Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: A Primary Case Study along the Adriatic Coast Investigated within a Probabilistic Framework
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Characterization of the Area of Interest
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Theoretical Framework
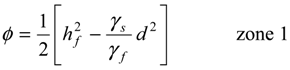

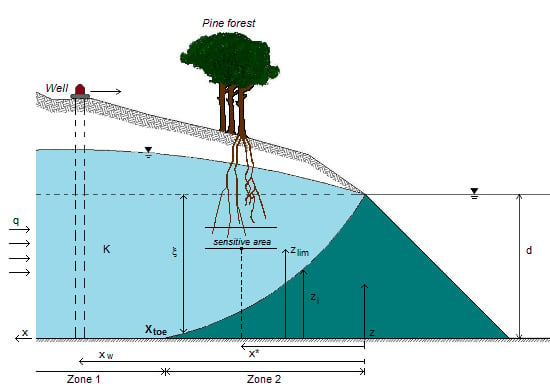
 , in the x-z plane. At the interface, substituting in Equations (3) or (4) the condition ξ = d, hence hf = (γs/γf) ξ, the potential is obtained as:
, in the x-z plane. At the interface, substituting in Equations (3) or (4) the condition ξ = d, hence hf = (γs/γf) ξ, the potential is obtained as:
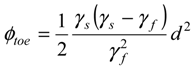

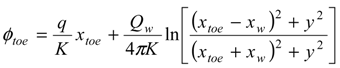

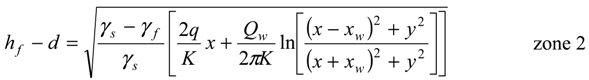
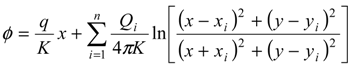
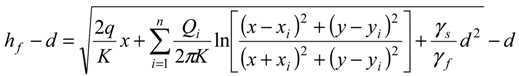
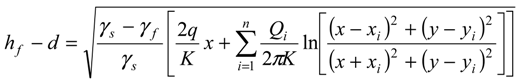

3.2. Problem Formulation
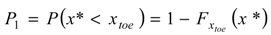
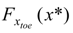 is the cumulative distribution function of the random variables xtoe. According to the data results P1 ≈ 1, i.e., the vegetation falls into zone 2 almost certainly within the selected case study. Secondly, the probability that the saltwater interface reaches the sensitive zone below the plants roots is evaluated in correspondence of the maximum intrusion, i.e., y = ycrit. This probability is conditional on the previous one as follows:
is the cumulative distribution function of the random variables xtoe. According to the data results P1 ≈ 1, i.e., the vegetation falls into zone 2 almost certainly within the selected case study. Secondly, the probability that the saltwater interface reaches the sensitive zone below the plants roots is evaluated in correspondence of the maximum intrusion, i.e., y = ycrit. This probability is conditional on the previous one as follows:
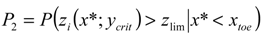
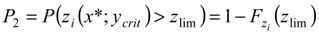 , where
, where 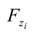 is the cumulative distribution function of the random variable zi. Consequently, in the following section the simplified formulation for the computation of the risk, i.e., R = P2, was considered.
is the cumulative distribution function of the random variable zi. Consequently, in the following section the simplified formulation for the computation of the risk, i.e., R = P2, was considered.| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| a (m) | 650 |
| b (m) | 300 |
| c (m) | 100 |
| e (m) | 300 |
| x1 (m) | 800 |
| y1 (m) | 950 |
| x2 (m) | 800 |
| y2 (m) | 550 |
| x3 (m) | 800 |
| y3 (m) | 150 |
| Q1, Q2 Q3 (m3/day) | 200 |
| Q (m3/day) | 600 |

| Parameters | Distribution |
|---|---|
| K (m/day) | N (μK = 40; cvK = 0.1) |
| q (m2/day) | N (μq = 0.9; cvq = 0.1) |
| d (m) | N (μd = 20; cvd = 0.001) |

3.3. Model Reduction Approach for Risk Analysis
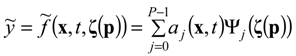
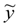 , of y. This metamodel is a simple polynomial function which is expressed in terms of a set of independent random variables, collected in vector ζ. Here,
, of y. This metamodel is a simple polynomial function which is expressed in terms of a set of independent random variables, collected in vector ζ. Here, 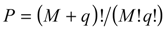 , is the number of terms of the expansion, and q is the maximum degree considered; aj represent unknown deterministic coefficients, while Ψj denote the suitable multivariate polynomial basis in the Hilbert space containing the response.
