Phosphorus Solubilizing and Releasing Bacteria Screening from the Rhizosphere in a Natural Wetland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Extraction, Isolation and Purification of Rhizosphere Bacteria
2.2.2. Preparation of P Medium
2.2.3. Measurement of P-Solubilizing and -Releasing Capability
2.2.4. P-Solubilizing and -Releasing Rate Calculation
2.2.5. Microbial Community Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. P-Solubilizing Capacity of Inorganic Insoluble P (Ca3(PO4)2)
3.2. P-Solubilizing Capacity of Organic P (Lecithin)
3.3. Correlation of Solubilized P and pH in Ca3(PO4)2 Liquid Medium
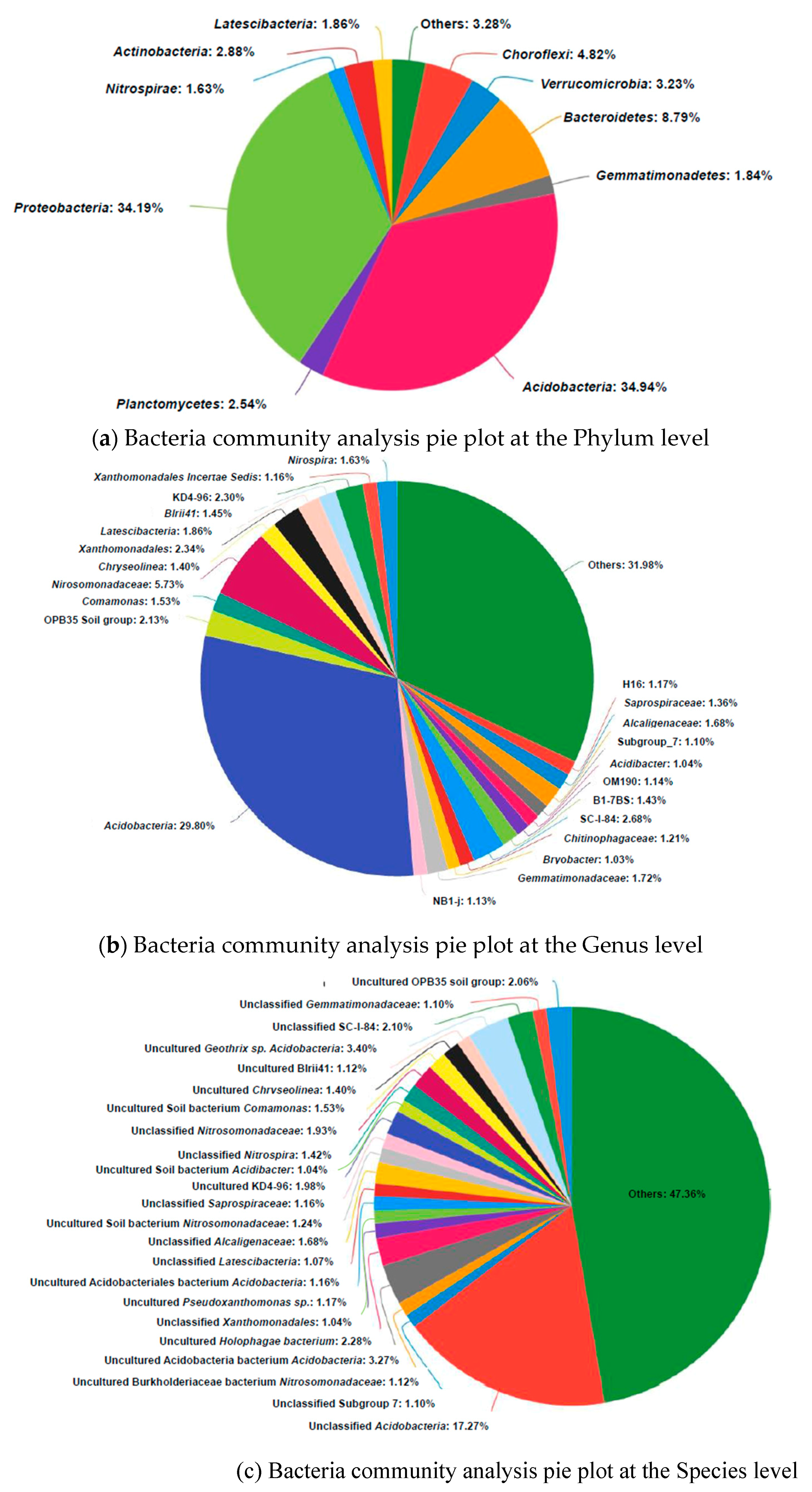
3.4. Microbial Community Analysis
4. Practical Applications and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contribution
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Yu, X. Effects of Aeration, Vegetation, and Iron Input on Total P Removal in a Lacustrine Wetland Receiving Agricultural Drainage. Water 2018, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Carlos, J.; McConnell, R.; Hall, G.; Champagne, P. Peat as Substrate for Small-Scale Constructed Wetlands Polishing Secondary Effluents from Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Water 2017, 9, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cui, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, M.; Xu, W.; Zhao, X.; Lei, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, J.; et al. Using a Backpropagation Artificial Neural Network to Predict Nutrient Removal in Tidal Flow Constructed Wetlands. Water 2018, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Xiao, J.; Rahaman, M.H.; John, Y.; Xiao, J. Seasonal Variation of Nutrient Removal in a Full-Scale Artificial Aerated Hybrid Constructed Wetland. Water 2016, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Otte, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Qin, L.; Tian, X.; Lu, X.; Jiang, M.; Zou, Y. Performance of Iron Plaque of Wetland Plants for Regulating Iron, Manganese, and Phosphorus from Agricultural Drainage Water. Water 2018, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Y.; Pan, X.; Cui, L.; Li, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wei, J. Effects of Plant Growth Form and Water Substrates on the Decomposition of Submerged Litter: Evidence of Constructed Wetland Plants in a Greenhouse Experiment. Water 2017, 9, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Shi, H.; Pan, X.; Liu, F.; Cui, Y.; Xie, H. Integrating Ecological Restoration of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in Poyang Lake Basin in China. Water 2017, 9, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.; Chagas, I.; Klimeski, A.; Lyngsie, G. A Review of Phosphorus Removal Structures: How to Assess and Compare Their Performance. Water 2017, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, C.; Norvell, W.A.; Bjorkman, T.; Harman, G.E. Solubilization of phosphates and micronutrients by the plant growth promoting and biocontrol fungus Trichoderma harzianum Fifai1295-22. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2926–2933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.R.; Delaune, R.D. Biogeochemistry of wetlands: Science and applications. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 73, 1779. [Google Scholar]
