-
 Sediment Transport Constraints for Restoration of the Ebro Delta
Sediment Transport Constraints for Restoration of the Ebro Delta -
 Comparative Analysis of Livestock Wastewater Reuse Under Summer and Winter Conditions at a Scale-Down Microalgae Culture
Comparative Analysis of Livestock Wastewater Reuse Under Summer and Winter Conditions at a Scale-Down Microalgae Culture -
 Insights to Estimate the Largest 1/3, 1/10, and 1/100 of Offshore Wave Heights and Periods Under Fetch-Limited Conditions in the Central Aegean Sea
Insights to Estimate the Largest 1/3, 1/10, and 1/100 of Offshore Wave Heights and Periods Under Fetch-Limited Conditions in the Central Aegean Sea -
 Waterway Regulation Effects on River Hydrodynamics and Hydrological Regimes: A Numerical Investigation
Waterway Regulation Effects on River Hydrodynamics and Hydrological Regimes: A Numerical Investigation -
 Asymmetric Impacts of Urbanization on Extreme Hourly Precipitation Across the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration During 1978–2012
Asymmetric Impacts of Urbanization on Extreme Hourly Precipitation Across the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration During 1978–2012
Journal Description
Water
Water
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal on water science and technology, including the ecology and management of water resources, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. Water collaborates with the Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI). In addition, the American Institute of Hydrology (AIH), The Polish Limnological Society (PLS) and Japanese Society of Physical Hydrology (JSPH) are affiliated with Water and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, GEOBASE, GeoRef, PubAg, AGRIS, CAPlus / SciFinder, Inspec, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Water Resources) / CiteScore - Q1 (Aquatic Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Water include: GeoHazards.
- Journal Clusters of Water Resources: Water, Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, Hydrology, Resources, Oceans, Limnological Review, Coasts.
Impact Factor:
3.0 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
Research Activities on Acid Mine Drainage Treatment in South Africa (1998–2025): Trends, Challenges, Bibliometric Analysis and Future Directions
Water 2025, 17(15), 2286; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152286 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Acid mine drainage (AMD) remains a critical environmental challenge in South Africa due to its severe impact on water quality, ecosystems and public health. Numerous studies on AMD management, treatment and resource recovery have been conducted over the past 20 years. This study
[...] Read more.
Acid mine drainage (AMD) remains a critical environmental challenge in South Africa due to its severe impact on water quality, ecosystems and public health. Numerous studies on AMD management, treatment and resource recovery have been conducted over the past 20 years. This study presents a comprehensive review of research activities on AMD in South Africa from 1998 to 2025, highlighting key trends, emerging challenges and future directions. The study reveals a significant focus on passive and active treatment methods, environmental remediation and the recovery of valuable resources, such as iron, rare earth elements (REEs) and gypsum. A bibliometric analysis was conducted to identify the most influential studies and thematic research areas over the years. Bibliometric tools (Biblioshiny and VOSviewer) were used to analyse the data that was extracted from the PubMed database. The findings indicate that research production has increased significantly over time, with substantial contributions from top academics and institutions. Advanced treatment technologies, the use of artificial intelligence and circular economy strategies for resource recovery are among the new research prospects identified in this study. Despite substantial progress, persistent challenges, such as scalability, economic viability and policy implementation, remain. Furthermore, few technologies have moved beyond pilot-scale implementation, underscoring the need for greater investment in field-scale research and technology transfer. This study recommends stronger industry–academic collaboration, the development of standardised treatment protocols and enhanced government policy support to facilitate sustainable AMD management. The study emphasises the necessity of data-driven approaches, sustainable technology and interdisciplinary cooperation to address AMD’s socioeconomic and environmental effects in the ensuing decades.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Collaborative Monitoring and Remediation of Mine or Industrial Soils and Water)
Open AccessArticle
Research on Startup Characteristics of Parallel Axial-Flow Pump Systems
by
Chao Yang, Chao Li, Lingling Deng and You Fu
Water 2025, 17(15), 2285; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152285 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
This study takes four parallel axial-flow pumps (three in operation + one on standby) as the research object. Using a 1D–3D coupling method, it explores the flow characteristics of axial-flow pumps under different startup strategies during multi-pump parallel operation. Through comparative analysis, the
[...] Read more.
This study takes four parallel axial-flow pumps (three in operation + one on standby) as the research object. Using a 1D–3D coupling method, it explores the flow characteristics of axial-flow pumps under different startup strategies during multi-pump parallel operation. Through comparative analysis, the following conclusions are drawn: when all three pumps start simultaneously, the internal pressure exceeds the rated head by 23.43%, and the reverse flow reaches 10.57% of the rated flow. When starting the pumps sequentially with 5 s intervals, the pressure can be reduced to 11.41% above the rated head, but the reverse flow increases to 13.87%. Further extending the startup interval to 15 s results in only minimal improvements compared to 5 s intervals: the maximum internal pressure and maximum reverse flow decrease by just 0.97% and 0.05%, respectively. When valve coordination is added to the 5 s sequential startup strategy (pre-opening the valve to 60% before pump startup), the pressure exceeds the rated head by 10.49%, and the reverse flow exceeds the rated flow by 6.04%. In this scenario, the high-pressure areas and high-turbulence zones on the blade back surfaces are significantly reduced, achieving optimal flow stability. Therefore, the parallel system startup should adopt a coordinated strategy combining moderate time intervals with 60% valve pre-opening. This approach can both avoid excessive pressure impact and effectively control reverse flow phenomena, providing an important basis for optimizing the startup of multi-pump parallel systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Hydraulics and Hydrodynamics)
►▼
Show Figures
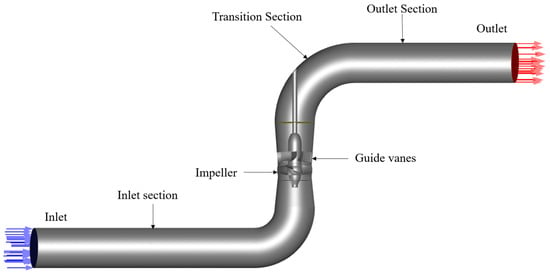
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Unraveling Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Response of Integrated Sulfur-Driven Partial Denitrification and Anammox Process in Saline Wastewater Treatment
by
Xiangchen Li, Jie Sun, Zonglun Cao, Junxi Lai, Haodi Feng and Minwen Guo
Water 2025, 17(15), 2284; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152284 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Increasing the discharge of saline wastewater from an industrial field poses a challenge for applicable Anammox-based technologies. This study established the integrated partial sulfur-driven denitrification and Anammox (SPDA) system to explore the effects of different salinity levels on nitrogen conversion features. The results
[...] Read more.
