The Optimal Width and Mechanism of Riparian Buffers for Storm Water Nutrient Removal in the Chinese Eutrophic Lake Chaohu Watershed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
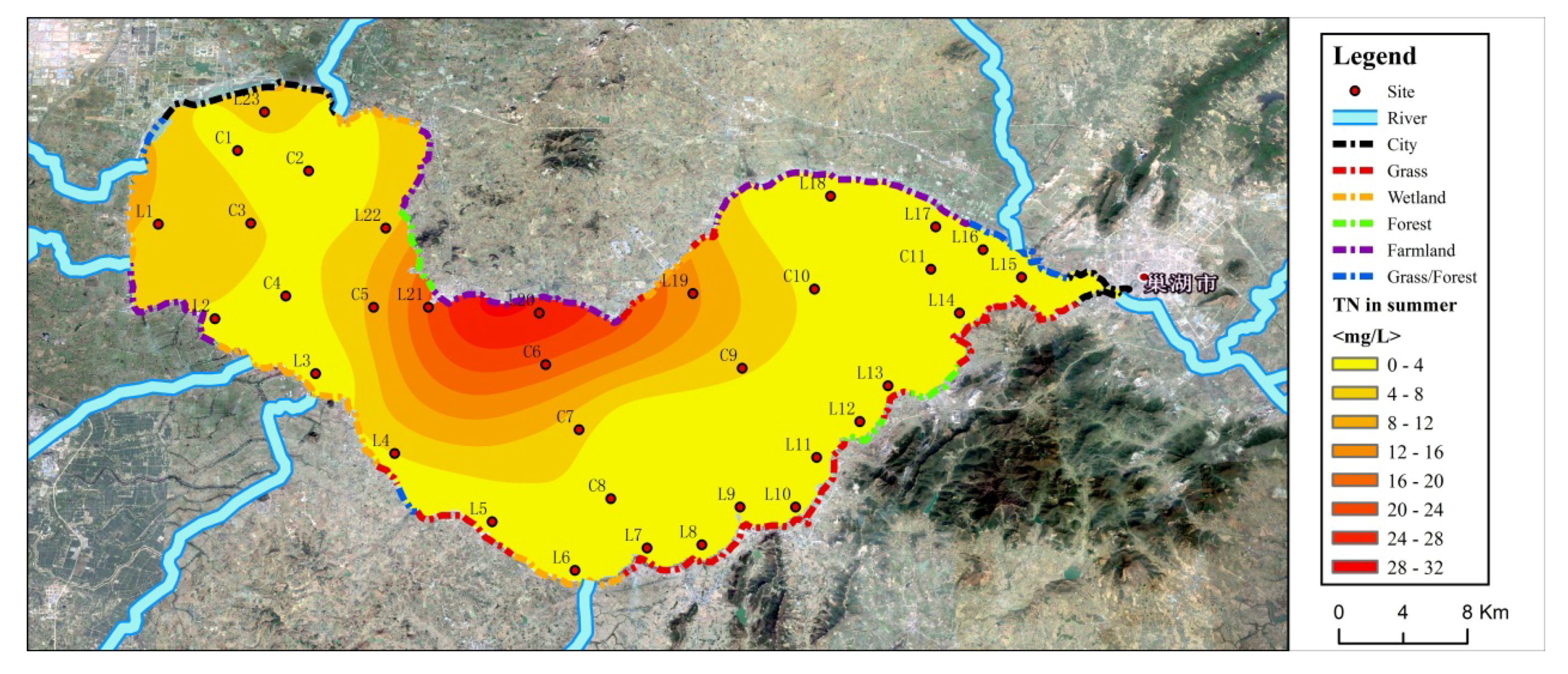
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Storm Water Collection and Sampling
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
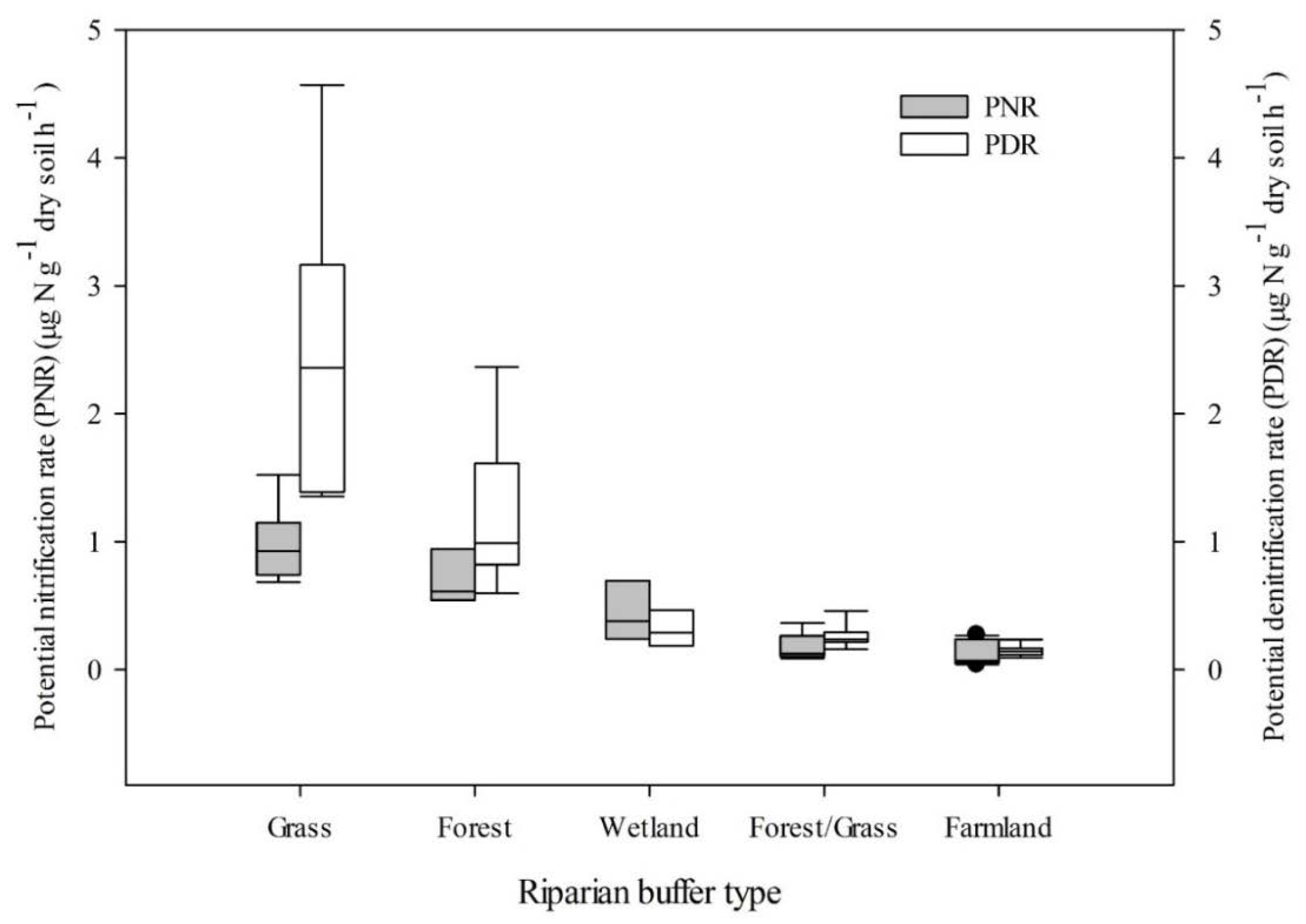
4. Discussion
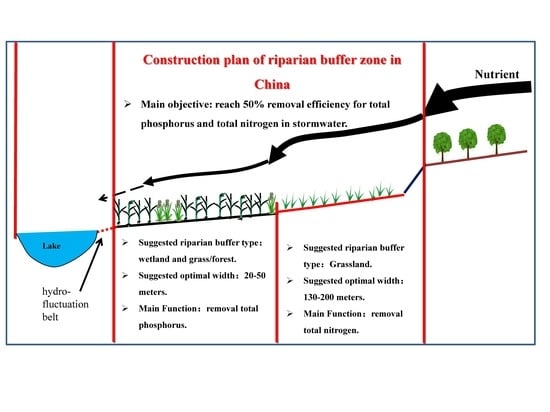
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klapproth, J.C.; Johnson, J.E. Understanding the science behind riparian forest buffers: Effects on water quality. Va. Polytech. Inst. State Univ. Publ. 2009, 22. Available online: https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/bitstream/handle/10919/48062/420-151_pdf.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 1 May 2005).