- Shenker, M.; Seitelbach, S.; Brand, S.; Haim, A.; Litaor, M.I. Redox reactions and phosphorus release in re-flooded soils of an altered wetland. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 56, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borggaard, O.K.; Raben-Lange, B.; Gimsing, A.L.; Strobel, B.W. Influence of humic substances on phosphate adsorption by aluminum and iron oxides. Geoderma 2005, 127, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfim, J.; Schoebitz, M.; Paulino, L.; Hirzel, J.; Zagal, E. Phosphorus Availability in Wheat, in Volcanic Soils Inoculated with Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacillus thuringiensis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Han, S.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Cho, B.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Koo, B.S.; Kim, Y.C. Cloning and expression of pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) genes from a phosphate-solubilizing bacterium Enterobacter intermedium. Curr. Microbiol. 2004, 47, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.C.; Tian, S.J.; Cai, M.Y.; Guang, H.X. Phosphate-Solubilizing and -Mineralizing Abilities of Bacteria Isolated from Soils. Pedosphere 2008, 4, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.A.; Alves, V.M.C.; Marriel, I.E.; Gomes, E.A.; Scotti, M.R.; Carneiro, N.P.; Guimarães, C.T.; Schaffert, R.E.; Sá, N.M.H. Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms isolated from rhizosphere of maize cultivated in an oxisol of the Brazilian Cerrado Biome. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1782–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A. Recent progress in understanding the moleculargenetics and biochemistry of calcium phosphate solubilization by gram negative bacteria. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 1995, 12, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illmer, P.; Schinner, F. Solubilization of inorganic phosphateby microorganisms isolated from forest soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1992, 24, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.M.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.S.; Tang, C. Acid Phosphatase Role in Chickpea/Maize Intercropping. Ann. Bot. 2004, 94, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, J.H.; Zeng, C.S.; Tong, C.; Wang, W.Q.; Liao, J. Organic and Inorganic Phosphorus in Sediments of the Min River Estuarine Wetlands: Contents and Profile Distribution. J. Subtropic. Res. Environ. 2010, 5, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Y.; Chong, Y.X.; Yu, G.W.; Zhong, H.T. Difference of P Content in Different Area Substrate of Constructed Wetland. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 4033–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Gao, B.; Hao, H. Study on the occurrence of phosphorus in the sediments of artificial wetland. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2014, 11, 3162–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Shao, X.X.; Wu, M.; Li, W.H.; Ye, X.Q.; Jiang, K.Y. Phosphorus fraction in the sediments from different vegetation type in hangzhou bay coastal wetlands. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 5025–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.Z. Study on the Morphological Characteristics and Adsorption Desorption Characteristics of Phosphorus in Wetland Soil under Different Tillage Year. Ph.D. Thesis, Anhwei Normal University, Wuhu, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, J.M.; Whipps, J.M. Substrate flow in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 1990, 129, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.E.; Simpson, R.J. Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability update on microbial phosphorus. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.J. Ion Uptake Mechanisms of Individual Cells and Roots: Shortdistance Transport. In Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 7–47. [Google Scholar]
