Characteristics of PM10 Level during Haze Events in Malaysia Based on Quantile Regression Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Air Pollutant Dataset
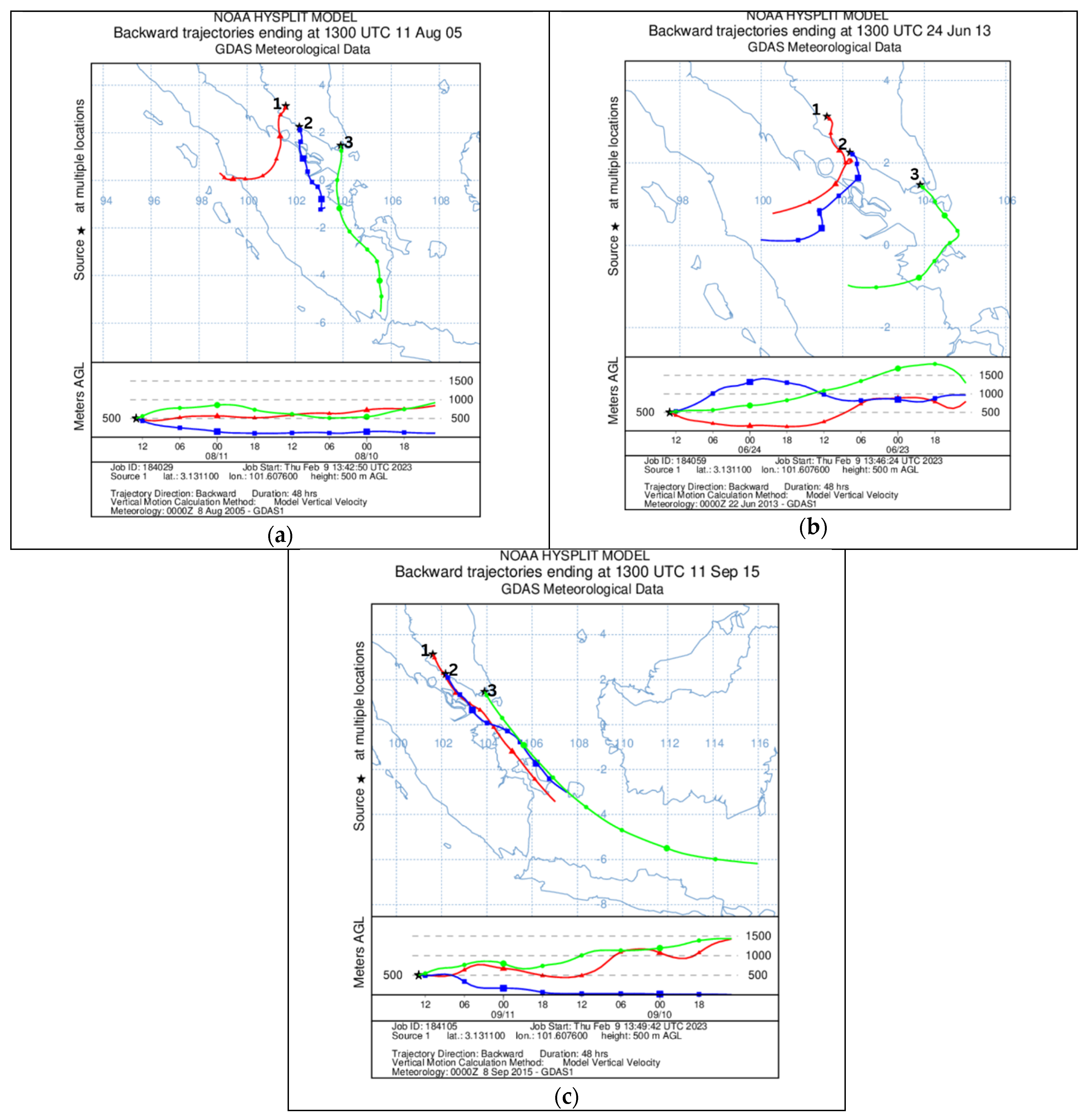
2.3. Trajectory Analysis
2.4. Measure of Association using Pearson Correlation
- r = correlation coefficient
- xi = values of the x-variable in a sample
- = mean of values of the x-variable
- yi = values of the y-variable in a sample
- = mean of values of the y-variable
2.5. Prediction Models
2.5.1. Multiple Linear Regression (MLR)
2.5.2. Quantile Regression (QR)
2.5.3. Performance Indicator
- where
- n = total number of hourly measurements of particular site;
- = predicted values of one set of hourly monitoring record;
- = observed values of one set of hourly monitoring record;
- = mean of the predicted values of one set of hourly monitoring record;
- = mean of the observed values of one set of hourly monitoring record;
- = standard deviation of the predicted values;
- = standard deviation of the observed values of one set.