Increasing the discharge of saline wastewater from an industrial field poses a challenge for applicable Anammox-based technologies. This study established the integrated partial sulfur-driven denitrification and Anammox (SPDA) system to explore the effects of different salinity levels on nitrogen conversion features. The results of batch tests suggested that sulfur-driven denitrification exhibited progressive suppression of nitrate reduction (97.7% → 12.3% efficiency at 0% → 4% salinity) and significant nitrite accumulation (56.4% accumulation rate at 2% salinity). Anammox showed higher salinity tolerance but still experienced drastic TN removal decline (97.6% → 17.3% at 0% → 4% salinity). Long-term operation demonstrated that the SPDA process could be rapidly established at 0% salinity and stabilize with TN removal efficiencies of 98.1% (1% salinity), 72.8% (2% salinity), and 70.2% (4% salinity). The robustness of the system was attributed to the appropriate strategy of gradual salinity elevation, the promoted secretion of protein-dominated EPS, the salinity-responsive enrichment of Sulfurimonas (replacing Thiobacillus and Ferritrophicum) as sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB), and the sustained retention and activity of Brocadia as AnAOB. The findings in this study deepen the understanding of the inhibitory effects of salinity on the SPDA system, providing a feasible solution for saline wastewater treatment with low cost and high efficiency.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biological Nitrogen Removal in the Multi-Omics Era: Coupling Anammox with Microbial-Mineral Synergy)
►▼
Show Figures
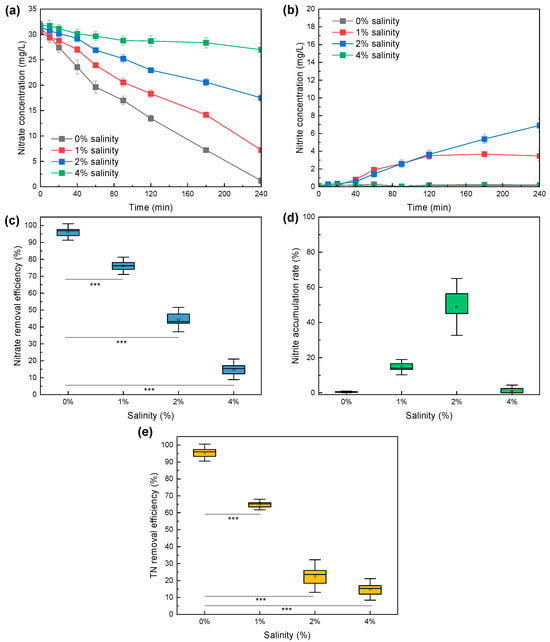
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Employing Cover Crops and No-Till in Southern Great Plains Cotton Production to Manage Runoff Water Quantity and Quality
by
Jack L. Edwards, Kevin L. Wagner, Lucas F. Gregory, Scott H. Stoodley, Tyson E. Ochsner and Josephus F. Borsuah
Water 2025, 17(15), 2283; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152283 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Conventional tillage and monocropping are common practices employed for cotton production in the Southern Great Plains (SGP) region, but they can be detrimental to soil health, crop yield, and water resources when improperly managed. Regenerative practices such as cover crops and conservation tillage
[...] Read more.
Conventional tillage and monocropping are common practices employed for cotton production in the Southern Great Plains (SGP) region, but they can be detrimental to soil health, crop yield, and water resources when improperly managed. Regenerative practices such as cover crops and conservation tillage have been suggested as an alternative. The proposed shift in management practices originates from the need to make agriculture resilient to extreme weather events including intense rainfall and drought. The objective of this study is to test the effects of these regenerative practices in an environment with limited rainfall. Runoff volume, nutrient and sediment concentrations and loadings, and surface soil moisture levels were compared on twelve half-acre (0.2 hectare) cotton plots that employed different cotton seeding rates and variable winter wheat cover crop presence. A winter cover implemented on plots with a high cotton seeding rate significantly reduced runoff when compared to other treatments (p = 0.032). Cover cropped treatments did not show significant effects on nutrient or sediment loadings, although slight reductions were observed in the concentrations and loadings of total Kjeldahl nitrogen, total phosphorus, total solids, and Escherichia coli. The limitations of this study included a short timeframe, mechanical failures, and drought. These factors potentially reduced the statistical differences in several findings. More efficient methods of crop production must continue to be developed for agriculture in the SGP to conserve soil and water resources, improve soil health and crop yields, and enhance resiliency to climate change.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Water, Agriculture and Aquaculture)
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from China’s Freshwater Aquaculture Industry Based on the LMDI and Tapio Decoupling Models
by
Meng Zhang, Weiguo Qian and Luhao Jia
Water 2025, 17(15), 2282; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152282 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Carbon emissions from freshwater aquaculture can exacerbate the greenhouse effect, thereby impacting human life and health. Consequently, it is of great significance to explore the carbon peak process and the role of emission reduction data in China’s freshwater aquaculture industry. This study innovatively
[...] Read more.