- Cerozi, B.S.; Fitzsimmons, K. The effect of pH on phosphorus availability and speciation in an aquaponics nutrient solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Gao, T.Y. Environmental Engineering Microbiology, 3rd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 380–448. ISBN 978-7-04-022265-4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nautiyal, C.S. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewolak, S. Occurrence of microorganisms in fertilized lakes. II. Lecithin-mineralizing microorganisms. Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1980, 27, 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Pepper, L.L.; Gerba, C.P.; Terry, J. Environmental Microbiology, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-12-394626-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.M.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.R.; Zhao, Z.J. The solubilizing ability of some bacteria and fungi and its mechanisms. Microbiol. China 2001, 28, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Ma, Z.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Wei, L. Screening of phosphorus bacteria and its effects on maize growth at seedling stage. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 7, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.B.; Yang, X.M.; Shen, Q.R.; Xu, Y.C. Mechanism on phosphate solubilization of pseudomonas sp. K_3 and its phosphate solubilization ability under buffering condition. Plant Nutr. Fertile Sci. 2010, 16, 354–361. [Google Scholar]
- Moorberg, C.J.; Vepraskas, M.J.; Niewoehner, C.P. Phosphorus dissolution in the rhizosphere of bald cypress trees in restored wetland soils wetland soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadamur, G.; Ross, E.M. Mammalian phospholipase C. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 127–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titball, R.W. Bacterial phospholipase C. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 57, 347–366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Essen, L.O.; Perisic, O.; Katan, M.; Wu, Y.; Roberts, M.F.; Williams, R.L. Structural mapping of the catalytic mechanism for a mammalian phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolesnikov, Y.S.; Nokhrina, K.P.; Kretynin, S.V.; Volotovski, I.D.; Martinec, J.; Romanov, G.A.; Kravets, V.S. Molecular structure of phospholipase D and regulatory mechanisms of its activity in plant and animal cells. Biochem. Biokhimiia 2012, 77, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.S. Screening of Phospholipase Producing Strain C and Study on Its Enzymatic Properties. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Shang, J. Screening and identification of high efficiency producing bacteria from phospholipase D. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 309–311. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.D. Screening and identification of high yield phospholipase D strain and optimization of fermentation conditions. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 521–525. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, D.A. Targeting Phospholipase D-mediated Survival Signals in Cancer. Curr. Signal Transduct. Ther. 2006, 1, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboa, M.A.; Firestein, B.L.; Godson, C.; Bell, K.S.; Insel, P.A. Protein kinase C alpha mediates phospholipase D activation by nucleotides and phorbol ester in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Stimulation of phospholipase D is independent of activation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C and phospholipase A. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10511–10516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierzynski, G.M.; Sims, J.T.; Vance, G.F. Soils and Environmental Quality, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 145–146. ISBN 0-8493-1616-2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Study on Soil Microbial Community Structure Based on High Throughput Sequencing Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Zhou, W.; Huang, J.; He, S.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, W. Nitrogen removal by the enhanced floating treatment wetlands from the secondary effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaiser, A.; Ochsenreiter, T.; Lanz, C.; Schuster, S.C.; Treusch, A.H.; Eck, J. Acidobacteria form a coherent but highly diverse group within the bacterial domain: Evidence from environmental genomics. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Strain No. | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R9 | R10 | R11 | R12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Concentration of dissolved P (mg·L−1) | 107.77 | 103.24 | 91.92 | 98.71 | 81.73 | 100.97 | 102.11 | 86.26 | 105.5 | 125.88 | 106.63 | 100.97 |
| Max Con. Day (day) | 10 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 9 |
| Max rate of solubilizing P (mg·L−1·h−1) | 2.37 | 2.23 | 3.03 | 1.06 | 0.93 | 1.44 | 1.46 | 1.30 | 1.11 | 1.80 | 0.66 | 0.73 |
| Max rate time (hours) | 24 | 24 | 24 | 48 | 72 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 72 | 120 |
| P releasing rate η in 10 days (mg·L−1·h−1) | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 0.3 | 0.27 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 0.44 | 0.41 |
| Strain No. | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R9 | R10 | R11 | R12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Concentration of P (mg·L−1) | 0.88 | 0.81 | 1.10 | 1.88 | 0.90 | 0.49 | 0.45 | 1.01 | 0.89 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.79 |
| Max Con. Day (day) | 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 6 | 9 | 6 | 7 |
| Max rate of releasing P (mg·L−1·h−1) | 0.0117 | 0.0053 | 0.0088 | 0.0078 | 0.0118 | 0.0178 | 0.0135 | 0.0126 | 0.0116 | 0.0106 | 0.0087 | 0.0093 |
| Max rate time (hours) | 24 | 144 | 24 | 240 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| P releasing rate η in 10 days (mg·L−1·h−1) | 0.0032 | 0.0033 | 0.0046 | 0.0078 | 0.0024 | 0.0012 | 0.0012 | 0.0042 | 0.0031 | 0.0026 | 0.0019 | 0.0019 |
| Sample | OTU | Sequences | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao | Species | Genus | Dominant Phylum | Proportion of Dominant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaoR1-B | 445 | 30212 | 5.521541 | 0.00652 | 445 | 445 | 274 | 179 | Acidobacteria | 34.9% |
| Yellow river Delta Wetland[47] | 30874 | Proteobacteria | 44.67% | |||||||
| Floating treatment wetland [48] | 11477 | 78242 | 8.49 | 0.9931 | 2105 | 1603 | Proteobacteria | 46.4% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Fu, D.; Liu, T.; Guo, G.; Hu, Z. Phosphorus Solubilizing and Releasing Bacteria Screening from the Rhizosphere in a Natural Wetland. Water 2018, 10, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020195
Cao Y, Fu D, Liu T, Guo G, Hu Z. Phosphorus Solubilizing and Releasing Bacteria Screening from the Rhizosphere in a Natural Wetland. Water. 2018; 10(2):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020195
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Ying, Dafang Fu, Tingfeng Liu, Guang Guo, and Zhixin Hu. 2018. "Phosphorus Solubilizing and Releasing Bacteria Screening from the Rhizosphere in a Natural Wetland" Water 10, no. 2: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020195
APA StyleCao, Y., Fu, D., Liu, T., Guo, G., & Hu, Z. (2018). Phosphorus Solubilizing and Releasing Bacteria Screening from the Rhizosphere in a Natural Wetland. Water, 10(2), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020195






