Isotopic Characteristics of Precipitation and Origin of Moisture Sources in Hemuqiao Catchment, a Small Watershed in the Lower Reach of Yangtze River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Instrumentation and Event Sampling
2.3. HYSPLIT Model
3. Results
3.1. Isotopic Characteristics of Atmospheric Precipitation
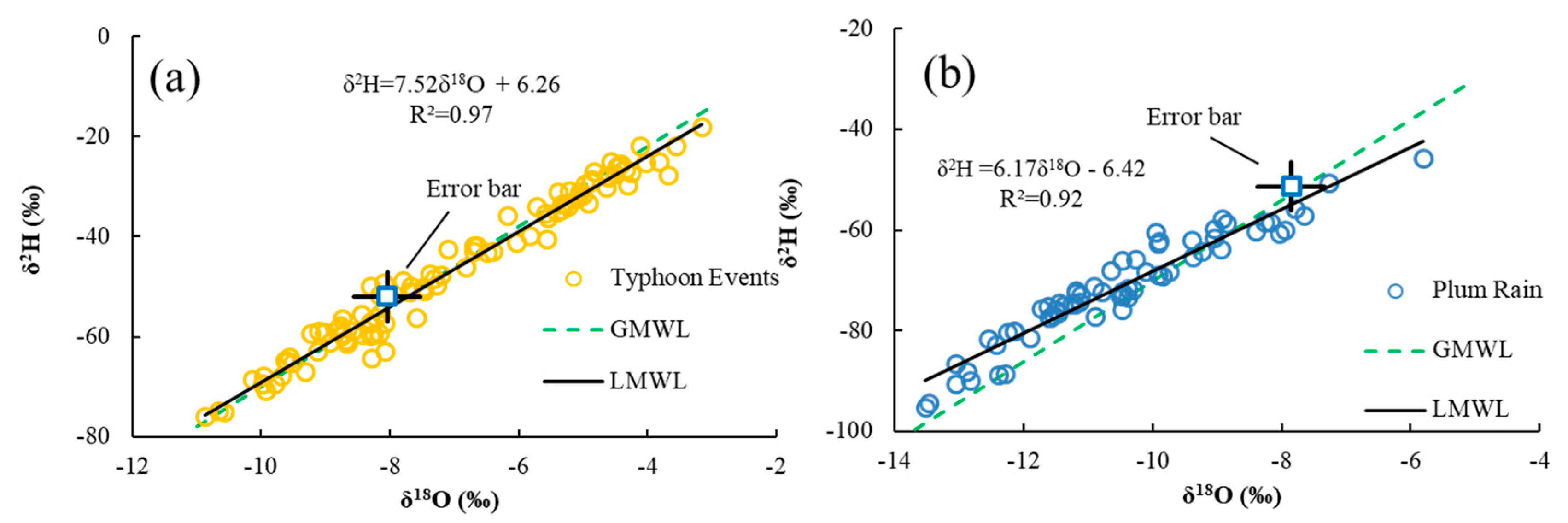
3.2. Meteoric Water Line and Deuterium Excess
3.3. Moisture Source Trajectories
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscarelli, R.; Caloiero, T. Analysis of daily and monthly rainfall concentration in Southern Italy (Calabria region). J. Hydrol. 2012, 416, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J. Spatial and temporal variation in precipitation isotopes in the Sydney Basin, Australia. J. Hydrol. 2013, 489, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.R.; Ingram, B.L. Spatial and temporal variability in the stable isotope systematics of modern precipitation in China: Implications for paleoclimate reconstructions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 220, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouzel, J.; Froehlich, K.; Schotterer, U. Deuterium and oxygen-18 in present-day precipitation: Data and modelling. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. Bull. 1997, 42, 747–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachniet, M.S.; Patterson, W.P. Oxygen isotope values of precipitation and surface waters in northern Central America (Belize and Guatemala) are dominated by temperature and amount effects. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 284, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Matthews, M.; Ayalon, A.; Kaufman, A. Late Quaternary Paleoclimate in the Eastern Mediterranean Region from Stable Isotope Analysis of Speleothems at Soreq Cave, Israel. Quat. Res. 1997, 47, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hren, M.T.; Bookhagen, B.; Blisniuk, P.M.; Booth, A.L.; Chamberlain, C.P. δ18O and δD of streamwaters across the Himalaya and Tibetan Plateau: Implications for moisture sources and paleoelevation reconstructions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 288, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araguásaraguás, L.; Froehlich, K.; Rozanski, K. Deuterium and oxygen-18 isotope composition of precipitation and atmospheric moisture. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 1341–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, T.B.; Yao, T.; Tian, L.; Zhang, X. Amount and temperature effects responsible for precipitation isotope variation in the southern slope of Himalayas. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2013, 5, 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Fu, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hand, D. Precipitation isotope characteristics and climatic controls at a continental and an island site in Northeast Asia. Clim. Res. 2011, 49, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastoe, C.J.; Dettman, D.L. Isotope amount effects in hydrologic and climate reconstructions of monsoon climates: Implications of some long-term data sets for precipitation. Chem. Geol. 2016, 430, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Li, J. Relation between rainfall duration and diurnal variation in the warm season precipitation over central eastern China. Geophys. Rese. Lett. 2007, 34, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Masson, V.; Jouzel, J.; Stievenard, M.; Weizhen, S.; Keqin, J. Relationships between δ18O in precipitation and surface air temperature in the Urumqi River Basin, East Tianshan Mountains, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 3473–3476. [Google Scholar]
