Effect of TiO2 on the Sintering Behavior of Chromium-Bearing Vanadium–Titanium Magnetite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Characterisation Methods
2.2. Experiments
2.3. Definition of Parameters
2.3.1. Productivity
2.3.2. Reduction Degradation Index
2.3.3. Reduction Index
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Assays and Characterisation
3.2. Effect of TiO2 on the Properties of CVTM Sinters
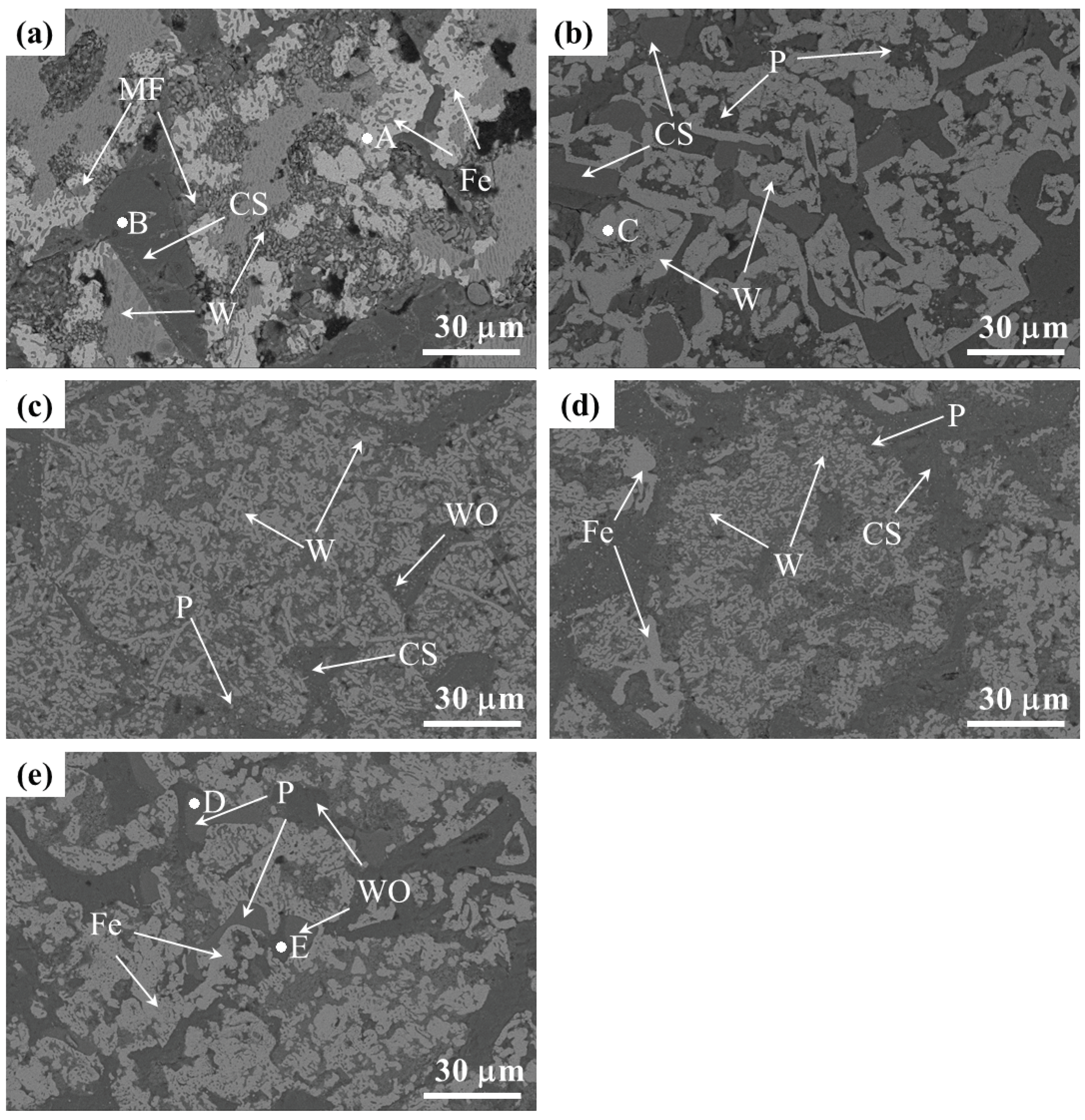
3.3. Microstructure
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The yield, vertical sintering speed, and productivity first rise with TiO2 content increases to 10.35% and then decreases when TiO2 content increases to 11.85%. The RI decreases from 67.92% to 47.15% with increasing TiO2 content. The principal effect on productivity value is sintering speed.