3. Results and Discussion
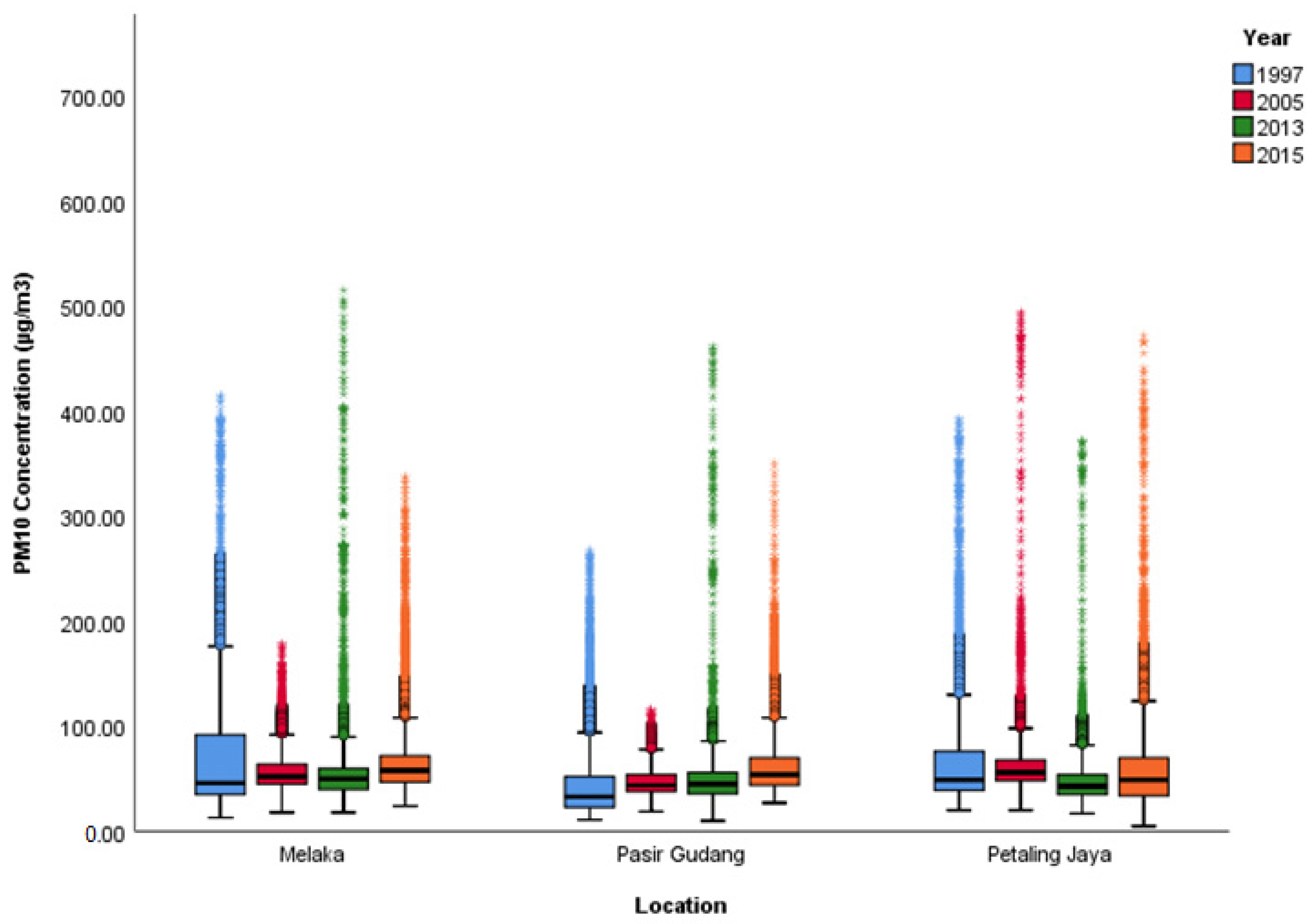
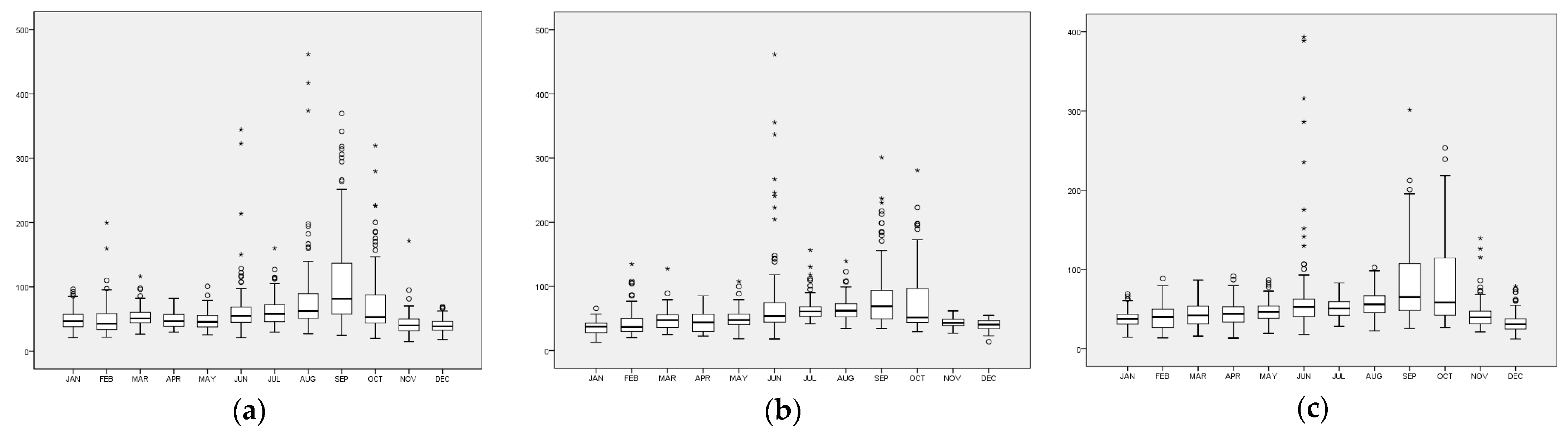
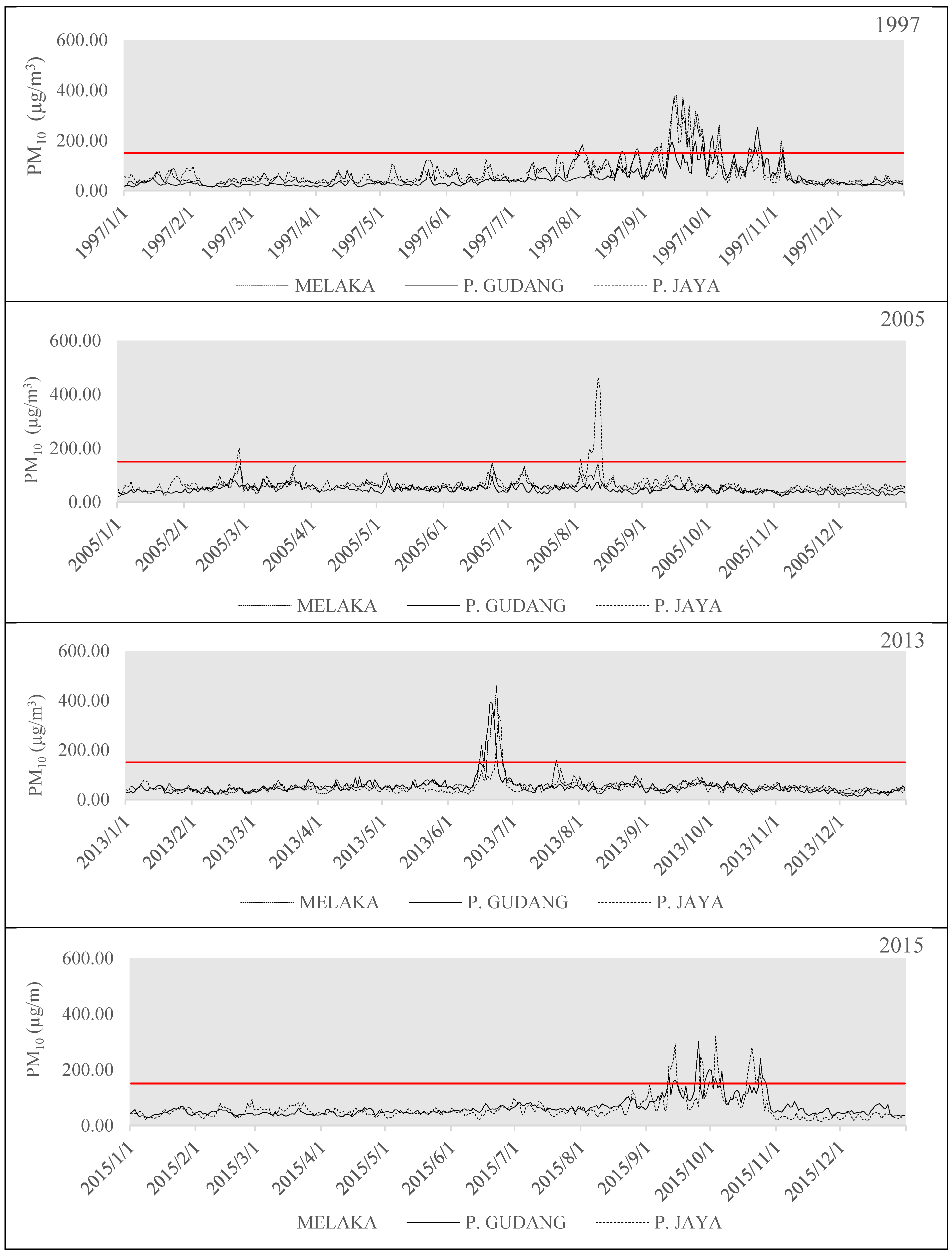
3.1. Variation of PM10 Level during Haze Event
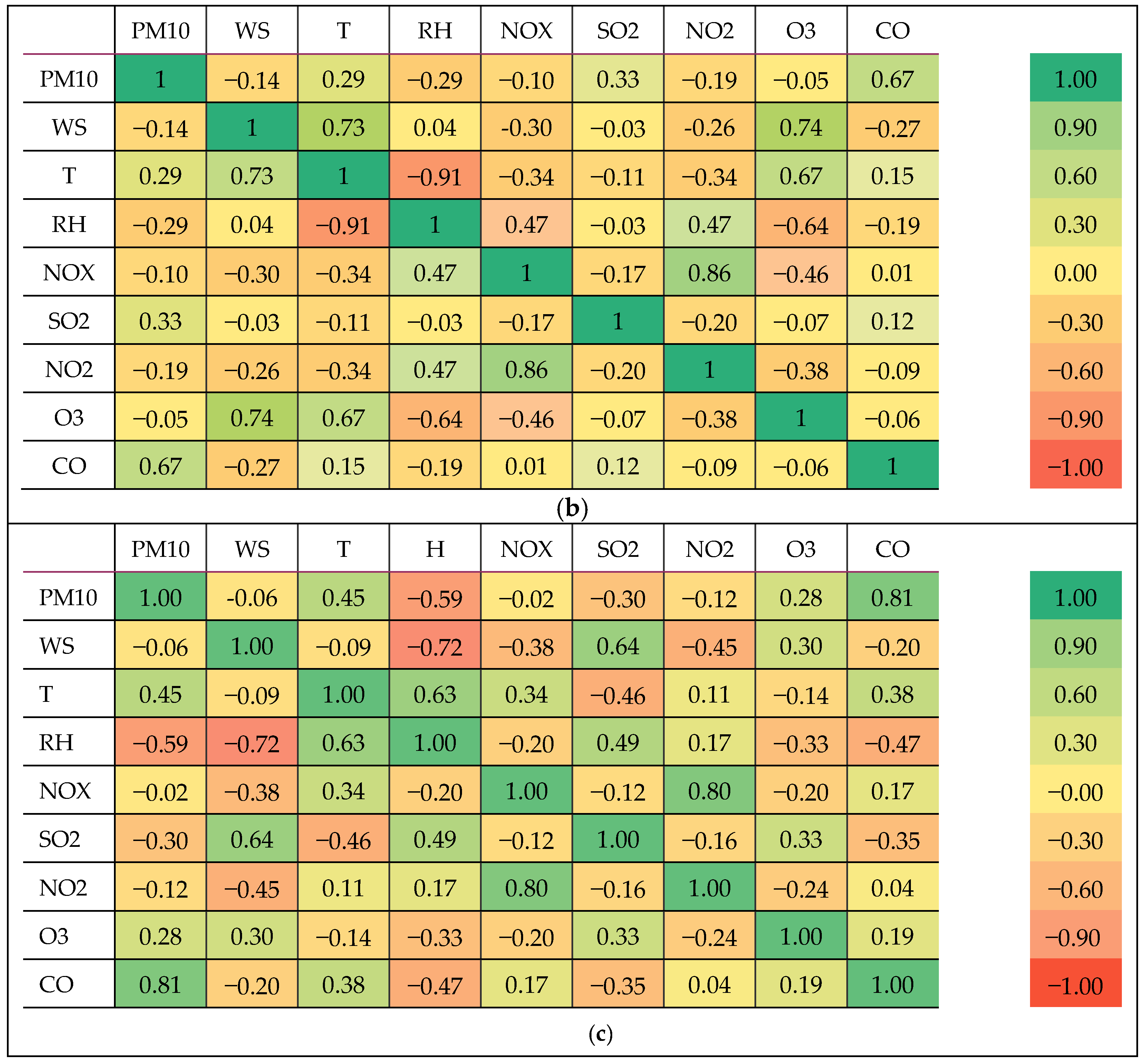
3.2. Association of PM10 Level with Other Air Pollutants and Weather Parameter during HPE
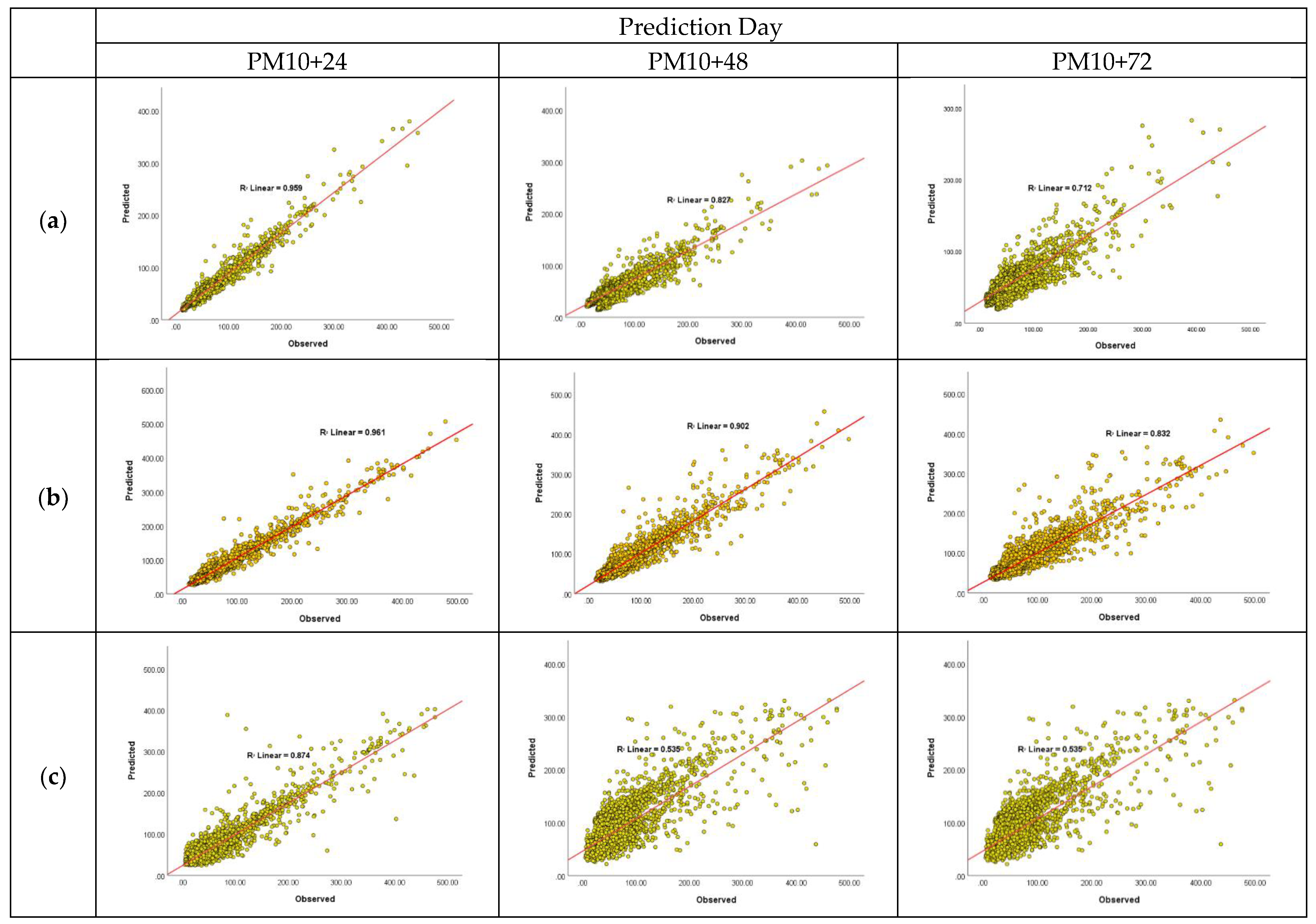
3.3. Predictive Models and Their Performances
3.4. Comparing the Effectiveness of the Quantile Regression (QR) with Other Predictive Models
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latif, M.T.; Dominick, D.; Ahamad, F.; Khan, M.F.; Juneng, L.; Hamzah, F.M.; Nadzir, M.S.M. Long term assessment of air quality from a background station on the Malaysian Peninsular. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, S.; Ismail, M.; Samat, N.N.A.; Ahmed, A.N. Modelling Particulate Matter (PM10) Concentration in Industrialized Area: A Comparative Study of Linear and Nonlinear Algorithms. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2019, 13, 8227–8235. [Google Scholar]
- Awang, M.B.; Jaafar, A.B.; Abdullah, A.M.; Ismail, M.B.; Hassan, M.N.; Abdullah, R.; Johan, S.; Noor, H. Air quality in Malaysia: Impacts, management issues and future challenges. Respirology 2000, 5, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Environment. Malaysia Environmental Quality Report 2015; Department of Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, D.; Jessup, T. Indonesia’s Fires and Haze: The Cost of Catastrophe; Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, International Development Research Centre: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Environment. Malaysia Environmental Quality Report 2005; Department of Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Environment. Malaysia Environmental Quality Report 2013; Department of Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Norela, S.; Saidah, M.S.; Mahmud, M. Chemical composition of the haze in Malaysia 2005. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahani, M.; Zainon, N.A.; Wan Mahiyuddin, W.R.; Latif, M.T.; Hod, R.; Khan, M.F.; Tahir, N.M.; Chan, C.C. A case-crossover analysis of forest fire haze events and mortality in Malaysia. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 96, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijnen, V.; Wooster, M.J.; Kaiser, J.W.; Gaveau, D.L.A.; Flemming, J.; Parrington, M. Fire carbon emissions over maritime southeast Asia in 2015 largest since 1997. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.M.; Yahaya, A.S.; Ramli, N.A.; Luca, F.A.; Al Bakri Abdullah, M.M.; Sandu, A.V. Variation of air pollutant (particulate matter-PM10) in peninsular Malaysia: Study in the southwest coast of peninsular Malaysia. Rev. Chim. 2015, 66, 1443–1447. [Google Scholar]
- Alifa, M.; Bolster, D.; Mead, M.I.; Latif, M.T.; Crippa, P. The influence of meteorology and emissions on the spatio-temporal variability of PM10 in Malaysia. Atmos Res. 2020, 246, 105107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payus, C.; Abdullah, N.; Sulaiman, N. Airborne Particulate Matter and Meteorological Interactions during the Haze Period in Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2013, 4, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afzali, A.; Rashid, M.; Sabariah, B.; Ramli, M. PM10 Pollution: Its prediction and meteorological influence in Pasir Gudang, Johor. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 18, 012100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gvozdić, V.; Kovač-Andrić, E.; Brana, J. Influence of Meteorological Factors NO2, SO2, CO and PM10 on the Concentration of O3 in the Urban Atmosphere of Eastern Croatia. Environ. Model. Assess. 