- Phillips, J.D. An evaluation of the factors determining the effectiveness of water quality buffer zones. J. Hydrol. 1989, 107, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syversen, N. Effect of a cold-climate buffer zone on minimizing diffuse pollution from agriculture. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syversen, N. Effect and design of buffer zones in the Nordic climate: The influence of width, amount of surface runoff, seasonal variation and vegetation type on retention efficiency for nutrient and particle runoff. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 24, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.I.; Langan, S.J.; Lunsdom, D.G. Vegetated buffer strips can lead toincreased release of phosphorus to waters: A biogeochemical assessment of themechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Eitzel, M. Review of vegetated buffers and a meta-analysis of their mitigation efficacy in reducing nonpoint source pollution. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwer, C.B.; Clausen, J.C. Vegetative filter treatment of dairy milkhouse wastewater. J. Environ. Qual. 1989, 18, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyehan, L.; Isenhart, T.M.; Schultz, R.C.; Mickelson, S.K. Multispecies riparian buffers trap sediment and nutrients during rainfall simulations. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance, R.R.; Todd, R.L.; Asmussen, L.E. Nutrient cycling in an agricultural watershed—I: Phreatic movement. J. Environ. Qual. 1984, 13, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Smyth, C.; Boutin, S. Quantitative review of riparian buffer width guidelines from Canada and the United States. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 70, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruill, T.B. Effectiveness of riparian buffers in controlling ground-water discharge of nitrate to streams in selected hydrogeological settings of the North Carolina Coastal Plain. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidon, P.G.F.; Hill, A.R. Landscape controls on nitrate removal in stream riparian zones. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, M.; Vianello, M.; Zanin, G. Effectiveness of buffer strips in removing pollutants in runoff from a cultivated field in North-East Italy. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefting, M.M.; Clement, J.; Bienkowski, P.; Dowrick, D.; Guenat, C.; Butturini, A.; Topa, S.; Pinay, G.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. The role of vegetation and litter in the nitrogen dynamics of riparian buffer zones in Europe. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 24, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissteiner, C.J.; Bouraoui, F.; Aloe, A. Reduction of nitrogen and phosphorus loads to european rivers by riparian buffer zones. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2013, 483, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, B.W.; Newbold, J.D. Streamside forest buffer width needed to protect stream water quality, habitat, and organisms: A literature review. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 560–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.J.; Curtis, T.; Chanasyk, D.S.; Reedyk, S. Influence of mowing and narrow grass buffer widths on reductions in se. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 95, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.G.; Liu, G.J.; Kang, Y.; Yang, R.K. Some potential hazardous trace elements contamination and their ecological risk in sediments of western Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 166, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.R.; Harr, C.A. (Eds.) Methods for Collection and Processing of Surface-Water and Bed-Material Samples for Physical and Chemical Analyses; U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1990; Volume 71, pp. 90–140.
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Istvanovics, V. Fractional composition, adsorption and release of sediment phosphorus in the Kis-Balaton reservoir. Water Res. 1994, 28, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Song, C.L.; Cao, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.Y. Effects of air-drying on phosphorus sorption in shallow lake sediment, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2012, 21, 672–678. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Liu, C.X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, C.F.; Zhu, G.F.; Liu, L. The effects of different substrates on ammonium removal in constructed wetlands: A comparison of their physicochemical characteristics and ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotic communities. Clean Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.L.; Zhang, F.S.; Lu, Y.H. Linking plant identity and interspecific competition to soil nitrogen cycling through ammonia oxidizer communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.K.; Minagawa, M. Assessment of denitrification process in lower Ishikari River system, Japan. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, T.K.; Ludwig, S.M. Retention and removal of nitrogen and phosphorus in saturated soils of arctic hillslopes. Biogeochemistry 2016, 127, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, T.R.; Rasera, K.; Parron, L.M.; Brito, A.G.; Ferreira, M.T. Nutrient removal effectiveness by riparian buffer zones in rural temperate watersheds: The impact of no-till crops practices. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 149, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, A.J.; Johnson, A.W.; Conolly, C. Wetland and stream buffer size requirements—A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, P.A.; Stevens, R.; Howe, F.P. A Handbook of Riparian Restoration and Revegetation for the Conservation of Land Birds in Utah with Emphasis on Habitat Types in Middle and Lower Elevations; Utah Division of Wildlife Resources: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1999; Volume 48, pp. 1–48.
