How Are Various Surrogate Indicators Consistent with Mechanical Reliability of Water Distribution Systems: From a Perspective of Many-Objective Optimization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Selected Surrogate Indicators
2.2. Many-Objective Optimization Model
2.3. Borg MOEA
2.4. Post Analysis of System Reliability due to Mechanical Failures
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Case Studies
3.2. Parameter Settings of Many-Objective Optimization
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klise, K.A.; Bynum, M.; Moriarty, D.; Murray, R. A software framework for assessing the resilience of drinking water systems to disasters with an example earthquake case study. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulter, I. Analytical and Simulation Models for Reliability Analysis in Water Distribution Systems. In Improving Efficiency and Reliability in Water Distribution Systems. Water Science and Technology Library; Cabrera, E., Vela, A.F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 14, pp. 235–266. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, S.; Farmani, R.; Memon, F.A.; Butler, D. Reliability Indicators for Water Distribution System Design: Comparison. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2014, 140, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanyimboh, T.T.; Templeman, A.B. A quantified assessment of the relationship between the reliability and entropy of water distribution systems. Eng. Optimiz. 2000, 33, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todini, E. Looped water distribution networks design using a resilience index based heuristic approach. Urban Water 2000, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, T.D.; Nam-Sik Park, M.A. Multiobjective Genetic Algorithms for Design of Water Distribution Network. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manage. ASCE 2004, 130, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, N.; Srinivasan, K. Performance-based optimal design and rehabilitation of water distribution networks using life cycle costing. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W01417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raad, D.N.; Sinske, A.N.; van Vuuren, J.H. Comparison of four reliability surrogate measures for water distribution systems design. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W05524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Maier, H.R.; Simpson, A.R. Surplus Power Factor as a Resilience Measure for Assessing Hydraulic Reliability in Water Transmission System Optimization. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2011, 137, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanyimboh, T.T.; Tietavainen, M.T.; Saleh, S. Reliability assessment of water distribution systems with statistical entropy and other surrogate measures. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2011, 11, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, D.; Kang, D.; Kim, J.H.; Lansey, K. Robustness-Based Design of Water Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2013, 140, 04014033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Savic, D.; Kapelan, Z.; Zhao, M.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, H. A diameter-sensitive flow entropy method for reliability consideration in water distribution system design. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5597–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Xin, K. Multi-objective Optimal Design of Large-scale Urban Water Distribution Network. China Water Wastewater 2014, 30, 52–55, 60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Creaco, E.; Franchini, M.; Todini, E. The combined use of resilience and loop diameter uniformity as a good indirect measure of network reliability. Urban Water J. 2016, 13, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Savic, D.; Kapelan, Z.; Creaco, E.; Yuan, Y. Reliability Surrogate Measures for Water Distribution System Design: Comparative Analysis. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2017, 143, 04016072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bin Mahmoud, A.A.; Piratla, K.R. Comparative evaluation of resilience metrics for water distribution systems using a pressure driven demand-based reliability approach. J. Water Supply Res Technol. Aqua. 2018, 67, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimorelli, L.; Morlando, F.; Cozzolino, L.; D’Aniello, A.; Pianese, D. Comparison Among Resilience and Entropy Index in the Optimal Rehabilitation of Water Distribution Networks Under Limited-Budgets. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 3997–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyimboh, T.T.; Siew, C.; Saleh, S.; Czajkowska, A. Comparison of Surrogate Measures for the Reliability and Redundancy of Water Distribution Systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 3535–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadka, D.; Reed, P. Borg: An Auto-Adaptive Many-Objective Evolutionary Computing Framework. Evol. Comput. 2013, 21, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossman, L.A. EPANET Users Manual; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Laumanns, M.; Thiele, L.; Deb, K.; Zitzler, E. Combining Convergence and Diversity in Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization. Evol. Comput. 2002, 10, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purshouse, R.C.; Fleming, P.J. On the Evolutionary Optimization of Many Conflicting Objectives. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2007, 11, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, P.M.; Hadka, D.; Herman, J.D.; Kasprzyk, J.R.; Kollat, J.B. Evolutionary multiobjective optimization in water resources: The past, present, and future. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 438–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Kasprzyk, J.; Zagona, E. Many-Objective Analysis to Optimize Pumping and Releases in Multireservoir Water Supply Network. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2016, 142, 04015049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujiwara, O.; Khang, D. A two-phase decomposition method for optimal design of looped water distribution networks. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reca, J.; Martínez, J. Genetic algorithms for the design of looped irrigation water distribution networks. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W05416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsef, H.; Naghashzadegan, M.; Farmani, R.; Jamali, A. Deficiency of Reliability Indicators in Water Distribution Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2019, 145, 04019026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

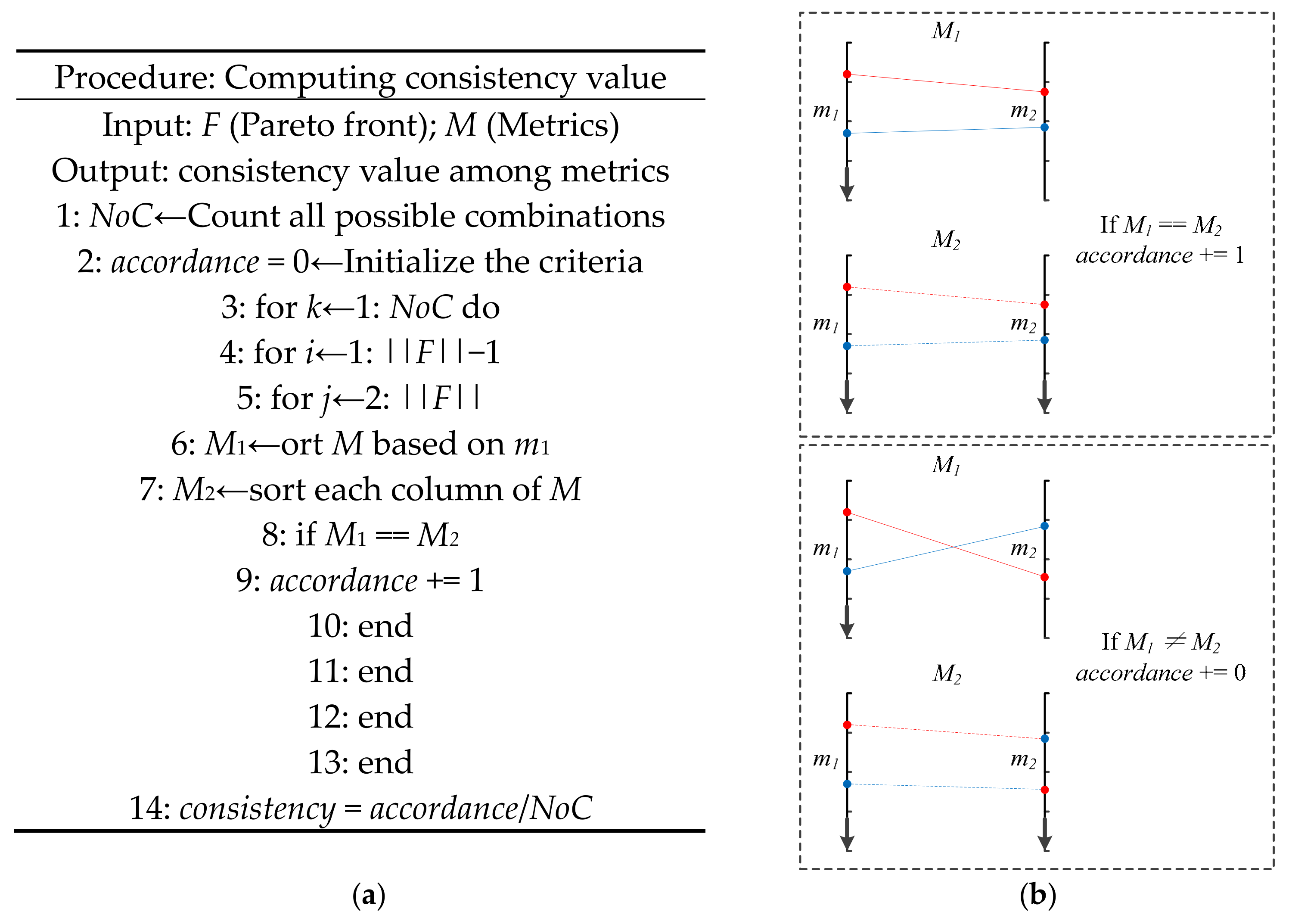






| Year | Authors | Surrogate Indicators | Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Tanyimboh & Templeman | flow entropy (FE) | (2) | [4] |
| 2000 | Todini | resilience index (RI) | (1) | [5] |