- (2)
- The TI increases from 45.81% to 52.09%, and the RDI increases from 74.99% to 96.74% with increasing TiO2 content. The RDI of CVTM sinter is well qualified, and the permeability of lumpy zone could be improved with the application of CVTM sinter on BF.
- (3)
- The main phases of reductive CVTM sinter are metallic iron, wustite, magnesium ferrite, perovskite, coulsonite, spinel Mg2TiO4, titanium monoxide, titanomagnetite, and titanomaghemite.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takano, C.; Zambrano, A.P.; Nogueira, A.E.A.; Mourao, M.B.; Iguchi, Y. Chromites reduction reaction mechanisms in carbon-chromites composite agglomerates at 1773K. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 1585–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Zou, X.L.; Lu, X.G.; Xie, X.L.; Zheng, K.; Xiao, W.; Cheng, H.W.; Li, G.S. Reductive kinetics of panzhihua ilmenite with hydrogen. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 2016, 26, 3266–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.J.; Xue, X.X.; Gao, Z.X.; Jiang, T.; Yang, H.; Duan, P.N. Effect of Cr2O3 on the reduction and smelting mechanism of high-chromium vanadium-titanium magnetite pellets. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, B.C.; Dresler, W.; Reilly, I.G. Extraction of titanium, vanadium and iron from titanomagnetite deposits at pipestone lake, manitoba, canada. Miner. Eng. 1995, 8, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Gao, Z.; Yang, H.; Xue, X. Effect of calcium oxide on the crushing strength, reduction, and smelting performance of high-chromium vanadium–titanium magnetite pellets. Metals 2017, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.J.; Xue, X.X.; Jiang, T.; Duan, P.N. Effect of TiO2 on the crushing strength and smelting mechanism of high-chromium vanadium–titanium magnetite pellets. Metall. Trans. B 2016, 47, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Zhou, M.; Tang, W.D.; Jiang, T.; Xue, X.X.; Zhang, W.J. Influence of coke ratio on the sintering behavior of high-chromium vanadium–titanium magnetite. Minerals 2017, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Tang, W.D.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, T.; Xue, X.X.; Zhang, W.J. Effects of dolomite on mineral compositions and metallurgical properties of chromium-bearing vanadium–titanium magnetite sinter. Minerals 2017, 7, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.J.; Xue, X.X. Effect of basicity on sintering behavior of low-titanium vanadium–titanium magnetite. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 2015, 25, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umadevi, T.; Nelson, K.; Mahapatra, P.C.; Prabhu, M.; Ranjan, M. Influence of magnesia on iron ore sinter properties and productivity. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2009, 36, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.K.; Li, J.S.; Yang, S.F. Sintering pot test on improving TiO2–containing ore’s allocated proportion. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 311–313, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Guo, X. Effect of Al2O3 and SiO2 on formation and crystal structure of calcium ferrite containing Al2O3 and SiO2. J. Chin. Rare Earth Soc. 2008, 26, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Wu, S.L.; Su, B.; Que, Z.G.; Hou, C.G.; Jiang, Y. Influencing factor of sinter body strength and its effects on iron ore sintering indexes. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2015, 22, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pinson, D.; Chew, S.; Rogers, H.; Monaghan, B.J.; Pownceby, M.I.; Webster, N.A.S.; Zhang, G. Behavior of New Zealand ironsand during iron ore sintering. Metall. Trans. B 2015, 47, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhang, J.L.; Wu, L.S.; Su, B.X.; Xing, X.D.; Zhu, G.Y. Effect of TiO2 on equilibrium phase sinter at oxygen partial pressure of 5 × 10−3 atm. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2013, 41, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Holmes, R.J.; Manuel, J.R. Effects of alumina on sintering performance of hematite iron ores. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwarapudi, S.; Ranjan, M. Influence of oxide and silicate melt phases on the RDI of iron ore pellets suitable for shaft furnace of direct reduction process. ISIJ Int. 2010, 50, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, N.J.; Loo, C.E. Sintering properties of iron ore mixes containing titanium. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yang, S.T.; Jiang, T.; Xue, X.X. Influence of MgO in form of magnesite on properties and mineralogy of high chromium, vanadium, titanium magnetite sinters. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2015, 42, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

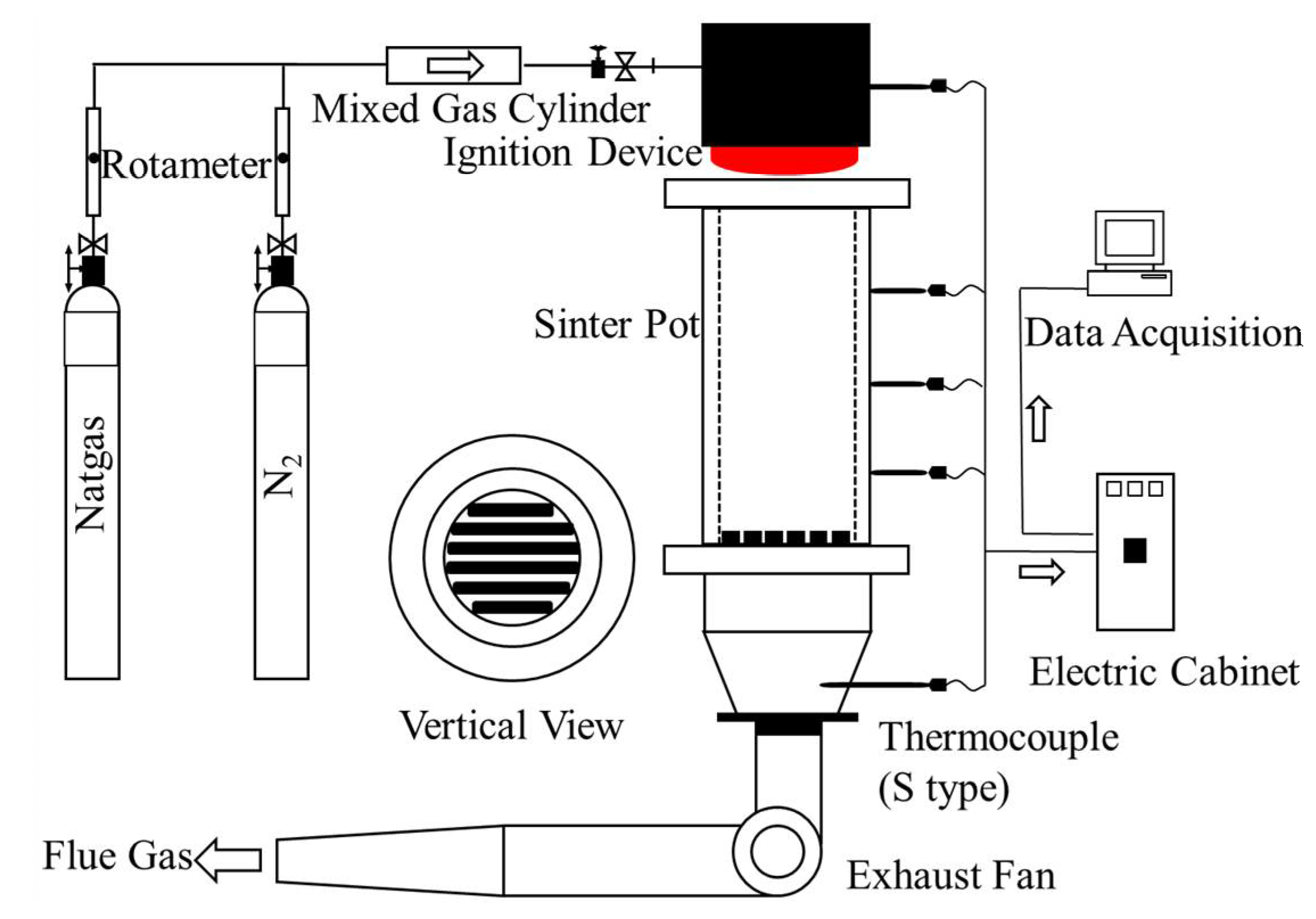










| Item | Parameter | Item | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sinter pot height | 700 mm | Sinter pot inner diameter | 320 mm |
| Sintering weight | 100 kg | Pelletizing time | 10 min |
| Ignition temperature | 1050 °C | Ignition time | 2 min |
| Height of grate layer | 20 mm | Moisture | 8.5 ± 0.5% |
| Ignition pressure | 8.00 kPa | Exhausting pressure | 12.0 kPa |
| Number | ω(TiO2) | Mixed Sinter Raw Materials | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVTM | OM 1 | RM 2 | GA 3 | MP 4 | Lime | Ilmenite | ||
| 1 | 5.85 | 35.9 | 30 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 12.2 | 0 |
| 2 | 7.35 | 30.9 | 30 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 12.4 | 4.8 |
| 3 | 8.85 | 26.7 | 30 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 12.4 | 8.9 |
| 4 | 10.35 | 22.9 | 30 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 12.8 | 12.3 |
| 5 | 11.85 | 19.5 | 30 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 12.9 | 15.6 |