2009, 16, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar, S.; Oztop, H.F.; Akpinar, E.K. Evaluation of relationship between meteorological parameters and air pollutant concentrations during winter season in Elaziğ, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 46, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, S.; Napi, N.N.L.M.; Ahmed, A.N.; Mansor, W.N.W.; Mansor, A.A.; Ismail, M.; Abdullah, A.M.; Ramly, Z.T.A. Development of multiple linear regression for particulate matter (PM10) forecasting during episodic transboundary haze event in Malaysia. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, S.Y.; Abdullah, S.; Ismail, M. Forecasting of Particulate Matter (PM10) Concentration Based On Gaseous Pollutants And Meteorological Factors For Different Monsoons Of Urban Coastal Area In Terengganu. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2018, 5, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, S.; Ismail, M.; Fong, S.Y.; Ahmed, A.N. Evaluation for Long Term PM10 Concentration Forecasting using Multi Linear Regression (MLR) and Principal Component Regression (PCR) Models. EnvironmentAsia 2016, 9, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Yahaya, A.S.; Ramli, A.; Hamid, H.A. Future PM 10 Concentration Prediction Using Quantile Regression Models. IPCBEE 2012, 37, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Baur, D.; Saisana, M.; Schulze, N. Modelling the Effects of Meteorological Variables on Ozone Concentration–A Quantile Regression Approach. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4689–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, A.S.; Munir, S.; Habeebullah, T.M. Comparing the performance of statistical models for predicting PM10 concentrations. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lingxin, H.; Naiman, D.Q. Quantile Regression; Sage Publications: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kudryavtsev, A.A. Using quantile regression for rate-making. Insur. Math. Econ. 2009, 45, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.Y.; Awang, N. Quantile regression for analysing PM10 concentrations in Petaling Jaya. Mal. J. Fund. Appl. Sci. 2017, 13, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S. Modelling the non-linear association of particulate matter (PM10) with meteorological parameters and other air pollutants—A case study in Makkah. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Fan, S.; Guo, H.; Gao, B.; Sun, J.; Chen, L. Assessing the impact of local meteorological variables on surface ozone in Hong Kong during 2000–2015 using quantile and multiple line regression models. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteor. 2015, 96, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogtay, N.J.; Thatte, U.M. Principles of correlation analysis. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2017, 65, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sukatis, F.F.; Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Noor, N.M.; Zakaria, N.A.; Suwardi, A. Estimation of Missing Values in Air Pollution Dataset by Using Various Imputation Methods. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2019, 10, 791–804. [Google Scholar]
- Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Yahaya, A.S.; Ramli, N.A.; Hamid, H.A. Performance of multiple linear regression model for longterm PM10 concentration prediction based on gaseous and meteorological parameters. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 12, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneng, L.; Latif, M.T.; Tangang, F.T.; Mansor, H. Spatio-temporal characteristics of PM10 concentration across Malaysia. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4584–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneng, L.; Latif, M.T.; Tangang, F. Factors influencing the variations of PM10 aerosol dust in Klang Valley, Malaysia during the summer. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4370–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, A.; Goldammer, J. Smoke-haze pollution: A review of the 1997 episode in Southeast Asia. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2001, 2, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Huang, W. Tracking the Indonesian forest fire using NOAA/AVHRR images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleiman, A.; Othman, M.; Samah, A.A.; Sulaiman, N.M.; Radojevic, M. The occurrence of haze in Malaysia: A case study in an urban industrial area. In Air Quality; Rao, G.V., Raman, S., Singh, M.P., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2003; pp. 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsuddin, N.A.C.; Khan, M.F.; Maulud, K.N.A.; Hamid, A.H.; Munna, F.T.; Rahim, M.A.A.; Latif, M.T.; Akhtaruzzaman, M. Local and transboundary factors’ impacts on trace gases and aerosol during haze episode in 2015 El Niño in Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Show, D.L.; Chang, S.-C. Atmospheric impacts of Indonesian fire emissions: Assessing Remote Sensing Data and Air Quality During 2013 Malaysian Haze. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.F.; Hamid, A.H.; Rahim, H.A.; Maulud, K.N.A.; Latif, M.T.; Nadzir, M.S.M. El Niño driven haze over the Southern Malaysian Peninsula and Borneo. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockwell, C.E.; Jayarathne, T.; Cochrane, M.A.; Ryan, K.C.; Putra, E.I.; Saharjo, B.H.; Ati, D.N.; Israr, A.; Donald, R.B.; Isobel, J.S.; et al. Field measurements of trace gases and aerosols emitted by peatland fires in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia during the 2015 El Niño. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11711–11732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grivas, G.; Chaloulakou, A.; Samara, C.; Spyrellis, N. Spatial and Temporal Variation of PM10 Mass Concentrations within the Greater Area of Athens, Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 158, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Zheng, W.; Yin, L. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of haze and pollution particles in China based on spatial statistics. Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Cheng, J.; Kang, S.; Stocker, R.; He, X.; Yao, M.; Wang, J. Effects of relative humidity on heterogeneous reaction of SO2 with CaCO3 particles and formation of CaSO4·2H2O crystal as secondary aerosol. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 268, 118776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah, A.Z.A.; Yau, Y.H.; Chew, B.T. Thermal Comfort Temperature Range for Industry Workers in a Factory in Malaysia. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2016, 5, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Schlink, U.; Thiem, A.; Kohajda, T.; Richter, M.; Strebel, K. Quantile regression of indoor air concentrations of volatile organic compound (VOC). Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3840–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.M.; Noor, N.M.; Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Sandu, A.V.; Vizureanu, P.; Deák, G.; Kheimi, M. Forecasting Daytime Ground-Level Ozone Concentration in Urbanized Areas of Malaysia Using Predictive Models. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaziayani, W.N.; Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Ahmat, H.; Al-Jumeily, D. Coupling of quantile regression into boosted regression trees (BRT) technique in forecasting emission model of PM10 concentration. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 1647–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W. Chapter 5-Machine learning for spatiotemporal big data in air pollution. In Spatiotemporal Analysis of Air Pollution and Its Application in Public Health; Li, L., Zhou, X., Tong, W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yin, L. Smog prediction based on the deep belief-BP neural network model (DBN-BP). Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Huang, W.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W.; Liu, S. A haze prediction method based on one-dimensional convolutional neural network. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaziayani, W.N.; Ahmat, H.; Razak, T.R.; Zainan Abidin, A.W.; Warris, S.N.; Asmat, A.; Noor, N.M.; Ul-Saufie, A.Z. A Novel Hybrid Model Combining the Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Boosted Regression Trees (BRT) Technique in Predicting PM10 Concentration. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Location | Station | Coordinates | Background of Study Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Petaling Jaya | Bandar Utama Primary School | 3.1311° N 101.6076° E | Heavy traffic particulars during the morning hour Industrial area and housing |
| Melaka | Bukit Rambai Secondary School | 2.2587° N 102.1729° E | Agriculture Residential area and housing |
| Pasir Gudang | Pasir Gudang 2 Secondary School | 1.4703° N 103.8956° E | Heavy industrial areas Commercial land Transportation and logistics |
| Air Quality and Weather Parameters | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particulate matter | PM10 | µg/m3 |
| Ground-level ozone | O3 | ppm |
| Nitrogen oxides | NOx | ppm |
| Nitrogen dioxides | NO2 | ppm |
| Sulfur dioxides | SO2 | ppm |
| Carbon monoxide | CO | ppm |
| Temperature | T | °C |
| Relative humidity | RH | % |
| Wind Speed | WS | km/h |
| Value of r | Description |
|---|---|
| 0.0–0.3 | Weak |
| 0.3–0.6 | Moderate |
| 0.6–1.0 | Strong |
| Performance Indicators | Equation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mean absolute error (MAE) | When the value of MAE is closer to zero, it indicates better method. | |
| Root mean square deviation (RMSE) | When the value of RMSE is closer to zero, it indicates better method. | |
| Coefficient of determination (R2) | When the value of R2 is closer to one, it indicates better method. | |
| Index of agreement (IA) | When the value of IA is closer to one, it indicates better method. |
| Place/ Year | Pasir Gudang | Melaka | Petaling Jaya | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1997 | 2005 | 2013 | 2015 | 1997 | 2005 | 2013 | 2015 | 1997 | 2005 | 2013 | 2015 | ||
| Total value, N | Valid | 8631 | 8715 | 8745 | 8710 | 8337 | 8669 | 8669 | 8759 | 8222 | 8727 | 8659 | 8591 |
| Missing | 129 | 45 | 15 | 50 | 423 | 91 | 91 | 1 | 538 | 33 | 101 | 169 | |
| Mean | 47.7 | 46.59 | 51 | 64.8 | 71.7 | 83.3 | 79.2 | 69.7 | 69.4 | 64.3 | 48.4 | 60.5 | |
| Median | 33.0 | 44.0 | 45.0 | 54.0 | 46.0 | 78.0 | 72.0 | 58.0 | 49.0 | 56.0 | 43.0 | 49.0 | |
| Standard deviation | 39.9 | 13.7 | 38.4 | 36.1 | 61.6 | 27.4 | 42.8 | 41.5 | 55.1 | 40.7 | 29.3 | 50.1 | |
| Minimum | 11 | 19 | 10 | 27 | 13.0 | 29 | 32 | 24 | 20 | 20 | 17 | 5 | |
| Maximum | 268 | 116 | 462 | 351 | 415.0 | 268 | 577 | 338 | 393 | 494 | 372 | 472 | |
| Area | Selected Parameter |
|---|---|
| Petaling Jaya | CO Temperature |
| Melaka | CO RH SO2 Temperature |
| Pasir Gudang | CO RH Temperature SO2 |
| Area | Method | Quantile | Prediction Day | PM10 | WS | T | RH | NOx | SO2 | NO2 | O3 | CO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pasir Gudang | MLR | Mean | PM10+24 | 0.791 | −0.097 | 0.228 | −0.036 | 0.015 | 0.041 | 0.107 | 0.006 | 1.701 |
