A New Analytical Simulation Code of Acoustic-Gravity Waves of Seismic Origin and Rapid Co-Seismic Thermospheric Disturbance Energetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
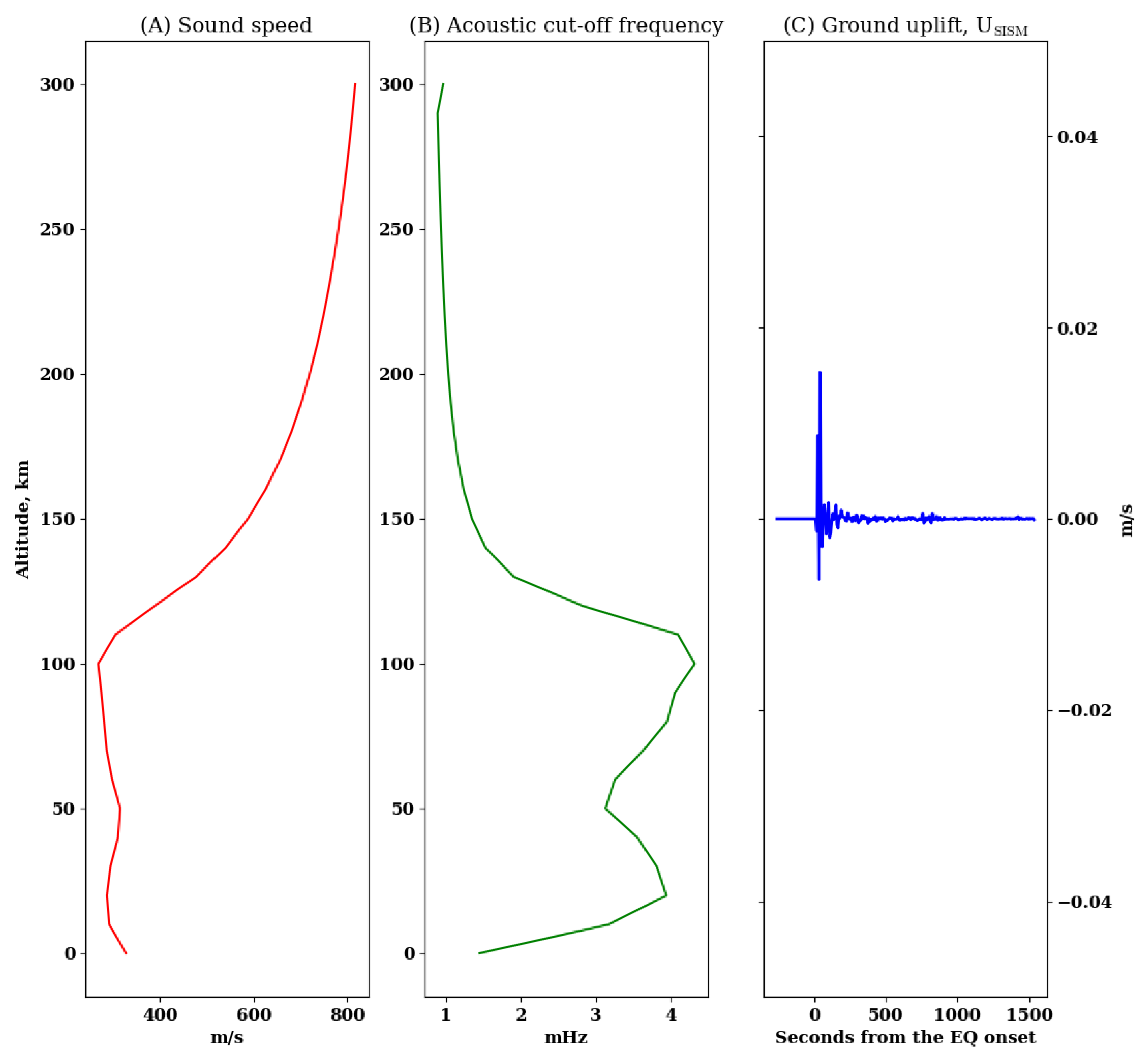
2. Analytical Simulation Code of AGWs
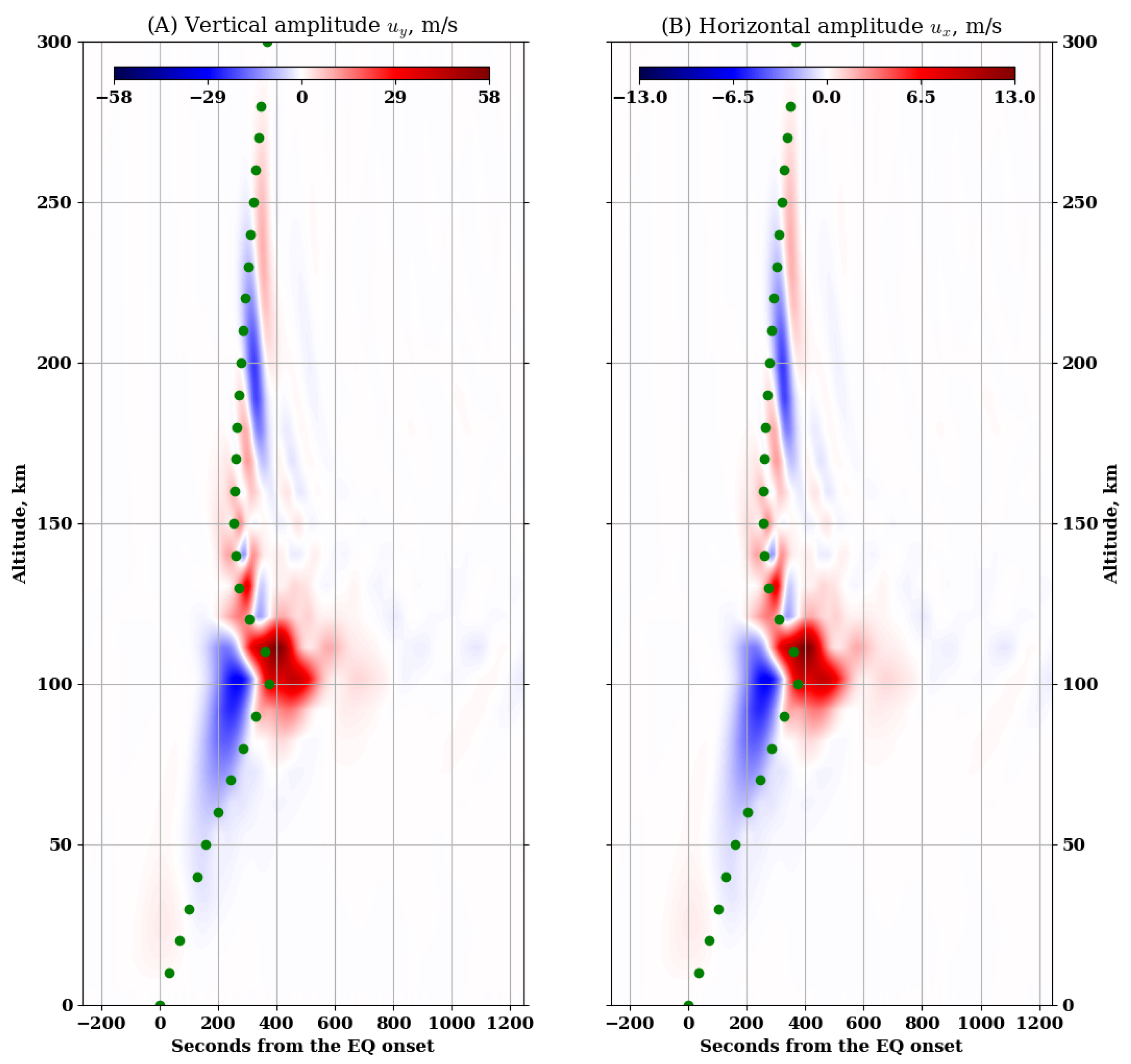
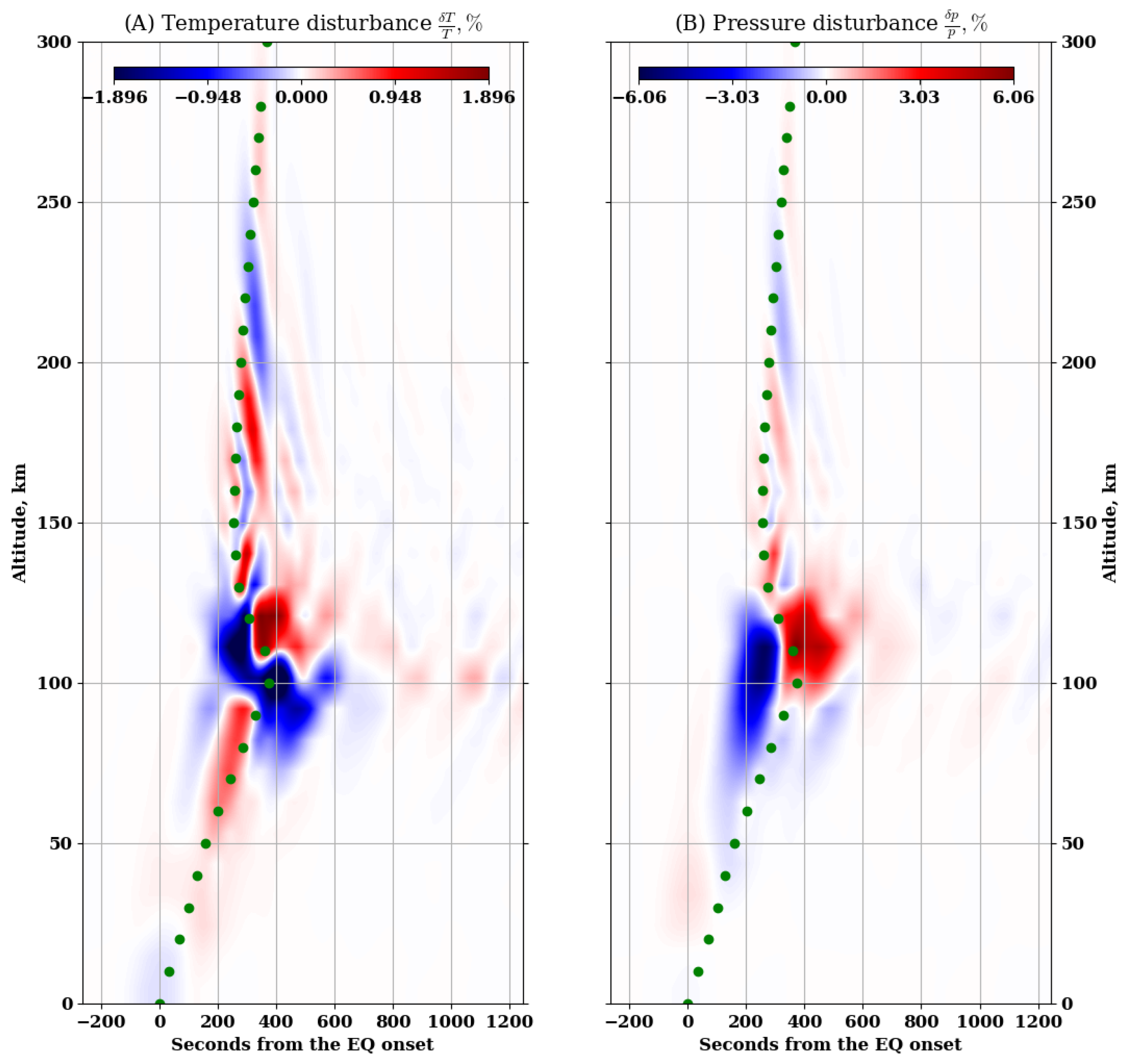
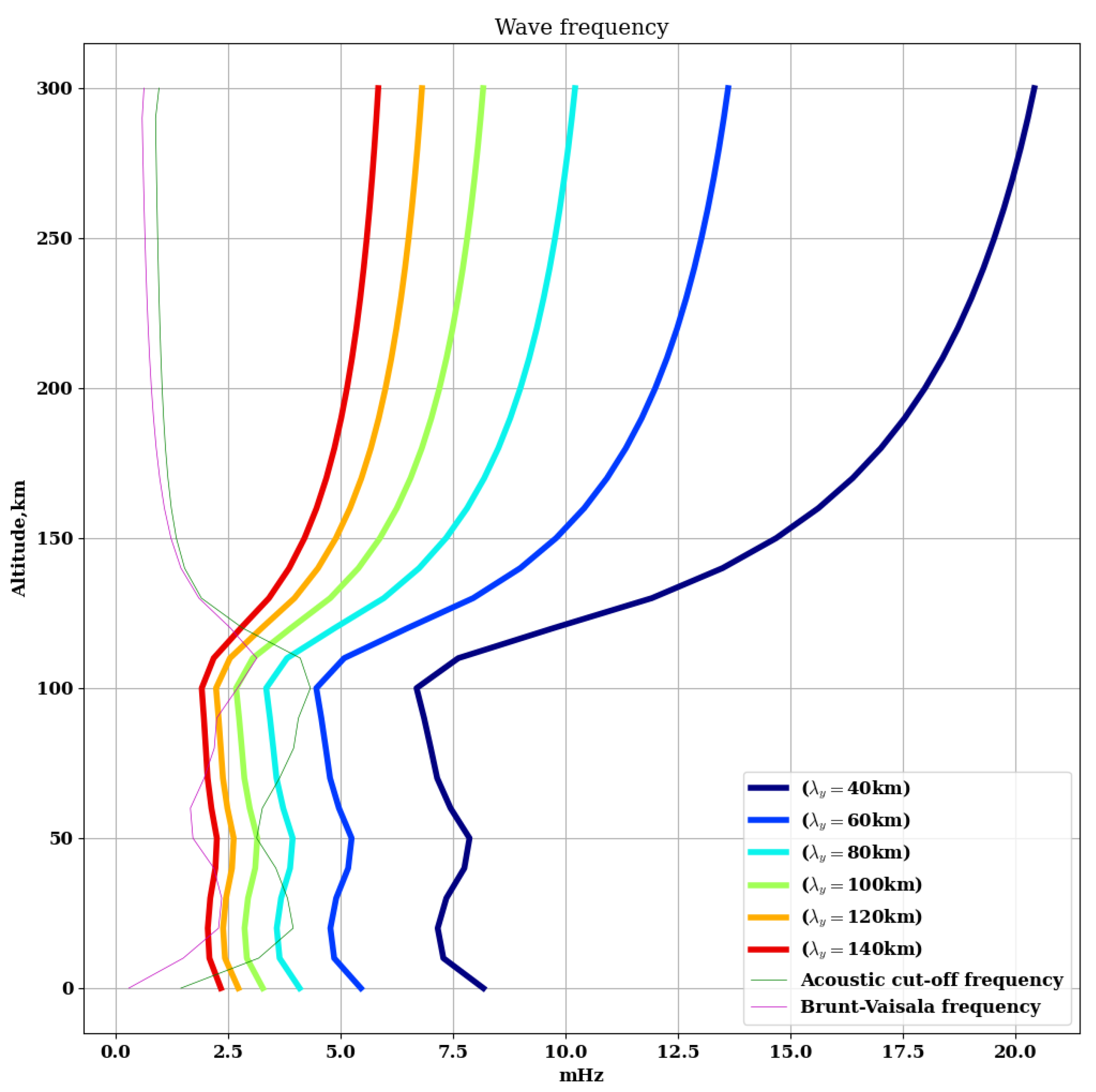
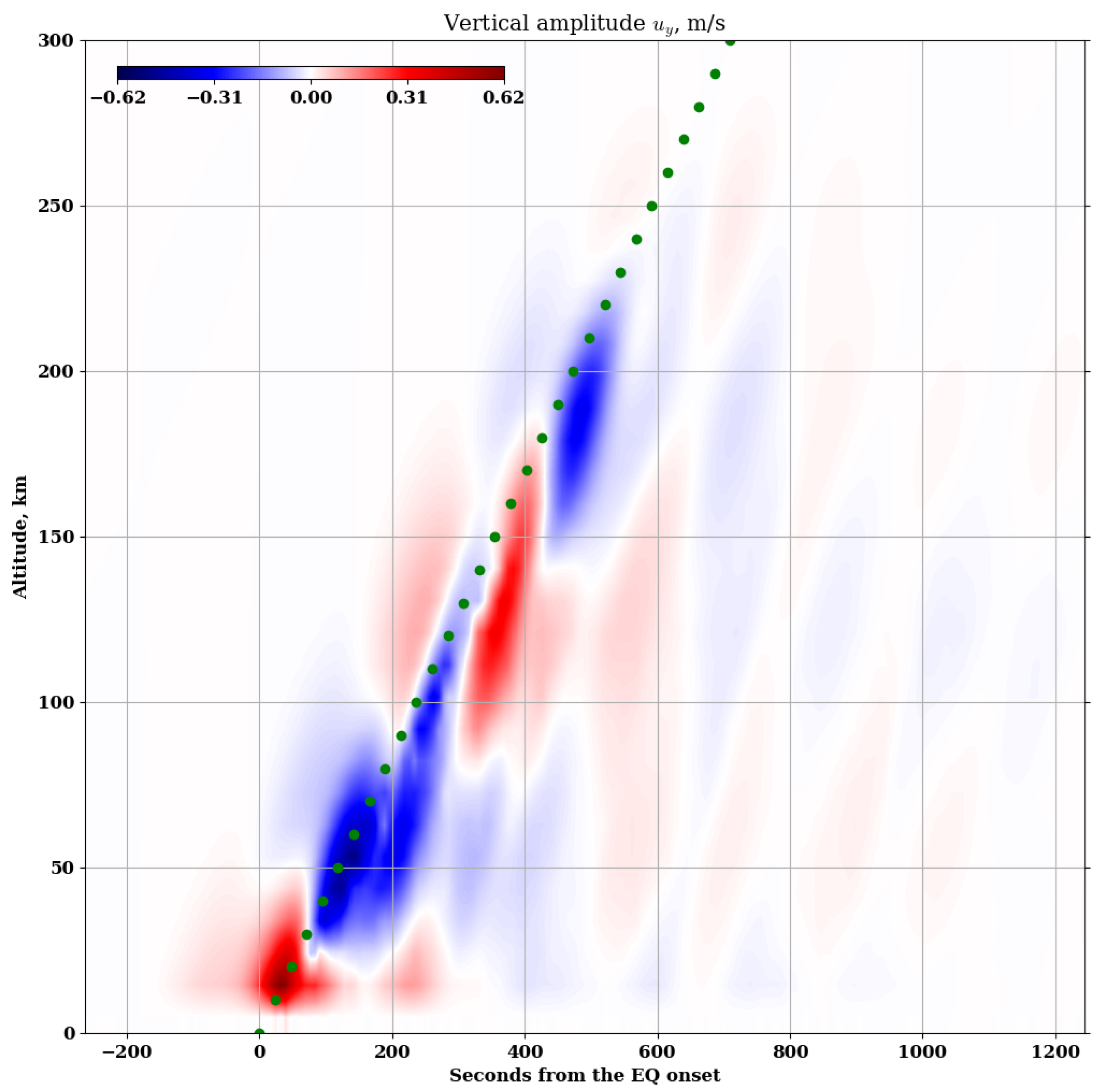
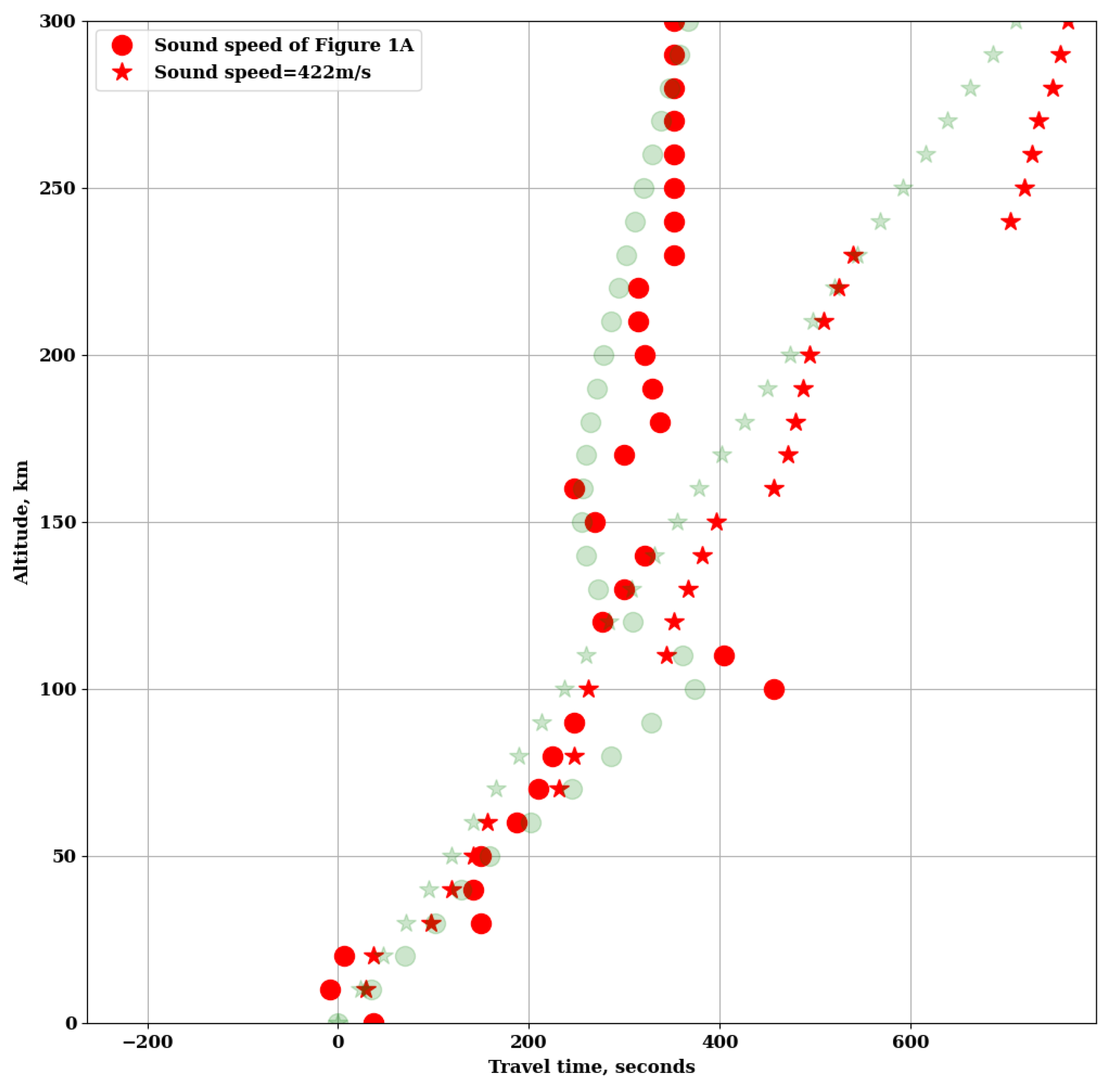
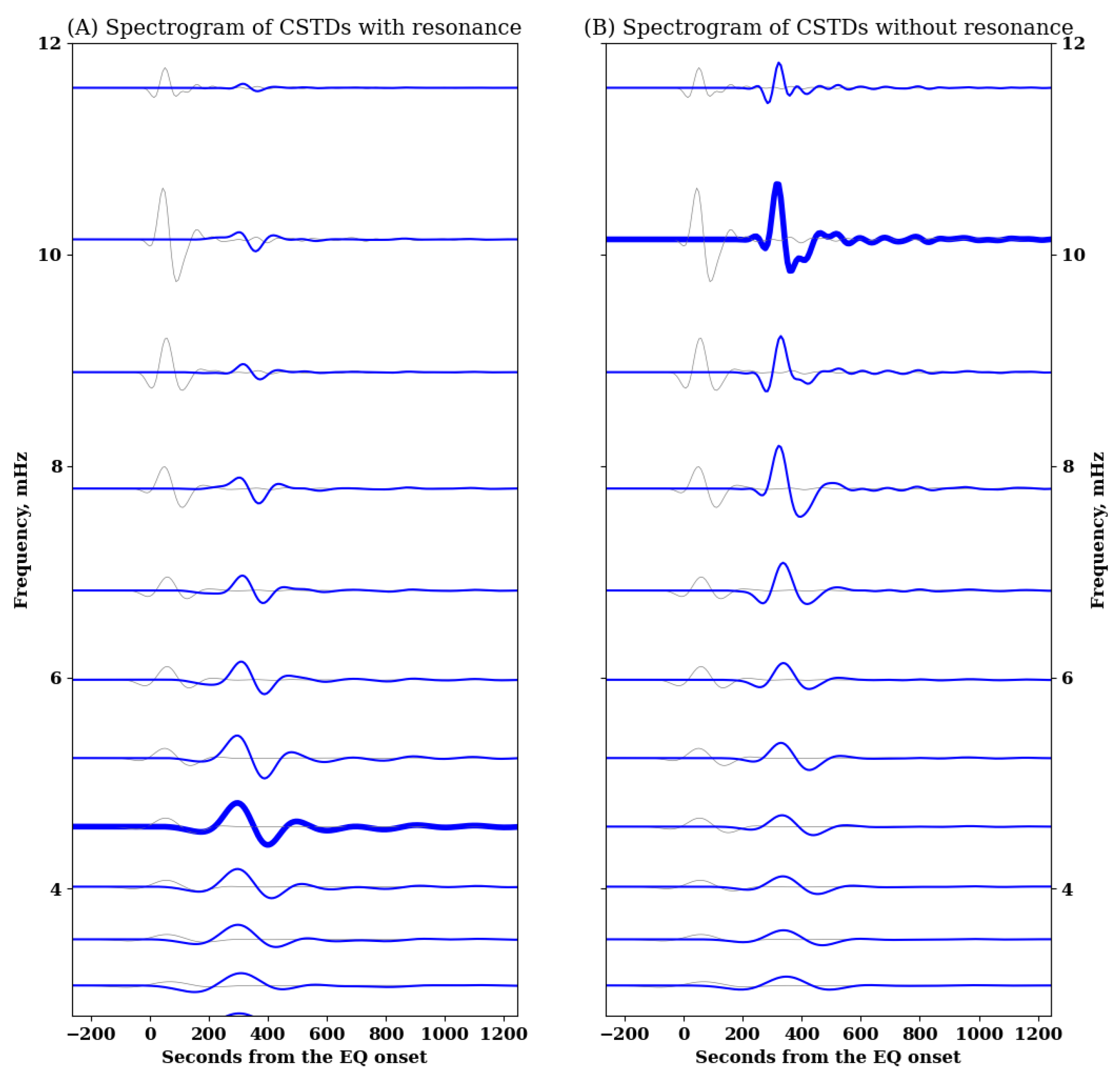
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGWs | Acoustic-gravity waves |
| SAI | Seismo-atmosphere–ionosphere |
| CSTDs | Coseismic thermospheric disturbances |
| Ionoquakes | Coseismic ionospheric disturbances |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Set of Equations Governing the SAI Coupling Mechanism
Appendix A.2. Analytical Solution of Space-Governing Equation (2)
Appendix A.3. Analytical Solution of Time-Governing Equation (3)
Appendix A.4. Viscous AGWs
References
- Calais, E.; Minster, J. GPS detection of ionospheric perturbations following the 17 January 1994, Northridge Earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afraimovich, E.L.; Perevalova, N.P.; Plotnikov, A.V.; Uralov, A.M. The shock-acoustic waves generated by earthquakes. Ann. Geophys. 