| 2004 | Prasad & Park | network resilience (NRI) | (1) | [6] |
| 2008 | Jayaram & Srinivasan | modified resilience index (MRI) | (1) | [7] |
| 2010 | Raad, et al. | mixed reliability surrogate (FE + RI) | (3) | [8] |
| 2011 | Wu, et al. | surplus power factor | (1) | [9] |
| 2011 | Tanyimboh, et al. | statistical entropy | (2) | [10] |
| 2014 | Jung, et al. | robustness index | - | [11] |
| 2014 | Liu, et al. | diameter sensitive flow entropy (DSFE) | (2) | [12] |
| 2014 | Liu, et al. | Redundancy | - | [13] |
| 2016 | Creaco, et al. | RI + loop diameter uniformity | (3) | [14] |
| 2016 | Liu, et al. | available power index (API)pipe hydraulic RI (PHRI) | (1) | [15] |
| 2018 | Bin Mahmoud & Piratla | probabilistic resilience index (PRI) | (1) | [16] |
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial population size | 100 | Crossover rate of DE | 0.6 |
| Population to archive ratio (γ) | 4 | Differential weight of DE | 0.6 |
| Selection ratio (τ) | 0.02 | Eta of PCX | 0.1 |
| Tournament size | Max [2, ⎣τ(γA)⎦] | Zeta of PCX | 0.1 |
| Probability of PM | 1/L | Zeta of UNDX | 0.5 |
| Distribution index of PM | 1.0 | Eta of UNDX | 0.35 |
| Probability of SBX | 0.9 | Expansion rate of SPX | 3.3 |
| Distribution index of SBX | 1.0 | Probability of UM | 1/L |
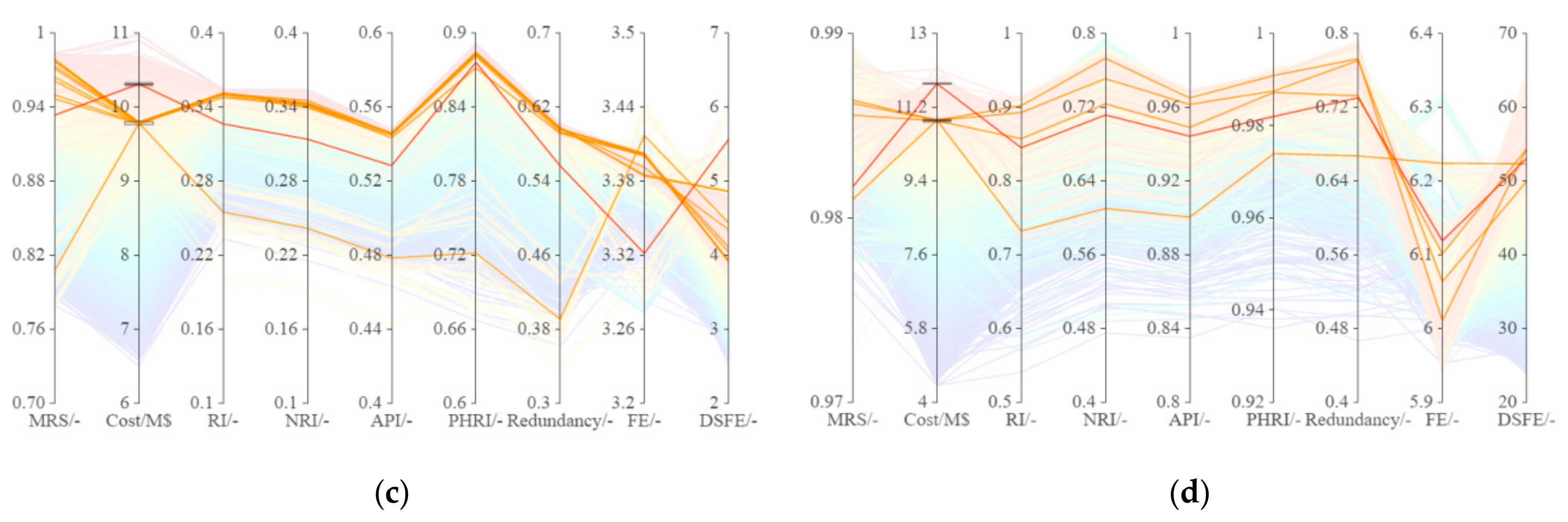
| Problem | Consistency | RI | NRI | API | PHRI | Redundancy | FE | DSFE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAN | MRS | 0.930 | 0.936 | 0.930 | 0.907 | 0.932 | 0.481 | 0.684 |
| Cost | 0.894 | 0.890 | 0.894 | 0.888 | 0.889 | 0.485 | 0.756 | |
| BIN | MRS | 0.775 | 0.799 | 0.777 | 0.757 | 0.760 | 0.404 | 0.489 |
| Cost | 0.722 | 0.645 | 0.721 | 0.721 | 0.726 | 0.505 | 0.840 |
| Solutions | MRS | Cost | RI | NRI | API | PHRI | Redundancy | FE | DSFE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-) | (M$) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | |
| Solution H | 0.78 | 9.65 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.47 | 0.67 | 0.36 | 3.44 | 4.55 |
| Solution L | 0.89 | 8.03 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.53 | 0.86 | 0.56 | 3.32 | 3.22 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhan, X.; Liu, S. How Are Various Surrogate Indicators Consistent with Mechanical Reliability of Water Distribution Systems: From a Perspective of Many-Objective Optimization. Water 2019, 11, 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081669
Wang Q, Huang W, Wang L, Zhan Y, Wang Z, Wang X, Zhan X, Liu S. How Are Various Surrogate Indicators Consistent with Mechanical Reliability of Water Distribution Systems: From a Perspective of Many-Objective Optimization. Water. 2019; 11(8):1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081669
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qi, Wen Huang, Libing Wang, Yongshi Zhan, Zhihong Wang, Xu Wang, Xuyi Zhan, and Shuming Liu. 2019. "How Are Various Surrogate Indicators Consistent with Mechanical Reliability of Water Distribution Systems: From a Perspective of Many-Objective Optimization" Water 11, no. 8: 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081669
APA StyleWang, Q., Huang, W., Wang, L., Zhan, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, X., Zhan, X., & Liu, S. (2019). How Are Various Surrogate Indicators Consistent with Mechanical Reliability of Water Distribution Systems: From a Perspective of Many-Objective Optimization. Water, 11(8), 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081669