, is the number of terms of the expansion, and q is the maximum degree considered; aj represent unknown deterministic coefficients, while Ψj denote the suitable multivariate polynomial basis in the Hilbert space containing the response. 
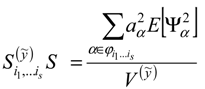
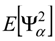 see e.g., [45].
see e.g., [45].4. Results and Discussion

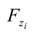 of the surface elevation zi computed in
of the surface elevation zi computed in  (Figure 4); and (d) Computed risk [see Equation (14)] resulting from different values of single pumping discharge Qi.
(Figure 4); and (d) Computed risk [see Equation (14)] resulting from different values of single pumping discharge Qi.
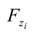 of the surface elevation zi computed in
of the surface elevation zi computed in 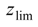 (Figure 4); and (d) Computed risk [see Equation (14)] resulting from different values of single pumping discharge Qi.
(Figure 4); and (d) Computed risk [see Equation (14)] resulting from different values of single pumping discharge Qi.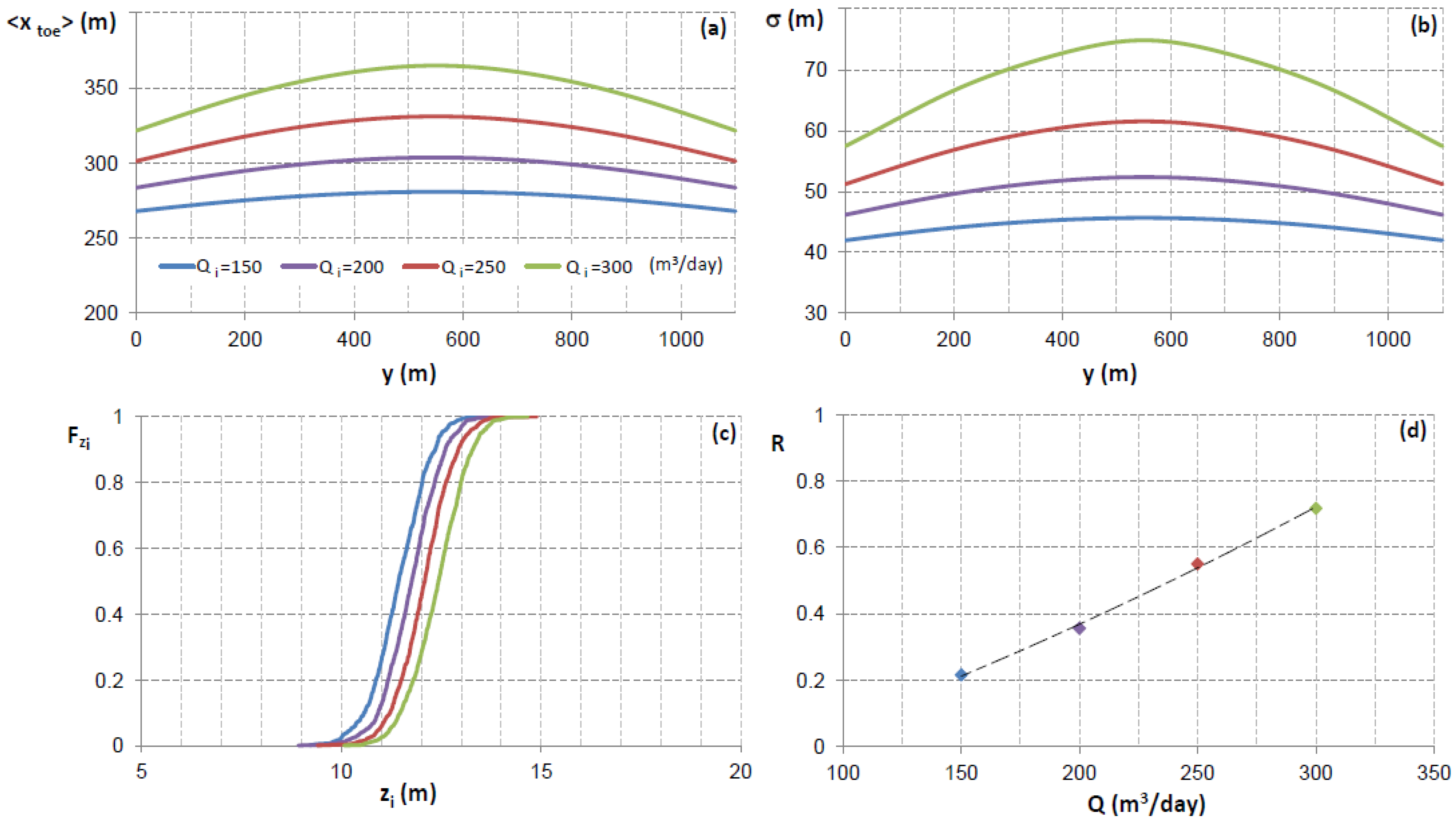

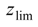 ,
, 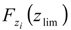 , tend to decrease with higher values of Qi and consequently the risk increases quasi-linearly (Figure 6d). When considering the value of
, tend to decrease with higher values of Qi and consequently the risk increases quasi-linearly (Figure 6d). When considering the value of 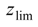 = 12 m as a fixed variable herein,
