Fungal Waste-Biomasses as Potential Low-Cost Biosorbents for Decolorization of Textile Wastewaters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Decolorization
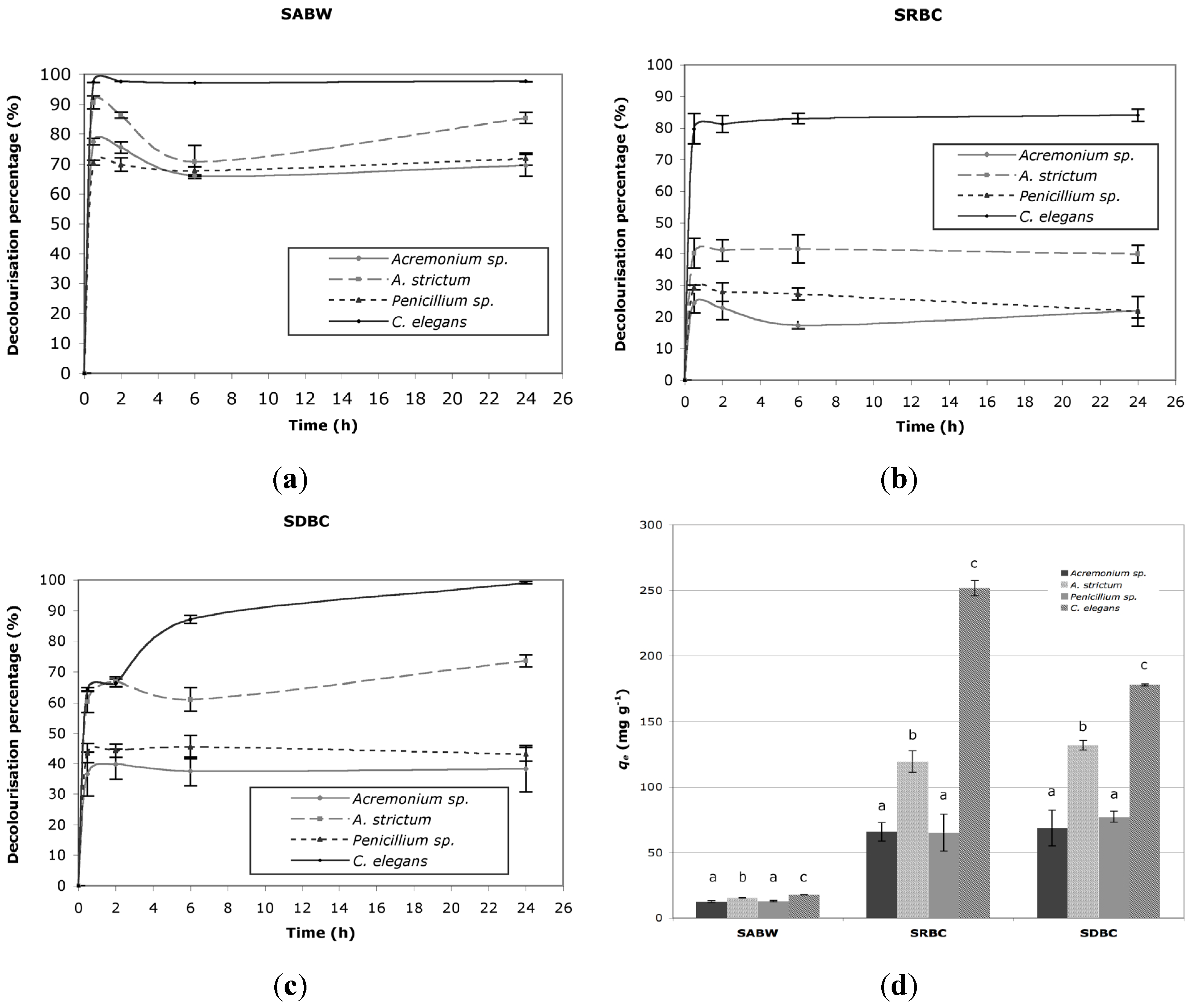
| Species | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
| qmax (mg g−1) | KL (L mg−1) | R2 | KF [mg(n−1)/n L1/n g−1] | n | R2 | |
| Cunninghamella elegans | 594.4 ± 11.82 | 0.0048 ± 0.0005 | 0.993 | 54.29 ± 2.14 | 3.13 | 0.946 |
| Acremonium strictum | 289.5 ± 5.35 | 0.0114 ± 0.0012 | 0.982 | 48.29 ± 9.32 | 3.99 | 0.913 |
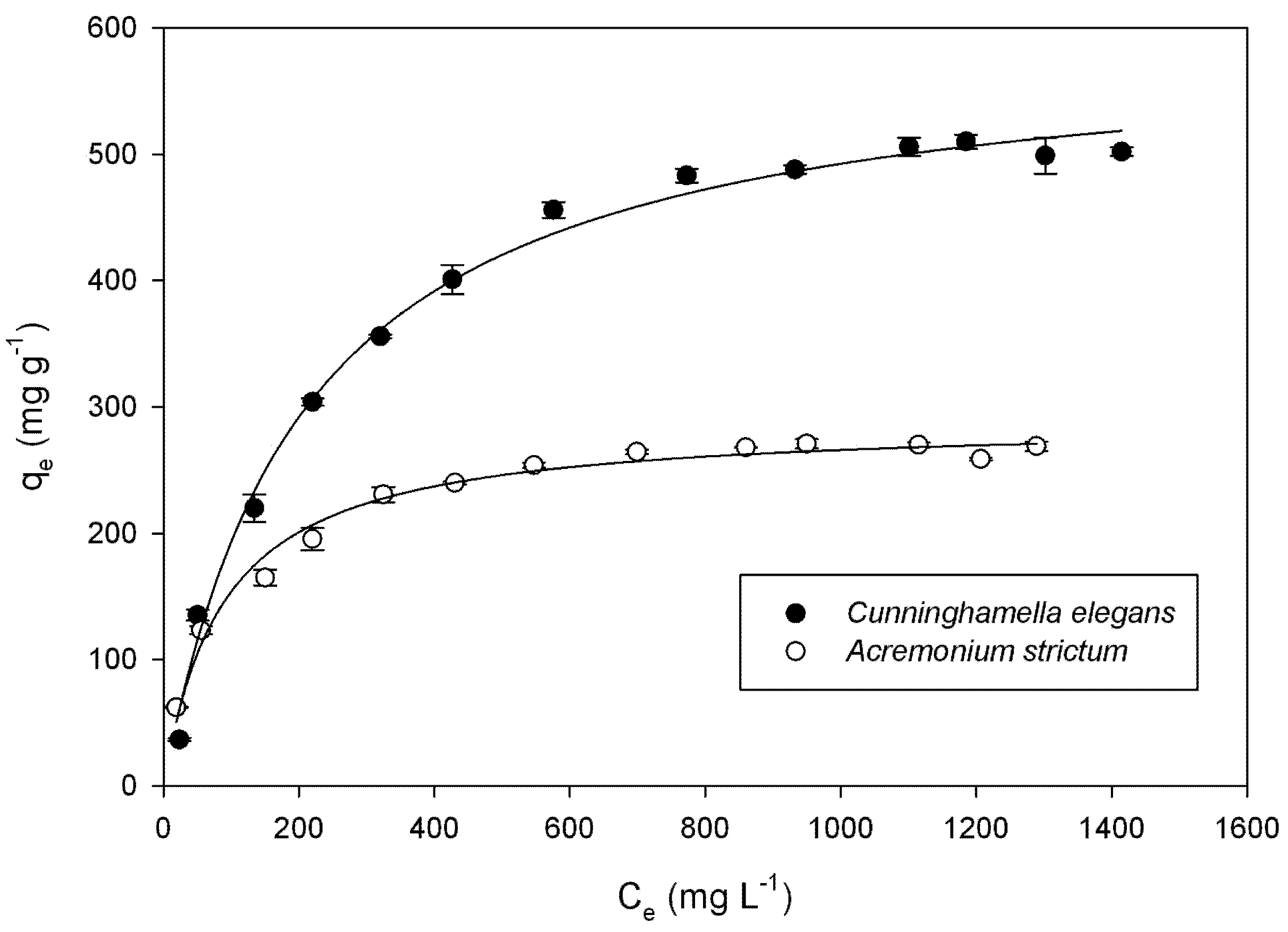
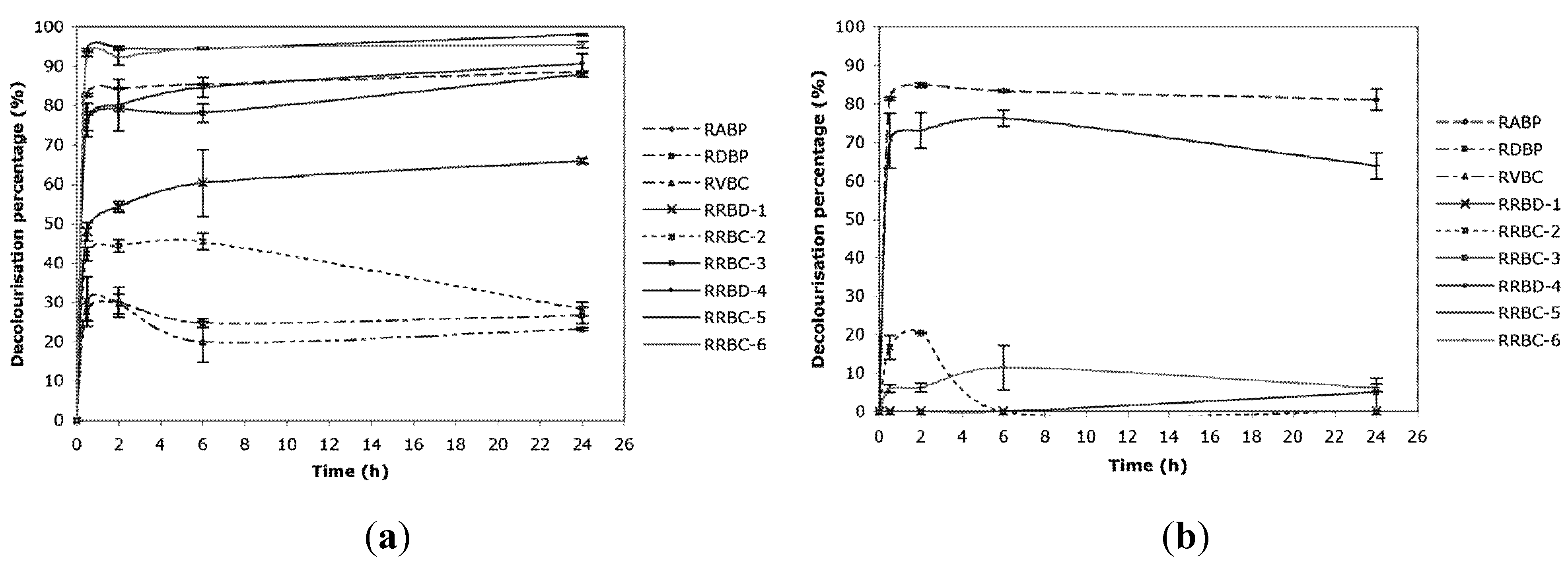
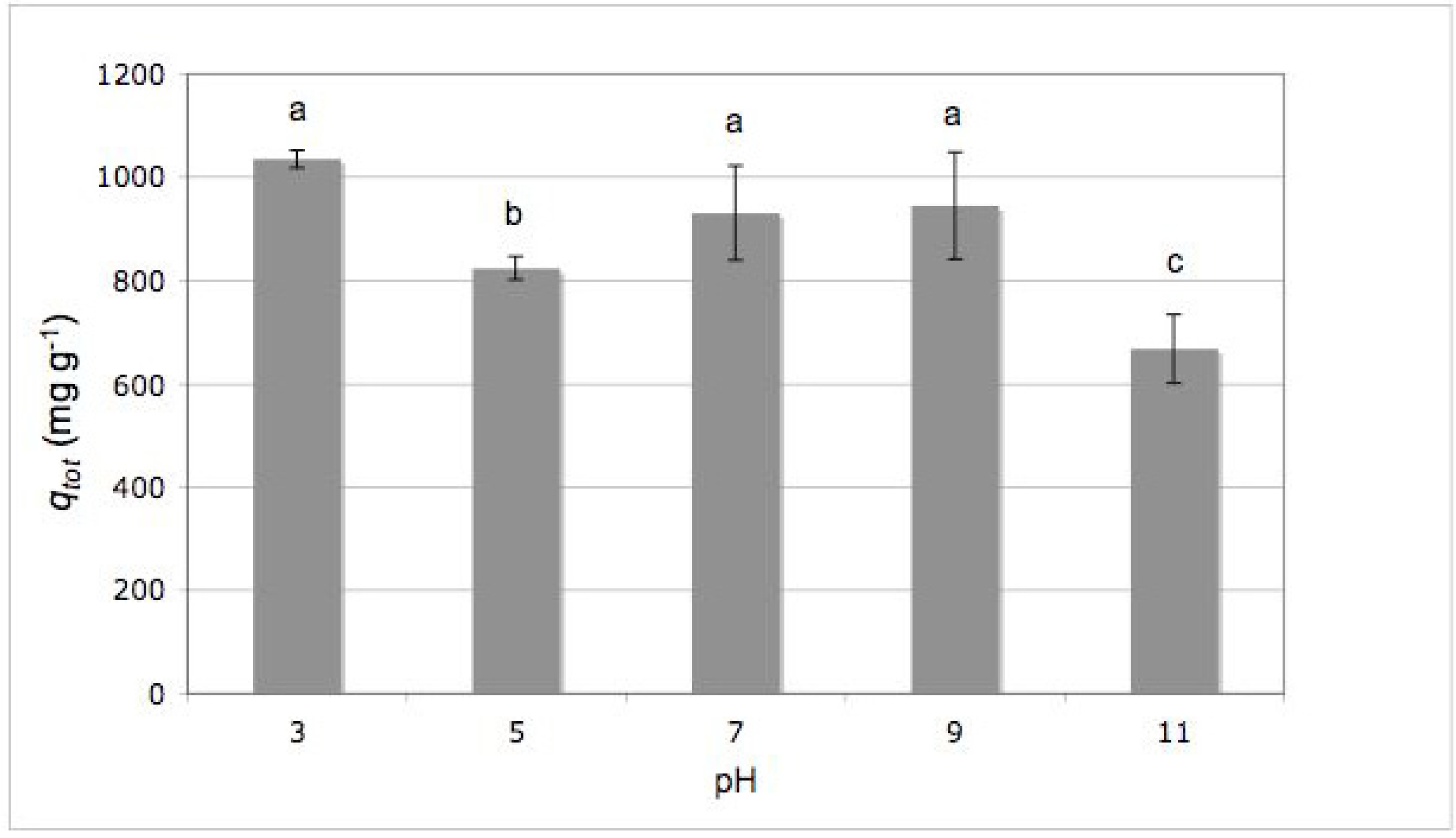
2.2. Effect of Initial pH

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Industrial Waste-Biomasses and Selected Test Organisms
3.2. Fungal Biomass Preparation
3.3. Simulated and Real Exhausted Dye Baths
| Exhausted dye bath | Acronym | Dyes | Dye concentration | Salt concentration | Auxiliaries | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulated Acid Bath for Wool | SABW | Mix of 3 dyes (Abu62, AY49, AR266) | 300 mg L−1 | 5 g L−1 | n.i. | 5.0 |
| Simulated Reactive Bath for Cotton | SRBC | Mix of 4 dyes (Rbu222, RR195, RY145, Rbk5) | 5000 mg L−1 | 70 g L−1 | n.i. | 10.0 |
| Simulated Direct Bath for Cotton | SDBC | Mix of 3 dyes (DrBu71, DrR80, DrY106) | 3000 mg L−1 | 2 g L−1 | n.i. | 9.0 |
| Real Acid Bath for Polyamide | RABP | Mix of 3 dyes | 433 mg L−1 | n.i. | Surfactants, weak acid, fixatives | 5.0 |
| Real Disperse Bath for Polyester | RDBP | 1 dye | 658 mg L−1 | n.i. | Dispersants, weak acid, strong base | 9.3 |
| Real Vat Bath for Cotton | RVBC | Mix of 2 dyes | 1424 mg L−1 | 20 g L−1 | Weak acid, strong base, glucose | 12.7 |
| Real Reactive Bath for Cotton 1 | RRBC-1 | Mix of 3 dyes | 542 mg L−1 | 77 g L−1 | Weak acid, strong base | 10.9 |
| Real Reactive Bath for Cotton 2 | RRBC-2 | 1 dye | 343 mg L−1 | 90 g L−1 | Ca and Mg sequestering, oil, weak acid, strong base | 11.3 |