Carbon emissions from freshwater aquaculture can exacerbate the greenhouse effect, thereby impacting human life and health. Consequently, it is of great significance to explore the carbon peak process and the role of emission reduction data in China’s freshwater aquaculture industry. This study innovatively employs the Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index model (LMDI) and the Tapio decoupling model to conduct an in-depth analysis of the relationship between carbon emissions and output values in the freshwater aquaculture industry, accurately identifying the main driving factors. Meanwhile, the global and local Moran’s I indices are introduced to analyze its spatial correlation from a new perspective. The results indicate that from 2013 to 2023, carbon emissions from China’s freshwater aquaculture industry exhibited a quasi-“N”-shaped trend, reaching a peak of 38 million tons in 2015. East China was the primary contributor to carbon emissions, accounting for 46%, while South China, Central China, and Northeast China each had an average annual share of around 14%, with Southwest, North China, and Northwest China contributing relatively small proportions. The global Moran’s I index showed a decreasing trend, with a p-value ≤ 0.0010 and a z-score > 3.3, indicating a 99% significant spatial correlation. High-high clusters were concentrated in some provinces of East China, while low-low clusters were found in Northwest, North, and Southwest China. The level of fishery economic development positively drove carbon emissions, whereas freshwater aquaculture production efficiency, industrial structure, and the scale of the aquaculture population had negative effects on carbon emissions. During the study period, carbon emissions exhibited three states: weak decoupling, strong decoupling, and expansive negative decoupling, with alternating strong and weak decoupling occurring after 2015.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Water, Agriculture and Aquaculture)
Open AccessReview
Evolution of Data-Driven Flood Forecasting: Trends, Technologies, and Gaps—A Systematic Mapping Study
by
Banujan Kuhaneswaran, Golam Sorwar, Ali Reza Alaei and Feifei Tong
Water 2025, 17(15), 2281; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152281 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
This paper presents a Systematic Mapping Study (SMS) on data-driven approaches in flood forecasting from 2019 to 2024, a period marked by transformative developments in Deep Learning (DL) technologies. Analysing 363 selected studies, this paper provides an overview of the technological evolution in
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a Systematic Mapping Study (SMS) on data-driven approaches in flood forecasting from 2019 to 2024, a period marked by transformative developments in Deep Learning (DL) technologies. Analysing 363 selected studies, this paper provides an overview of the technological evolution in this field, methodological approaches, evaluation practices and geographical distribution of studies. The study revealed that meteorological and hydrological factors constitute approximately 76% of input variables, with rainfall/precipitation and water level measurements forming the core predictive basis. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks emerged as the dominant algorithm (21% of implementations), whilst hybrid and ensemble approaches showed the most dramatic growth (from 2% in 2019 to 10% in 2024). The study also revealed a threefold increase in publications during this period, with significant geographical concentration in East and Southeast Asia (56% of studies), particularly China (36%). Several research gaps were identified, including limited exploration of graph-based approaches for modelling spatial relationships, underutilisation of transfer learning for data-scarce regions, and insufficient uncertainty quantification. This SMS provides researchers and practitioners with actionable insights into current trends, methodological practices, and future directions in data-driven flood forecasting, thereby advancing this critical field for disaster management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Computer Modelling Techniques in Environmental Hydraulics and Water Resource Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
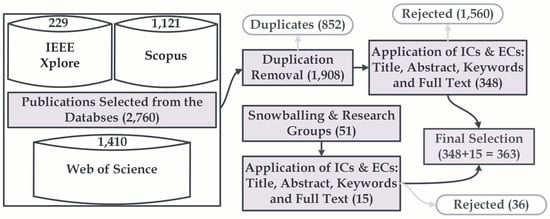
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Vegetation Cover and Soil Properties on Water Infiltration: A Study in High-Andean Ecosystems of Peru
by
Azucena Chávez-Collantes, Danny Jarlis Vásquez Lozano, Leslie Diana Velarde-Apaza, Juan-Pablo Cuevas, Richard Solórzano and Ricardo Flores-Marquez
Water 2025, 17(15), 2280; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152280 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Water infiltration into soil is a key process in regulating the hydrological cycle and sustaining ecosystem services in high-Andean environments. However, limited information is available regarding its dynamics in these ecosystems. This study evaluated the influence of three types of vegetation cover and
[...] Read more.
Water infiltration into soil is a key process in regulating the hydrological cycle and sustaining ecosystem services in high-Andean environments. However, limited information is available regarding its dynamics in these ecosystems. This study evaluated the influence of three types of vegetation cover and soil properties on water infiltration in a high-Andean environment. A double-ring infiltrometer, the Water Drop Penetration Time (WDPT, s) method, and laboratory physicochemical characterization were employed. Soils under forest cover exhibited significantly higher quasi-steady infiltration rates (is, 0.248 ± 0.028 cm·min−1) compared to grazing areas (0.051 ± 0.016 cm·min−1) and agricultural lands (0.032 ± 0.013 cm·min−1). Soil organic matter content was positively correlated with is. The modified Kostiakov infiltration model provided the best overall fit, while the Horton model better described infiltration rates approaching is. Sand and clay fractions, along with K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+, were particularly significant during the soil’s wet stages. In drier stages, increased Na+ concentrations and decreased silt content were associated with higher water repellency. Based on WDPT, agricultural soils exhibited persistent hydrophilic behavior even after drying (median [IQR] from 0.61 [0.38] s to 1.24 [0.46] s), whereas forest (from 2.84 [3.73] s to 3.53 [24.17] s) and grazing soils (from 4.37 [1.95] s to 19.83 [109.33] s) transitioned to weakly or moderately hydrophobic patterns. These findings demonstrate that native Andean forest soils exhibit a higher infiltration capacity than soils under anthropogenic management (agriculture and grazing), highlighting the need to conserve and restore native vegetation cover to strengthen water resilience and mitigate the impacts of land-use change.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Soil–Water Interaction and Management)
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of a Volcanic Rock-Derived Coagulant for Water Purification: A Study of Its Preparation Process
by
Lei Zhou, Zhangrui Yang, Xiaoyong Liu, Xiaoben Yang, Xuewen Wu, Yong Zhou and Guocheng Zhu
Water 2025, 17(15), 2279; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152279 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Volcanic rock is a natural mineral material which has garnered interest for its potential application in water treatment due to its unique physicochemical properties. In this study, we prepared a polysilicate aluminum chloride (PSAC) coagulant using volcanic rock which exhibited good coagulation–flocculation performance.
[...] Read more.
Volcanic rock is a natural mineral material which has garnered interest for its potential application in water treatment due to its unique physicochemical properties. In this study, we prepared a polysilicate aluminum chloride (PSAC) coagulant using volcanic rock which exhibited good coagulation–flocculation performance. Further investigation into the influence of synthetic parameters, such as calcination temperature, reaction time, and alkali types, on the structure and performance of a volcanic rock-derived coagulant was conducted. Techniques including Scanning Electron Microscopy, Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy, Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, and X-Ray Diffraction were utilized to characterize it. Also, a ferron-complexation timed spectrophotometric method was used to study the distribution of aluminum species in the coagulant. Results indicated that the volcanic rock that was treated with acidic and alkaline solutions had the potential to form PSAC with Al-OH, Al-O-Si, Fe-OH, and Fe-O-Si bonds, which influenced the coagulation–flocculation efficiency. An acid leaching temperature of 90 °C, 8 mL of 2 mol/L NaOH, a reaction time of 0.5 h, and a reaction temperature of 60 °C were conducive to the preparation. A higher temperature could result in a higher proportion of Alb species, and, at 100 °C, the Ala, Alc, and Alb were 29%, 24%, and 47%, respectively, achieving a residual turbidity lower than 1 NTU at an appropriate dosage, as well as a reduction of over 0.1 to 0.018 in the level of UV254. The findings of this study provide a feasible method to prepare a flocculant using volcanic rock. Further application is expected to yield good results in wastewater/water treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Micropollutants in Water and Wastewater: Recent Tendencies, Treatment Options and Perspectives)
Open AccessArticle
An Approach to Improve Land–Water Salt Flux Modeling in the San Francisco Estuary
by
John S. Rath, Paul H. Hutton and Sujoy B. Roy
Water 2025, 17(15), 2278; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152278 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
In this case study, we used the Delta Simulation Model II (DSM2) to study the salt balance at the land–water interface in the river delta of California’s San Francisco Estuary. Drainage, a source of water and salt for adjacent channels in the study
[...] Read more.
