Deficiency of ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1 in macrophages increases inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis in mice. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, E.J.; Anthanont, P.; Diffenderfer, M.R.; Polisecki, E.; Asztalos, B.F. Diagnosis and treatment of high density lipoprotein deficiency. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 59, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayden, M.R.; Clee, S.M.; Brooks-Wilson, A.; Genest, J., Jr.; Attie, A.; Kastelein, J.J. Cholesterol efflux regulatory protein, Tangier disease and familial high-density lipoprotein deficiency. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2000, 11, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldoni, F.; Sinke, R.J.; Kuivenhoven, J.A. Mendelian disorders of high-density lipoprotein metabolism. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, S.A.; Llabre, M.M.; Allison, M.A.; Wilkins, J.T.; Mendez, A.J.; Arnan, M.K.; Schneiderman, N.; Sacco, R.L.; Carnethon, M.; Delaney, J.C. HDL cholesterol and stroke risk: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodward, M.; Barzi, F.; Feigin, V.; Gu, D.; Huxley, R.; Nakamura, K.; Patel, A.; Ho, S.; Jamrozik, K. Associations between high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and both stroke and coronary heart disease in the Asia Pacific region. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 2653–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietschy, J.M.; Turley, S.D.; Spady, D.K. Role of liver in the maintenance of cholesterol and low density lipoprotein homeostasis in different animal species, including humans. J. Lipid. Res. 1993, 34, 1637–1659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reaves, S.K.; Wu, J.Y.; Wu, Y.; Fanzo, J.C.; Wang, Y.R.; Lei, P.P.; Lei, K.Y. Regulation of intestinal apolipoprotein B mRNA editing levels by a zinc-deficient diet and cDNA cloning of editing protein in hamsters. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2166–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safronetz, D.; Ebihara, H.; Feldmann, H.; Hooper, J.W. The Syrian hamster model of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. Antivir. Res. 2012, 95, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagai, N.; Vanlinthout, I.; Collen, D. Comparative effects of tissue plasminogen activator, streptokinase, and staphylokinase on cerebral ischemic infarction and pulmonary clot lysis in hamster models. Circulation 1999, 100, 2541–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Gao, M.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Yang, L.; Cong, N.; An, X.; Wang, F.; Qu, K.; Yu, L.; et al. LDL Receptor Gene-ablated Hamsters: A Rodent Model of Familial Hypercholesterolemia With Dominant Inheritance and Diet-induced Coronary Atherosclerosis. EBioMedicine 2018, 27, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Ye, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. Formononetin mediates neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats via downregulation of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and upregulation PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 344, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Qi, R.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. Severe hypertriglyceridemia does not protect from ischemic brain injury in gene-modified hypertriglyceridemic mice. Brain Res. 2016, 1639, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’donnell, M.J.; Xavier, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Chin, S.L.; Rao-Melacini, P.; Rangarajan, S.; Islam, S.; Pais, P.; McQueen, M.J.; et al. Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral haemorrhagic stroke in 22 countries (the INTERSTROKE study): A case-control study. Lancet 2010, 376, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bonilla, L.; Rosell, A.; Torregrosa, G.; Salom, J.B.; Alborch, E.; Gutiérrez, M.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; Martínez-Murillo, R.; Agulla, J.; Ramos-Cabrer, P.; et al. Recommendations guide for experimental animal models in stroke research. Neurologia 2011, 26, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Winkle, J.A.; Chen, B.; Lei, I.F.; Pereira, B.; Rajput, P.S.; Lyden, P.D. Concurrent middle cerebral artery occlusion and intra-arterial drug infusion via ipsilateral common carotid artery catheter in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 2013, 213, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleheen, D.; Khanum, S.; Haider, S.R.; Nazir, A.; Ahmad, U.; Khalid, H.; Hussain, I.; Shuja, F.; Shahid, K.; Habib, A.; et al. A novel haplotype in ABCA1 gene effects plasma HDL-C concentration. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007, 115, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korniluk, A.; Koper-Lenkiewicz, O.M.; Kamińska, J.; Kemona, H.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V. Mean Platelet Volume (MPV): New Perspectives for an Old Marker in the Course and Prognosis of Inflammatory Conditions. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 9213074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licata, G.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Corrao, S.; Di Raimondo, D.; Fernandez, P.; Caruso, C.; Avellone, G.; Pinto, A. Immunoinflammatory activation during the acute phase of lacunar and non-lacunar ischemic stroke: Association with time of onset and diabetic state. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2006, 19, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Di Sciacca, R.; Di Raimondo, D.; Pedone, C.; La Placa, S.; Pinto, A.; Licata, G. Effects of clinical and laboratory variables and of pretreatment with cardiovascular drugs in acute ischaemic stroke: A retrospective chart review from the GIFA study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 151, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, I. Update on the molecular biology of dyslipidemias. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 454, 143–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Xian, X.; Liu, G. Loss of LCAT activity in the golden Syrian hamster elicits pro-atherogenic dyslipidemia and enhanced atherosclerosis. Metabolism 2018, 83, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohula, E.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Giugliano, R.P.; Blazing, M.A.; Park, J.G.; Murphy, S.A.; White, J.A.; Mach, F.; Van de Werf, F.; Dalby, A.J.; et al. Prevention of Stroke with the Addition of Ezetimibe to Statin Therapy in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome in IMPROVE-IT (Improved Reduction of Outcomes: Vytorin Efficacy International Trial). Circulation 2017, 136, 2440–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, S.; Saku, K. Beneficial effects of ezetimibe-based therapy in patients with dyslipidemia. J. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| RBC (1012/L) | WBC (109/L) | HGB (g/L) | HCT (%) | MCV (fl) | MCH (pg) | MCHC (g/L) | PLT (109/L) | MPV (fl) | PDW | LYM | LYM% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 6.3 ± 0.7 | 10.9 ± 1.6 | 145.6 ± 21.6 | 43.15 ± 2.1 | 60.95 ± 3.1 | 20.9 ± 1.6 | 359 ± 44.6 | 343 ± 129 | 4.8 ± 1.7 | 20.9 ± 0.5 | 2.9 ± 0.8 | 36.9 ± 4.1 |
| LDLR+/– | 7.1 ± 0.4 | 9.7 ± 1.1 | 140.8 ± 6.7 | 41.3 ± 1.6 | 61.8 ± 2.4 | 19.9 ± 2.1 | 326.3 ± 39 | 456.7 ± 32.5 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 17.6 ± 0.6 | 5.5 ± 1.7 | 33.5 ± 2.8 |
| LDLR–/– | 8.3 ± 0.7 * | 11.9 ± 1.57 | 153.7 ± 17.4 | 41.1 ± 1.5 | 59.9 ± 2.9 | 21.5 ± 1.8 | 344.8 ± 15.5 | 432.2 ± 18.7 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 17.6 ± 0.5 | 6.3 ± 1.8 * | 52.7 ± 2.5 * |
| ABCA1–/– | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 22.8 ± 2.4 ** | 167.3 ± 3.7 | 42.4 ± 0.9 | 55.9 ± 3.4 | 20.3 ± 1.0 | 413 ± 20.3 | 239.8 ± 33.7 ** | 1.53 ± 0.3 ** | 14.3 ± 0.3 ** | 6.1 ± 1.9* | 51.8 ± 1.9 ** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, L.; Shi, H.; Lin, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Xian, X. Impact of Cholesterol on Ischemic Stroke in Different Human-Like Hamster Models: A New Animal Model for Ischemic Stroke Study. Cells 2019, 8, 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091028
Wei L, Shi H, Lin X, Zhang X, Wang Y, Liu G, Xian X. Impact of Cholesterol on Ischemic Stroke in Different Human-Like Hamster Models: A New Animal Model for Ischemic Stroke Study. Cells. 2019; 8(9):1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091028
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Lili, Haozhe Shi, Xiao Lin, Xin Zhang, Yuhui Wang, George Liu, and Xunde Xian. 2019. "Impact of Cholesterol on Ischemic Stroke in Different Human-Like Hamster Models: A New Animal Model for Ischemic Stroke Study" Cells 8, no. 9: 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091028
APA StyleWei, L., Shi, H., Lin, X., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Liu, G., & Xian, X. (2019). Impact of Cholesterol on Ischemic Stroke in Different Human-Like Hamster Models: A New Animal Model for Ischemic Stroke Study. Cells, 8(9), 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091028




