Hedgehog Signaling in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Abstract
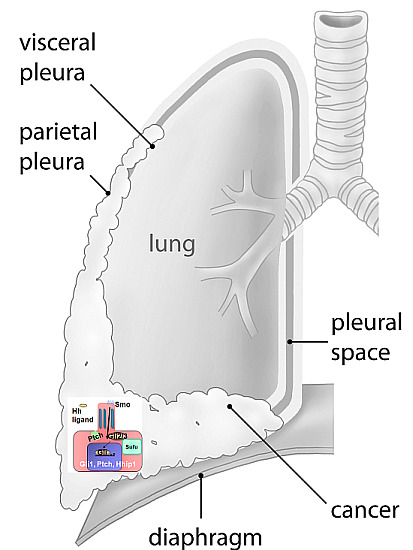
:1. Introduction: Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma

2. The Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in MPM

| Pathway Name | Average No. of Perturbations |
|---|---|
| WT1 (Nephrin/Neph1/Yap/TEAD) | 18 |
| Ephrin A reverse signaling | 13 |
| Syndecan-1-mediated signaling | 11 |
| Hedgehog signaling | 10 |
| IL-4-mediated signaling | 10 |
| Signaling regulated by Ret | 10 |
| Ephrin B reverse signaling | 10 |
| Endothelins | 10 |
| CDKN2A (Rb pathway) | 10 |
| Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network | 9 |

3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, E.K.; Takahashi, K.; Hoshuyama, T.; Cheng, T.J.; Delgermaa, V.; le, G.V.; Sorahan, T. Global magnitude of reported and unreported mesothelioma. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.C.; Sleggs, C.A.; Marchand, P. Diffuse pleural mesothelioma and asbestos exposure in the north western cape province. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1960, 17, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lianes, P.; Remon, J.; Bover, I.; Isla, D. Seom guidelines for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2011, 13, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinaccio, A.; Binazzi, A.; Cauzillo, G.; Cavone, D.; Zotti, R.D.; Ferrante, P.; Gennaro, V.; Gorini, G.; Menegozzo, M.; Mensi, C.; et al. Analysis of latency time and its determinants in asbestos related malignant mesothelioma cases of the italian register. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 2722–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peto, J.; Decarli, A.; La Vecchia, C.; Levi, F.; Negri, E. The european mesothelioma epidemic. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Kratzke, R.A.; Testa, J.R. The pathogenesis of mesothelioma. Semin. Oncol. 2002, 29, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, J.R.; Cheung, M.; Pei, J.; Below, J.E.; Tan, Y.; Sementino, E.; Cox, N.J.; Dogan, A.U.; Pass, H.I.; Trusa, S.; et al. Germline bap1 mutations predispose to malignant mesothelioma. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Rusthoven, J.J.; Symanowski, J.; Denham, C.; Kaukel, E.; Ruffie, P.; Gatzemeier, U.; Boyer, M.; Emri, S.; Manegold, C.; et al. Phase iii study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin vs. cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weder, W.; Kestenholz, P.; Taverna, C.; Bodis, S.; Lardinois, D.; Jerman, M.; Stahel, R.A. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3451–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusch, V.; Baldini, E.H.; Bueno, R.; de Perrot, M.; Flores, R.; Hasegawa, S.; Klepetko, W.; Krug, L.; Lang-Lazdunski, L.; Pass, H.; et al. The role of surgical cytoreduction in the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: Meeting summary of the international mesothelioma interest group congress, 11–14 September 2012, Boston, Mass. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 145, 909–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Tian, D.H.; Pataky, K.A.; Yan, T.D. Systematic review of pleurectomy in the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2013, 81, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.Q.; Yan, T.D.; Bannon, P.G.; McCaughan, B.C. A systematic review of extrapleural pneumonectomy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1692–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Tian, D.; Manganas, C.; Matthews, P.; Yan, T.D. Systematic review of trimodality therapy for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 1, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedberg, J.S. Photodynamic therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma: The future of treatment? Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2011, 5, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilleman, T.R.; Richards, W.G.; Zellos, L.; Johnson, B.E.; Jaklitsch, M.T.; Mueller, J.; Yeap, B.Y.; Mujoomdar, A.A.; Ducko, C.T.; Bueno, R.; et al. Extrapleural pneumonectomy followed by intracavitary intraoperative hyperthermic cisplatin with pharmacologic cytoprotection for treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: A phase II prospective study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 138, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opitz, I.; Lauk, O.; Meerang, M.; Bommeli, C.; Jetter, A.; Günther, D.; Stahel, R.; Weder, W. Mo 14.05 intracavitary cisplatin-fibrin chemotherapy after resection for malignant pleural mesothelioma patients (influence-meso)—Preliminary results. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 343. [Google Scholar]
- Stahel, R.A.; Weder, W.; Felley-Bosco, E.; Petrausch, U.; Curioni-Fontecedro, A.; Schmitt-Opitz, I.; Peters, S. Searching for targets for the systemic therapy of mesothelioma. Ann. Oncol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Moura, U.; Opitz, I.; Soltermann, A.; Rehrauer, H.; Thies, S.; Weder, W.; Stahel, R.A.; Felley-Bosco, E. Role of hedgehog signaling in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4646–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, R.; Joyner, A.L. Roles for hedgehog signaling in adult organ homeostasis and repair. Development 2014, 141, 3445–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, P.T.; McMahon, A.P. Vertebrate hedgehog signalling modulated by induction of a hedgehog-binding protein. Nature 1999, 397, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svard, J.; Heby-Henricson, K.; Persson-Lek, M.; Rozell, B.; Lauth, M.; Bergstrom, A.; Ericson, J.; Toftgard, R.; Teglund, S. Genetic elimination of suppressor of fused reveals an essential repressor function in the mammalian hedgehog signaling pathway. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.F.; Yu, K.P.; Brueckner, M.; Brailey, L.L.; Johnson, L.; McGrath, J.M.; Bale, A.E. Cardiac and cns defects in a mouse with targeted disruption of suppressor of fused. Development 2005, 132, 4407–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbit, K.C.; Aanstad, P.; Singla, V.; Norman, A.R.; Stainier, D.Y.; Reiter, J.F. Vertebrate smoothened functions at the primary cilium. Nature 2005, 437, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, R.; Ai, X.; Fine, A. Derivation of lung mesenchymal lineages from the fetal mesothelium requires hedgehog signaling for mesothelial cell entry. Development 2013, 140, 4398–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, H.; Yue, D.; Wang, C.; Jablons, D.M.; He, B.; Lui, N. SMO expression level correlates with overall survival in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehlenborg, N.; Noble, M.S.; Getz, G.; Chin, L.; Park, P.J. Nozzle: A report generation toolkit for data analysis pipelines. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broad institute tcga genome data analysis center (2014): Paradigm pathway analysis of mrnaseq expression and copy number data. Broad institute of mit and harvard. Available online: http://gdac.broadinstitute.org/runs/analyses__2014_10_17/reports/cancer/MESO-TP/Pathway_Paradigm_RNASeq_And_Copy_Number/nozzle.html (accessed on 12 May 2015).
- Broad institute tcga genome data analysis center (2014): Clustering of mrnaseq gene expression: Consensus nmf. Broad institute of mit and harvard. Available online: http://gdac.broadinstitute.org/runs/analyses__2014_10_17/reports/cancer/MESO-TP/mRNAseq_Clustering_Consensus_Plus/nozzle.html (accessed on 12 May 2015).
- Broad institute tcga genome data analysis center (2014): Correlation between aggregated molecular cancer subtypes and selected clinical features. Broad institute of mit and harvard. Available online: http://gdac.broadinstitute.org/runs/analyses__2014_10_17/reports/cancer/MESO-TP/Correlate_Clinical_vs_Molecular_Subtypes/nozzle.html (accessed on 12 May 2015).