2001, 19, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artru, J.; Farges, T.; Lognonné, P. Acoustic waves generated from seismic surface waves: Propagation properties determined from Doppler sounding observations and normal-mode modelling. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 158, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artru, J.; Ducic, V.; Kanamori, H.; Lognonné, P.; Murakami, M. Ionospheric detection of gravity waves induced by tsunamis. Geophys. J. Int. 2005, 160, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafyeva, E.; Heki, K.; Kiryushkin, V.; Afraimovich, E.; Shalimov, S. Two-mode long-distance propagation of coseismic ionosphere disturbances. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, A10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, L.M.; Lognonné, P.; Munekane, H. Detection and modeling of Rayleigh wave induced patterns in the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, A05320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafyeva, E.; Lognonné, P.; Rolland, L. First ionospheric images of the seismic fault slip on the example of the Tohoku-oki earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L22104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhipinti, G.; Rolland, L.; Lognonné, P.; Watada, S. From Sumatra 2004 to Tohoku-Oki 2011: The systematic GPS detection of the ionospheric signature induced by tsunamigenic earthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 3626–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, L.M.; Vergnolle, M.; Nocquet, J.M.; Sladen, A.; Dessa, J.X.; Tavakoli, F.; Nankali, H.R.; Cappa, F. Discriminating the tectonic and non-tectonic contributions in the ionospheric signature of the 2011, Mw7. 1, dip-slip Van earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2518–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Occhipinti, G.; Jin, R. GNSS ionospheric seismology: Recent observation evidences and characteristics. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 147, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafyeva, E. Ionospheric detection of natural hazards. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 1265–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, K.; Chai, H.; Wei, G. Rapid Tsunami Potential Assessment Using GNSS Ionospheric Disturbance: Implications from Three Megathrusts. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesnin, A.; Yasyukevich, Y.; Perevalova, N.; Şentürk, E. Ionospheric Response to the 6 February 2023 Turkey–Syria Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagiya, M.S.; Heki, K.; Gahalaut, V.K. Anisotropy