In this case study, we used the Delta Simulation Model II (DSM2) to study the salt balance at the land–water interface in the river delta of California’s San Francisco Estuary. Drainage, a source of water and salt for adjacent channels in the study area, is affected by channel salinity. The DSM2 approach has been adopted by several hydrodynamic models of the estuary to enforce water volume balance between diversions, evapotranspiration and drainage at the land–water interface, but does not explicitly enforce salt balance. We found deviations from salt balance to be quite large, albeit variable in magnitude due to the heterogeneity of hydrodynamic and salinity conditions across the study area. We implemented a procedure that approximately enforces salt balance through iterative updates of the baseline drain salinity boundary conditions (termed loose coupling). We found a reasonable comparison with field measurements of drainage salinity. In particular, the adjusted boundary conditions appear to capture the range of observed interannual variability better than the baseline periodic estimates. The effect of the iterative adjustment procedure on channel salinity showed substantial spatial variability: locations dominated by large flows were minimally impacted, and in lower flow channels, deviations between baseline and adjusted channel salinity series were notable, particularly during the irrigation season. This approach, which has the potential to enhance the simulation of extreme salinity intrusion events (when high channel salinity significantly impacts drainage salinity), is essential for robustly modeling hydrodynamic conditions that pre-date contemporary water management infrastructure. We discuss limitations associated with this approach and recommend that—for this case study—further improvements could best be accomplished through code modification rather than coupling of transport and island water balance models.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Coastal Hydrological and Geological Processes)
►▼
Show Figures
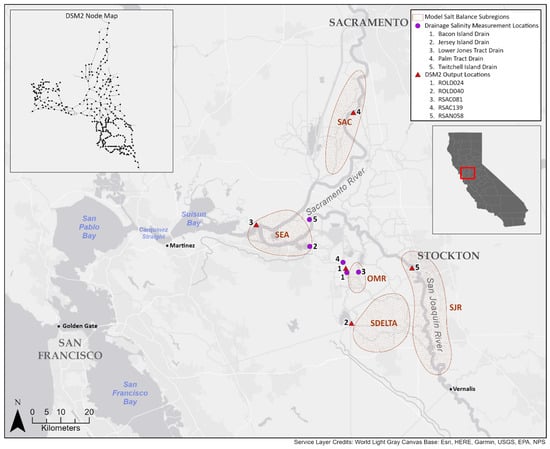
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Contribution of the Gravity Component and Surface Type During the Initial Stages of Biofilm Formation at Solid–Liquid Interfaces
by
Elisavet Malea, Maria Petala, Margaritis Kostoglou and Theodoros Karapantsios
Water 2025, 17(15), 2277; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152277 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Water systems are highly vulnerable to biofilm formation, which can compromise water quality, operational efficiency, and public health. Factors such as surface material properties and gravitational orientation of the surface play critical roles in the early stages of microbial attachment and biofilm development.
[...] Read more.
Water systems are highly vulnerable to biofilm formation, which can compromise water quality, operational efficiency, and public health. Factors such as surface material properties and gravitational orientation of the surface play critical roles in the early stages of microbial attachment and biofilm development. This study examines the impact of gravity and surface composition on the initial adhesion of Pseudomonas fluorescens AR11—a model organism for biofilm research. Focusing on stainless steel (SS) and polycarbonate (PC), two materials commonly used in water and wastewater infrastructure, bacterial adhesion was evaluated at surface inclinations of 0°, 45°, 90°, and 180° to assess gravitational impact. After three hours of contact, fluorescence microscopy and image analysis were used to quantify surface coverage and cluster size distribution. The results showed that both material type and orientation significantly affected early biofilm formation. PC surfaces consistently exhibited higher bacterial adhesion at all angles, with modest variations, suggesting that material properties are a dominant factor in initial colonization. In contrast, SS showed angle-dependent variation, indicating a combined effect of gravitational convection and surface characteristics. These insights contribute to a deeper understanding of biofilm dynamics under realistic environmental conditions, including those encountered in space systems, and support the development of targeted strategies for biofilm control in water systems and spaceflight-related infrastructure.
Full article
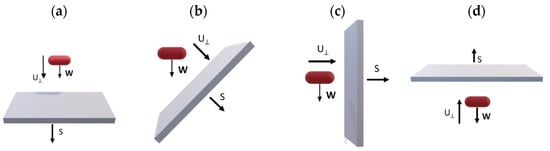
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Paradigm Shift in Scientific Interest on Flood Risk: From Hydraulic Analysis to Integrated Land Use Planning Approaches
by
Ángela Franco and Salvador García-Ayllón
Water 2025, 17(15), 2276; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152276 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Floods are natural hazards that have the greatest socioeconomic impact worldwide, given that 23% of the global population live in urban areas at risk of flooding. In this field of research, the analysis of flood risk has traditionally been studied based mainly on
[...] Read more.