- Lim, C.B.; Prele, C.M.; Cheah, H.M.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Klebe, S.; Reid, G.; Watkins, D.N.; Baltic, S.; Thompson, P.J.; Mutsaers, S.E. Mutational analysis of hedgehog signaling pathway genes in human malignant mesothelioma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teglund, S.; Toftgard, R. Hedgehog beyond medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1805, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuutila, S.; Aalto, Y.; Autio, K.; Bjorkqvist, A.M.; El-Rifai, W.; Hemmer, S.; Huhta, T.; Kettunen, E.; Kiuru-Kuhlefelt, S.; Larramendy, M.L.; et al. DNA copy number losses in human neoplasms. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minobe, K.; Onda, M.; Iida, A.; Kasumi, F.; Sakamoto, G.; Nakamura, Y.; Emi, M. Allelic loss on chromosome 9q is associated with lymph node metastasis of primary breast cancer. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1998, 89, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, D.C.; Vanderveer, L.; Buetow, K.H.; Boente, M.P.; Ozols, R.F.; Hamilton, T.C.; Godwin, A.K. Characterization of chromosome 9 in human ovarian neoplasia identifies frequent genetic imbalance on 9q and rare alterations involving 9p, including cdkn2. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 2150–2157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Islam, F.; Gopalan, V.; Smith, R.A.; Lam, A.K. Translational potential of cancer stem cells: A review of the detection of cancer stem cells and their roles in cancer recurrence and cancer treatment. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 335, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takebe, N.; Miele, L.; Harris, P.J.; Jeong, W.; Bando, H.; Kahn, M.; Yang, S.X.; Ivy, S.P. Targeting notch, hedgehog, and wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodell, M.A.; Brose, K.; Paradis, G.; Conner, A.S.; Mulligan, R.C. Isolation and functional properties of murine hematopoietic stem cells that are replicating in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Schuetz, J.D.; Bunting, K.D.; Colapietro, A.M.; Sampath, J.; Morris, J.J.; Lagutina, I.; Grosveld, G.C.; Osawa, M.; Nakauchi, H.; et al. The abc transporter bcrp1/abcg2 is expressed in a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular determinant of the side-population phenotype. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharenberg, C.W.; Harkey, M.A.; Torok-Storb, B. The abcg2 transporter is an efficient hoechst 33342 efflux pump and is preferentially expressed by immature human hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 2002, 99, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, C.; Opitz, I.; Soltermann, A.; Fischer, B.; Moura, U.; Rehrauer, H.; Weder, W.; Stahel, R.; Felley-Bosco, E. Pleural mesothelioma side populations have a precursor phenotype. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasai, K.; Romer, J.T.; Lee, Y.; Finkelstein, D.; Fuller, C.; McKinnon, P.J.; Curran, T. Shh pathway activity is down-regulated in cultured medulloblastoma cells: Implications for preclinical studies. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4215–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Lombardi, D.G.; Pilozzi, E.; Biffoni, M.; Todaro, M.; Peschle, C.; de Maria, R. Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature 2007, 445, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, V.; Sanchez, P.; de Tribolet, N.; Radovanovic, I.; Ruiz, I.A.A. Hedgehog-gli1 signaling regulates human glioma growth, cancer stem cell self-renewal, and tumorigenicity. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrinello, S.; Samper, E.; Krtolica, A.; Goldstein, J.; Melov, S.; Campisi, J. Oxygen sensitivity severely limits the replicative lifespan of murine fibroblasts. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renganathan, A.; Kresoja-Rakic, J.; Echeverry, N.; Ziltener, G.; Vrugt, B.; Opitz, I.; Stahel, R.A.; Felley-Bosco, E. GAS5 long non-coding RNA in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Mol. Cancer 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerang, M.; Bérard, K.; Felley-Bosco, E.; Vrugt, B.; Boss, A.; Kenkel, D.; Broggini-Tenzel, A.; Stahel, R.; Lauk, O.; Arni, S.; et al. Effects of vismodegib in an orthotopic immunocompetent rat model of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Unpublished data. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yauch, R.L.; Gould, S.E.; Scales, S.J.; Tang, T.; Tian, H.; Ahn, C.P.; Marshall, D.; Fu, L.; Januario, T.; Kallop, D.; et al. A paracrine requirement for hedgehog signalling in cancer. Nature 2008, 455, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.M.; Mohr, A.M.; Hollingsworth, M.A. Sonic hedgehog paracrine signaling regulates metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3513–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, L.D.; Zhang, Y.; Marler, R.J.; Herreros-Villanueva, M.; Zhang, L.; Almada, L.L.; Couch, F.; Wetmore, C.; Pasca di Magliano, M.