= 12 m as a fixed variable herein, 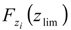 ranged from 0.78 to 0.28, as Qi varied between 150 and 300 m3/day. In Figure 7c, obtained for different values of a, a different trend is revealed, whereby
ranged from 0.78 to 0.28, as Qi varied between 150 and 300 m3/day. In Figure 7c, obtained for different values of a, a different trend is revealed, whereby 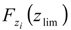 increases and risk decreases, as expected for higher values of a (Figure 7d). In this case,
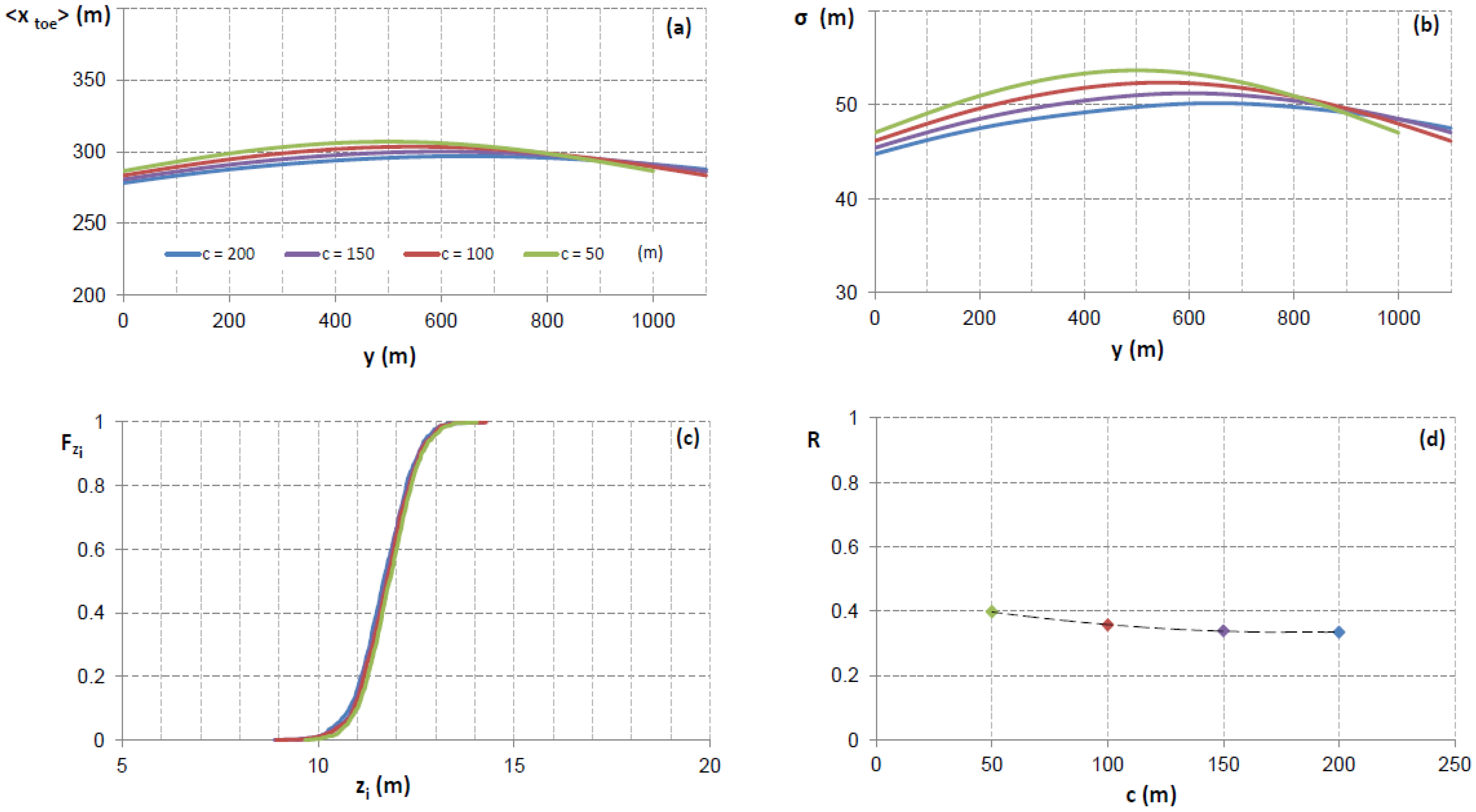
increases and risk decreases, as expected for higher values of a (Figure 7d). In this case, 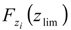 increases from 0.60 to 0.71 while varying a between 600–750 m. Finally, in the last simulation whereby different values of c were utilized, a similar trend to the one described above was observed, albeit less pronounced (Figure 8c,d). For example, a value of
increases from 0.60 to 0.71 while varying a between 600–750 m. Finally, in the last simulation whereby different values of c were utilized, a similar trend to the one described above was observed, albeit less pronounced (Figure 8c,d). For example, a value of 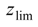 = 12 m, produced a narrow range of values of
= 12 m, produced a narrow range of values of 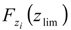 from 0.61 to 0.67 when varying c between 50 and 200 m.