- Jontos, R. Vegetative buffers for water quality protection: An introduction and guidance document. Connecticut Association of Wetland Scientists White Paper on Vegetative Buffers, Draft Version; 2004, Volume 1. Available online: http://www.ctwetlands.org/downloads/Draft%20Buffer%20Paper%20Version%201.0.doc (accessed on 21 October 2018).
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Xue, S.; Wang, G. Changes in rhizospheric microbial community structure and function during the natural recovery of abandoned cropland on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramae, E.E.; Etienne, Y.; Wong, L.C.; Pijl, A.S.; Veen, J.A.; Kowalchuk, G.A. Soil characteristics more strongly influence soil bacterial, communities than land-use type. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, I.R. Nitrogen and phosphorus transport in soil using simulated waterlogged conditions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2001, 32, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaor, M.I.; Reichmann, O.; Haim, A.; Auerswald, K.; Shenker, M. Sorption characteristics of phosphorus in peat soils of a semiarid altered wetland. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiberg, L.; Pedersen, T.V.; Jensen, H.S.; Kjaergaard, C.; Hansen, H.C.B. A comparative study of phosphate sorption in lowland soils under oxic and anoxic conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janardhanan, L.; Daroub, S.H. Phosphorus sorption in organic soils in south Florida. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Reverchon, F. Review of denitrification in tropical and subtropical soils of terrestrial ecosystems. J. Soil. Sediments 2013, 13, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowrance, R.; Vellidis, G.; Hubbard, R.K. Denitrification in a restored riparian forest wetland. J. Environ. Qual. 1995, 24, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


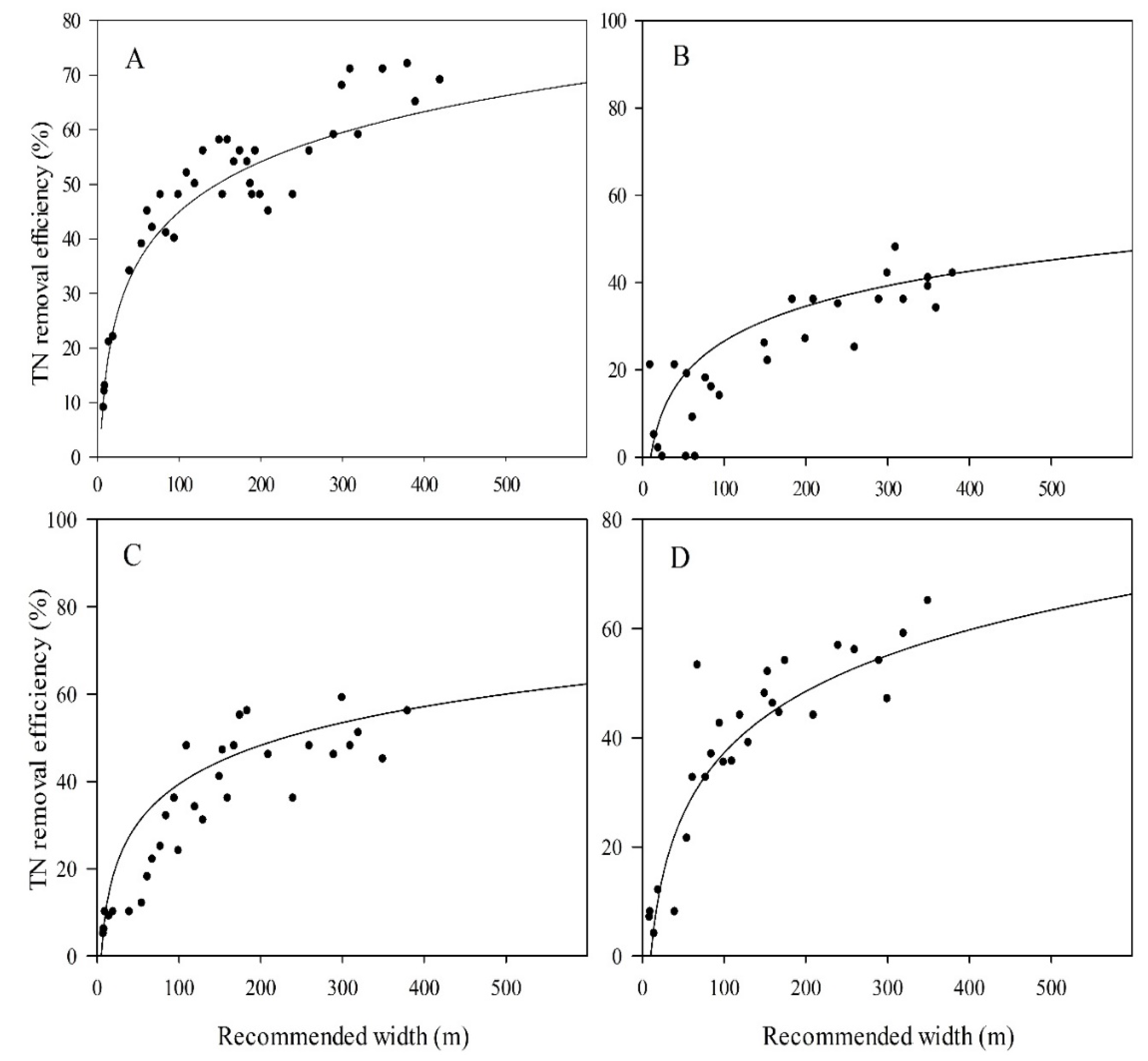