Floods are natural hazards that have the greatest socioeconomic impact worldwide, given that 23% of the global population live in urban areas at risk of flooding. In this field of research, the analysis of flood risk has traditionally been studied based mainly on approaches specific to civil engineering such as hydraulics and hydrology. However, these patterns of approaching the problem in research seem to be changing in recent years. During the last few years, a growing trend has been observed towards the use of methodology-based approaches oriented towards urban planning and land use management. In this context, this study analyzes the evolution of these research patterns in the field by developing a bibliometric meta-analysis of 2694 scientific publications on this topic published in recent decades. Evaluating keyword co-occurrence using VOSviewer software version 1.6.20, we analyzed how phenomena such as climate change have modified the way of addressing the study of this problem, giving growing weight to the use of integrated approaches improving territorial planning or implementing adaptive strategies, as opposed to the more traditional vision of previous decades, which only focused on the construction of hydraulic infrastructures for flood control.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Spatial Analysis of Flooding Phenomena: Challenges and Case Studies)
►▼
Show Figures
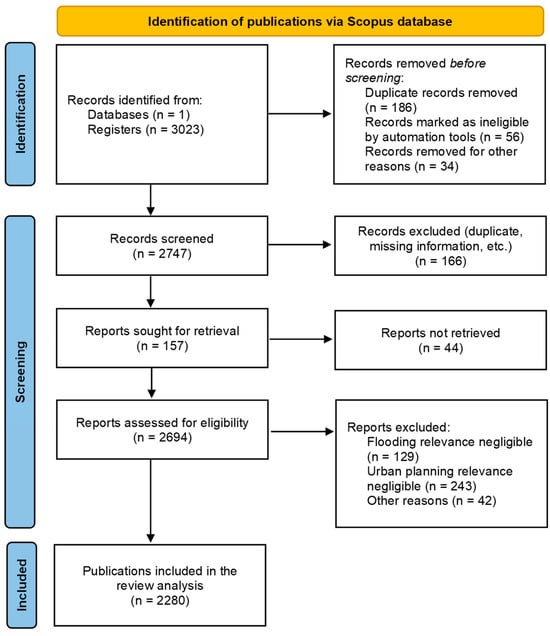
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Wastewater Reuse to Address Climate Change: Insight from Legionella Contamination During Wastewater Treatment
by
Manuela Macrì, Marta Catozzo, Silvia Bonetta and Sara Bonetta
Water 2025, 17(15), 2275; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152275 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Climate change is significantly affecting water availability, emphasising the need for sustainable strategies such as wastewater reuse. While this represents a promising alternative resource, insufficiently treated wastewater may pose health risks, particularly through aerosol formation during irrigation, which can facilitate Legionella transmission. This
[...] Read more.
Climate change is significantly affecting water availability, emphasising the need for sustainable strategies such as wastewater reuse. While this represents a promising alternative resource, insufficiently treated wastewater may pose health risks, particularly through aerosol formation during irrigation, which can facilitate Legionella transmission. This study aimed to evaluate the presence of Legionella across various stages in a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) that reuses effluent for agricultural purposes. Samples from the influent, four treatment phases, and the final effluent were analysed using both culture-based methods and quantitative PCR (qPCR) for Legionella spp. and L. pneumophila. qPCR detected Legionella spp. in all samples and L. pneumophila in 66% of them. In contrast, the culture-based analysis showed much lower detection levels, with only one positive sample at the influent stage—likely due to microbial interference or growth inhibition. Although contamination decreased in the final effluent, Legionella was still detected in water designated for reuse (Legionella spp. in 100% and L. pneumophila in 17% of samples). No treatment stage appeared to promote Legionella proliferation, likely due to WWTP characteristics, in addition to wastewater temperature and COD. These findings underscore the importance of monitoring Legionella in reclaimed water and developing effective control strategies to ensure the safe reuse of treated wastewater in agriculture.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Legionella: A Key Organism in Water Management)
►▼
Show Figures
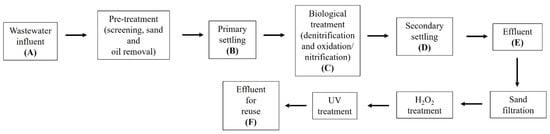
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Challenges and Opportunities in Using Fish Metrics for Reservoir Water Quality Evaluation
by
Alexandre Moreira, Sara Rodrigues, Lucas Ferreira, Nuno E. Formigo and Sara C. Antunes
Water 2025, 17(15), 2274; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152274 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
The Water Framework Directive (WFD) was designed to protect the quality of all water resources. For reservoirs, the ecological potential classification assesses biological parameters, evaluating only the phytoplankton community. Thus, this study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of using fish communities to determine
[...] Read more.
The Water Framework Directive (WFD) was designed to protect the quality of all water resources. For reservoirs, the ecological potential classification assesses biological parameters, evaluating only the phytoplankton community. Thus, this study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of using fish communities to determine water quality in reservoirs. A literature review was conducted to gather information on how fish community data were integrated into reservoir water quality assessment under the WFD. This work includes an exploratory case study of the Aguieira Reservoir (Portugal), evaluating the ichthyofauna community, along with physical, chemical, and biological assessment of the water. The results of the review show that fish abundance and composition (sensitive metrics) should be used to develop ecological indices for assessing water quality in reservoirs. However, the effects of anthropogenic pressures and invasive species are not included in the calculation of most proposed indices. The case study serves as an illustrative example and demonstrates low abundance and composition of the fish community with a high percentage of invasive species, revealing a poor water quality, regarding ichthyofauna biotic index results (F-IBIP). Nevertheless, including these metrics in the classification of ecological potential can help guide restoration strategies to mitigate the effects of anthropogenic pressures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Water Quality and Contamination)
►▼
Show Figures
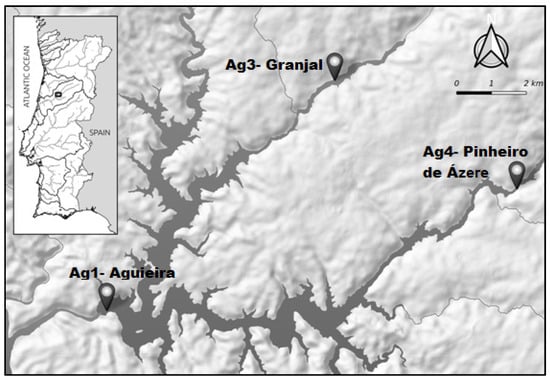
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Ecosystem Services in Urban Blue-Green Infrastructure: A Bibliometric Review
by
Xuefei Wang, Qi Hu, Run Zhang, Chuanhao Sun and Mo Wang
Water 2025, 17(15), 2273; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152273 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
Urban blue-green infrastructure (UBGI) is a comprehensive solution that balances environmental, social, and economic development objectives and has emerged as a critical approach for fostering urban resilience and sustainable development. This paper conducts a systematic bibliometric analysis of 975 academic articles published between
[...] Read more.