from 0.61 to 0.67 when varying c between 50 and 200 m.5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cassardo, C.; Jones, J.A.J. Managing water in a changing world. Water 2011, 3, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, A.K.; Giupponi, C.; Renaud, F.G. Climate change adaptation and vulnerability assessment of water resources systems in developing countries: A generalized framework and a feasibility study in Bangladesh. Water 2012, 4, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolster, D.T.; Tartakovsky, D.M.; Dentz, M. Analytical models of contaminant transport in coastal aquifers. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, B.D.; Evans, K.R. Saltwater intrusion in Los Angeles area coastal aquifers—The marine connection; USGS Fact Sheet 030–02. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2002/fs030-02/ (accessed on 6 June 2013).
- Bray, B.; Tsai, F.T.C.; Sim, Y.; Yeh, W.W.G. Model development and calibration of a saltwater intrusion model in southern California. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 1329–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaccioni, B.; Didero, M.; Paletta, C.; Didero, L. Saline intrusion and refreshening in a multilayer coastal aquifer in the Catania Plain (Sicily, southern Italy): Dynamics of degradation processes according to the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2005, 307, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Preziosi, E.; Giuliano, G.; Mastroianni, D.; Falconi, F. First evaluation of the saltwater intrusion in the Tiber delta area (Rome, central Italy). In Proceedings of 18th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, Cartagena, Spain, 31 May–3 June 2004; p. 34.