| Real reactive Bath for Cotton—continuous dyeing | RRBC-3 | Mix of 3 dyes | 43 mg L−1 | 200 g L−1 | Sodium carbonate | 10.3 |
| Real reactive Bath for Cotton—washing with cold water | RRCB-4 | Mix of 3 dyes | 34 mg L−1 | 200 g L−1 | n.i. | 10.0 |
| Real reactive Bath for Cotton—neutralization and washing at 40 °C | RRCB-5 | Mix of 3 dyes | 98 mg L−1 | 200 g L−1 | Acetic acid | 5.9 |
| Real reactive Bath for Cotton—boiling soaping | RRCB-6 | Mix of 3 dyes | 60 mg L−1 | 200 g L−1 | Surfactants | 7.8 |
3.4. Sorption Experiments

3.5. Adsorption Isotherms


3.6. Effect of Initial pH
4. Conclusions
- (1) A. strictum biomass was more efficient than the other two industrial waste-biomasses, being able to substantially decolorize the simulated dye baths; however, it was effective only towards the real ones characterized by acidic pH. Hence, at the moment, industrial waste-biomasses such as A. strictum can be considered competitive and potentially useful for the treatment of specific types of wastewater (e.g., acid exhausted dye baths) only;
- (2) C. elegans biomass is endowed with a high ability to remove dyes belonging to different chemical classes, not only from simulated dye baths but also from many real ones;
- (3) The high applicative potentialities of C. elegans biomass for the decolorization of textile wastewater was demonstrated by the very good biosorption yields even under extreme conditions of pH (3–11); for this reason, this biomass can be considered an excellent and exceptionally versatile biosorbent material.
Acknowledgments
References
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Marinas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Badot, P.M. Application of chitosan, a natural aminopolysaccharide, for dye removal from aqueous solution by adsorption process using batch studies: A review of recent literature. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 399–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjaneya, A.; Santoshkumar, M.; Anand, S.N.; Karegoudar, T.B. Biosorption of acid violet dye from aqueous solutions using native biomass of a new isolate of Penicillium sp. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Yamamoto, K.; Fukushi, K. Hybrid treatment systems for dye wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 315–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z. Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: A review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 997–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svecova, L.; Spanelova, M.; Kubal, M.; Guibal, E. Cadmium, lead and mercury biosorption on waste fungal biomass issued from fermentation industry. I. Equilibrium studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 52, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, R.; Saxena, R.K.; Gupta, R. Fermentation waste of Aspergillus terreus: A potential copper biosorbent. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 18, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, G.M. Biosorption: Critical review of scientific rationale, environmental importance and significance for pollution treatment. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 1, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gochev, V.K.; Velkova, Z.I.; Stoytcheva, M.S. Hexavalent chromium removal by waste mycelium of Aspergillus awamori. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2010, 75, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, H.J.; Li, W.; Gao, T.Y.; Ma, P. Biosorption of cadmium(II) and lead(II) from aqueous solutions by fruiting body waste of fungus Flammulina velutipes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 20, 160–167. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, P.; Malik, A. Fungal dye decolourisation: Recent advances and future potential. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigione, V.; Tigini, V.; Pezzella, C.; Anastasi, A.; Sannia, G.; Varese, G.C. Decolourisation and detoxification of textile effluents by fungal biosorption. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2911–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigione, V.; Varese, G.C.; Casieri, L.; Filippello Marchisio, V. Biosorption of simulated dyed effluents by inactivated fungal biomasses. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3559–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigione, V.; Zerlottin, M.; Refosco, D.; Tigini, V.; Anastasi, A.; Varese, G.C. Chromium removal from a real tanning effluent by autochthonous and allochthonous fungi. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2770–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigini, V.; Prigione, V.; Donelli, I.; Anastasi, A.; Freddi, G.; Giansanti, P.; Mangiavillano, A.; Varese, G.C. Cunninghamella elegans biomass optimisation for textile wastewater biosorption treatment: an analytical and ecotoxicological approach. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, J. Fungal Biology, 4th ed; Blackwell Publishing Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasi, A.; Prigione, V.; Casieri, L.; Varese, G.C. Decolourisation of model and industrial dyes by mitosporic fungi in different culture conditions. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigini, V.; Prigione, V.; Donelli, I.; Freddi, G.; Varese, G.C. Influence of culture medium on fungal biomass composition and biosorption effectiveness. Curr. microbiol. 2012, 64, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sadhasivam, S.; Savitha, S.; Swaminathan, K. Exploitation of Trichoderma harzianum mycelial waste for the removal of rhodamine 6G from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Yun, Y.S. Utilization of fermentation waste (Corynebacterium glutamicum) for biosorption of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Dye biosorption sites in Aspergillus niger. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 82, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyurt, M.; Ozer, A.; Atacag, H. Decolourisation of Setopers Black RD-ECO by Aspergillus oryzae. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2005, 14, 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Tigini, V. Fungal Biosorption in Wastewater Treatment: Decolourisation and Detoxification of Textile and Tannery Effluents. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Turin, Turin, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Aksu, Z.; Tatli, A.İ.; Tunç, Ö. A comparative adsorption/biosorption study of Acid Blue 161: Effect of temperature on equilibrium and kinetic parameters. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 142, 23–39. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Lee, M.W.; Yun, Y.S. A new approach to study the decolorization of complex reactive dye bath effluent by biosorption technique. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5778–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xia, S.; Zhao, J. Biosorption of Direct Black 38 by dried anaerobic granular sludge. Front. Environ. Sci. Engin. China 2008, 2, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, I.; Akar, T.; Ozcan, A.S.; Ozcan, A.; Tunali, S. Biosorption kinetics and isotherm studies of Acid Red 57 by dried Cephalosporium aphidicola cells from aqueous solution. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 31, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z.; Çağatay, S.S. Investigation of biosorption of Gemazol Turquise Blue-G reactive dye by dried Rhizopus arrhizus in batch and continuous systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 48, 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Khambhaty, Y.; Mody, K.; Basha, S. Efficient removal of Brilliant Blue G (BBG) from aqueous solutions by marine Aspergillus wentii: Kinetics, equilibrium and process design. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 41, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varese, G.C.; Prigione, V.P.; Casieri, L.; Voyron, S.; Bertolotto, A.; Filipello Marchisio, V. Use of Cunninghamella elegans Lendner in Methods for Treating Industrial Wastewaters Containing Dyes. Eur. Pat. Appl. EP07118877.5, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- SYSTAT, version 10; SPSS Inc.: Chicago, CA, USA, 2000.
- Ilhan, S.; Iscen, C.F.; Caner, N.; Kiran, I. Biosorption potential of dried Penicillium restrictum for Reactive Orange 122: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Prigione, V.; Grosso, I.; Tigini, V.; Anastasi, A.; Varese, G.C. Fungal Waste-Biomasses as Potential Low-Cost Biosorbents for Decolorization of Textile Wastewaters. Water 2012, 4, 770-784. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4040770
Prigione V, Grosso I, Tigini V, Anastasi A, Varese GC. Fungal Waste-Biomasses as Potential Low-Cost Biosorbents for Decolorization of Textile Wastewaters. Water. 2012; 4(4):770-784. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4040770
Chicago/Turabian StylePrigione, Valeria, Irene Grosso, Valeria Tigini, Antonella Anastasi, and Giovanna Cristina Varese. 2012. "Fungal Waste-Biomasses as Potential Low-Cost Biosorbents for Decolorization of Textile Wastewaters" Water 4, no. 4: 770-784. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4040770
APA StylePrigione, V., Grosso, I., Tigini, V., Anastasi, A., & Varese, G. C. (2012). Fungal Waste-Biomasses as Potential Low-Cost Biosorbents for Decolorization of Textile Wastewaters. Water, 4(4), 770-784. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4040770