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E. Loss of the transcription factor gli1 identifies a signaling network in the tumor microenvironment mediating kras oncogene-induced transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11786–11794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amakye, D.; Jagani, Z.; Dorsch, M. Unraveling the therapeutic potential of the hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoRusso, P.M.; Rudin, C.M.; Reddy, J.C.; Tibes, R.; Weiss, G.J.; Borad, M.J.; Hann, C.L.; Brahmer, J.R.; Chang, I.; Darbonne, W.C.; et al. Phase i trial of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (gdc-0449) in patients with refractory, locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2502–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, Y.; Robinson, D.M.; Amakye, D.D.; Rose, K.L.; Cho, Y.J.; Ligon, K.L.; Sharp, T.; Haider, A.S.; Bandaru, R.; Ando, Y.; et al. A five-gene hedgehog signature developed as a patient preselection tool for hedgehog inhibitor therapy in medulloblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberger, F.; Ruiz, I.A.A. Context-dependent signal integration by the gli code: The oncogenic load, pathways, modifiers and implications for cancer therapy. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 33, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedres, S.; Montero, M.A.; Martinez, P.; Martinez, A.; Rodriguez-Freixinos, V.; Torrejon, D.; Gabaldon, A.; Salcedo, M.; Ramon, Y.C.S.; Felip, E. Exploratory analysis of activation of pten-pi3k pathway and downstream proteins in malignant pleural mesothelioma (mpm). Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitanihirwe, B.K.; Meerang, M.; Friess, M.; Soltermann, A.; Frischknecht, L.; Thies, S.; Felley-Bosco, E.; Tsao, M.S.; Allo, G.; de Perrot, M.; et al. Pi3k/mtor signaling in mesothelioma patients treated with induction chemotherapy followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Yen, C.J.; Xia, W.; Izzo, J.G.; Lang, J.Y.; Li, C.W.; Hsu, J.L.; Miller, S.A.; Wang, X.; et al. The crosstalk of mtor/s6k1 and hedgehog pathways. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, J.; Gardner, D.; Beachy, P.A. Arsenic antagonizes the hedgehog pathway by preventing ciliary accumulation and reducing stability of the Gli2 transcriptional effector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13432–13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchamp, E.M.; Ringer, L.; Bulut, G.; Sajwan, K.P.; Hall, M.D.; Lee, Y.C.; Peaceman, D.; Ozdemirli, M.; Rodriguez, O.; Macdonald, T.J.; et al. Arsenic trioxide inhibits human cancer cell growth and tumor development in mice by blocking hedgehog/gli pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Nagano, S.; Nagao, H.; Ishidou, Y.; Yokouchi, M.; Abematsu, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Komiya, S.; Setoguchi, T. Arsenic trioxide prevents osteosarcoma growth by inhibition of gli transcription via DNA damage accumulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauth, M.; Bergstrom, A.; Shimokawa, T.; Toftgard, R. Inhibition of gli-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8455–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonnissen, A.; Isebaert, S.; Haustermans, K. Targeting the hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: Beyond smoothened. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13899–13913. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lui, N.; Cheng, T.; Tseng, H.H.; Yue, D.; Giroux-Leprieur, E.; Do, H.T.; Sheng, Q.; Jin, J.Q.; Luh, T.W.; et al. Gli as a novel therapeutic target in malignant pleural mesothelioma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.B.; Prele, C.M.; Baltic, S.; Arthur, P.G.; Creaney, J.; Watkins, D.N.; Thompson, P.J.; Mutsaers, S.E. Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species drive GANT61-induced mesothelioma cell apoptosis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- You, M.; Varona-Santos, J.; Singh, S.; Robbins, D.J.; Savaraj, N.; Nguyen, D.M. Targeting of the hedgehog signal transduction pathway suppresses survival of malignant pleural mesothelioma cells in vitro. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Felley-Bosco, E.; Opitz, I.; Meerang, M. Hedgehog Signaling in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Genes 2015, 6, 500-511. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030500
Felley-Bosco E, Opitz I, Meerang M. Hedgehog Signaling in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Genes. 2015; 6(3):500-511. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030500
Chicago/Turabian StyleFelley-Bosco, Emanuela, Isabelle Opitz, and Mayura Meerang. 2015. "Hedgehog Signaling in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma" Genes 6, no. 3: 500-511. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030500
APA StyleFelley-Bosco, E., Opitz, I., & Meerang, M. (2015). Hedgehog Signaling in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Genes, 6(3), 500-511. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030500