| PM10+48 | 0.610 | −0.181 | 0.788 | −0.006 | −0.069 | 0.213 | −0.139 | −0.071 | 0.800 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.482 | −0.352 | 1.428 | 0.095 | −0.104 | 0.213 | −0.037 | −0.100 | −3.572 | |||
| QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 0.471 | −0.115 | −0.111 | −0.118 | 0.021 | 0.206 | 0.072 | −0.078 | −0.409 | |
| PM10+48 | 0.272 | 0.057 | 0.282 | −0.033 | 0.170 | 0.54 | 0.002 | −0.089 | −1.271 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.169 | 0.009 | 0.574 | 0.030 | 0.025 | 0.428 | −0.100 | −0.139 | −0.810 | |||
| 0.50 | PM10+24 | 0.679 | −0.112 | 0.154 | −0.035 | −0.058 | 0.212 | −0.034 | −0.067 | −0.537 | ||
| PM10+48 | 0.529 | −0.193 | 0.424 | −0.029 | −0.100 | 0.355 | 0.084 | −0.045 | −2.021 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.429 | −0.163 | 0.673 | 0.025 | −0.083 | 0.391 | −0.025 | −0.027 | −3.761 | |||
| 0.75 | PM10+24 | 0.772 | −0.173 | 0.732 | 0.082 | −0.015 | 0.270 | −0.018 | 0.067 | 0.683 | ||
| PM10+48 | 0.704 | −0.243 | 0.687 | 0.037 | −0.203 | 0.216 | 0.093 | 0.036 | −1.092 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.580 | −0.183 | 0.860 | 0.089 | −0.139 | 0.284 | 0.031 | 0.094 | −3.843 | |||
| Pearson–QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 0.585 | −0.108 | −0.086 | 0.125 | −0.682 | |||||
| PM10+48 | 0.385 | 0.263 | −0.065 | 0.499 | −1.373 | |||||||
| PM10+72 | 0.310 | 0.586 | 0.021 | 0.320 | −1.958 | |||||||
| 0.50 | PM10+24 | 0.678 | 0.177 | −0.010 | 0.229 | −0.487 | ||||||
| PM10+48 | 0.533 | 0.415 | 0.012 | 0.370 | −1.981 | |||||||
| PM10+72 | 0.429 | 0.682 | 0.061 | 0.404 | −3.580 | |||||||
| 0.75 | PM10+24 | 0.771 | 0.700 | 0.110 | 0.319 | 1.011 | ||||||
| PM10+48 | 0.702 | 0.639 | 0.076 | 0.260 | −0.601 | |||||||
| PM10+72 | 0.587 | 0.855 | 0.129 | 0.314 | −3.896 | |||||||
| Melaka | MLR | Mean | PM10+24 | 0.771 | –0.275 | –0.004 | –0.195 | 100.596 | 29.012 | –53.149 | 17.090 | 0.483 |
| PM10+48 | 0.663 | –0.221 | –0.121 | –0.207 | 63.996 | 204.937 | –91.668 | 18.432 | 1.021 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.594 | –0.205 | –0.009 | –0.198 | 63.783 | 208.651 | 144.208 | 41.880 | 0.737 | |||
| QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 0.549 | 0.037 | –0.695 | –0.193 | 21.083 | −52.16 | 151.800 | 61.620 | 0.531 | |
| PM10+48 | 0.430 | 0.084 | –1.023 | –0.245 | –5.578 | –143.956 | 159.496 | 50.740 | –0.477 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.325 | 0.170 | –0.897 | –0.218 | –23.562 | –60.339 | 246.029 | 57.959 | –0.376 | |||
| 0.50 | PM10+24 | 0.766 | –0.132 | –0.201 | –0.108 | 4.391 | –7.639 | 105.473 | 23.218 | 1.313 | ||
| PM10+48 | 0.578 | –0.105 | –0.342 | –0.118 | 23.58 | –48.032 | 159.496 | 50.74 | 0.477 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.581 | –0.250 | –0.391 | –0.117 | 13.265 | –79.94 | 132.925 | 24.141 | –0.655 | |||
| 0.75 | PM10+24 | 0.860 | 0.218 | 0.227 | 0.068 | 48.006 | 173.937 | 42.777 | 22.264 | 8.331 | ||
| PM10+48 | 0.778 | –0.166 | 0.134 | –0.088 | 33.346 | 86.984 | 15.279 | –17.932 | 6.667 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.732 | –0.05 | –0.135 | –0.113 | 14.284 | 162.531 | 45.815 | –18.58 | 6.259 | |||
| Pearson–QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 0.567 | –0.685 | –0.201 | –29.625 | 0.823 | |||||
| PM10+48 | 0.447 | –0.932 | –0.249 | –112.707 | –0.340 | |||||||
| PM10+72 | 0.857 | 0.196 | –0.068 | –172.322 | 9.725 | |||||||
| 0.50 | PM10+24 | 0.776 | –0.135 | –0.099 | 36.943 | 1.824 | ||||||
| PM10+48 | 0.583 | –0.296 | –0.105 | –14.280 | 1.820 | |||||||
| PM10+72 | 0.774 | 0.004 | –0.087 | 108.901 | 7.559 | |||||||
| 0.75 | PM10+24 | 0.857 | 0.196 | –0.068 | –172.322 | 9.725 | ||||||
| PM10+48 | 0.774 | 0.004 | –0.087 | 108.901 | 7.559 | |||||||
| PM10+72 | 0.731 | –0.254 | –0.110 | 164.423 | 6.914 | |||||||
