Impact of Nutrient and Stoichiometry Gradients on Microbial Assemblages in Erhai Lake and Its Input Streams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Physicochemical Analyses
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
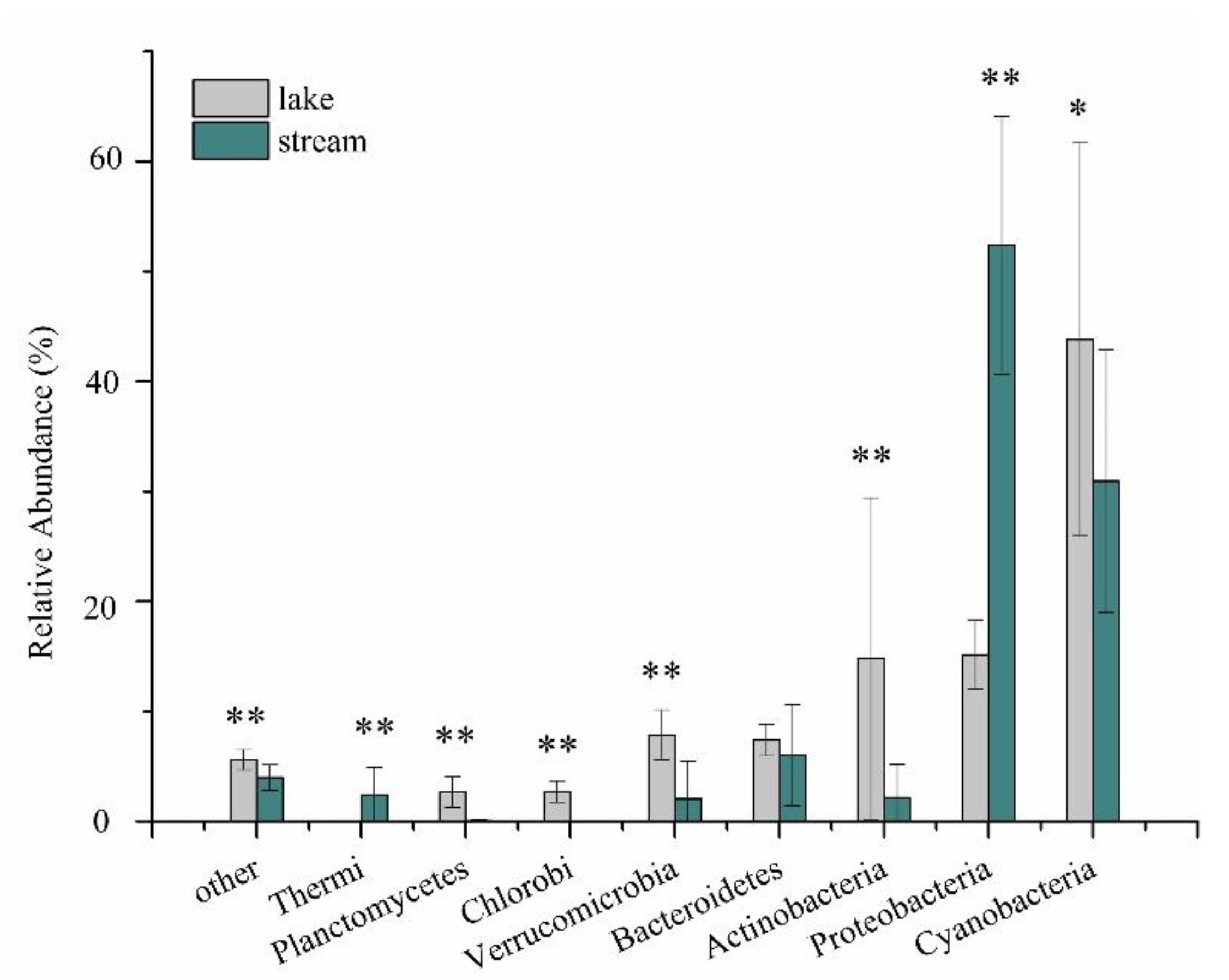
3.1. Environmental Conditions and Nutrients
3.2. Bacterial Assemblages
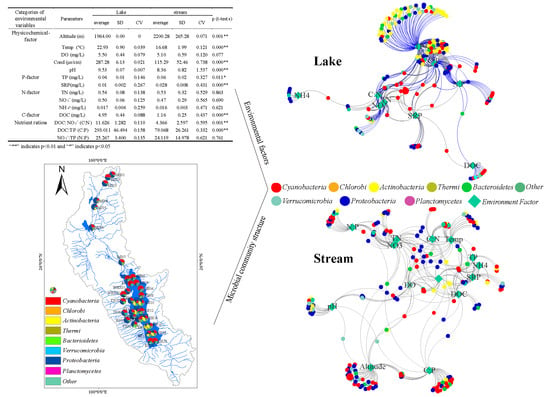
3.3. Bacteria Co-Occurrence
3.4. Environmental Factors Associated with the Bacterial Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elser, J.J.; Goldman, C.R. Zooplankton effects on phytoplankton in lakes of contrasting trophic status. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreau, M. Microbial diversity, producer-decomposer interactions and ecosystem processes: A theoretical model. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 268, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, H.; Sommaruga, R. Shifts in diversity and function of lake bacterial communities upon glacier retreat. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieczan, T.; Adamczuk, M.; Pawlik-Skowronska, B.; Toporowska, M.; Pawlik, S. Eutrophication of peatbogs: Consequences of P and N enrichment for microbial and metazoan communities in mesocosm experiments. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 74, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieczan, T.; Adamczuk, M.; Tarkowska-Kukuryk, M.; Nawrot, D. Effect of water chemistry on zooplanktonic and microbial communities across freshwater ecotones in different macrophyte-dominated shallow lakes. J. Limnol. 2015, 75, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alonso, M.; Méndez-Álvarez, S.; Ramírez-Moreno, S.; González-Toril, E.; Amils, R.; Gaju, N. Spatial Heterogeneity of Bacterial Populationsin Monomictic Lake Estanya (Huesca, Spain). Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the Nitrogen Cycle: Recent Trends, Questions, and Potential Solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Rivas-ubach, A.; Janssens, I.A. The human-induced imbalance between C, N and P in Earth’s life system. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 18, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.M.; Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F. Human Impact on Erodable Phosphorus and Eutrophication. Bioscience 2001, 51, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Fenchel, T.; Delong, E.F. The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles. Science 2008, 320, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, B.C.; Adams, H.E.; Hobbie, J.E.; Kling, G.W. Biogeography of bacterioplankton in lakes and streams of an arctic tundra catchment. Ecology 2007, 88, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipphut, G.W.; O’Brien, W.J.; Kling, G.W.; Miller, M.M. Integration of lakes and streams in a landscape perspective: The importance of material processing on spatial patterns and temporal coherence. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 43, 477–497. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, C.E.; Dodds, W.; Kratz, T.K.; Palmer, M.A. Lakes and streams as sentinels of environmental change in terrestrial and atmospheric processes. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, P.S.; Starnawski, P.; Poulsen, B.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Schramm, A.; Riis, T. Microbial community diversity and composition varies with habitat characteristics and biofilm function in macrophyte-rich streams. Oikos 2017, 126, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney, P.J.; Rees, G.N. Co-invasion hypothesis explains microbial community structure changes in upland streams affected by riparian invader. Freshw. Sci. 2017, 36, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, F.; Qu, X.; Elser, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Chu, L. Taxonomic and Functional Differences between Microbial Communities in Qinghai Lake and Its Input Streams. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findlay, S.E.G. Stream microbial ecology. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dopheide, A.; Lear, G.; He, Z.; Jizhong, Z.; Lewis, G.D. Functional Gene Composition, Diversity and Redundancy in Microbial Stream Biofilm Communities. PLoS ONE 2016, 10, e0123179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Qin, H.; Guo, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Liang, J. Bacterial communities of four adjacent fresh lakes at different trophic status. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, D.J.; Theis, K.R.; Uzarski, D.G.; Learman, D.R. Microbial community structure and microbial networks correspond to nutrient gradients within coastal wetlands of the Laurentian Great Lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lars-Anders, H.; Kenneth, P. Nutrient Control to Prevent the Occurrence of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Eutrophic Lake in Southern Sweden, Used for Drinking Water Supply. Water 2018, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M. Sediment amino acids as indicators of anthropogenic activities and potential environmental risk in Erhai Lake, Southwest China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 551, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Nadykto, A.B.; Xu, Y.; Shi, Q.; Jiang, B.; Qian, W. Characterization of dissolved organic nitrogen in wet deposition from Lake Erhai basin by using ultrahigh resolution FT-ICR mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2016, 156, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Lei, B.; Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Zhai, L.; Mao, Y.; Fu, B.; Zhang, D. Temporal-spatial variations and influencing factors of nitrogen in the shallow groundwater of the nearshore vegetable field of Erhai Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4858–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Peng, W. Influences of anthropogenic land use on microbial community structure and functional potentials of stream benthic biofilms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal variation of planktonic and sediment bacterial assemblages in two plateau freshwater lakes at different trophic status. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4161–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Xie, P.; Wang, S.; Niu, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, W. Sources of organic matter affect depth-related microbial community composition in sediments of Lake Erhai, Southwest China. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, H.; Li, N.; Wu, Z.; Wen, Z.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y. Spatio-temporal shifts in the archaeal community of a constructed wetland treating river water. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 605, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xie, S. Aerobic and nitrite-dependent methane-oxidizing microorganisms in sediments of freshwater lakes on the Yunnan Plateau. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downing, J.A.; McCauley, E. The nitrogen: Phosphorus relationship in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhulidov, A.V.; Kämäri, J.; Robarts, R.D.; Pavlov, D.F.; Rekolainen, S.; Gurtovaya, T.Y.; Meriläinen, J.J.; Lugovoy, V.V.; Pavlov, D. Long-term dynamics of water-borne nitrogen, phosphorus and suspended solids in the lower Don River basin (Russian Federation). J. Water Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, B.C.; Hobbie, J.E. Synchrony and seasonality in bacterioplankton communities of two temperate rivers. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1718–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, H.; Romaní, A.M.; Tranvik, L.J.; Ylla, I. Different diversity-functioning relationship in lake and stream bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Hou, Z.; Li, Z.; Chu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zheng, B. Succession of phytoplankton functional groups and their driving factors in a subtropical plateau lake. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Zhao, L.; Cao, X.; Sun, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Jiang, D.; Fan, H.; Huang, Y. Cyanobacteria in lakes on Yungui Plateau, China are assembled via niche processes driven by water physicochemical property, lake morphology and watershed land-use. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Li, S.; Bu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G. Eutrophication in the Yunnan Plateau lakes: The influence of lake morphology, watershed land use, and socioeconomic factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, Z.B.; Zak, D.R. Atmospheric N Deposition Alters Connectance, but not Functional Potential among Saprotrophic Bacterial Communities. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 3170–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.M.; Pimm, S.L.; Solé, R.V. Ecological networks and their fragility. Nature 2006, 442, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, S.; Stouffer, D.B.; Uzzi, B.; Bascompte, J. Strong contributors to network persistence are the most vulnerable to extinction. Nature 2011, 478, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.J. Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8577–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brenda, L.H.; Jane, C.M.; Mary, E.W. Early bacterial and fungal colonization of leaf litter in Fossil Creek. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2009, 28, 383–396. [Google Scholar]
- Fazi, S.; Amalfitano, S.; Pernthaler, J.; Puddu, A. Bacterial communities associated with benthic organic matter in headwater stream microhabitats. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findlay, R.H.; Yeates, C.; Hullar, M.A.J.; Stahl, D.A.; Kaplan, L.A. Biome-Level Biogeography of Streambed Microbiota. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3014–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, Q.; Yu, Y.; Dai, L. Spatiotemporal pattern of bacterioplankton in Donghu Lake. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2014, 32, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwirglmaier, K.; Keiz, K.; Engel, M.; Geist, J.; Raeder, U. Seasonal and spatial patterns of microbial diversity along a trophic gradient in the interconnected lakes of the Osterseen Lake District, Bavaria. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Jiao, L. Features and influencing factors of nitrogen and phosphorus diffusive fluxes at the sediment-water interface of Erhai Lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Meng, Z. Characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen in overlying water of typical lakes of Yunnan Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Shen, H.; Deng, X. Use the predictive models to explore the key factors affecting phytoplankton succession in Lake Erhai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, A.; Corner, R.; Telfer, T. How do land-based salmonid farms affect stream ecology? Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaei, C.D.; Piggott, J.J.; Townsend, C.R. Multiple stressors in agricultural streams: Interactions among sediment addition, nutrient enrichment and water abstraction. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, H.; Ylla, I.; Gudasz, C.; Romani, A.M.; Sabater, S.; Tranvik, L.J. Multifunctionality and diversity in bacterial biofilms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, P.J.; Helton, A.M.; Poole, G.C.; Hall, R.O.; Hamilton, S.K.; Peterson, B.J.; Tank, J.L.; Ashkenas, L.R.; Cooper, L.W.; Dahm, C.N.; et al. Stream denitrification across biomes and its response to anthropogenic nitrate loading. Nature 2008, 452, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valett, H.M.; Thomas, S.A.; Mulholland, P.J.; Webster, J.R.; Dahm, C.N.; Fellows, C.S.; Crenshaw, C.L.; Peterson, C.G. Endogenous and exogenous control of ecosystem function: N cycling in headwater streams. Ecology 2008, 89, 3515–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, L.; Besemer, K.; Fragner, L.; Peter, H.; Weckwerth, W.; Battin, T.J. Altitudinal patterns of diversity and functional traits of metabolically active microorganisms in stream biofilms. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2454–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ernst, A.; Deicher, M.; Herman, P.M.J.; Wollenzien, U.I.A. Nitrate and Phosphate Affect Cultivability of Cyanobacteria from Environments with Low Nutrient Levels. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3379–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Correll, D. Phosphorus: A rate limiting nutrient in surface waters. Poult. Sci. 1999, 78, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrede, T.; Ballantyne, A.; Algesten, G.; Gudasz, C.; Lindahl, S.; Brunberg, A.K.; Mille-Lindblom, C.; Mille-Lindblom, C. Effects of N:P loading ratios on phytoplankton community composition, primary production and N fixation in a eutrophic lake. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Song, G.; Tan, W.; Zhu, M.; Li, R. Variation of Microcystis and microcystins coupling nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in Lake Erhai, a drinking-water source in Southwest Plateau, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9887–9898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolai, S.J.; Dzialowski, A.R. Effects of internal phosphorus loading on nutrient limitation in a eutrophic reservoir. Limnologica 2014, 49, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Chen, M.; Gong, M.; Fan, X.; Qin, B.; Xu, H.; Gao, S.; Jin, Z.; Tsang, D.C.; Zhang, C. Internal phosphorus loading from sediments causes seasonal nitrogen limitation for harmful algal blooms. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 625, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, P.C.; Elser, J.J. Effects of light and nutrients on the net accumulationand elemental composition of epilithon in boreal lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, M.; Persson, L.; De Roos, A.M.; Jones, R.I.; Tranvik, L.J. Terrestrial carbon and intraspecific size-variation shape lake ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.-P.; Donoghue, P.C.J.; Cheng, H.; Liu, J.-B. Fossil embryos from the Middle and Late Cambrian period of Hunan, south China. Nature 2004, 427, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Qu, X.; Peng, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, M. Nutrients Drive the Structures of Bacterial Communities in Sediments and Surface Waters in the River-Lake System of Poyang Lake. Water 2019, 11, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Categories of Environmental Variables | Parameters | Lake | Stream | p (t-tests) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | SD | CV | Average | SD | CV | |||