- Carbognin, L.; Tosi, L.; Teatini, P. Analysis of actual land subsidence in Venice and its hinterland (Italy). In Land Subsidence; Barends, F.B.J., Brouwer, F.J.J., Schröder, F.H., Eds.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Bau, D.; Gambolati, G.; Teatini, P. Residual land settlement near abandoned gas fields raises concern over Northern Adriatic coastland. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2000, 81, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Teatini, P.; Ferronato, M.; Gambolati, G.; Gonella, M. Groundwater pumping and land subsidence in the Emilia-Romagna coastland, Italy: Modeling the past occurence and the future trend. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Preti, M.; De Nigris, N.; Morelli, M.; Monti, M.; Bonsignore, F.; Aguzzi, M. Stato del litorale emiliano-romagnolo all’anno 2007 e piano decennale di gestione; Agenzia regionale per la prevenzione e l’ambiente (ARPA): Emilia-Romagna, Italy, 2009; p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Manfreda, S.; Caylor, K.K. On the vulnerability of water limited ecosystems to climate change. Water 2013, 5, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonellini, M.; Mollema, P.N. Impact of groundwater salinity on vegetation species richness in the coastal pine forests and wetlands of Ravenna, Italy. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambastiani, B.M.S.; Mollema, P.N.; Antonellini, M. Groundwater management in the Northern Adriatic Coast (Ravenna, Italy): New strategies to protect the coastal aquifer from saltwater intrusion. In Groundwater. Modeling, Management, and Contamination; König, L.F., Weiss, J.L., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 203–230. [Google Scholar]
- Marconi, V.; Dinelli, E.; Antonellini, M.; Capaccioni, B.; Balugani, E.; Gabbianelli, G. Hydrogeochemical characterization of the phreatic system of the coastal wetland located between Fiumi Uniti and Bevano rivers in the southern Po plain (Northern Italy). In Proceedings of European Geosciences Union General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 19–24 April 2009; p. 9771.
- Henry, H.R. Salt intrusion into fresh-water aquifers. J. Geophys. Res. 1959, 64, 1911–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servan-Camas, B.; Tsai, F.T.-C. Two-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann method for the anisotropic dispersive Henry problem. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.H.-D.; Halhal, D.; Naji, A.; Ouazar, D. Pumping optimization in saltwater-intruded coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantoglou, A. Pumping management of coastal aquifers using analytical models of saltwater intrusion. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantoglou, A.; Papantoniou, M. Optimal design of pumping networks in coastal aquifers using sharp interface models. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Ward, J.D.; Morgan, L.K.; Simmons, C.T.; Robinson, N.I.; Teubner, M.D. Vulnerability indicators of sea water intrusion. Ground Water 2012, 50, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strack, O.D.L. A single-potential solution for regional interface problems in coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, A.; Cheng, A.H.-D.; Ouazar, D. Analytical stochastic solutions of saltwater/freshwater interface in coastal aquifers. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 1998, 12, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chen, Y.; Luo, J. Boundary condition effects on maximum groundwater withdrawal in coastal aquifers. Ground Water 2012, 50, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Barros, F.P.J.; Bolster, D.; Sanchez-Vila, X.; Nowak, W. A divide and conquer approach to cope with uncertainty, human health risk, and decision making in contaminant hydrology. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartakovsky, D.M. Assessment and management of risk in subsurface hydrology: A review and perspective. Adv. Water Resour. 2012, 51, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US National Research Council. Review of Recommendations for Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis: Guidance on Uncertainty and Use of Experts; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; p. 84. [Google Scholar]
- European Communities (EC). Common Implementation Strategy for the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC); Guidance Document No. 11; Planning Processes, Working Group 2.9.; Office for the Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tartakovsky, D.M. Probabilistic risk analysis in subsurface hydrology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, Y. Applied Stochastic Hydrogeology, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Sudret, B. Global sensitivity analysis using polynomial chaos expansions. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safety 2008, 93, 964–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Vialaneix, N.; Follador, M.; Ratto, M.; Leip, A. A comparison of eight metamodeling techniques for the simulation of N2O fluxes and N leaching from corn crops. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 34, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E-R Ambiente Home Page. Available online: http://ambiente.regione.emilia-romagna.it/geologia/cartografia/webgis-banchedati (accessed on 3 October 2013).