| Item | TFe | FeO | TiO2 | V2O5 | Cr2O3 | CaO | SiO2 | MgO | Al2O3 | P | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVTM | 53.35 | 26.91 | 11.60 | 0.57 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 4.71 | 3.33 | 2.82 | 0.02 | 0.26 |
| OM | 63.79 | 28.35 | 0.89 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.38 | 7.15 | 0.38 | 1.25 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Ilmenite | 34.65 | 17.93 | 45.12 | 0.36 | 0.79 | 4.93 | 1.02 | 0.89 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| GA | 32.39 | 1.79 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 5.16 | 5.95 | 1.79 | 2.69 | 0.07 | 0.17 | |
| MP | 0.14 | 0.03 | 29.4 | 2.58 | 20.65 | 0.90 | |||||
| lime | 60.80 | 3.42 | 2.87 | 1.11 |
| Item | Fixed Carbon | Volatile | Organic Compounds | Ash | ∑ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | SiO2 | MgO | Al2O3 | Others | |||||
| Coke | 76.90 | 0.559 | 1.48 | 1.35 | 6.4 | 0.28 | 4.18 | 8.85 | 100.00 |
| Coal | 85.40 | 0.147 | 1.35 | 0.74 | 4.6 | 0.18 | 3.35 | 4.23 | 100.00 |
| −38 μm | 38–45 μm | 45–53 μm | 53–75 μm | 75–150 μm | +150 μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 44.55 | 7.88 | 15.73 | 4.31 | 21.21 | 5.82 |
| No. | Phase | Chemical Formula | ICSD No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Magnetite | Fe3O4 | 79-0418 |
| 2 | Titanomagnetite | Fe2.75Ti0.25O4 | 75-1373 |
| 3 | Ilmenite | FeTiO3 | 75-0519 |
| 4 | Coulsonite | Fe2VO4 | 75-1519 |
| 5 | Chromite | FeCr2O4 | 34-0140 |
| 6 | Hematite | Fe2O3 | 33-0664 |
| 7 | Perovskite | CaTiO3 | 88-0228 |
| 8 | Kirschsteinite | CaFeSiO4 | 34-0098 |
| 9 | Fayalite | Fe2SiO4 | 76-0512 |
| 10 | Magnesium ferrite | MgFe2O4 | 17-0464 |
| 11 | Magnesium titanate | MgTiO3 | 06-0494 |
| 12 | Metallic iron | Fe | 87-0721 |
| 13 | Wustite | FeO | 74-1880 |
| 14 | Maghemite | γ–Fe2O3 | 79-1741 |
| 15 | Titanium monoxide | TiO | 86-2352 |
| 16 | Spinel | Mg2TiO4 | 87-1173 |
| 17 | Titanomagnetite | Fe2.5Ti0.5O4 | 75-1375 |
| 18 | Titanomaghemite | Fe0.23(Fe1.95Ti0.42)O4 | 84-1595 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, W.; Yang, S.; Cheng, G.; Gao, Z.; Yang, H.; Xue, X. Effect of TiO2 on the Sintering Behavior of Chromium-Bearing Vanadium–Titanium Magnetite. Minerals 2018, 8, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8070263
Tang W, Yang S, Cheng G, Gao Z, Yang H, Xue X. Effect of TiO2 on the Sintering Behavior of Chromium-Bearing Vanadium–Titanium Magnetite. Minerals. 2018; 8(7):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8070263
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Weidong, Songtao Yang, Gongjin Cheng, Zixian Gao, He Yang, and Xiangxin Xue. 2018. "Effect of TiO2 on the Sintering Behavior of Chromium-Bearing Vanadium–Titanium Magnetite" Minerals 8, no. 7: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8070263
APA StyleTang, W., Yang, S., Cheng, G., Gao, Z., Yang, H., & Xue, X. (2018). Effect of TiO2 on the Sintering Behavior of Chromium-Bearing Vanadium–Titanium Magnetite. Minerals, 8(7), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8070263