| Riparian Buffer Type | N | Relationship between TP Removal Efficiency and Buffer Width | Approximate Buffer Width (m) by Predicted TP Effectiveness | Relationship between TN Removal Efficiency and Buffer Width | Approximate Buffer Width (m) by Predicted TN Effectiveness | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | R2 | 50% | 75% | 90% | Model | R2 | 50% | 75% | 90% | ||
| Grass | 37 | y = 0.1155ln(x) − 0.0367 | 0.7124 | 104 | 908 | 3325 | y = 0.1426ln(x) − 0.1938 | 0.9043 | 130 | 749 | 2143 |
| Forest | 27 | y = 3.6864 + 0.0436x | 0.4493 | 1062 | 1636 | 1980 | y = 0.1108ln(x) − 0.2841 | 0.6577 | 1184 | 11305 | 43775 |
| Wetland | 33 | y = 0.1628ln(x) − 0.1157 | 0.8073 | 44 | 204 | 512 | y = 0.1327ln(x) − 0.2678 | 0.8336 | 325 | 2142 | 6636 |
| Grass/Forest | 27 | y = 0.1142ln(x) + 0.1432 | 0.7411 | 23 | 203 | 755 | y = 0.1586ln(x) − 0.3401 | 0.8513 | 200 | 966 | 2488 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, X.; Song, C.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, Y. The Optimal Width and Mechanism of Riparian Buffers for Storm Water Nutrient Removal in the Chinese Eutrophic Lake Chaohu Watershed. Water 2018, 10, 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101489
Cao X, Song C, Xiao J, Zhou Y. The Optimal Width and Mechanism of Riparian Buffers for Storm Water Nutrient Removal in the Chinese Eutrophic Lake Chaohu Watershed. Water. 2018; 10(10):1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101489
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Xiuyun, Chunlei Song, Jian Xiao, and Yiyong Zhou. 2018. "The Optimal Width and Mechanism of Riparian Buffers for Storm Water Nutrient Removal in the Chinese Eutrophic Lake Chaohu Watershed" Water 10, no. 10: 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101489
APA StyleCao, X., Song, C., Xiao, J., & Zhou, Y. (2018). The Optimal Width and Mechanism of Riparian Buffers for Storm Water Nutrient Removal in the Chinese Eutrophic Lake Chaohu Watershed. Water, 10(10), 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101489