Study of the Effects of Land Use on Hydrochemistry and Soil Microbial Diversity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Hydrochemical Detection
2.2.2. Soil Analysis
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.2.4. Ion Proportional Coefficient Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Granularity
3.2. Hydrochemical Characteristics
3.2.1. The Statistical Results
3.2.2. Hydrochemical Composition
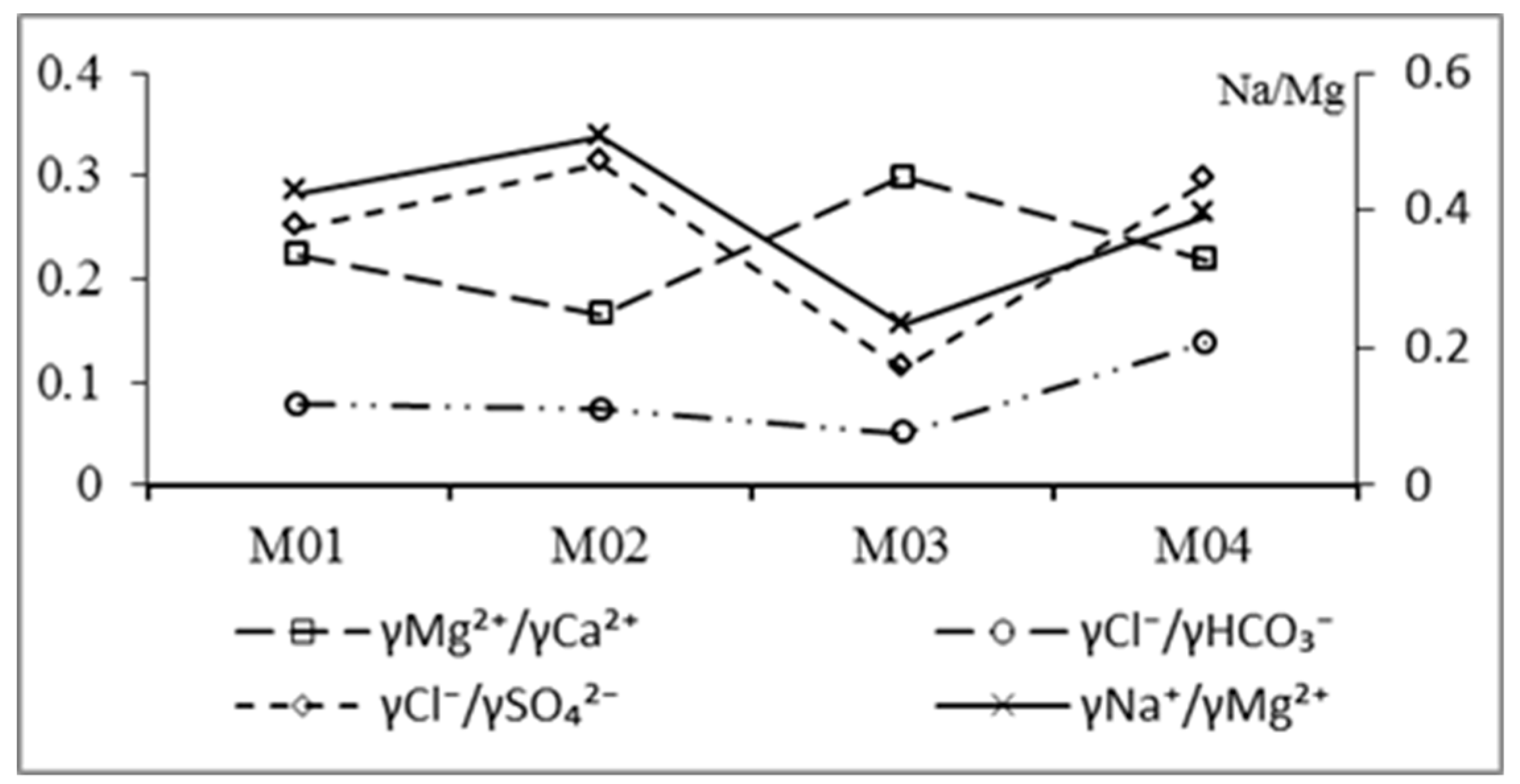
3.2.3. Ion Proportional Coefficient
3.3. Soil Microbial Diversity
3.3.1. Venn Diagram of Species
3.3.2. Alpha Diversity
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil CO2
4.2. Soil CO2 and Soil Microbial
4.3. The CO2 and Water Quality
4.4. Correlation between Soil CO2, Hydrochemical and Soil Microbial
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.W.; Hwang, S.J.; Lee, S.B.; Hwang, H.S.; Sung, H.C. Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.P.; Bode, R.W.; Smith, A.J.; Kleppel, G.S. Land-use proximity as a basis for assessing stream water quality in New York State (USA). Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Cho, K.H.; Ki, S.J.; Cha, S.M.; Kim, J.H. Linking land-use type and stream water quality using spatial data of fecal indicator bacteria and heavy metals in the Yeongsan river basin. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4143–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Don, A.; Kalbitz, K. Amounts and degradability of dissolved organic carbon from foliar litter at different decomposition stages. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonover, J.E.; Lockaby, B.G. Land cover impacts on stream nutrients and fecal coliform in the lower Piedmont of West Georgia. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.I.; Langan, S.J.; Demars, B.O.L. River sediments provide a link between catchment pressures and ecological status in a mixed land use Scottish River system. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2803–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronstert, A.; Niehoff, D.; Bürger, G. Effects of climate and land-use change on storm runoff generation: Present knowledge and modelling capabilities. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-J.; Yuan, D.-X.; Zhang, G.; He, R.-S. Effect of land use change on griundwater quality in karst watershed—A case study in Xiaojiang water of Yunnan province. J. Nat. Resour. 2004, 19, 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Yuan, D.-X.; He, D. A study on the relationship between land use change and karst groundwater quality. J. Southwest China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2006, 31, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.; Jiang, G.-H.; Xia, Q.; Li, K. Hydro-chemical variation of karst groundwater under the impact of land use in Donghe catchment, Hunan. Carsologica Sin. 2007, 26, 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Yue, H.Y. Correlation between the spatial water quality and land use /cover in the Ebinur Lake area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7971–7980. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, J. Spatially varying relationships between land use and water quality across an urbanization gradient explored by geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; An, Y.; Su, X.; Wu, Q.; Jin, T.; Yiliang, H.; Wu, J. Effect of multi-scale land use on water quality in Sancha river. Environ. Pollut. Control 2017, 39, 525–529. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Chen, J.; Cao, W.; Li, S.; Zi, H.; Huang, X.; Deng, Y. Spatial and seasonal geochemical chaeacteristics of shallow groundwater in response to land use in Guangzhou. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 26, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narany, T.S.; Aris, A.Z.; Sefie, A.; Keesstra, S. Detecting and predicting the impact of land use changes on groundwater quality, a case study in Northern Kelantan, Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, M.; Yu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y. Study on the Effects of Different Land Use Patterns on Microbial Community Structure in Aquic Brown Soil by Utilizing PLFA Method. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2010, 43, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Mäder, P.; Berner, A. Development of reduced tillage systems in organic farming in Europe. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2012, 27, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Hallett, P.D.; Caul, S.; Daniell, T.J.; Hopkins, D.W. Distribution of soil carbon and microbial biomass in arable soils under different tillage regimes. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, P.H.B.; Magid, J.; Luxhøi, J.; Neergaard, A.D. Effects of fertilization with urban and agricultural organic wastes in a field trial—Waste imprint on soil microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss-Souza, D.; Mendes, L.W.; Borges, C.D.; Baretta, D.; Tsai, S.M.; Jlm, R. Soil microbial community dynamics and assembly under long-term land use change. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.-J.; Zhu, W.-X.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Yin, Y.; Bai, X.-J.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Qin, S.-J. Effect of different land use patterns on the soil microbial community diversity in montane region of eastern Liaoning province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.-N.; Xi, Y.-G.; Chen, E.; He, L.-P.; Wang, L.; Xiao, X.-J.; Tian, W. Effects of tillage and green manure crop on composition and diversity of soil microbial community. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2018, 34, 342–348. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.J.; Li, X.Y.; He, X.Y. Advances in the study of the relationship between landscape pattern and river water quality at the watershed scale. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 5460–5465. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, I.; Hu, R.; Feng, M.; Lin, S.; Saadatullah, M.; Ibrahimmohamed, A. Microbial biomass, and dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen strongly affect soil respiration in different land uses: A case study at Three Gorges Reservoir Area, South China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Tan, G.; Wang, H.; Gai, X. Effect of biochar additions to soil on nitrogen leaching, microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wei, Q. Pyrosequencing technology reveals the impact of different manure doses on the bacterial community in apple rhizosphere soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 78, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Thomas, R.; Hall, J.R.; Martin, H.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, L.; Ye, D.; Wang, X.; Settles, M.L.; Wang, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhou, L.; Ping, D.; Yong, J.; Ma, Z. Soil bacterial communities of different natural forest types in Northeast China. Plant Soil 2014, 383, 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, A.; Dick, W.A. Bacterial Community Diversity in Soil Under two Tillage Practices as Determined by Pyrosequencing. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamir, G.; Shenker, M.; Heller, H.; Bloom, P.R.; Fine, P.; Bar-Tal, A. Dissolution and Re-crystallization Processes of Active Calcium Carbonate in Soil Developed on Tufa. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerdahl, B. Biological Control of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes: Soil Ecosystem Management in Sustainable Agriculture, Second Edition. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, W.R.; Christopher, S.P.; Dwipen, B. Intrtannual variability in global soil respirtion, 1980–1994. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 800–812. [Google Scholar]
- Carrera, M.A.; Marques, M.J.; Carral, P.; Alvarez, A.M.; López, C.; Martín-López, B.; González, J.A. Impacts of land-use intensity on soil organic carbon content, soil structure and water-holding capacity. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, O.; Baykara, M. Changes in soil microbial biomass and aggregate stability under different land uses in the northeastern Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 3801–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, R.; Schulp, C.J.; Hengeveld, G.M.; Verburg, P.H.; Clevers, J.G.; Schelhaas, M.J.; Herold, M. Assessing the influence of historic net and gross land changes on the carbon fluxes of Europe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 2526–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.G.; Li, T.C.; Ju, Z.W.; Shui, W.J. Decomposition of Organic Matter by Soil Microorganisms in Terrestrial Carbon Cycling and Its Influence Factors. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 36, 605–609. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, S.J.; Campbell, C.D.; Puri, G. Native woodland expansion: Soil chemical and microbiological indicators of change. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.S.; Laurent, P. Insights into the resistance and resilience of the soil microbial community. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuntz, M.; Berner, A.; Gattinger, A.; Scholberg, J.M.; Mäder, P.; Pfiffner, L. Influence of reduced tillage on earthworm and microbial communities under organic arable farming. Pedobiologia 2013, 56, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.J.; Edwards, N.T.; Garten, C.T.; Andrews, J.A. Separating root and soil microbial contributions to soil respiration: A review of methods and observations. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Yin, J.-J.; Xu, S.-Q.; Shen, L.-C. The variations of soil CO2 and hydrochemistry of Epikarst spring above Xueyue cave. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 27, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yin, C.; Zhang, S. Effects of partial pressure of CO2 of water/gas on hydro-chemical process of cave water: A case study in Dolomite Cave System of Shuanghe Cave in Guizhou province. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 40, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X. Assessment of the impact on shallow groundwater system by leakage of CO2 geological storage. Geotech. Investig. Surv. 2014, 42, 44–50. [Google Scholar]








| Sample | M01 | M02 | M03 | M04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land-use type | Bare | Peach | Castanea | Pine |
| Ions | pH | TDS | HCO3− | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | F− | Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| TDS | 0.55 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| HCO3− | 0.54 | 0.98 * | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Cl− | 0.46 | 0.97 * | 0.93 | 1.00 | |||||||
| NO3− | 0.52 | 0.99 ** | 0.97 * | 0.99 * | 1.00 | ||||||
| SO42− | 0.50 | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | 0.96 * | 0.99 ** | 1.00 | |||||
| F− | 0.54 | −0.37 | −0.32 | −0.50 | −0.42 | −0.40 | 1.00 | ||||
| Na+ | 0.55 | 1.00 ** | 0.98 * | 0.97 * | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | −0.37 | 1.00 | |||
| K+ | 0.56 | 0.97 * | 0.93 | 0.99 ** | 0.98 * | 0.95 * | −0.39 | 0.97 * | 1.00 | ||
| Mg2+ | 0.54 | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | 0.96 * | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | −0.37 | 0.99 ** | 0.96 * | 1.00 | |
| Ca2+ | 0.56 | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | 0.97 * | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | −0.35 | 1.00 ** | 0.97 * | 0.99 ** | 1.00 |
| Sample | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M01 | 5.992 | 0.004827 | 1207.113 | 1229.795 |
| M02 | 5.987 | 0.005312 | 1277.150 | 1301.102 |
| M03 | 5.981 | 0.005407 | 1260.625 | 1265.838 |
| M04 | 5.655 | 0.017962 | 1256.507 | 1274.106 |
| Sample | Atmosphere | M01 | M02 | M03 | M04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 (mg/m3) | 450 | 1863 | 2005 | 3059 | 2561 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Shi, M.; Fang, S.; Xu, H.; Cui, Y.; Liu, J. Study of the Effects of Land Use on Hydrochemistry and Soil Microbial Diversity. Water 2019, 11, 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030466
Zhang H, Gao Z, Shi M, Fang S, Xu H, Cui Y, Liu J. Study of the Effects of Land Use on Hydrochemistry and Soil Microbial Diversity. Water. 2019; 11(3):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030466
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hongying, Zongjun Gao, Mengjie Shi, Shaoyan Fang, Hailong Xu, Yechen Cui, and Jiutan Liu. 2019. "Study of the Effects of Land Use on Hydrochemistry and Soil Microbial Diversity" Water 11, no. 3: 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030466
APA StyleZhang, H., Gao, Z., Shi, M., Fang, S., Xu, H., Cui, Y., & Liu, J. (2019). Study of the Effects of Land Use on Hydrochemistry and Soil Microbial Diversity. Water, 11(3), 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030466