of the Near-Field Coseismic Ionospheric Perturbation Amplitudes Reflecting the Source Process: The 2023 February Turkey Earthquakes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL103931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maletckii, B.; Astafyeva, E.; Sanchez, S.A.; Kherani, E.A.; de Paula, E.R. The 6 February 2023 Türkiye Earthquake Sequence as Detected in the Ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2023, 128, e2023JA031663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.S.; Klaassen, G.P.; Yiğit, E. On the Dynamical Importance of Gravity Wave Sources Distributed over Different Heights in the Atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2023, 128, e2022JA031152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snively, J.B. Mesospheric hydroxyl airglow signatures of acoustic and gravity waves generated by transient tropospheric forcing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4533–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchin, P.A.; Snively, J.B.; Zettergren, M.D.; Komjathy, A.; Verkhoglyadova, O.P.; Tulasi Ram, S. Modeling of Ionospheric Responses to Atmospheric Acoustic and Gravity Waves Driven by the 2015 Nepal 7.8 Gorkha Earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2019JA027200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artru, J.; Lognonné, P.; Blanc, E. Normal modes modelling of post-seismic ionospheric oscillations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 28, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chum, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Laštovička, J.; Fišer, J.; Mošna, Z.; Baše, J.; Sun, Y.Y. Ionospheric signatures of the 25 April 2015 Nepal earthquake and the relative role of compression and advection for Doppler sounding of infrasound in the ionosphere. Earth Planets Space 2016, 68, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, S.A.; Kherani, E.A.; Astafyeva, E.; de Paula, E.R. Ionospheric Disturbances Observed Following the Ridgecrest Earthquake of 4 July 2019 in California, USA. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Bagiya, M.S.; Sunil, P.S.; Rolland, L.; Sunil, A.S.; Mikesell, T.D.; Nayak, S.; Mangalampalli, S.; Ramesh, D.S. Revelation of early detection of co-seismic ionospheric perturbations in GPS-TEC from realistic modelling approach: Case study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafyeva, E.; Shults, K. Ionospheric GNSS imagery of seismic source: Possibilities, difficulties, and challenges. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, S.A.; Kherani, E.A.; Astafyeva, E.; de Paula, E.R. Rapid Detection of Co-Seismic Ionospheric Disturbances Associated With the 2015 Illapel, the 2014 Iquique and the 2011 Sanriku-Oki Earthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2023, 128, e2022JA031231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyadi, M.N.; Heki, K. Coseismic ionospheric disturbance of the large strike-slip earthquakes in North Sumatra in 2012: Mw dependence of the disturbance amplitudes. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 200, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.H.; Tsai, H.F.; Chen, C.H.; Kamogawa, M. Ionospheric disturbances triggered by the 11 March 2011 M9.0 Tohoku earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherani, E.A.; Lognonné, P.; Hébert, H.; Rolland, L.; Astafyeva, E.; Occhipinti, G.; Coïsson, P.; Walwer, D.; de Paula, E.R. Modelling of the total electronic content and magnetic field anomalies generated by the 2011 Tohoku-Oki tsunami and associated acoustic-gravity waves. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1049–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherani, E.A.; Sanchez, S.A.; de Paula, E.R. Numerical Modeling of Coseismic Tropospheric Disturbances Arising from the Unstable Acoustic Gravity Wave Energetics. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C. The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Picone, J.M.; Hedin, A.E.; Drob, D.P.; Aikin, A.C. NRLMSISE-00 empirical model of the atmosphere: Statistical comparisons and scientific issues. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, SIA 15-1–SIA 15-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoto, T. Acoustic Resonance of the Atmospheric at 3.7 Hz. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 2670–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heki, K.; Ping, J. Directivity and apparent velocity of the coseismic ionospheric disturbances observed with a dense GPS array. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 236, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.M.; Georges, T.M. Infrasound from convective storms. III. Propagation to the ionosphere. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1976, 59, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, L.M.; Lognonné, P.; Astafyeva, E.; Kherani, E.A.; Kobayashi, N.; Mann, M.; Munekane, H. The resonant response of the ionosphere imaged after the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake. Earth Planets Space 2011, 63, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherani, E.A.; Rolland, L.; Lognonne, P.H.; Sladen, A.; Klausner, V.; de Paula, E.R. Traveling ionospheric disturbances propagating ahead of the Tohoku-Oki tsunami: A case study. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 204, 148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez, S.A.; Kherani, E.A. A New Analytical Simulation Code of Acoustic-Gravity Waves of Seismic Origin and Rapid Co-Seismic Thermospheric Disturbance Energetics. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050592
Sanchez SA, Kherani EA. A New Analytical Simulation Code of Acoustic-Gravity Waves of Seismic Origin and Rapid Co-Seismic Thermospheric Disturbance Energetics. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(5):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050592
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez, Saul A., and Esfhan A. Kherani. 2024. "A New Analytical Simulation Code of Acoustic-Gravity Waves of Seismic Origin and Rapid Co-Seismic Thermospheric Disturbance Energetics" Atmosphere 15, no. 5: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050592
APA StyleSanchez, S. A., & Kherani, E. A. (2024). A New Analytical Simulation Code of Acoustic-Gravity Waves of Seismic Origin and Rapid Co-Seismic Thermospheric Disturbance Energetics. Atmosphere, 15(5), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050592