| Physicochemical-factor | Altitude (m) | 1964.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 2200.28 | 265.28 | 0.071 | 0.001 ** |
| Temp (°C) | 22.93 | 0.90 | 0.039 | 16.68 | 1.99 | 0.121 | 0.000 ** | |
| DO (mg/L) | 5.50 | 0.44 | 0.079 | 5.10 | 0.59 | 0.120 | 0.077 | |
| Cond (μs/cm) | 287.28 | 6.13 | 0.021 | 115.29 | 52.46 | 0.738 | 0.000 ** | |
| pH | 9.53 | 0.07 | 0.007 | 8.36 | 0.82 | 1.537 | 0.000 ** | |
| P-factor | TP (mg/L) | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.146 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.327 | 0.011 * |
| SRP(mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.267 | 0.028 | 0.008 | 0.431 | 0.000 ** | |
| N-factor | TN (mg/L) | 0.54 | 0.08 | 0.138 | 0.53 | 0.32 | 0.529 | 0.863 |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 0.50 | 0.06 | 0.125 | 0.47 | 0.29 | 0.565 | 0.690 | |
| NH4+ (mg/L) | 0.017 | 0.004 | 0.259 | 0.016 | 0.003 | 0.471 | 0.621 | |
| C-factor | DOC (mg/L) | 4.95 | 0.44 | 0.088 | 1.16 | 0.25 | 0.437 | 0.000 ** |
| Nutrient ratios | DOC:NO3− (C:N) | 11.626 | 1.282 | 0.110 | 4.366 | 2.597 | 0.595 | 0.001 ** |
| DOC:TP (C:P) | 293.011 | 46.494 | 0.158 | 79.068 | 26.261 | 0.332 | 0.000 ** | |
| NO3−:TP (N:P) | 25.267 | 3.400 | 0.135 | 24.119 | 14.978 | 0.621 | 0.761 | |
| Topological Parameter | Lake and Streams | Lake | Stream | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random | Real | Random | Real | Random | Real | |
| Number of nodes | 511 | 511 | 416 | 416 | 435 | 435 |
| Average number of neighbors | 65.840 | 67.037 | 28.351 | 28.351 | 12.906 | 12.906 |
| Network Centralization | 0.045 ± 0.003 * | 0.232 | 0.038 ± 0.004 * | 0.193 | 0.028 ± 0.008 * | 0.044 |
| Network Heterogeneity | 0.116 ± 0.004 * | 0.745 | 0.182 ± 0.006 * | 1.128 | 0.272 ± 0.001 * | 0.700 |
| Characteristic Path Length | 1.880 ± 0.001 * | 2.654 | 2.060 ± 0.001 * | 3.799 | 2.651 ± 0.002 * | 5.134 |
| Clustering Coefficient | 0.125 ± 0.006 * | 0.705 | 0.069 ± 0.001 * | 0.538 | 0.029 ± 0.002 * | 0.596 |
| Modularity | 0.439 ± 0.021 * | 0.639 | 0.438 ± 0.011 * | 0.572 | 0.446 ± 0.018 * | 0.784 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Qu, X.; Elser, J.J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Impact of Nutrient and Stoichiometry Gradients on Microbial Assemblages in Erhai Lake and Its Input Streams. Water 2019, 11, 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081711
Liu Y, Qu X, Elser JJ, Peng W, Zhang M, Ren Z, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Yang H. Impact of Nutrient and Stoichiometry Gradients on Microbial Assemblages in Erhai Lake and Its Input Streams. Water. 2019; 11(8):1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081711
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yang, Xiaodong Qu, James J. Elser, Wenqi Peng, Min Zhang, Ze Ren, Haiping Zhang, Yuhang Zhang, and Hua Yang. 2019. "Impact of Nutrient and Stoichiometry Gradients on Microbial Assemblages in Erhai Lake and Its Input Streams" Water 11, no. 8: 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081711
APA StyleLiu, Y., Qu, X., Elser, J. J., Peng, W., Zhang, M., Ren, Z., Zhang, H., Zhang, Y., & Yang, H. (2019). Impact of Nutrient and Stoichiometry Gradients on Microbial Assemblages in Erhai Lake and Its Input Streams. Water, 11(8), 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081711