- Giambastiani, B.M.S.; Antonellini, M.; Oude Essink, G.H.P.; Stuurman, R.J. Saltwater intrusion in the unconfined coastal aquifer of Ravenna (Italy): A numerical model. J. Hydrol. 2007, 340, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonellini, M.; Mollema, P.; Giambastiani, B.; Bishop, K.; Caruso, L.; Minchio, A.; Pellegrini, L.; Sabia, M.; Ulazzi, E.; Gabbianelli, G. Saltwater intrusion in the coastal aquifer of the southern Po Plain, Italy. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 1541–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondesan, M.; Favero, V.; Viñals, M.J. New evidence on the evolution of the Po-delta coastal plain during the Holocene. Quat. Int. 1995, 29–30, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorosi, A.; Centineo, M.C.; Dinelli, E.; Lucchini, F.; Tateo, F. Geochemical and mineralogical variations as indicators of provenance changes in late Quaternary deposits of SE Po Plain. Sediment. Geol. 2002, 151, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulazzi, E.; Antonellini, A.; Gabbianelli, G. Coastal phreatic aquifer characterization of the Cervia Area. In Stratigraphy and Sedimentology of Aquifers; Vallone, R., Ed.; APAT: Parma, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, E.V. Salt tolerance of plants. In Handbook of Plant Science in Agriculture; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984; pp. 57–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, I. Salinity Tolerances of Plants of Estuarine Wetlands and Associated Uplands; Washington State Department of Ecology Report; Washington State Shorelands and Coastal Zone Management Program, Wetlands Section: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, A.H.-D.; Ouazar, D. Analytical solutions. In Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers—Concepts, Methods and Practices, 1st ed.; Bear, J., Cheng, A.H.-D., Sorek, S., Ouazar, D., Herrera, I., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 1999; Volume 14, pp. 163–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, N. The homogeneous chaos. Am. J. Math. 1938, 60, 897–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, R.G.; Spanos, P.D. Stochastic Finite Elements: A Spectral Approach; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Ciriello, V.; Di Federico, V.; Riva, M.; Cadini, F.; De Sanctis, J.; Zio, E.; Guadagnini, A. Polynomial chaos expansion for global sensitivity analysis applied to a model of radionuclide migration in a randomly heterogeneous aquifer. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriello, V.; Di Federico, V. Analysis of a benchmark solution for non-Newtonian radial displacement in porous media. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 2013, 52, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Aral, M.M. Multi-objective optimization of pumping rates and well placement in coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2004, 290, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Felisa, G.; Ciriello, V.; Di Federico, V. Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: A Primary Case Study along the Adriatic Coast Investigated within a Probabilistic Framework. Water 2013, 5, 1830-1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041830
Felisa G, Ciriello V, Di Federico V. Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: A Primary Case Study along the Adriatic Coast Investigated within a Probabilistic Framework. Water. 2013; 5(4):1830-1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041830
Chicago/Turabian StyleFelisa, Giada, Valentina Ciriello, and Vittorio Di Federico. 2013. "Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: A Primary Case Study along the Adriatic Coast Investigated within a Probabilistic Framework" Water 5, no. 4: 1830-1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041830
APA StyleFelisa, G., Ciriello, V., & Di Federico, V. (2013). Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: A Primary Case Study along the Adriatic Coast Investigated within a Probabilistic Framework. Water, 5(4), 1830-1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041830