- Siegenthaler, U.; Oeschger, H. Correlation of 18O in precipitation with temperature and altitude. Nature 1980, 285, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J. A new precipitation weighted method for determining the meteoric water line for hydrological applications demonstrated using Australian and global GNIP data. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464–465, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J. A rainfall amount weighted meteoric water line for use in hydrological applications. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 19–24 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Voelker, S.L.; Brooks, J.R.; Meinzer, F.C.; Roden, J.; Pazdur, A.; Pawelczyk, S.; Hartsough, P.; Snyder, K.; Plavcová, L.; Santrůcek, J. Reconstructing relative humidity from plant delta 18O and delta D as deuterium deviations from the global meteoric water line. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 960–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacelle, D. On the δ18O, δD and D-excess relations in meteoric precipitation and during equilibrium freezing: theoretical approach and field examples. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2011, 22, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouzel, J.; Merlivat, L.; Lorius, C. Deuterium excess in an East Antarctic ice core suggests higher relative humidity at the oceanic surface during the last glacial maximum. Nature 1982, 299, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenni, B.; Genoni, L.; Flora, O.; Guglielmin, M. An oxygen isotope record from the Foscagno rock-glacier ice core, Upper Valtellina, Italian Central Alps. Holocene 2007, 17, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fu, G.; Song, X.; Charles, S.P.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, S. Stable isotopic composition in Australian precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 6696–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.T.; Ehleringer, J.R. Deuterium excess reveals diurnal sources of water vapor in forest air. Oecologia 2011, 165, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Wei, G.; Deng, W.; Zhao, X. Daily δ18O and δD of precipitations from 2007 to 2009 in Guangzhou, South China: Implications for changes of moisture sources. J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Kennedy, C.D.; Henne, P.D.; Zhang, T. Footprint of recycled water subsidies downwind of Lake Michigan. Ecosphere 2012, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Yuan, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Stable isotopes of summer monsoonal precipitation in southern China and the moisture sources evidence from δ18O signature. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizen, V.; Aizen, E.; Melack, J.; Martma, T. Isotopic measurements of precipitation on central Asian glaciers (southeastern Tibet, northern Himalayas, central Tien Shan). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 9185–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, L.; Yao, T.; MacClune, K.; White, J.W.C.; Schilla, A.; Vaughn, B.; Vachon, R.; Ichiyanagi, K. Stable isotopic variations in west China: A consideration of moisture sources. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brimelow, J.C.; Reuter, G.W. Transport of Atmospheric Moisture during Three Extreme Rainfall Events over the Mackenzie River Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, L.B.; Konrad, C.E.; Schmidlin, T.W. Antecedent Upstream Air Trajectories Associated with Northwest Flow Snowfall in the Southern Appalachians. Weather Forecast. 2007, 22, 334–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, V.C.; Zellweger, G.W.; Avanzino, R.J. Variation of rain chemistry during storms at two sites in northern California. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenninkmeijer, C.A.M.; Geel, B.V.; Mook, W.G. Variations in the D/H and 18O/16O ratios in cellulose extracted from a peat bog core. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1982, 61, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R. Standards for stable isotope measurements in natural compounds. Nature 1978, 271, 534–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the hysplit-4 modeling system for trajectories. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Moroz, B.E.; Beck, H.A.; Simon, S.L. Predictions of dispersion and deposition of fallout from nuclear testing using the NOAA-HYSPLIT meteorological model. Health Phys. 2010, 99, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Neelin, J.D. Mechanisms of Global Warming Impacts on Regional Tropical Precipitation. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2688–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; David Neelin, J.; Chen, C.-A.; Tu, J.-Y. Evaluating the “rich-get-richer” mechanism in tropical precipitation change under global warming. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 1982–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourcy, L.L.; Groening, M.; Aggarwal, P.K. Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in precipitation. In Isotopes in the Water Cycle: Past, Present and Future of Developing Science; Aggarwal, P.K., Gat, J.R., Froehlich, K.F.O., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Weyhenmeyer, C.E.; Burns, S.J.; Waber, H.N.; Macumber, P.G.; Matter, A. Isotope study of moisture sources, recharge areas, and groundwater flow paths within the eastern Batinah coastal plain, Sultanate of Oman. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.; Hughes, C.E.; Lykoudis, S. Alternative least squares methods for determining the meteoric water line, demonstrated using GNIP data. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.S.; Ramesh, R. Rayleigh fractionation of stable isotopes from a multicomponent source. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Qu, S.; Shi, P.; Li, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Si, W. Application of Stable Isotope Tracer to Study Runoff Generation during Different Types of Rainfall Events. Water 2018, 10, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayres, D.S.; Pfister, L.; Hanisco, T.F.; Moyer, E.J.; Smith, J.B.; St. Clair, J.M.; OBrien, A.S.; Witinski, M.F.; Leg, M. Influence of convection on the water isotopic composition of the tropical tropopause layer and tropical stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D00J20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimeux, F.; Masson, V.; Jouzel, J.; Petit, J.-R.; Steig, E.J.; Stiévenard, M.; Vaikmäe, R.; White, J.W.C. Holocene hydrological cycle changes in the Southern Hemisphere documented in East Antarctic deuterium excess records. Clim. Dyn. 2001, 17, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, K.; Kralik, M.; Papesch, W.; Rank, D.; Scheifinger, H.; Stichler, W. Deuterium excess in precipitation of Alpine regions—Moisture recycling. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2008, 44, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitoh, A.; Uchiyama, T. Changes in Onset and Withdrawal of the East Asian Summer Rainy Season by Multi-Model Global Warming Experiments. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 84, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I: Observed evidences. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 1139–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.F.; Li, J.F.; Shi, P.J.; He, Y.Q.; Cai, A.; Tong, H.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Yang, L. Relationship between sub-cloud secondary evaporation and stable isotope in precipitation in different regions of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Huang, Y. Seasonal variations of deuterium and oxygen-18 isotopes and their response to moisture source for precipitation events in the subtropical monsoon region. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.K.; Ding, Y.; Ye, B.