Urban blue-green infrastructure (UBGI) is a comprehensive solution that balances environmental, social, and economic development objectives and has emerged as a critical approach for fostering urban resilience and sustainable development. This paper conducts a systematic bibliometric analysis of 975 academic articles published between 2000 and 2023 in the Web of Science Core Collection, focusing specifically on the ecosystem services associated with UBGI. Employing CiteSpace visualization technology, this study elucidates the major research trends, thematic clusters, and international collaboration patterns shaping this field. The research delves into the diverse range of ecosystem services provided by blue-green infrastructure and analyzes their contributions to urban well-being. Findings indicate that regulatory services—particularly climate regulation, biodiversity enhancement, and water resource management—have become central research foci within the contexts of urban green infrastructure (UGI), urban blue infrastructure (UBI), and UBGI. Co-citation and keyword analyses reveal that nature-based solutions, hybrid green–gray infrastructure, and the application of urban resilience frameworks are gaining increasing scholarly attention. By summarizing the evolutionary trajectory and priority directions of UBGI research, this study provides significant insights for future interdisciplinary research aimed at enhancing the supply of urban environmental ecosystem services.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Water Treatment Systems: Green Infrastructure and Bioremediation)
►▼
Show Figures
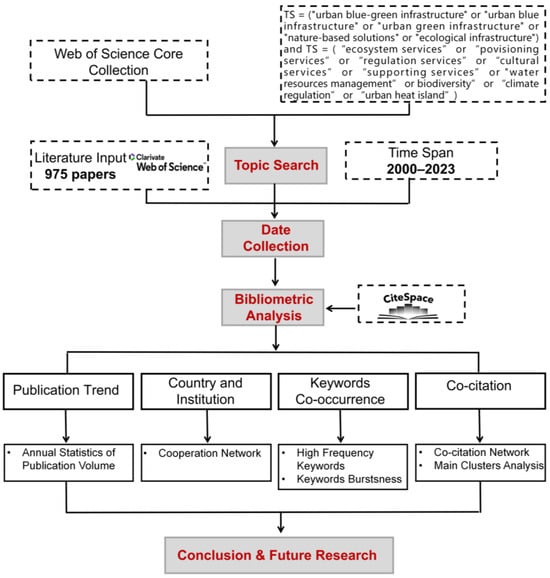
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Daily Reference Evapotranspiration Derived from Hourly Timestep Using Different Forms of Penman–Monteith Model in Arid Climates
by
A A Alazba, Mohamed A. Mattar, Ahmed El-Shafei, Farid Radwan, Mahmoud Ezzeldin and Nasser Alrdyan
Water 2025, 17(15), 2272; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152272 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
In arid and semi-arid climates, where water scarcity is a persistent challenge, accurately estimating reference evapotranspiration (ET) becomes essential for sustainable water management and agricultural planning. The objectives of this study are to compare hourly ET among P–M ASCE, P–M FAO, and P–M
[...] Read more.
In arid and semi-arid climates, where water scarcity is a persistent challenge, accurately estimating reference evapotranspiration (ET) becomes essential for sustainable water management and agricultural planning. The objectives of this study are to compare hourly ET among P–M ASCE, P–M FAO, and P–M KSA mathematical models. In addition to the accuracy assessment of daily ET derived from hourly timestep calculations for the P–M ASCE, P–M FAO, and P–M KSA. To achieve these goals, a total of 525,600-min data points from the Riyadh region, KSA, were used to compute the reference ET at multiple temporal resolutions: hourly, daily, hourly averaged over 24 h, and daily as the sum of 24 h values, across all selected Penman–Monteith (P–M) models. For hourly investigation, the comparison between reference ET computed as average hourly values and as daily/24 h values revealed statistically and practically significant differences. The Wilcoxon test confirmed a statistically significant difference (p < 0.0001) with R2 of 94.75% for ASCE, 94.87% for KSA at hplt = 50 cm, 92.41% for FAO, and 92.44% for KSA at hplt = 12 cm. For daily investigation, comparing the sum of 24 h ET computations to daily ET measurements revealed an underestimation of daily ET values. The Wilcoxon test confirmed a statistically significant difference (p < 0.0001), with R2 exceeding 90% for all studied reference ET models. This comprehensive approach enabled a rigorous evaluation of reference ET dynamics under hyper-arid climatic conditions, which are characteristic of central Saudi Arabia. The findings contribute to the growing body of literature emphasizing the importance of high-frequency meteorological data for improving ET estimation accuracy in arid and semi-arid regions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Hydrology)
►▼
Show Figures
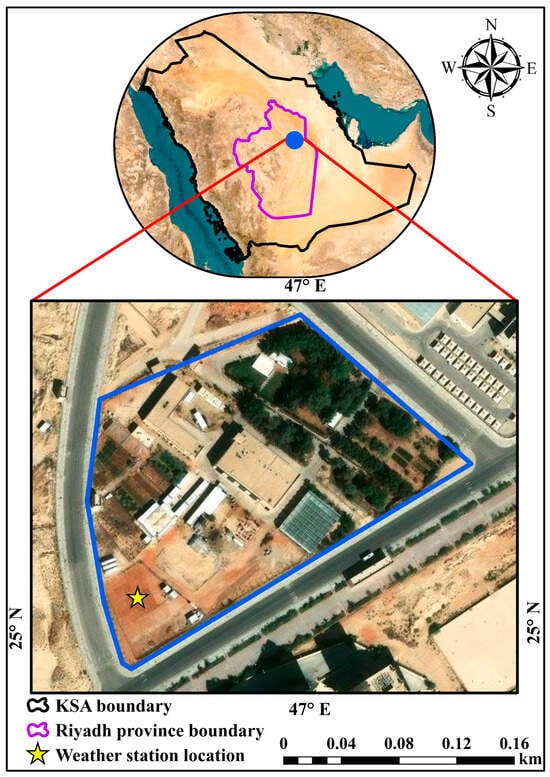
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study on Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow and Wear Characteristics in Multistage Centrifugal Pumps Based on the Euler-Lagrange Approach
by
Zhengyin Yang, Yandong Gu, Yingrui Zhang and Zhuoqing Yan
Water 2025, 17(15), 2271; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152271 (registering DOI) - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
Multistage centrifugal pumps, owing to their high head characteristics, are commonly applied in domains like subsea resource exploitation and groundwater extraction. However, the wear of flow passage components caused by solid particles in the fluid severely threatens equipment lifespan and system safety. To
[...] Read more.