| Petaling Jaya | MLR | Mean | PM10+24 | 0.599 | –0.675 | –1.106 | –0.434 | –0.065 | –0.163 | 0.552 | 0.147 | 3.867 |
| PM10+48 | 0.457 | –0.68 | –1.506 | –0.536 | 0.119 | 0.367 | 0.360 | 0.082 | –0.11 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.353 | –0.281 | –1.846 | –0.563 | 0.129 | 0.811 | 0.725 | 0.01 | –1.647 | |||
| QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 0.365 | –0.790 | –0.705 | –0.273 | 0.060 | 0.659 | 0.624 | –0.196 | 1.516 | |
| PM10+48 | 0.240 | –0.654 | –0.796 | –0.292 | –0.048 | 1.071 | 0.433 | –0.200 | –0.520 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.141 | –0.467 | –0.925 | –0.279 | 0.004 | 1.250 | 0.563 | –0.076 | –1.194 | |||
| 0.50 | PM10+24 | 0.526 | –0.749 | –0.746 | –0.299 | –0.090 | 0.173 | 0.724 | –0.009 | 1.477 | ||
| PM10+48 | 0.358 | –0.436 | –1.277 | –0.415 | –0.031 | 0.475 | 0.276 | –0.068 | 0.178 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.288 | –0.355 | –1.356 | –0.397 | –0.001 | 0.737 | 0.313 | 0.084 | –1.410 | |||
| 0.75 | PM10+24 | 0.802 | –0.524 | –1.254 | –0.419 | –0.117 | –0.590 | 0.460 | 0.233 | –0.033 | ||
| PM10+48 | 0.631 | –0.181 | –2.025 | –0.609 | 0.050 | –0.484 | 1.159 | 0.111 | –0.903 | |||
| PM10+72 | 0.497 | –0.085 | –2.053 | –0.621 | 0.01 | –0.011 | 0.293 | 0.041 | –1.515 | |||
| Pearson–QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 0.381 | 0.143 | 2.856 | |||||||
| PM10+48 | 0.261 | 0.172 | 1.331 | |||||||||
| PM10+72 | 0.173 | 0.151 | 0.698 | |||||||||
| 0.50 | PM10+24 | 0.554 | 0.176 | 1.863 | ||||||||
| PM10+48 | 0.386 | 0.166 | 0.329 | |||||||||
| PM10+72 | 0.322 | 0.095 | 0.995 | |||||||||
| 0.75 | PM10+24 | 0.810 | 0.193 | 0.596 | ||||||||
| PM10+48 | 0.643 | 0.321 | 2.342 | |||||||||
| PM10+72 | 0.514 | 0.202 | 2.444 |
| Area | Method | Time | MAE | RMSE | R2 | IA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pasir Gudang | MLR | PM10+24 | 5.11 | 8.90 | 0.96 | 0.98 | |
| PM10+48 | 7.83 | 13.61 | 0.89 | 0.94 | |||
| PM10+72 | 9.86 | 17.03 | 0.82 | 0.90 | |||
| QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 10.43 | 16.90 | 0.95 | 0.90 | |
| 0.50 | 5.25 | 9.89 | 0.96 | 0.97 | |||
| 0.75 | 8.58 | 10.33 | 0.96 | 0.98 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+48 | 12.98 | 22.01 | 0.88 | 0.82 | ||
| 0.50 | 7.73 | 14.37 | 0.89 | 0.93 | |||
| 0.75 | 10.17 | 13.43 | 0.90 | 0.96 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+72 | 14.12 | 24.52 | 0.80 | 0.76 | ||
| 0.50 | 9.53 | 17.63 | 0.81 | 0.89 | |||
| 0.75 | 12.00 | 16.42 | 0.82 | 0.93 | |||
| Pearson–QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 10.92 | 17.64 | 0.94 | 0.90 | |
| 0.50 | 7.34 | 13.29 | 0.96 | 0.95 | |||
| 0.75 | 8.86 | 12.75 | 0.91 | 0.96 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+48 | 15.06 | 25.05 | 0.84 | 0.73 | ||
| 0.50 | 10.96 | 20.12 | 0.87 | 0.86 | |||
| 0.75 | 10.78 | 16.00 | 0.86 | 0.93 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+72 | 29.56 | 39.25 | 0.84 | 0.55 | ||
| 0.50 | 13.71 | 25.65 | 0.69 | 0.73 | |||
| 0.75 | 13.37 | 21.64 | 0.70 | 0.84 | |||
| Melaka | MLR | PM10+24 | 8.93 | 14.43 | 0.93 | 0.9656 | |
| PM10+48 | 13.05 | 20.85 | 0.85 | 0.9162 | |||
| PM10+72 | 16.48 | 25.55 | 0.76 | 0.8576 | |||
| QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 16.56 | 25.77 | 0.93 | 0.87 | |
| 0.50 | 9.50 | 14.47 | 0.94 | 0.96 | |||
| 0.75 | 13.05 | 16.38 | 0.93 | 0.96 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+48 | 45.39 | 52.93 | 0.81 | 0.60 | ||
| 0.50 | 12.77 | 22.27 | 0.84 | 0.90 | |||
| 0.75 | 16.67 | 21.65 | 0.85 | 0.93 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+72 | 22.71 | 37.02 | 0.74 | 0.67 | ||
| 0.50 | 15.24 | 26.36 | 0.76 | 0.84 | |||
| 0.75 | 19.25 | 25.56 | 0.77 | 0.89 | |||
| Pearson–QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 13.48 | 22.28 | 0.90 | 0.91 | |