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Spatio-temporal variation of stable isotopes in precipitation in the Heihe River Basin, Northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Climatic controls on the stable isotopic composition of precipitation in Northeast Asia. Clim. Res. 2003, 23, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landais, A.; Risi, C.; Bony, S.; Vimeux, F.; Descroix, L.; Falourd, S.; Bouygues, A. Combined measurements of 17 O excess and d-excess in African monsoon precipitation: Implications for evaluating convective parameterizations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 298, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorre, E.B.; Criss, R.E.; Rose, T.P. Oxygen and carbon isotope study of natural and synthetic azurite. Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criss, R.E.; Farquhar, J. Abundance, notation, and fractionation of light stable isotopes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2008, 68, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingraham, N.L.; Criss, R.E. Effects of surface area and volume on the rate of isotopic exchange between water and water vapor. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1993, 98, 20547–20553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criss, R.E.; Fernandes, S.A.; Winston, W.E. Isotopic, geochemical and biological tracing of the source of an impacted karst spring, Weldon spring, Missouri. Environ. Forensics 2001, 2, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Event Number | Rainfall Types | Date | Rainfall Amount/mm | Sample Numbers | Average/‰ | Maximum/‰ | Minimum/‰ | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Soudelor Typhoon | 20150809 | 99.2 | 26 | −4.78 | −3.56 | −6.82 | 0.76 |
| 2 | Hato Typhoon | 20150823 | 47.4 | 40 | −9.31 | −7.48 | −10.66 | 1.10 |
| 3 | Dujuan Typhoon | 20150930 | 13.2 | 21 | −6.94 | −4.65 | −9.64 | 1.68 |
| 4 | Meranti Typhoon | 20160915 | 88.8 | 17 | −10.87 | −8.25 | −13.52 | 1.13 |
| 5 | Plum rain | 20160624 | 62 | 50 | −8.13 | −5.81 | −10.38 | 1.29 |
| 6 | Plum rain | 20160710 | 145.6 | 16 | −7.23 | −5.39 | −9.14 | 1.42 |
| Event Number | Rainfall Types | Date | Sample Numbers | Average/‰ | Maximum/‰ | Minimum/‰ | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Soudelor Typhoon | 20150809 | 26 | −30.02 | −21.85 | −46.12 | 5.74 |
| 2 | Hato Typhoon | 20150823 | 40 | −58.26 | −41.72 | −75.80 | 9.36 |
| 3 | Dujuan Typhoon | 20150930 | 21 | −38.06 | −17.98 | −64.80 | 13.08 |
| 4 | Meranti Typhoon | 20160915 | 17 | −64.65 | −45.71 | −77.21 | 10.29 |
| 5 | Plum rain | 20160624 | 50 | −54.77 | −30.94 | −64.31 | 9.67 |
| 6 | Plum rain | 20160710 | 16 | −74.24 | −57.61 | −95.28 | 8.76 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, P.; Shan, S.; Gou, J.; Jiang, P. Isotopic Characteristics of Precipitation and Origin of Moisture Sources in Hemuqiao Catchment, a Small Watershed in the Lower Reach of Yangtze River. Water 2018, 10, 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091170
Qu S, Chen X, Wang Y, Shi P, Shan S, Gou J, Jiang P. Isotopic Characteristics of Precipitation and Origin of Moisture Sources in Hemuqiao Catchment, a Small Watershed in the Lower Reach of Yangtze River. Water. 2018; 10(9):1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091170
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Simin, Xueqiu Chen, Yifan Wang, Peng Shi, Shuai Shan, Jianfeng Gou, and Peng Jiang. 2018. "Isotopic Characteristics of Precipitation and Origin of Moisture Sources in Hemuqiao Catchment, a Small Watershed in the Lower Reach of Yangtze River" Water 10, no. 9: 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091170
APA StyleQu, S., Chen, X., Wang, Y., Shi, P., Shan, S., Gou, J., & Jiang, P. (2018). Isotopic Characteristics of Precipitation and Origin of Moisture Sources in Hemuqiao Catchment, a Small Watershed in the Lower Reach of Yangtze River. Water, 10(9), 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091170