Multistage centrifugal pumps, owing to their high head characteristics, are commonly applied in domains like subsea resource exploitation and groundwater extraction. However, the wear of flow passage components caused by solid particles in the fluid severely threatens equipment lifespan and system safety. To investigate the influence of solid-liquid two-phase flow on pump performance and wear, this study conducted numerical simulations of the solid-liquid two-phase flow within multistage centrifugal pumps based on the Euler–Lagrange approach and the Tabakoff wear model. The simulation results showed good agreement with experimental data. Under the design operating condition, compared to the clear water condition, the efficiency under the solid-liquid two-phase flow condition decreased by 1.64%, and the head coefficient decreased by 0.13. As the flow rate increases, particle momentum increases, the particle Stokes number increases, inertial forces are enhanced, and the coupling effect with the fluid weakens, leading to an increased impact intensity on flow passage components. This results in a gradual increase in the wear area of the impeller front shroud, back shroud, pressure side, and the peripheral casing. Under the same flow rate condition, when particles enter the pump chamber of a subsequent stage from a preceding stage, the fluid, after being rectified by the return guide vane, exhibits a more uniform flow pattern and reduced turbulence intensity. The particle Stokes number in the subsequent stage is smaller than that in the preceding stage, weakening inertial effects and enhancing the coupling effect with the fluid. This leads to a reduced impact intensity on flow passage components, resulting in a smaller wear area of these components in the subsequent stage compared to the preceding stage. This research offers critical theoretical foundations and practical guidelines for developing wear-resistant multistage centrifugal pumps in solid-liquid two-phase flow applications, with direct implications for extending service life and optimizing hydraulic performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Hydrodynamics for Pumping Systems: Modeling, Optimization, and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
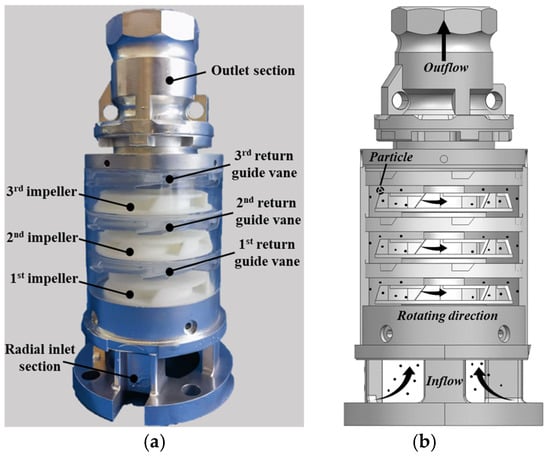
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transboundary Water–Energy–Food Nexus Management in Major Rivers of the Aral Sea Basin Through System Dynamics Modelling
by
Sara Pérez Pérez, Iván Ramos-Diez and Raquel López Fernández
Water 2025, 17(15), 2270; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152270 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
Central Asia (CA) faces growing Water–Energy–Food (WEF) Nexus challenges, due to its complex transboundary water management, legacy Soviet-era water infrastructure, and increasing climate and socio-economic pressures. This study presents the development of a System Dynamics Model (SDM) to evaluate WEF interdependencies across the
[...] Read more.
Central Asia (CA) faces growing Water–Energy–Food (WEF) Nexus challenges, due to its complex transboundary water management, legacy Soviet-era water infrastructure, and increasing climate and socio-economic pressures. This study presents the development of a System Dynamics Model (SDM) to evaluate WEF interdependencies across the Aral Sea Basin (ASB), including the Amu Darya and Syr Darya river basins and their sub-basins. Different downscaling strategies based on the area, population, or land use have been applied to process open-access databases at the national level in order to match the scope of the study. Climate and socio-economic assumptions were introduced through the integration of already defined Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs) and Representative Concentration Pathways (RCPs). The resulting SDM incorporates more than 500 variables interacting through mathematical relationships to generate comprehensive outputs to understand the WEF Nexus concerns. The SDM was successfully calibrated and validated across three key dimensions of the WEF Nexus: final water discharge to the Aral Sea (Mean Absolute Error, MAE, <5%), energy balance (MAE = 4.6%), and agricultural water demand (basin-wide MAE = 1.2%). The results underscore the human-driven variability of inflows to the Aral Sea and highlight the critical importance of transboundary coordination to enhance future resilience.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Insights on the Water–Energy–Food Nexus and Sustainable Development)
►▼
Show Figures
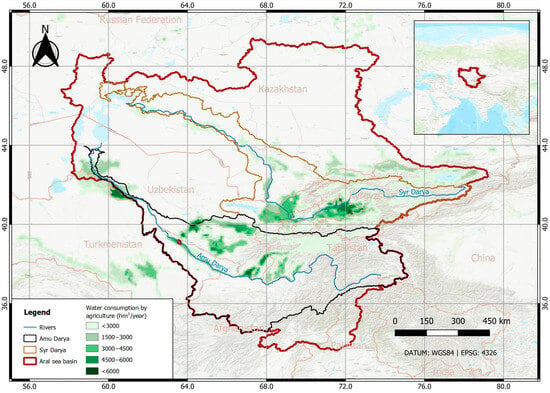
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Adaptive Pluvial Flood Disaster Management in Taiwan: Infrastructure and IoT Technologies
by
Sheng-Hsueh Yang, Sheau-Ling Hsieh, Xi-Jun Wang, Deng-Lin Chang, Shao-Tang Wei, Der-Ren Song, Jyh-Hour Pan and Keh-Chia Yeh
Water 2025, 17(15), 2269; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152269 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In Taiwan, hydro-meteorological data are fragmented across multiple agencies, limiting the effectiveness of coordinated flood response. To address this challenge and the increasing uncertainty associated with extreme rainfall, a real-time disaster prevention platform has been developed. This system integrates multi-source data and geospatial
[...] Read more.
In Taiwan, hydro-meteorological data are fragmented across multiple agencies, limiting the effectiveness of coordinated flood response. To address this challenge and the increasing uncertainty associated with extreme rainfall, a real-time disaster prevention platform has been developed. This system integrates multi-source data and geospatial information through a cluster-based architecture to enhance pluvial flood management. Built on a Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and incorporating Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, AI-based convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and 3D drone mapping, the platform enables automated alerts by linking sensor thresholds with real-time environmental data, facilitating synchronized operational responses. Deployed in New Taipei City over the past three years, the system has demonstrably reduced flood risk during severe rainfall events. Region-specific action thresholds and adaptive strategies are continually refined through feedback mechanisms, while integrated spatial and hydrological trend analyses extend the lead time available for emergency response.
Full article
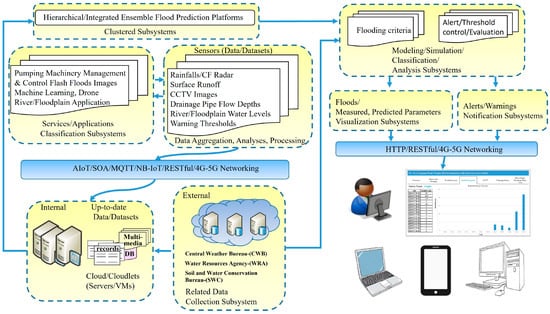
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Modeling Water Table Response in Apulia (Southern Italy) with Global and Local LSTM-Based Groundwater Forecasting
by
Lorenzo Di Taranto, Antonio Fiorentino, Angelo Doglioni and Vincenzo Simeone
Water 2025, 17(15), 2268; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152268 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
For effective groundwater resource management, it is essential to model the dynamic behaviour of aquifers in response to rainfall. Here, a methodological approach using a recurrent neural network, specifically a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network, is used to model groundwater levels of the
[...] Read more.