| 0.50 | 7.12 | 12.43 | 0.85 | 0.98 | |||
| 0.75 | 9.73 | 12.26 | 0.96 | 0.98 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+48 | 17.13 | 29.03 | 0.77 | 0.82 | ||
| 0.50 | 11.92 | 21.43 | 0.89 | 0.91 | |||
| 0.75 | 12.90 | 17.34 | 0.90 | 0.96 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+72 | 19.39 | 34.08 | 0.68 | 0.71 | ||
| 0.50 | 13.14 | 23.62 | 0.82 | 0.89 | |||
| 0.75 | 15.45 | 21.53 | 0.83 | 0.93 | |||
| Petaling Jaya | MLR | PM10+24 | 10.72 | 19.45 | 0.85 | 0.93 | |
| PM10+48 | 14.68 | 25.88 | 0.74 | 0.84 | |||
| PM10+72 | 24.41 | 38.00 | 0.34 | 0.70 | |||
| QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 17.94 | 32.48 | 0.83 | 0.73 | |
| 0.50 | 11.08 | 21.47 | 0.85 | 0.90 | |||
| 0.75 | 14.44 | 19.93 | 0.85 | 0.94 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+48 | 21.35 | 38.83 | 0.73 | 0.56 | ||
| 0.50 | 15.20 | 29.12 | 0.74 | 0.77 | |||
| 0.75 | 17.42 | 24.87 | 0.74 | 0.89 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+72 | 23.23 | 42.74 | 0.26 | 0.45 | ||
| 0.50 | 16.82 | 32.34 | 0.64 | 0.69 | |||
| 0.75 | 19.29 | 28.51 | 0.64 | 0.82 | |||
| Pearson–QR | 0.25 | PM10+24 | 19.27 | 34.20 | 0.86 | 0.73 | |
| 0.50 | 12.55 | 24.11 | 0.87 | 0.88 | |||
| 0.75 | 13.92 | 19.30 | 0.87 | 0.94 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+48 | 21.66 | 40.12 | 0.75 | 0.58 | ||
| 0.50 | 16.20 | 31.96 | 0.76 | 0.73 | |||
| 0.75 | 17.69 | 26.17 | 0.76 | 0.87 | |||
| 0.25 | PM10+72 | 23.29 | 44.00 | 0.67 | 0.45 | ||
| 0.50 | 17.86 | 35.22 | 0.67 | 0.64 | |||
| 0.75 | 20.13 | 30.70 | 0.67 | 0.79 | |||
| Area | Prediction Day | Best Method |
|---|---|---|
| Petaling Jaya | PM10+24 | Pearson–QR (p = 0.75) |
| PM10+48 | QR (p = 0.75) | |
| PM10+72 | QR (p = 0.75) | |
| Melaka | PM10+24 | Pearson–QR (p = 0.75) |
| PM10+48 | Pearson–QR (p = 0.75) | |
| PM10+72 | Pearson–QR (p = 0.75) | |
| Pasir Gudang | PM10+24 | MLR |
| PM10+48 | MLR | |
| PM10+72 | QR (p = 0.75) |
| Area | Method | Dependent Variable | Prediction Time | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban area in Malaysia [17] |
| PM10 |
|
|
| Petaling Jaya [25] |
| PM10 |
|
|
| Peninsular Malaysia [47] |
| PM10 |
|
|
| Sichuan, China [48] |
| PM10PM2.5 |
|
|
| China [49] |
| PM2.5 |
|
|
| Malaysia [50] |
| PM10 |
|
|
| West coast of peninsular Malaysia [This study] |
| PM10 |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Redzuan, S.N.; Noor, N.M.; Rahim, N.A.A.A.; Jafri, I.A.M.; Baidrulhisham, S.E.; Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Sandu, A.V.; Vizureanu, P.; Zainol, M.R.R.M.A.; Deák, G. Characteristics of PM10 Level during Haze Events in Malaysia Based on Quantile Regression Method. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020407
Redzuan SN, Noor NM, Rahim NAAA, Jafri IAM, Baidrulhisham SE, Ul-Saufie AZ, Sandu AV, Vizureanu P, Zainol MRRMA, Deák G. Characteristics of PM10 Level during Haze Events in Malaysia Based on Quantile Regression Method. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020407
Chicago/Turabian StyleRedzuan, Siti Nadhirah, Norazian Mohamed Noor, Nur Alis Addiena A. Rahim, Izzati Amani Mohd Jafri, Syaza Ezzati Baidrulhisham, Ahmad Zia Ul-Saufie, Andrei Victor Sandu, Petrica Vizureanu, Mohd Remy Rozainy Mohd Arif Zainol, and György Deák. 2023. "Characteristics of PM10 Level during Haze Events in Malaysia Based on Quantile Regression Method" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020407
APA StyleRedzuan, S. N., Noor, N. M., Rahim, N. A. A. A., Jafri, I. A. M., Baidrulhisham, S. E., Ul-Saufie, A. Z., Sandu, A. V., Vizureanu, P., Zainol, M. R. R. M. A., & Deák, G. (2023). Characteristics of PM10 Level during Haze Events in Malaysia Based on Quantile Regression Method. Atmosphere, 14(2), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020407