For effective groundwater resource management, it is essential to model the dynamic behaviour of aquifers in response to rainfall. Here, a methodological approach using a recurrent neural network, specifically a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network, is used to model groundwater levels of the shallow porous aquifer in Southern Italy. This aquifer is recharged by local rainfall, which exhibits minimal variation across the catchment in terms of volume and temporal distribution. To gain a deeper understanding of the complex interactions between precipitation and groundwater levels within the aquifer, we used water level data from six wells. Although these wells were not directly correlated in terms of individual measurements, they were geographically located within the same shallow aquifer and exhibited a similar hydrogeological response. The trained model uses two variables, rainfall and groundwater levels, which are usually easily available. This approach allowed the model, during the training phase, to capture the general relationships and common dynamics present across the different time series of wells. This methodology was employed despite the geographical distinctions between the wells within the aquifer and the variable duration of their observed time series (ranging from 27 to 45 years). The results obtained were significant: the global model, trained with the simultaneous integration of data from all six wells, not only led to superior performance metrics but also highlighted its remarkable generalization capability in representing the hydrogeological system.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Hydrogeology)
►▼
Show Figures
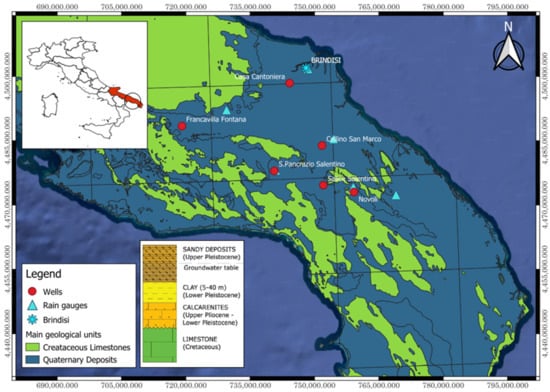
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hydrological Responses to Territorial Spatial Change in the Xitiaoxi River Basin: A Simulation Study Using the SWAT Model Driven by China Meteorological Assimilation Driving Datasets
by
Dongyan Kong, Huiguang Chen and Kongsen Wu
Water 2025, 17(15), 2267; https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152267 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
The use of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model driven by China Meteorological Assimilation Driving Datasets (CMADS) for runoff simulation research is of great significance for regional flood prevention and control. Therefore, from the perspective of production-living-ecological space, this article combined
[...] Read more.
The use of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model driven by China Meteorological Assimilation Driving Datasets (CMADS) for runoff simulation research is of great significance for regional flood prevention and control. Therefore, from the perspective of production-living-ecological space, this article combined multi-source data such as DEM, soil texture and land use type, in order to construct scenarios of territorial spatial change (TSC) across distinct periods. Based on the CMADS-L40 data and the SWAT model, it simulated the runoff dynamics in the Xitiaoxi River Basin, and analyzed the hydrological response characteristics under different TSCs. The results showed that The SWAT model, driven by CMADS-L40 data, demonstrated robust performance in monthly runoff simulation. The coefficient of determination (R2), Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE), and the absolute value of percentage bias (|PBIAS|) during the calibration and validation period all met the accuracy requirements of the model, which validated the applicability of CMADS-L40 data and the SWAT model for runoff simulation at the watershed scale. Changes in territorial spatial patterns are closely correlated with runoff variation. Changes in agricultural production space and forest ecological space show statistically significant negative correlation with runoff change, while industrial production space change exhibits a significant positive correlation with runoff change. The expansion of production space, particularly industrial production space, leads to increased runoff, whereas the enlargement of agricultural production space and forest ecological space can reduce runoff. This article contributes to highlighting the role of land use policy in hydrological regulation, providing a scientific basis for optimizing territorial spatial planning to mitigate flood risks and protect water resources.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Natural Hazards and Disaster Risks Reduction, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
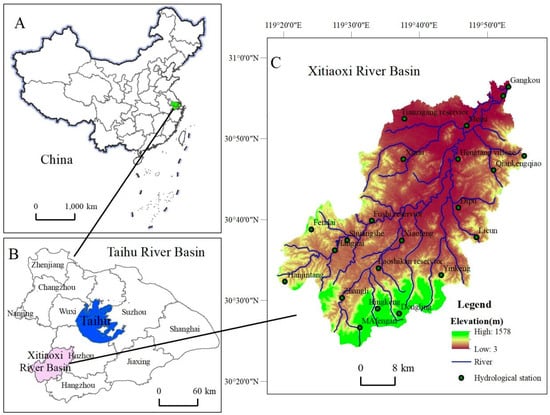
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Water Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agrochemicals, Environments, Water, Toxics, Soil Systems, Microplastics, Microorganisms, Sustainability
The Challenges and Future Trends in Anthropogenic and Natural Pollution Control Engineering
Topic Editors: Chenyang Zhang, Fujing Pan, Xiaoyu Gao, Weiqi Fu, Anxu Sheng, Zhiqiang Kong, Lei He, Sining Zhong, Jie ChenDeadline: 1 August 2025
Topic in
Membranes, Polymers, Sustainability, Water, C
Towards Energy-Positive and Carbon-Neutral Technology for Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation
Topic Editors: Xin Zhou, Dongqi Wang, Qiulai He, Xiaoyuan ZhangDeadline: 31 August 2025
Topic in
Energies, IJMS, Membranes, Separations, Water
Membrane Separation Technology Research
Topic Editors: Chenxiao Jiang, Zhe Yang, Ying MeiDeadline: 15 September 2025
Topic in
Energies, Geosciences, JMSE, Minerals, Water
Basin Analysis and Modelling
Topic Editors: Jingshou Liu, Wenlong Ding, Ruyue Wang, Lei Gong, Ke Xu, Ang LiDeadline: 30 September 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Water
Assessment of Groundwater Quality and Pollution Remediation
Guest Editors: Yong Qian, Zhi DouDeadline: 10 August 2025
Special Issue in
Water
Sustainable Remediation of Pesticides in Contaminated Water and Sites
Guest Editors: Limin Ma, Deyang KongDeadline: 10 August 2025
Special Issue in
Water
Research on the Dynamics of Phytoplankton in Eutrophic Water
Guest Editors: Xinxin Lu, Lei Cui, Da HuoDeadline: 10 August 2025
Special Issue in
Water
Environmental Fate and Transport of Organic Pollutants in Water
Guest Editors: Tengyi Zhu, Rajendra Prasad Singh, Haomiao ChengDeadline: 10 August 2025









